Documents required for first-time employment
The documents presented when concluding an employment contract for the first time generally do not differ from the main list specified in Art. 65 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, as stated above, if this is the applicant’s first main job, executed under an employment contract, then he may not provide a work book due to its absence. In this case, the employer undertakes to issue the person with such a personal document, which is prescribed in Art. 66 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It should be noted that according to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 16, 2003 No. 225, an official form for maintaining, storing and issuing a work book is provided. So, the employer issues this personal document on a person’s employment for each employee who works in the organization for more than 5 days. Filling out information by the employer (legal entity) occurs only in the state language of the Russian Federation. Information included in this document may indicate:
- on hiring an applicant;
- about the type of work activity performed;
- about transfer to another specialty, etc.
Information about recovery from the employee is not entered into the work book. However, there is also an exception - the necessary information about the person’s disciplinary liability, in particular, about dismissal, is entered into the personal employment document.
Documents required for employment in any organization
Regardless of whether you plan to go to work every day or work remotely, as well as the area of your professional interests, you will have to present several documents to the employer upon official employment. This:
- identification;
- employment history;
- pension certificate.
For those liable for military service, it is mandatory to present a military ID or a certificate of a citizen subject to conscription.
It would seem that everything is clear with these documents, but in fact there are many nuances here. What if the work book is in another office or is kept in electronic format? What should foreigners who do not have a Russian citizen passport do? Can I show my driver's license instead? Where can I get SNILS if these cards are no longer issued? Let's figure it out.
Identification
According to the law, not every ID can be considered an identity document. One of the following documents is suitable for employment:
- passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation;
- an identity card of a citizen of the Russian Federation, issued at the time of registration of a general passport;
- a passport of a citizen of a foreign state or a document recognized as an identity document of a foreign citizen on the basis of an international treaty of the Russian Federation;
- a document issued to a person for identification by the migration service while it is considering his application for Russian citizenship or recognition as a citizen of the Russian Federation;
- refugee certificate or other documents depending on the status of a foreigner.
A driver's license or proof of membership in any public organization or trade union is not included in this list.
Employment history
If you did not work anywhere before January 1, 2021, you do not and cannot have a work book on paper. It will be conducted (or is already being conducted) exclusively in electronic form. It is the task of your first employer to prepare this document.
Even those who expressed a desire to have this document in electronic format and wrote a corresponding statement at one of their previous places of work may not have a paper work record book. Then the previous employer must give you a paper or electronic document of the established form with information about your work activity.
It is possible that for some reason your former boss does not want or cannot give you the required document. There is no reason to worry about this. You can obtain the necessary paper by contacting the MFC or the Pension Fund, as well as on the government services portal. In the latter case, the document will be electronic, but this is enough.
The work book is located at the citizen’s main place of work. If you get a part-time job, then no one can demand this document from you. To confirm your length of service and work experience, you can show your future boss a copy of your work record, certified by the personnel officer at your main place of work.
Pensioner's ID
Until April 1, 2021, Russian citizens were issued SNILS cards confirming registration in the personalized accounting system. Now an alternative to this document is a notification of registration in this system. It can be issued either on paper or electronically.
Currently, registration in the individual accounting system occurs after the first job. The employer provides the relevant information to the Pension Fund. So, when you are hired for the first time, you are not required to present the relevant document.

List of documents required when applying for a position requiring special knowledge
In some cases, the employer may require additional and more specific documents from the applicant that are necessary to occupy a position in an organization that requires special knowledge and skills.
In particular, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that in order to attract subjects of legal relations in the conditions of the Far North, it is necessary to submit a medical report, within the framework of which it will be stated about the person’s ability to work in such extremely difficult weather conditions (see Article 324 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
A personal medical record will also be required for those workers who wish to get a job in production related to the food industry (Order of Rospotrebnadzor No. 402).
In addition, specific documents are required from vehicle drivers (in particular, having a license with a certain category), law enforcement representatives (since their position is related to the carrying of firearms), etc.
If a resident of another country gets a job, then the employer has the legal right to require additional documents from the applicant for a vacant position: a voluntary health insurance policy, a temporary residence permit in Russia or a residence permit, which is regulated by Art. 327.3 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Body check
As a general rule, undergoing a medical examination when hiring is not a mandatory requirement . Nevertheless, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes a whole list of exceptions to this rule. Thus, an employer, under penalty of administrative liability, does not have the right to hire an employee who has not passed a medical examination if he:
- is a minor;
- will work in conditions that are duly recognized as harmful and unsafe;
- intends to work in the food industry, catering or trade;
- will work in transport or in the field of water supply;
- accepted into the team of medical workers;
- will work in a children's institution;
- works in the Far North;
- gets a job as an athlete.
If the need to undergo a medical examination is established, the employer, before concluding an employment agreement, issues the citizen a referral to a medical institution, with which, as a rule, he has previously concluded an agreement. Payment for the inspection can be made both at the expense of the employer and at the expense of the employee (depending on what conditions in this regard are contained in the company’s legal regulations).

An organization can independently develop a referral form for a medical examination
Depending on the situation (what are the grounds for which a medical examination is required, what are the special conditions for a particular profession or position), various highly specialized medical specialists may be included in the commission. In any case, you will have to see several doctors at once.
What documents does an employer not have the right to request?
If we turn to Russian legislation, then a complete list of documents that an employer cannot require from an applicant is not prescribed either within the Labor Code or the Civil Code. Therefore, this question can be answered, but only based on the content of Art. 65 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, an employer cannot require a future employee to:
- certificates confirming that the applicant’s relatives have infectious diseases and mental disorders;
- a certificate from the woman confirming the absence of pregnancy;
- documents on the ownership of movable or immovable property, etc.
If an employer requires such documents from an applicant, then, according to current legislation, such actions are considered illegal. In particular, for the reason that this may violate the Law on Personal Data. In addition, some documents, in particular, a certificate confirming that a woman is pregnant, can become a cause of discrimination when hiring. In such cases, a citizen has the legal right to contact labor protection and safety authorities, namely the Labor Inspectorate.
Author of the article
We announce a reprimand or reprimand
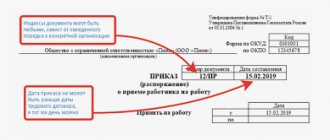
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, upon a written application from an employee, the employer is also obliged to provide him with duly certified copies of documents related to work.
Which documents are considered related to work, in Art. 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is not explained. From the meaning of Art. 62 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which is a general norm of labor legislation, it follows that such documents include an order for employment, orders for transfers to another job, an order for dismissal from work; An employer has the right to punish its employee for committing guilty or illegal actions. One such punishment is a reprimand. This is stated in Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. An employer has the right to punish an employee only for committing a disciplinary offense.
A disciplinary offense is a violation by an employee of the provisions of his job description, as well as internal regulations or labor discipline. For such violations, the employer has the right to impose disciplinary sanctions, one of which is a reprimand. A reprimand can be simple and severe. Depending on the degree of guilt of the employee and the damage caused to him, the employer may issue one of the types of reprimand.
In order to impose a disciplinary sanction on an employee in the form of a reprimand, it is necessary to document the violation and prove the employee’s guilt. To do this, you need to take several steps.
Experts from the legal service of the Trade Union answer the question about the procedure for imposing disciplinary sanctions in the organization. How to properly reprimand an employee if he refuses to perform his assigned duties? The Trade Union lawyer answers: According to part one of Art. 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, for the commission of a disciplinary offense by an employee, that is, for the failure or improper performance by an employee of the labor duties assigned to him through his fault, the employer has the right to apply a disciplinary sanction. This may be a reprimand, reprimand or dismissal for appropriate reasons.
Other disciplinary sanctions may be provided for certain categories of employees only by federal laws, charters and regulations on discipline. For each disciplinary offense, only one disciplinary sanction can be applied (part five of Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). As stated in paragraph.
What documents does an employee have the right to demand from the employer upon dismissal of his own free will? On the day of termination of the employment contract, the employer is obliged to issue the employee the following documents: - a work book (part four of Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation); - a certificate of the amount of earnings for the two calendar years preceding the year of termination of work, and the current calendar year for which insurance benefits were accrued contributions, and on the number of calendar days falling in the specified period for periods of temporary disability, maternity leave, parental leave, the period of release of the employee from work with full or partial retention of wages in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, if for the retained wages for this period, insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund of Russia were not accrued (clause 3, part 2, article 4.
1 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ). Situation from practice Is it possible to apply a disciplinary sanction to an employee who is late for work by an hour, having mixed up the start time of the shift established by the shift schedule? A penalty can only be applied if the employee is properly familiar with the shift schedule. According to Part 4 of Art.
103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, shift schedules are brought to the attention of employees no later than one month before they come into force. In this situation, it is possible to hold the seller accountable only if he is familiar with the shift schedule a month before it comes into effect under signature. In the case where the schedule is posted in an open place (without the signature of employees to familiarize themselves with it), the seller cannot be held liable.
Thus, if the employer familiarized the employee with the schedule within the time period established by law, then the application of the penalty is legal. Situation from practice Is a violation of labor discipline considered repeated if the employee was transferred to another position before committing the second offense? Violation of labor discipline will be considered repeated, even if the employee is transferred to another position, provided that the validity period of the first disciplinary sanction has not expired. According to Part 1 of Art.
194 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if within a year from the date of application of the disciplinary sanction the employee is not subject to a new disciplinary sanction, then he is considered to have no disciplinary sanction. The employer also has the right, on its own initiative, to remove a previously imposed disciplinary sanction from an employee before the end of the year (Part 2 of Article 194 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).