Free legal consultation over the Internet 24 hoursLawyer on housing issues in St. Petersburg. Free legal consultation on labor disputes.
4.77/5 (13)
The employee did not show up for work: the employer’s actions
Sometimes an employee does not show up for work for several days. However, no news or explanations are received from him. The question arises: how to find a missing employee, how can he be punished? And quite naturally you want to know how to terminate an employment contract with him through the court?
You can’t just fire a person just because he didn’t show up for work..
There are a huge number of reasons for missing work, ranging from unexpected illness to detention by law enforcement agencies. It is clear that the reasons for missing work can be valid or disrespectful.
Recording absence
If a person does not show up for work, this fact must be recorded. Draw up an act indicating the last name, first name and patronymic of the employee, the position he holds, and the date of absence from work. If the employee was not absent all day, then the time of arrival at work is specified. Sign the document and ask him to sign three witnesses, who thus confirm the fact of the person’s absence from the workplace.
Important! If absences continue, draw up such a report every day.
Make appropriate entries about the employee’s absence for unknown reasons in the work time sheet (form T-12, T-13, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 No. 1).
The report card contains a specific code:
- alphabetic – “NN”;
- digital "30".
Perform the steps described above daily until the reasons for the person’s absence from the workplace are clarified or until the employer decides to dismiss the employee.
When the employee eventually comes to his senses and appears at the workplace, he can present a sick leave certificate. But if it turns out that some of the missed days are not confirmed by a medical document, the employee can be fired legally.
Although it is almost impossible to part with an employee during his absence, it is possible to ensure that the company’s losses are minimal. If a person does not go to work for an unexcused reason, no one pays him for those days. That is, there are no costs for an absent employee. If an employee is absent for too long, and his position is important for the enterprise, another person is hired to take his place.
ATTENTION! View the completed sample absence from work report:

Watch the video. 7 tips on how to fire an employee:
How to record absenteeism and punish for it
First of all, we emphasize that absenteeism is a gross violation of labor discipline. That is why, even for a one-time commission of this offense, the employer has the right to dismiss the employee.
This is the main difference between absenteeism and less serious violations of labor discipline, for example, being late.
It should be noted that for absenteeism, the employer has the right to both dismiss an employee and apply other disciplinary sanctions provided for in Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Please note! Whatever disciplinary liability the employer chooses for the employee who committed absenteeism, the following will be required:
- properly record the fact that the employee is absent from the workplace for more than 4 hours;
- establish the reason for this absence by obtaining an explanation from the employee.
Recording absence from work
You can record the fact that an employee is absent from the workplace using:
- information from an automated access system, provided that the employer has established an access regime and uses this system;
- a memorandum drawn up by the immediate superior of this employee;
- an act drawn up upon the absence of an employee from the workplace. This act can be drawn up by both the employer’s personnel service employees and the immediate supervisor of the absent employee. When drawing up the act, it is necessary to ensure the presence of 2 witnesses.
ATTENTION! Look at the completed sample of the employee’s absence from work report:
Further actions
What to do next depends on your specific circumstances. Let's look at some of them.
Situation No. 1.
A few days later the employee comes to work. Demand from him a written explanation of the reasons for absenteeism. Depending on whether the reason was valid, you need to proceed further. If a person is simply playing hooky, hold him accountable.
Situation No. 2.
The employee still explained the reason for his absence, but did so by mail. As it turned out, he did not and does not have any compelling reasons for being absent from work. But he still doesn’t go to work. In this case, write an order to hold him accountable or an order to terminate the employment agreement (subparagraph “a”, paragraph 6, part 1, article 81, article 192, article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation No. 3.
There were no explanations from the employee; he never showed up at work. Although you know that he received your letter demanding clarification of the situation, according to the notification from the post office. By and large, you have the right to fire him. But there is no need to rush in such a matter.
The fact is that there are no guarantees that the employee will receive the letter. It is possible that one of your relatives received the message, and they are not obligated to answer you.
Suddenly, at this time the person is under treatment, and you fire him. So, before you fire an employee, get specific explanations from him. And then you will decide whether to fire him or not.
Situation No. 4.
The employee doesn’t come to work, no one explains anything, you don’t know whether he received your requirements or not, or the letter was returned without an answer, etc.
In this situation, you can go two ways:
- every day when the employee does not show up at his workplace, draw up a report. Record absences from work on your report card. This must be done until the reasons for the omissions are clarified. In this case, a dismissal order is not drawn up. The fact is that management is playing it safe, because by dismissing a person without finding out the reasons, you can break the law. It is possible that there are valid reasons for a person’s absence, but he cannot report them;
- if the employee is absent for a long time, it is impossible to contact him, and the workplace must be occupied, management makes a decision to terminate the employment relationship with him. If someday a legal dispute arises on this matter, the decision will be made in favor of the management.
Although sometimes the court is very cautious about the situation when management sent a written demand, but received it back without any explanation. Practice shows that such a circumstance is unlikely to allow an employee fired for absenteeism to be reinstated in the workplace.
Deadline for issuing a work book upon dismissal.
Under what article is one fired for absenteeism, read here.
Who can be laid off at work first of all according to the law, read the link:
Note! Do not fire a person immediately after he arrives at work. Talk to him, get an explanation.
Otherwise, when the court finds your actions illegal, you will be obliged not only to reinstate him at work, but also to pay the average salary for the period when he was forced not to work.
No manager is immune from the fact that one fine day a lost employee will appear at the workplace along with proof that he had good reason not to go to work.
He can also prove that he simply could not answer the boss’s demand for a good reason. In this situation, you will have to cancel the dismissal order and reinstate him in the workplace. Remember that if you do not do this of your own free will, you will have to do it by court order.
But in this case, you will have additional expenses (payment of average earnings for a period of temporary unemployment) (Article 394 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 41, paragraph 62 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2).
By the way, you will not have to pay for the period when the person did not work before the order. This is only possible if a sick leave certificate is provided. Previously, it was mentioned about the daily drawing up of a truancy report. In addition, you need to ensure that the person does not receive wages for missed days.
Please note! If, by a court decision, a person has to be reinstated in his workplace (Article 394 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), but instead of him you have already hired another employee, you can deal with him as follows:
- offer another position that meets the qualifications or transfer to a lower position (if he agrees to perform it taking into account his state of health);
- if there are no other vacancies, or the new employee does not agree with his transfer, he will have to terminate his employment contract. You cannot do otherwise, since the court ordered you to reinstate the dismissed employee (clause 2, part 1, article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Please note that you are obliged to pay severance pay to the dismissed employee (in the amount of two weeks’ earnings (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)).
Sometimes management, without waiting for a court decision, cancels the dismissal order as soon as the missing employee appears at work.
With a new employee in this situation:
- agree on a transfer to another position (Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- terminate the employment agreement by agreement of the parties (Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
What should a personnel officer do if an employee disappears?
Work under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation requires discipline from both the employee and the employer. But what should a personnel officer do if an employee suddenly disappears? How many days to wait for the missing person? When and how to fire? In our article we revealed the main nuances of the topic.
An employee may be absent from work for various reasons. It happens that people have unforeseen circumstances that are quite difficult and do not allow them to return to everyday life. In all situations, employers have to find out the reasons for absenteeism and sometimes even fire the missing employee.
How long can an employer wait for a missing employee to show up?
The Labor Code does not establish an obligation for an employee to notify the employer of absence from work. But such an obligation can be provided for in a local document of the organization, for example, internal labor regulations. And employees will have to comply with it, since by virtue of Art. 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee must comply with labor discipline and internal labor regulations. However, this will not give the employer much, since it will still not be possible to fire an employee for absenteeism if he did not report his absence on time. Any court will recognize such dismissal as illegal if the reason for the employee’s absence is considered valid.
In fact, employees usually warn the employer that they will not come to work or have not come to work for one reason or another. Well, if this does not happen, the employer has to find out the reason.
How long can an employer wait for a missing employee to appear? There is no answer to this question in labor legislation.
First of all, the personnel officer or immediate supervisor calls the employee by phone (cell phone, landline). If it was not possible to find out the reason on the first day, it is too early to draw conclusions that the employee is absent, but the fact of his absence from the workplace will have to be recorded. To do this, you need to draw up an act in any form - it is drawn up by a commission of at least three employees.
At first, it is advisable to draw up such acts daily. Then, if the employee does not show up, you can compile them once every few days or once a week. Don’t forget to also note the employee’s absence on the time sheet. The days when he was absent will be indicated by the letter code “NN” - failure to appear for unknown reasons.
If the employee has not gotten in touch, it is worth contacting the employee’s close relatives and friends, if possible. It also makes sense to go to the employee’s home. If these actions do not lead to anything, you should send him a letter (valuable with an inventory of the attachment and notification) or a telegram demanding an explanation of the reasons for absence from work.
Keep in mind that if an employee is registered at one address and lives at another, letters should be sent to both addresses. Moreover, you can not limit yourself to one letter, but send them, for example, every week for a month.
If no answers were received from the employee, and the notifications were returned due to the absence of the addressee or after the expiration of the storage period at the post office, you need to draw up a statement about the impossibility of receiving an explanation.
Nobody, by and large, obliges the employer to carry out a further search for an employee who has been absent for a long time. Many simply fire such employees for absenteeism. But there is a risk: the employee may return to work with evidence that he was absent for a valid reason. And then, by a court decision, he will have to not only be reinstated at work, but also pay all amounts due to him and compensate for the time of forced absence. Therefore, the employer must still have grounds for dismissal.
Are there grounds for dismissing a missing employee for long absence?
The specifics of dismissing a missing employee who does not go to work for a long time are not defined by law. You can fire him if there are documents that confirm the reason for his absence. The procedure for registering dismissal will depend on this reason. So, if you have a court decision recognizing the employee as missing or documents confirming the fact of the employee’s death, formalize the dismissal on the basis of clause 6, part 1, art. 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, taking into account the peculiarities inherent in each case. If there are no documents justifying the employee’s long-term absence and it is not possible to establish the reasons for such absence, we do not recommend filing a dismissal before the employee returns to work.
We do not recommend firing an employee for long absences until he returns to work.
The fact is that you may not be able to establish the real reasons for its absence. But they may turn out to be respectful, it’s just that the employee could not warn you about it. For example, the employee was absent due to being in custody or was in a hospital in serious condition and was not able to inform you about it.
It is important to note that dismissal for absenteeism is a disciplinary sanction (Part 3 of Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, it is necessary to follow the procedure for bringing to disciplinary liability. In particular, before dismissal, you need to request from the employee a written explanation of the reason for absence (Part 1 of Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But if he disappears (does not get in touch), this is difficult to do. And without a written explanation, it is difficult to determine whether the employee was absent without a good reason, that is, whether absenteeism occurs and, accordingly, whether dismissal is permissible under paragraphs. “a” clause 6, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, it is better to wait until the employee returns to work to find out the reasons for his absence, and then follow the procedure for applying disciplinary action. Moreover, waiting does not incur any financial or other costs for you.
How to find an employee?
So, the first thing you need to do to find an employee is to contact the police department with a request to conduct a search (Article 12 of the Federal Law of 02/07/2011 No. Z-FZ “On the Police”). After submitting such an application, the employer will have in his hands a tear-off notification coupon confirming his application (Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation dated August 29, 2014 No. 736 “On approval of the Instructions on the procedure for receiving, registering and resolving in the territorial bodies of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation applications and reports of crimes, administrative offenses, incidents”).
For your information. During the search, the employee may be found in a hospital, in custody, etc. This will confirm that he has valid reasons for being absent from work.
If the employee has no relatives, then by virtue of Art. 42 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the employer himself has the right to apply to the court to recognize the employee as missing. This can be done only if at the employee’s place of residence there is no information about his place of stay during the year. This period is calculated from the moment the last information about the person is received.
The application is submitted to the court at the place of residence of the employee or at the location of the interested person, that is, the employer (Article 276 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
According to Art. 277 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, in an application to recognize a citizen as missing, it must indicate for what purpose the applicant needs to recognize the citizen as missing, and the circumstances confirming the citizen’s unknown absence must also be stated.
For the employer, the purpose of recognizing an employee as missing is to terminate the employment contract under clause 6, part 1, art. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
What is the procedure for dismissing a missing (unknown) employee?
The procedure for dismissing a missing (unknown) employee is as follows. Dismissal is carried out on the basis of a court decision declaring the employee missing. You need to fill out standard dismissal documents (in particular, a dismissal order and a work book).
Terminate the employment contract on the date the specified court decision enters into legal force. But the dismissal documents may have to be drawn up later, in case you received the court decision after its entry into force.
Give the work record book and amounts due to the employee on the date of dismissal to his relatives (other persons) only if this is provided for by a court decision.
The date of dismissal of an employee recognized by the court as missing is the date the corresponding court decision enters into legal force. This follows from clause 6, part 1, art. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, para. 1 tbsp. 42 Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Part 2, Art. 13, art. 210 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, Letters of Rostrud dated 09/05/2006 No. 1552-6.
You can check the date of entry into force of the court decision on the official website of this court.
Execute the dismissal documents (in particular, the order and work book) only when you have a court decision in your hands, but not before it comes into force. In practice, it is possible that such documents will have to be drawn up later than the date of dismissal. For example, if a relative of a missing employee contacts you with such a decision some time after it came into force. Then it is better to draw up the dismissal documents on the day the court decision is presented to you.
In this case, in order to avoid questions from regulatory authorities, we recommend that you draw up a report in any form, recording in it the date you received the court decision. Such an act will help you justify the execution of dismissal documents later than the date of termination of the employment contract.
What if a worker is found?
Situations in life are different, and an employee declared missing in action may turn up. And it is possible that he will want to return to his previous job. What should the employer do in this case?
First of all, the employee must be sent to court with an application to cancel the court decision declaring him missing (Article 280 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). Then you need to give him a work book, if it has not been handed over to relatives.
After this, you can consider whether to take the employee back or not (after all, the employer does not have such an obligation; the employee was fired legally). Of course, if a misfortune really happened to him, you can meet him halfway, but if he behaved irresponsibly and simply decided to “change the situation,” it’s up to you to decide.
And if you decide to hire him back, the question will arise: what to do with the employee who has already been hired for this position? There are no legal grounds to offer him a transfer to another position, as well as grounds for dismissal. Therefore, everything will have to be decided by agreement with the employees on who is offered which vacant position.
If a compromise is reached, the employee who shows up is hired in accordance with the general procedure: all necessary documents are requested in accordance with Art. 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, draw up an employment contract, etc.
As you can see, the procedure for dismissing a missing employee is quite troublesome (fortunately, not too frequent). If the missing person has relatives, then the main concerns will fall on their shoulders, and you will be left with the dismissal based on a court decision. When there are no relatives, the employer will have to take care of everything. And special care should be taken in the first stage - finding out the reasons for the employee’s absence. Perhaps everything will be resolved at this stage if the employee simply skips work. Then he can be fired for absenteeism. If the employee really disappeared, then the employer will have to act according to the proposed scheme.
In any case, we do not recommend dismissing an employee for absenteeism if the reason for his absence is unknown and the employer is unable to comply with the established dismissal procedure. Under these circumstances, there is a high probability that the dismissal will be considered illegal and the employer, as a result, will have to reinstate the employee at work and pay him the average salary for the entire period of forced absence. Other consequences unfavorable for the employer are also possible.
Types of truancy
Absenteeism is conventionally divided into two categories. The first category includes classic absenteeism (short-term) (Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, the employer knows where the employee who did not come to work is or was. This information came from the employee himself, who showed up for work or was contacted by telephone or otherwise.
What an employer should do in case of short-term absenteeism of an employee is described in Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Before applying a disciplinary sanction, namely dismissal, management must communicate with the employee and find out the reasons why he did not come to work.
Remember! The request is submitted in writing. The employee has two days to respond. If this is not done on time, a specific act will be drawn up. The fact that no explanation is provided does not prevent disciplinary action from being taken.
Please note that the act of refusal to give explanations is drawn up in the presence of other employees who sign this document.
On the day when the employee did not show up for work, you need to draw up a corresponding report. You can also collect testimony from witnesses, reports from the boss of the negligent employee, and take an extract from the accounting journal, which is located at the entrance of the enterprise.
The employer has the right to dismiss an employee in case of absenteeism, if he did not give an explanation, or if the reasons presented as circumstances that prevented him from coming to work are disrespectful.
Having issued such an order, the employer must, within three days (except for the time the person is absent from work), submit a document for review to the dismissed employee against signature. When the employee refused to read the order and sign it, an act is drawn up again.
The second category includes long absences.
During long absences, management is unable to contact the missing employee. He does not go to work for a long time, does not answer calls and does not send a response to the demand for an explanation of what is happening.
Attention! Our qualified lawyers will assist you free of charge and around the clock on any issues. Find out more here.
Cut off the path of return
When the employee appears, he must be required to provide a written explanation (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Without such a document, dismissal for absenteeism will be an extremely risky step - the employee may well appeal it and be reinstated at work, having received earnings for the entire period of forced absence. If the situation is a conflict, it is better to state the reasons for absence in writing and hand it to the employee against signature. The Labor Code allows two working days (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) for preparing explanations.
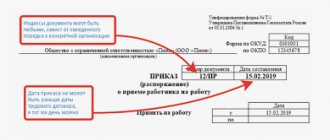
If the reason for missing work is recognized by the manager as disrespectful, then he has grounds for parting with the offender. The decision to dismiss for absenteeism is formalized by an appropriate order using the unified form No. T-8. It must directly indicate that the specialist is being dismissed for absenteeism, and provide a link to subparagraph “a” of paragraph 6 of part 1 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Please note that in the event of a long absence, the order is not issued retroactively, but when the document is actually issued. In this case, the date of dismissal will be the specialist’s last working day. Sometimes an employee refuses to sign an order, thinking that this will help avoid dismissal. Then you need to make a note on the document that the employee refused to familiarize yourself with it, and certify the paper with the signature of a personnel service employee or another person tasked with familiarizing yourself with the order. At this point, the dismissal procedure can be considered completed.
What should an employer do in case of long absences?

Oddly enough, it is more difficult to fire a absentee who does not appear at work for a long time than with short absences. The employer must comply with the requirements of the law, namely Art. 193 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
When a person is away from work for a long time, it is almost impossible to get an explanation from him for what is happening. Management can send a telegram or letter to the lost employee's home address demanding an explanation.
In this situation, it is important to send the letter correctly. What does this mean? First of all, the letter must be registered with a list of attachments and a receipt. If you send a regular letter, the court may not consider the receipt to be sufficient evidence of your desire to contact the employee.
Telegrams are sent in the same way. In addition, you should take a certified copy of the sent telegram from the telegraph office.
As mentioned above, a person has two days to give an explanation. In this case, they are counted from the date of receipt of the letter. Also, another 3-4 days are added to the two days for the so-called mail mileage.
This is when the employee decides to send an explanation in writing by mail. But if after this time no explanations follow, you will have to draw up an act of non-receipt of explanations. The act is signed by the HR department employee, the truant’s manager, and other employees.
If the employee has received a letter, as in the case of returning correspondence to the place of departure, a report on the employee’s absence from the workplace is drawn up daily. In addition to the act, reports from the boss, witness statements and documentary evidence are used (for example, the employee’s signatures are missing in the logbook at the checkpoint).
Important! Do not write reports of employee absence “retrospectively”; do it daily.
If the case goes to court and it turns out that the acts were written later, nothing good will come of it. If a letter or telegram was delivered to a truant worker, and there is confirmation of this, but he never began to fulfill his work duties and did not explain the situation in any way, he can be safely fired.
How to establish the reason for absence
The employee did not show up for work. How should an employer proceed? Based on the norms enshrined in the current legislation of the Russian Federation, the absence of an employee from the workplace without a valid reason for more than 4 hours during a shift or working day is recognized as absenteeism. And the absence of a valid reason in this case is the defining moment.
Note that the employer can learn about the presence or absence of a valid reason either from the employee himself or from the relevant authorities.
Special cases of missing employee
If a person quits his job, he needs to work for two weeks (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But sometimes the parties to the employment agreement make a common decision, and the resigning employee does not work the allotted time.
When there was no agreement and the person does not show up for work after submitting an application, a letter is sent to his address demanding an explanation. The letter also states that if the employee fails to show up for work on the 14th day from the date of submission of the application, it will be recognized as withdrawn, and the person will be fired under the article for absenteeism (Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
When a person does not return to work at the end of his vacation, a corresponding report is drawn up daily. In addition, you need to contact the absentee and clarify the reasons for his absence from work.
Note! Until you have proof that the employee is really absent for an unexcused reason, or until the court recognizes him as missing, you should not write a dismissal order.
In such a situation, you need to use all possible ways to find a person, starting from calls to contacting the police. All this time, do not forget to draw up absence reports. If they are not there, the dismissal will be illegal.
How long does a person have to stay away from work to draw up an order to hold him accountable?
Since absenteeism is a disciplinary offense, the appropriate punishment should follow:
- within one month after the employer learned about absenteeism (the time when the person was sick or on vacation is not taken into account);
- within six months after the commission of a disciplinary offense.
If an employee does not come to work for a long time, you may think that the period for applying disciplinary action will expire.
This is wrong. The fact is that the period that begins to count from the date of discovery of the misconduct begins not from the first day, but from the moment when you definitely found out that the employee is absent.
Strictly documented
It is important to understand the reason for the employee’s absence from work. If the reason is not valid, then it is truancy. They recognize the absence of a specialist in the workplace:
- throughout the entire working day (shift), regardless of its duration;
- more than four hours in a row during a working day.
For such an offense (even for a one-time incident), the employee can be fired. But only if the employee really has no reason that prevented him from performing his duties. As a rule, reasons for absence are considered valid if they are documented and indicate that the person simply did not have the opportunity to be present at work at that moment: he was visiting a doctor, a sick relative, he was urgently called to school or a preschool institution, there were emergencies in the apartment, or on transport on the way to work, etc. This fact can be confirmed by any available document.