Home / Labor Law / Payment and benefits / Wages
Back
Published: 03/07/2016
Reading time: 8 min
0
4367
One of the progressive and most modern forms of remuneration is commission. It allows you to establish a direct relationship between an employee’s salary and his work achievements, thus stimulating him to better results.
More details about the advantages and disadvantages of this system below.
- When and where is the commission system used?
- What factors does it depend on?
- Types of commission wages Commission-piecework
- Commission and bonus
Piece wage system
The piecework wage system involves payment per unit of products produced by an employee of appropriate quality. It differs from the payment of remuneration under civil contracts in that with the piecework system, periodic payment of wages is carried out in an amount not lower than the minimum established by the state (from January 1, 2014 - 5554 rubles per month // Article 1 of the Federal Law of December 2, 2013 No. 336-FZ), but based on the quantity and quality of products produced by the employee. Remuneration under civil contracts is paid only for the result of labor.
On a note
With piece-rate regressive wages, the same payment per unit of production is made up to a certain norm, and above the norm - with a reducing factor.
There are several subtypes of the piecework wage system.
- Direct piecework means that the same payment is made for each unit of good quality production.
- With piecework-progressive wages, the same payment per unit of production is made up to a certain norm, and above the norm they pay at an increased rate. When applying this remuneration system, the worker’s earnings grow faster than his output, so it is introduced for a short period if there is a problem of non-fulfillment of the plan.
- With piece-rate regressive wages, the same payment per unit of production is made up to a certain norm, and above the norm - with a reducing factor. Such a system is introduced for a short period of time if there is a problem of overproduction.
- With piece-rate
wages and bonuses, a standard of units of production that are paid equally is also established. For products produced in excess of this norm, employees are paid a bonus depending on the number of units produced in excess of the norm. However, in contrast to the piece-rate progressive payment system, products can be paid in the same amount as those included in the established norm. - With lump sum
wages, the wages are set for the range of work performed. In this case, during the period of work, employees are also periodically paid wages not lower than the minimum established by the state, but after the commissioning of a complex facility, they receive an amount determined at the conclusion of the contract for performing a set of works. The cord payment system is appropriate in shipbuilding, where the production cycle is long, in construction when carrying out urgent construction work, and for urgent repairs of large production units. - Indirect piecework
wage: an auxiliary worker receives wages depending on the amount of output produced by the pieceworker whose work he directly supported. The use of this payment system is effective for drivers, loaders, crane operators, and equipment adjusters.
The piecework wage system can be individual or collective.
Individual
payment is applied when the work of each employee can be accurately accounted for. Each employee receives wages for the number of units of products he produces of appropriate quality.
Collective
The nature of the piecework wage system means that the team as a whole receives wages for the number of units of products produced by it, and then the collective determines the wages of each employee using the labor participation coefficient. Collective piecework payment is effective in teams in the coal and mining industry, in logging, in construction teams, in team maintenance, monitoring and control of large apparatus and mechanisms.
How commission trading is processed
In a simplified form, this diagram looks like this. The supplier (principal) gives his goods for sale to an intermediary (commission agent). In this case, the ownership of the goods does not pass to the latter. The commission agent sells the goods to the buyer, acting on his own behalf, but at the expense of the principal. As soon as the goods are sold, the principal ceases to be its owner. The commission agent reports to the supplier, gives him the proceeds for the goods and receives his remuneration.
So, how to arrange a commission correctly? Let’s say a certain company is going to sell a product to a store. First of all, the supplier and the store draw up a commission agreement, which states which of them is the commission agent, which is the principal, and also indicates that the first, on behalf of the second, will sell goods for a fee. It is also better to specify the amount of remuneration in the contract. This can be either a fixed amount for each product sold, or a certain percentage of sales. The law, namely Article 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, obliges the commission agent to report to the committent on sales. The deadlines for submitting the report are not regulated, but it is also better to write them down in advance. A commission agreement can be concluded for a specific period or be indefinite. Entrepreneurs themselves also decide whether to indicate the territory for its execution. A sample commission agreement can be downloaded from our library of document forms.
The commission agreement has been concluded. What's next? Then the goods are transferred to the store, which is accompanied by an act of acceptance and transfer of goods for commission and a TORG-12 invoice. You can download a sample transfer and acceptance certificate, as well as an invoice, on our website. An act of acceptance and transfer of goods for commission is required if this is specified in the contract. If there is no such condition, then an invoice is sufficient.
The shipment of goods has arrived safely at the store, and the commission agent begins selling. By law, the sale of goods must begin no later than the next day after its acceptance. After a certain quantity has been sold, or the reporting period specified in the contract has passed, the store draws up a commission agent’s report. It states how many units of the product were sold, at what price and what the reward amount was. As we wrote above, it is better to stipulate the deadlines for submitting the report in the contract, although this is not required by law. You can agree to provide it every week or every month. We have a sample commissioner's report on our website.
In addition to the report, it is recommended to draw up and sign an agreement on the provision of services between the parties. After all, by making transactions on behalf of the principal, the commission agent provides him with a service. A document is being drawn up about this. The amount in the act is the amount of the commission agent's remuneration for the reporting period.
Along with the report, the intermediary transfers the proceeds to the supplier and retains his commission. Another option is also possible when the committent takes all the proceeds and only then transfers the remuneration to the commission agent. Then the cooperation continues or ends.
If the principal is not satisfied with the commission agent’s report in any way, he must report this within 30 days from the date of receipt of the document. However, this period can be changed with the help of a preliminary agreement of the parties.
Automation greatly simplifies the commission trading process. The MoySklad service offers the optimal solution for both the principal and the commission agent. In the system itself, you can create a commission agreement, take into account the shipment and acceptance of goods, record sales of commission goods, and automatically generate commission agent reports. At the same time, in all created forms and reports, revenue for goods sold, commission agent's remuneration, VAT and other necessary amounts are instantly calculated.
Now let's see what the law tells us about special cases. Commission trading: special cases
The commission agent sold the goods more expensive or cheaper than expected
Let's say the goods were selling so well that the store decided to raise prices on them. In this case, the commission agent managed to obtain additional benefits, which, by law, he must equally share with the principal. Unless, of course, other conditions are provided for in the contract. And here you need to pay attention to one important detail regarding the processing and payment of this money. According to the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 5, 2008 No. 03-03-06/1/347, before part of the profit is paid to the commission agent, the committent must display this entire amount in income that is subject to income tax. And only after that accrue what is due to the commission agent.
If for some reason the goods were not sold at the agreed price, and the store reduced it, then there are two possible scenarios.
- The store proved to the consignor that it did not have the opportunity to sell the goods at a higher price, and this move prevented even greater losses. In this case, the commission agent will not be required to return the difference.
- The store failed to prove that the price reduction was a necessary step. Then, alas, the commission agent will have to compensate the supplier for the loss.
By the way, it is not forbidden to include these cases in the commission agreement. In addition, you can add conditions to it that, before changing prices, the commission agent must ask permission from the principal.
The contract was not fulfilled
Let's say that part of the goods that the principal delivered to the store turned out to be defective, or the agreed quantity of goods was not delivered, or for some other reason the commission agreement cannot be fulfilled due to the fault of the supplier. In this case, the law requires the principal to still pay the commission agent remuneration, as well as reimburse expenses. If the commission agreement cannot be executed due to the fault of the store, then, in turn, it will have to compensate the principal for damages.
Subcommission
Let's imagine that the store has found another profitable point of sale of goods, which is managed by another company. In this case, he has the right to conclude a subcommission agreement with this company. Then the commission agent is responsible for the actions of the sub-commission agent to his principal, and for the second store he himself becomes the principal. And a few important notes. Subcommission is possible unless otherwise specified in the commission agreement. In this case, the principal does not have the right to enter into relations with the subcommissioner, unless, again, otherwise provided by agreement of the parties.
The commission agent did not sell a single product during the reporting period
If all the goods remain in the warehouses and shelves of the store, the store has the right to return them to the consignor. The return of the goods, as well as its receipt, is issued with a TORG-12 invoice.
The trade management service MoySklad will help to significantly facilitate the process of returning goods from the commission agent to the consignor. The system has special forms in which returns are registered, and the entered data is automatically transferred to all reports that are related to the execution of the commission agreement.
Time-based wage system
The use of this system involves payment per unit of time worked by the employee. The main criteria for a time-based wage system are the qualifications of the employee and the complexity of the work he performs.
Depending on what unit of time is used in the time-based wage system, we can distinguish hourly, daily and monthly wages, depending on the qualifications and complexity of the work performed by the employee.
The time-based remuneration system is effective when providing consulting services.
Return of goods to the commission agent from the buyer
Let’s say that a retail buyer wants to return an item for some reason.
Considering that, when selling goods to a client, the commission agent, on his own behalf, entered into a purchase and sale agreement with him, then he formalizes the refusal of this transaction.
If the buyer returns the goods due to detected defects, responsibility for them must be distributed between the commission agent and the consignor. If the goods were damaged due to the fault of the store, then the buyer will reimburse the costs. And if it turns out that the supplier is at fault, the commission agent will be entitled to reimbursement of expenses and remuneration.
The goods can be returned before the commission agent's report is signed by the parties, or after. In the first case, the intermediary makes an entry in the report for the amount of the return with a minus sign. In the second, the wholesale buyer, returning the goods, issues an invoice in the name of the commission agent. If the final buyer is a retailer, then he must write a statement to return the goods. After this, the commission agent returns the goods to the consignor, accompanied by a return note in his name, as well as an invoice. Based on these documents, the principal will be able to reduce his VAT payable.
Tariff system of remuneration
Tariff remuneration systems are remuneration systems based on the tariff system of differentiation of wages for workers of different categories (Article 143 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Tariff system
differentiation of wages for workers of various categories includes tariff rates, salaries (official salaries), tariff schedule and tariff coefficients.
Tariff schedule
– a set of tariff categories of work (professions, positions), determined using tariff coefficients depending on the complexity of the work and the requirements for the qualifications of workers.
Tariff category
– a value that reflects the complexity of work and the level of qualifications of the worker.
Qualification category
– a value reflecting the level of professional training of the employee.
Tariffication of works
– assignment of types of labor to tariff categories or qualification categories depending on the complexity of the work.
...tariff wage systems - wage systems based on the tariff system of differentiation of wages for workers of various categories (Article 143 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)...
Tariff systems of remuneration are established by collective agreements, agreements, local regulations in accordance with the law, taking into account the unified tariff and qualification directory of works and professions of workers, the unified qualification directory of positions of managers, specialists and employees or professional standards, as well as taking into account state guarantees for payment labor (Article 143 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For employees of state and municipal institutions, the recommendations of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations (Part 3 of Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and the opinions of the relevant trade unions (associations of trade unions) and associations of employers (Article 144 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) are also taken into account.
Advantages and disadvantages
The benefits of the commission system for the employee include:
- the ability to independently plan working hours and expected earnings;
- flexibility in choosing methods and work schedule;
- the presence of motivation to work on constantly improving the level of professional skills, which makes it possible to increase one’s competitiveness in the labor market.
Question: An employee has a commission system of remuneration. Does the employer have an obligation to pay extra up to the minimum wage if the employee earns less? View answer
Disadvantages for employees:
- frequent refusal of employers to introduce a fixed minimum salary, which could be received even in the absence of positive sales dynamics;
- dependence of labor results on the brand and characteristics of the products sold;
- the possibility of a lack of new business due to current negative trends in the financial or political sectors;
- lack of material stability.
The benefits for employers come down to the presence of a strong motivational factor and the opportunity to save on labor costs at a low level of sales. An additional advantage is the promotion of certain categories of goods at a faster pace by establishing increased premiums for transactions on them.
How to calculate earnings using a commission system of remuneration ?
The negative side is the need to thoroughly study the legal issues of introducing a commission system to reduce the likelihood of unscheduled inspections by the labor inspectorate and prevent labor disputes.
Grading
Russian companies currently widely use a foreign analogue of the tariff schedule - grading, developed by Edward Hay in 1943. In accordance with this system, all positions in the company are given points, depending on which the salary of each employee is calculated using score tables. In practice, there are 2 approaches.
- Grading of positions or jobs, when a position is evaluated, regardless of which employee occupies it. The grade depends on the value and importance of this position for the company. This system is used by LUKOIL Overseas Holding Ltd., LLC LUKOIL Perm, OJSC Zarubezhneft, but it can be successfully applied by any medium and large manufacturing and trading companies.
- Grading of employees, when employees are assigned to grades personally, taking into account the value of the work performed and the skill level of the employee himself. Such a system exists in the companies IBS and MTI, but can be implemented in consulting firms and other small organizations where high demands are placed on the level of education and qualifications of employees.
When and where is the commission system used?
The essence of the commission system is that the employee receives a salary in the form of a fixed percentage of the revenue that the enterprise received from its activities. This payment system is a type of mixed one and is itself divided into several separate types.
The most common application of the commission system is sales.
It is in this area that the use of such a system is most effective. It allows you to stimulate not only sales in general, but also the volume of sales of a particular product by setting a higher commission payment on them.
Examples of enterprises and departments where this system is most often used:
- sales departments;
- advertising agencies;
- enterprises that sell finished products;
- foreign economic services;
- companies that provide various services to the population;
- marketing departments.
In some cases, this system can also be used in manufacturing enterprises, especially if there is a need to increase production volumes of a particular product. In this case, the employee may be given a fixed amount of additional payment for each unit of product manufactured.
The main advantages of this system include:
- high interest of employees in the results of their work;
- the ability to increase sales volumes of only one or several types of products;
- the employee’s ability to independently plan and calculate their wages;
- flexibility (an employee can determine his own work plan and sell goods in accordance with it, at the most convenient time).
The disadvantages are:
- instability of wages;
- the inability of an employee in some cases to influence sales volume;
- dependence of wages on the market situation.
All of the listed disadvantages are almost completely eliminated by establishing a fixed salary or a minimum rate for the employee, which he will receive regardless of the results of his activities. At the same time, all the advantages of this system are still preserved, because the employee will be directly interested in increasing his salary.
Conclusion
Lump sum, mixed, commission, direct, indirect, piecework-regressive, daily, monthly, hourly, tariff, floating... Each organization uses its own remuneration system, reflecting its goals and traditions of the company, taking into account available financial resources, therefore a universal effective system there is no wages.
Magazine "Consultant"
Invaluable experience of top managers of leading Russian companies in solving current and fundamental corporate problems in the Consultant magazine. Subscribe now >>
Types of commission wages
The commission system, which itself is a type of mixed, is also divided into two types.
Commission and piecework
In this case, the employee’s salary depends entirely on his output and can be determined as:
- the product of the established percentage by the cost of products sold by the employee;
- the product of a fixed monetary amount and the volume of products sold (produced).
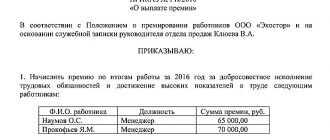
An example of calculation according to this scheme:
Salary of the seller Nakhimov A.I. depends on the sales volume of several types of products and is set as follows:
- 150 rub. from the sale of each electric kettle;
- 400 rub. from the sale of one multicooker;
- 700 rub. from the sale of a TV.
During the month the seller sold the following quantity of goods:
- 28 electric kettles;
- 18 multicookers;
- 14 TVs.
Nakhimov’s final salary will be:
Salary = 28 * 150 + 18 * 400 + 14 * 700 = = 21,200 rub.
Commission and bonus
In this case, the salary consists of two components:
- established salary (usually it is determined in the amount of the minimum wage);
- percentage of sales (represents additional payment, the so-called performance bonus).
The specific method depends on what goals the enterprise pursues and what kind of activity it is engaged in.
Example of salary calculation using the commission-bonus system:
- Her final salary will be:
- Salary = 900,000 * 7% + 8000 = 63,000 + 8000 = 71,000 rub.
- If the employee had not found a single buyer for the products, she would have received her minimum wage - 8,000 rubles.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Question No. 1 . Can the commission system of remuneration be used in enterprises that are not involved in the sale or distribution of goods and services?
In the current economy, this option in many cases turns out to be convenient for both the employer and the employee. However, if it turns out to be impossible or difficult to find out for sure the level of profit that an employee brought, then such a payment system can be combined with another.
Question number 2 . Can an employer change the predetermined commission percentage?
Yes, but for this he will need to obtain the consent of all other management officials at the enterprise, issue an order, and also be sure to familiarize the employee with the changes, having received a receipt from him for familiarization.
Question number 3 . If the company operates a commission system of remuneration with a set minimum income, which the employee did not earn in a month, what salary will he receive?
In accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, an employee will still have to receive the established minimum, even if he has not earned it in a month (see → minimum wage by year).
Question number 4 . Can an employer change the established minimum wage at the enterprise (base rate)?
Yes, it can, but in order to do this, he will need to obtain consent from other management officials at the enterprise, issue an order and be sure to introduce it to all employees who will be affected by this issue.
Main features and nuances
This system has many unique features and characteristics, which are clearly reflected in the following table.
| Feature name | Content |
| Many forms of establishing commission amounts | Among these forms, several of the most frequently used ones can be identified:
|
| Compatibility | This payment system can act as an independent one or serve as an addition to another system. For example, a combination is often encountered when an employee is assigned a fixed salary, to which, based on work results, a percentage of the work performed is added. |
| Stimulation | For many employees, the commission system of remuneration serves as a good incentive for more active sales and increased sales volumes. |
| Mutual benefit | Such a remuneration system is beneficial not only for the employee as a reliable incentive, but also for the employer. It is beneficial for the director of an enterprise if he pays less to someone who has worked little in a month, since this is fair. The result of the work can also be clearly monitored. |
| Openness of regulatory documentation | Documents regulating wages within the company must be publicly available to any employee. They must include information such as bonus conditions (if any); the number of employees receiving salaries according to the specified scheme; the amounts and timing of these payments. |
Among the features, in most cases only positive features can be noted - therefore, recently there are more and more adherents of this particular remuneration system.