What is an “extension” and why should it be legalized?
An extension is a part of a building erected on the local area after the construction of the house has been completed and it has been put into operation, that is, this area was not included in the plan . Any documentation for the house should be put in order in a timely manner, otherwise you will not be able to take any legal actions with the property. The legalization of the extension is carried out with the help of a court in civil proceedings. You file a claim and the local municipality is the defendant.
What is the cost of legalizing an extension?
If the amounts given above seem illegally extortionate, then let’s figure out what the procedure for legitimizing an extension consists of. Let's start with the fact that the construction of an extension requires permission from local authorities. That is, ideally the procedure is as follows:
- Obtaining permission for an extension.
- Construction of an extension.
- Legalization of the extension.
But often citizens skip the first point, some intentionally, some out of ignorance, but, as they say, ignorance of the law does not exempt you from responsibility, so sooner or later it will still have to be brought into line with the norms of the law. I would like to note that option 1 will cost much less, because if you “accidentally” missed obtaining a building permit, then the extension is considered unauthorized and is subject to demolition. In this case, you first need to prove its legality , and then only start the process of legalizing it.
Also, the difference in price is mainly due to the participation of a representative by proxy . Drawing up a claim, submitting requests for examinations, collecting and analyzing available documents - this is all the work of lawyers. If you understand these subtleties, then the costs will only be in terms of examinations and state payments. duties. It can be assumed that you do not know everything thoroughly, but only have a general idea. Then it would be advisable for you to seek the help of a professional .

How to legalize a commercial extension to a house?
The process of legalizing a commercial extension is much simpler than commissioning residential buildings.
You can legalize an extension to your house in one of two ways:
- Having previously collected all permits before construction.
- By going to court after the construction of the structure.
The second method is called legalizing an unauthorized extension.
To carry out this procedure, you need to collect the following documents:
- Confirming ownership of property.
- Extract from the house register.
- Technical documentation from BTI.
- Permission issued by housing and communal services or a partnership for an extension.
- Consent of neighbors to erect a structure (for an extension to an apartment building).
- Acts on inspections from public utilities (fire, gas and other inspection bodies).
- Redevelopment project.
- Photo of the object.
Additionally, the owner of the extension must provide paper confirming the rights to the plot on which the buildings are located.
At the second stage of registration, the owner needs to go to court to legalize the extension. The case will be considered in a lawsuit, and the city administration will be the defendant. After filing a claim, you must attach a receipt for payment of the state fee to the package of documents.
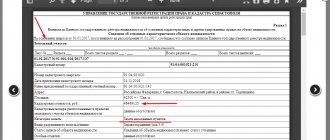
During the consideration of the case, the court will send special commissions to the site, which will assess the extent of changes and their compliance with previously submitted documents . If the outcome of the case is positive and the court makes a decision in favor of the owner, the decision must be submitted with the remaining documents to the State Registration Authority. After registration, this structure will issue documents of ownership.
Ways to resolve the issue of legalizing an extension with example prices
This procedure includes the following costs:
- The state fee is 200-500 rubles .
- Cadastral chamber services - 20,000 rubles .
- Expertise carried out in court - 15,000 rubles .
This “minimum” set is suitable for those who deal with this issue on their own. These payments are mandatory and, unfortunately, cannot be avoided.
The situation is completely different for those who decide to seek the help of a lawyer. A one-time consultation costs about 1000 rubles. , representation in litigation 1 time – 6 tr. , on an ongoing basis - from 30 tr . Don’t forget about the power of attorney for the representative, executed by a notary – 2 tr .
The difference in the procedure and prices for legalizing an “extension” and an “unauthorized extension”
Registration of an extension for which permission has been given from the administration begins with the payment of state fees. duties in the amount of 350 rubles .
If an extension is planned during the construction phase of a residential building, the technical plan and design of the house should be agreed upon. Coordination of redevelopment – 20 tr. , reworking the technical plan and other documentation - 10 tr . If construction is nearing completion, no adjustments or approvals are required.
During the trial, it will be necessary to carry out an examination of the building - 15 tr . To legalize an unauthorized extension, you must first justify its safety; this work is carried out by a visiting engineering team - from 2500 to 5000 rubles .
And the most unpleasant part of this procedure is paying the fine:
- For the construction of an extension without permission - 2000-5000 rubles , based on Art. 9.5 Code of Administrative Offences.
- For using an unauthorized extension - 500-1000 rubles under the same article.
From the point of view of urban planning, the construction of an extension to a residential building is its reconstruction, since this changes the area of the residential building and its number of storeys may change (clause 14 of Article 1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In order for the construction of an extension to a residential building to be legal, a number of administrative procedures must be followed. To do this, we recommend following the following algorithm.
1. Prepare a project for a future extension. Contact an architect or an architectural bureau, who will develop an extension project for you, taking into account the characteristics and limitations of your land plot and cottage. When constructing or reconstructing a detached residential building with a height of no more than three floors, intended for single-family residence, it is not necessary to prepare design documentation. However, you have the right to prepare it on your own initiative (Part 3 of Article 48 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). 2. Obtain permission for the construction and reconstruction of a residential building Contact the authorized executive body at the location of the residential building and submit the following documents (part 9, 10.2 of article 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation; paragraph 12 of article 60 of the Law of June 25, 2002 N 73 -FZ): - application for a permit for the construction and reconstruction of a residential building; — title documents for the land plot; - urban development plan of the land plot, issued no earlier than three years before the date of submission of the application for a building permit; — a diagram of the planning organization of the land plot indicating the location of the residential building; - a description of the external appearance of a residential building if it is located within the territory of a historical settlement of federal or regional significance, with the exception of the case of using a standard architectural solution (the use of a standard solution must be indicated in the application). If the Unified State Register of Real Estate (USRN) does not contain information about the plot, you must submit a title document (Parts 9.1, 9.2 of Article 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The application and documents can be submitted either in person or through the MFC (Part 9, Article 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The issuance of a building permit is not required in the case (Part 17 of Article 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation): 1) construction of a garage on a land plot provided to a citizen for purposes not related to business activities, or construction on a land plot provided for gardening, summer cottage farms; 2) construction, reconstruction of objects that are not capital construction objects (kiosks, sheds and others); 3) construction of buildings and structures for auxiliary use on the land plot; 4) changes to capital construction projects and (or) their parts, if such changes do not affect the structural and other characteristics of their reliability and safety and do not exceed the maximum parameters of permitted construction and reconstruction established by town planning regulations; 5) major repairs. Within seven days, the authorized body must issue a construction permit or refuse to issue it, indicating the reason for the refusal (Part 11, Article 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Note: There is no need to obtain permission to put a reconstructed residential building into operation before March 1, 2018 (Part 4, Article 8 of Law No. 191-FZ of December 29, 2004). 3. Contact a cadastral engineer to prepare a technical plan for a reconstructed residential building. For subsequent state cadastral registration of changes, it is necessary to conclude an agreement with the cadastral engineer to carry out cadastral work, as a result of which the cadastral engineer will prepare a technical plan (Article 24 of the Law of July 13, 2015 N 218- Federal Law; Article 29 of the Law of July 24, 2007 N 221-FZ). The technical plan is prepared, among other things, in the form of an electronic document and is signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature of the cadastral engineer (Part 12 of Article 24 of Law No. 218-FZ). The technical plan may be placed for temporary storage in an electronic storage facility maintained by the rights registration authority. The contract for the performance of cadastral works may provide for the obligation of the cadastral engineer to place the technical plan prepared by him in the electronic storage (Parts 3, 5 of Article 20 of Law No. 218-FZ). 4. Prepare documents for cadastral registration and registration of property rights. For cadastral registration of a reconstructed residential building and state registration of ownership rights to it, you will need, in particular (parts 1 - 3 of article 14, part 4 of article 18, article 21, Part 7 of Article 70 of Law No. 218-FZ): - application for cadastral registration and registration of property rights; — a notarized power of attorney, if a representative will submit the application; — a title document for the land plot on which the residential building is located (may not be required if the right to the land plot was previously registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate). If the technical plan is placed in electronic storage, the identifying number of the technical plan can be indicated in the application. In this case, its presentation will not be required (Part 4, Article 20 of Law No. 218-FZ). Pay a state fee of 350 rubles. Subject to filing an application for registration and paying the state fee through public service portals, it is calculated taking into account the coefficient of 0.7 (clause 24, clause 1, article 333.33, clause 4, article 333.35 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). 5. Submit documents to the MFC for cadastral registration and registration of property rights. When submitting an application through a personal appeal, the applicant presents a passport, and his representative also presents a notarized power of attorney confirming his authority (Part 8 of Article 18 of Law No. 218-FZ). Authorized bodies are required to carry out cadastral registration of changes in the property and state registration of ownership within 12 working days from the date of receipt of the documents (clauses 5, 6, part 1, article 16 of Law No. 218-FZ). The completed cadastral registration and state registration are certified by an extract from the Unified State Register, which can be sent to you in electronic form (Part 1, Article 28, Part 6, Article 62 of Law No. 218-FZ).