Pension before and after the revolution in Russia and the Soviet Union
In Russia, pensions began to be paid for the first time after the revolution.
In August 1918, pensions were introduced for former military personnel, in particular for disabled military personnel who served in the Red Army.
In 1923, party activists joined them. But this applied only to the category of old Bolsheviks and political prisoners, and not at all to those who conditionally joined the party in 1918.
In 1928 there was another expansion: pensions began to be paid to people working in the mining and textile industries.
In 1935, the payment of pensions for disability and old age was assigned to artels, in which a special fund was created.
Peasants in pre-revolutionary Russia, in principle, did not receive any pensions. Under Soviet rule, pensions were not paid to collective farmers right away. Only in the early 60s did additional changes begin to occur in the social sphere. It was then that the universal pension system appeared.
There were 2 basic designs:
- pensions for workers and employees of state enterprises;
- pension for collective farmers.
Until this time, the Soviet government did not pay any attention to this.
In 1974, disability and survivors' pensions were introduced. At the same time, some categories of citizens received the right to receive a long-service pension. But these norms were regulated by special laws.
It is interesting that in 1920 a special decree on “personal pensions” was signed. This applied to persons who had “special services” to the revolution. The maximum personal pension amount was 1.2 thousand rubles.
Average pension in Russia by region
The average pension amount depends on several factors. First of all, it is influenced by the subject of the Russian Federation in which the pensioner lives, as well as his profession.
Thus, from 2021, the average pension in the Rostov region became equal to 12,250 rubles.
It must be said that as of the beginning of 2021, insurance pensions in the Rostov region are paid to approximately 1.31 million citizens, which is an order of magnitude more than in 2021. In the Moscow region, the average pension amount is 13,900. In the Sverdlovsk region, this figure is 15,400.
First reform
By a special resolution of the USSR Central Executive Committee of October 29, 1924, a code of laws on benefits and benefits for military personnel of the Red Army, for persons serving in the navy, as well as for members of their families, including children, was approved.
Universal pensions were introduced only in 1937, on the 20th anniversary of the Great October Socialist Revolution.
On the eve of the Second World War, a decree was introduced that determined the size of pensions in the USSR. It depended on the length of service, the amount of wages and the reasons for the military personnel’s incapacity for work.
Second reform
The law on state pensions was adopted in 1956. Additions to this USSR law were issued in 1964 (the law on pensions and benefits for members of collective farms). Only after this did collective farmers receive relatively equal rights to workers.
According to the USSR law on state pensions, the formation and calculation of pensions was possible in relation to:
- workers and employees;
- military personnel;
- citizens who became disabled (they were paid a disability pension);
- family members, including children of the above citizens (in case of loss of a breadwinner).
Old age pensions and long service pensions were also paid.
When they went on vacation
Men retired at 60, women at 55. This bar has existed since the early 30s.
At the same time, raising the age limit for pensions was unprofitable for the state. Early retirement was designated as compensation for the low amount of pension payments themselves.
Pension minimum in the USSR
The minimum pension in the USSR (old-age pension) was officially 35 rubles.
The average pension in the USSR was 65 rubles. The maximum pension in the USSR was 120 rubles.
Work experience
When calculating pensions, length of service was taken into account. This applied to absolutely all professions. After the reform of 1956, it was established that retirement was allowed after 25 years (men) and after 20 years (women) of work.
Going on vacation early
The right to early retirement appeared only in 1991. This applied to men with 42 years of work experience and women with 37 years of work experience.
Their pension was assigned 2 years earlier than the generally established retirement age. This law came into force in all republics of the former USSR.
Early retirement was permitted in the following cases:
- hazardous working conditions;
- work in extreme conditions (first of all, this applied to citizens who worked in the Far North, they were awarded a “northern pension”).
What does an insurance pension consist of?
The main type of pension that almost all Russian pensioners receive is old-age insurance pensions.
. In other words, these pensions:
- calculated taking into account contributions to compulsory pension insurance (until 2001, the system was slightly different);
- are due to those who have reached a certain age (in 2021 these are women born in 1965 and men born in 1960).
The insurance nature of pensions means that the more a person (and his employer) contributed to the Pension Fund, the higher his pension.
The old-age insurance pension consists of two main parts:
- The insurance pension itself is a variable value, depending on the number of pension points. In 2021, each costs 98.86 rubles;
- a fixed payment is the “basic” part of the pension that everyone is entitled to. In 2021 it is equal to 6044.48 rubles.
It is these two parts that make up the pension. All additional payments are included in them in one way or another - for example, additional payments for children are taken into account in the form of additional pension points, and additional payments for dependent children or 30 years of experience in rural areas are added to the fixed payment.
But the amounts are calculated according to the same rules throughout Russia
, although the standard of living (and most importantly, its cost) is different everywhere. In order for pensioners to somehow live on their pensions, the Pension Fund cannot pay less than the subsistence level. Moreover, the cost of living is established in each region separately, once a year, and is calculated using a rather complex formula.
What about those whose pensions are below the subsistence level? Then everything depends on the region. As a rule, the higher the prices in the region, the larger the budget. Therefore, if the cost of living of a pensioner in the region is higher than the national one, and the pensioner does not work, the regional budget will pay extra to the minimum (and this will be a regional social supplement - RSD
).
And if the cost of living in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation is lower or equal to the Russian one, the federal budget pays extra (federal social supplement - FSD
).
So far, among the regions, the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug holds the highest living wage - 19 thousand rubles. High minimum pensions are paid in oil-producing regions (KhMAO, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Autonomous Okrug), as well as in regions with difficult climatic conditions (Murmansk region).
If the insurance pension is below the subsistence level
, then it is calculated using a more complex system, and already consists of 4 parts:
- the actual insurance pension;
- fixed payment;
- the amount of indexation in the current year (calculated from the sum of points and a fixed payment, in 2021 it is 6.3%);
- amount of social supplement.
What’s interesting is that the total amount is equal to the sum of the cost of living and indexation
- this was done so that the annual indexation would not be “eaten up” by the low increase in the cost of living.
However, there is a place in Russia where, in addition to these amounts, pensioners also receive other additional payments - this is Moscow.
How much did you receive under the Soviet Union?
In the 60-80s there was a concept of a pension of union significance. The average size of such a pension, according to the Constitution of the USSR, was 252 rubles per month. The size of republican and local pensions in the USSR is 162 rubles. and 140 rub. respectively.
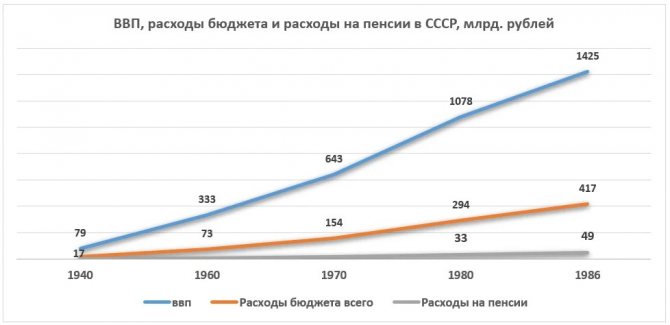
Expenses on pensions in the USSR from 1940 to 1986
An increase in pension was expected - an annual payment for health improvement.
The average level of the pension system was quite low (especially in comparison with European countries, at least those that were part of the socialist camp).
As soon as oil prices began to fall, it became clear that it was impossible to plug the budget holes. Accordingly, pensioners were among the first to suffer, their numbers increased from 14 million to 34 million over 30 years. Pension rates remained unchanged.
In 1980, the share of budget subsidies to the social insurance fund reached 60%. The Constitution of the USSR declared general social guarantees. At the same time, the general standard of living steadily declined.
Up to 80% of low-income people were pensioners, predominantly older and elderly. There was no way to increase their pensions (in the amount of 15-20 rubles).
Occupational pension benefits
The additional payment (pension supplement) to qualified specialists was paid for life: first in the form of a salary supplement, and then in the form of a pension.
The amount by Soviet standards was gigantic. But there were few people who could receive additional payments. Everyone else's social pensions were much more modest.
How much did the workers get paid?
In the 1930s, preferential supplements were introduced for elderly collective farmers and individual farmers.
In the 60s, pensions on collective farms were paid at 6-8 rubles. For some, with a total length of service of 40 years, the pension experience was incomplete, since collective farm service was not taken into account when retiring from a state-owned enterprise.
In the mid-60s, a collective farmer-peasant received 12-14 rubles, then (around the mid-70s) 20-24 rubles.
Collective farmers who retired in 1962, having had 31 years of service at that time, could receive pensions in the amount of 6 rubles. In 1974, their pension was increased to 12 rubles, and in 1984 they increased it again, and the payment became 40 rubles.
There were no benefits for collective farmers. They only helped disabled war veterans.
Teacher with a salary of 220 rubles. received a pension of 130 rubles. The teacher's pension was calculated based on length of service.
An estimator who decided to retire in 1965 and had a salary of 120-140 rubles received a pension of 85 rubles.
During the Soviet era, the minimum miner’s pension was calculated at the following rate: 10 years – 120 rubles, 15 years – 140 rubles, 20 years – 160 rubles, 25 years – 180 rubles.
Military pensions
There were millions of military pensioners in the union. USSR military pensions were 2 times higher than those of ordinary workers.
Retired army officers (for example, those with the rank of colonel) and state security could receive a pension salary of 250 rubles per month. Employees of the USSR Ministry of Internal Affairs received 220 rubles per month.
Heroes of the USSR were paid a monetary allowance only for the medal itself in the amount of 240 rubles per year or 20 rubles per month. WWII veterans received additional benefits for housing, cars, and travel by any type of public transport.
Payments to disabled people
Minimum amounts (minimum) of disability pension payments:
- 1st group: 75 rub.;
- Group 2: 50 rub.;
- Group 3: 26 rub.
Maximum sizes: for groups 1–2 – 120 rubles, group 3 – 60 rubles.
Amounts of survivor's pensions:
- 3 or more family members: 75 rubles;
- 2 family members: 50 rub.;
- 1 family member: 28 rub.
The highest pensions in Russia: Cosmonauts receive five times more than people's artists
Despite the almost 60-year history of our space Odyssey, we still have a little more than a hundred people who have been in orbit
Photo: GLOBAL LOOK PRESS
There are almost 50 million pensioners in Russia. Most of them receive insurance pensions. Previously, they were called labor. They are determined based on accumulated pension points. But there are also separate categories: military, civil servants, judges. There is a percentage of the salary. And then there are the elite – those who receive ultra-high pensions. Who is better to work for in order to receive a high pension in the future? Komsomolskaya Pravda compiled a rating of the most important professions and positions.
BECOME PRESIDENT OF RUSSIA
In 2021, the salary of head of state Vladimir Putin is 773 thousand rubles. When he finishes his job, he will be able to receive 75% of this level. That is 580 thousand rubles. Now the president receives only a military pension (its amount is not disclosed). But he did not submit an application for a civil pension to the Pension Fund. For comparison, the first and last president of the USSR, Mikhail Gorbachev, receives more than 800 thousand rubles per month. This is 40 times the minimum wage in Moscow. This is stated in the law adopted in the early nineties.
WORK AS A PRIME MINISTER
The salary of the head of government is also quite large. In 2021 it is 620 thousand rubles. If a person works in this position for one to three years, he has the right to receive 55% of the average salary. And if more than three years – 75%. In money it is 465 thousand rubles. This is exactly how much Dmitry Medvedev will receive when he retires at 65.
Dmitry Medvedev will receive 465 thousand rubles
Photo: REUTERS
FLY INTO SPACE
Despite the almost 60-year history of our space Odyssey, we still have a little more than a hundred people who have been in orbit. Cosmonauts are granted pensions after 25 years of service. At the initial stage, it will be 55% of earnings. And if a person does not stop working, then in ten years it can increase to 85%. According to the Cosmonaut Training Center for 2021, the average salary of team members was 170 thousand rubles, and the most experienced - 300 thousand. Thus, their pension in the future will range from 165 to 255 thousand rubles per month.
TO JUDGE AND NOT BE JUDGED
Judges of various categories receive from 70 to 250 thousand rubles. In theory, such a sum should make the judge incorruptible. Salary is affected by position, class, length of service, region of work and academic titles. The pension is calculated based on the salary received by an active judge of the same category. If you have more than 25 years of experience (but before reaching retirement age), this is 50% of the salary. And when entering a well-deserved retirement in old age – 80%. Thus, a judge's pension ranges from 35 to 200 thousand rubles per month.
LEAD THE REGION
The authorities of some regions came up with an interesting move in 2021. They raised their own pensions. For example, deputies of Kamchatka passed a law according to which they increased regional pension supplements for themselves, their loved ones. As a result, the pensions of the region’s top officials (including the governor) more than doubled – to 100–150 thousand rubles per month. The convenience of the situation was that the funds came from the regional budget. That is, there was no need to coordinate the reform with the federal authorities. The officials were not at all embarrassed that the budget of Kamchatka, despite all its riches, is still in deficit.
PERFORM A HEROIC ACTION
But not an ordinary one, but one that will be recognized at the state level. On average, 10–15 people a year receive the title of Hero of Russia. To do this, you need, for example, to land a plane in a corn field, as Damir Yusupov and Georgy Murzin did in August 2021. Or conduct successful special operations in Syria, like generals Sergei Rudskoy and Andrei Serdyukov, who received ranks earlier this year. Amount – 65.6 thousand rubles per month. If a person lives in Moscow, then the capital’s authorities add another 25 thousand. At the same time, payments to Heroes of the Russian Federation are assigned immediately, regardless of age. So it’s more likely not a pension, but a lifetime passive income.
LEAD THE MINISTRY
Ordinary ministers have much lower pensions than top officials of the state. Their calculation comes not from the official salary, but from monetary remuneration. It is only 85 thousand rubles per month. And the requirements for length of service are slightly higher than those of the head of the Cabinet of Ministers. To receive an additional payment of 55%, you need to work for three years, and to receive 75%, you need to work for more than six years. In rubles this is 46.6 and 63.6 thousand rubles per month, respectively.
TO BE ELECTED AS A DEPUTY OF THE STATE DUMA
In 2021, the speaker of the lower house of parliament, Vyacheslav Volodin, decided to dot all the i's on the topic of deputy pensions. He clarified that although deputies earn 400 thousand rubles a month, their pension is calculated from the same monetary remuneration that ministers receive. Only the timing differs. They are a little longer. You can receive 46.6 thousand rubles if you have worked as a deputy for more than five years, and 63.6 thousand for more than 10 years.
Although deputies earn 400 thousand rubles a month, their pension is calculated from monetary remuneration
Photo: Vladimir VELENGURIN
ENTERTAIN THE PEOPLE
After retirement, people's and honored artists of Russia receive an increase of 30 thousand rubles. But only if they are registered in Moscow. Of the federal allowances, there are only payments for Knights of the Order of Merit for the Fatherland. They add another 18.5 to 23 thousand per month. The average pension of a famous artist is 40 – 70 thousand rubles.
DEFEND THE HOMELAND
Military pensions now exceed civilian ones. They got a big raise about 10 years ago. But they haven't increased it since then. The long-service pension is 50% of the salary. It can be obtained after 20 years of service. And if you continue to serve further, then every year another 3% will be added. The maximum you can receive is 85%. But there are also nuances here. The salary in law enforcement agencies is small. Even generals receive 60-70 thousand rubles a month, and junior officers - 20-30 thousand. Plus there is a reduction factor. As a result, the average military pension in 2021 was 26 thousand rubles. The amount depends on the position, rank and length of service and ranges from 20 to 40 thousand rubles.
SERVE THE STATE
For civil servants (that is, employees of federal and regional authorities), pensions also depend on salary. And the replacement rate is decent. With 17 years of experience, 45% of the salary is due. And if you work another 10 years, then 75%. True, there is a nuance.
Firstly, to receive such a pension, you need to retire from the civil service. If you leave earlier, you will be assigned a regular insurance pension. Secondly, the retirement age for officials is now higher than for everyone else. This means you will have to wait longer. Thirdly, civil servants' salaries are usually small. Therefore, for many it is more profitable to retire according to the usual rules. That is, use pension points for calculations, and not the replacement rate. The exception is high-ranking officials.
Clearly.
WHAT ELSE DO THEY ADD FOR?
There are still many different coefficients and nuances that can affect the size of the pension. Here are the main ones: - Military personnel can receive two pensions at once if they also worked in civilian life. With a minimum required experience of 20 years, this is quite possible.
— Those who live in the harsh conditions of the North or have lived there for 15–20 years receive a higher pension. This gives an increase of 30 - 50%.
— Supplements are awarded for disability of one degree or another. This applies to all categories of citizens.
— An increasing coefficient is given to those who deliberately postpone their retirement. If you apply to the Pension Fund only five years after reaching retirement age, income from the state will increase by one and a half times. — They also pay extra for those who have reached their 80th birthday. Their fixed payment is doubled. That is, the pension increases by 5,700 rubles.
Note:
The overall size of the pension in Russia is influenced by many factors. Each person has individual work experience and a list of merits. There are social and regional additional payments, allowances specified in special laws, and corporate pensions that large companies pay their employees. Many of the charges are cumulative. One thing is for sure. A high pension is usually for those who worked a lot, received a lot, held a high position and live in a large city or rich region.
QUESTION - RIB Why do officials and military personnel receive so much?
Tatyana Omelchuk, senior researcher at the Research Financial Institute (NIFI):
— There are several reasons why pensions for military and civil servants are considered differently. Firstly, the specifics of the work. They have a responsible job and, in fact, irregular working hours, for which, unlike employees of state-owned companies, they are not paid anything extra. Secondly, tradition. These laws have hardly changed since Soviet times. Thirdly, the desire to retain more experienced employees in the service. Linking to length of service encourages people not to leave work.
There are almost 50 million pensioners in Russia.
Photo: Ekaterina MARTINOVICH
REFERENCE "KP" What about ordinary people?
Most pensioners in Russia receive a regular insurance pension. Since 2015, its size is determined by a new pension formula. It converts our official salary into pension points. And upon retirement they will be converted into rubles. The idea is simple - the more a person works and the more he earns, the higher his pension will be in the future. The formula consists of two parts:
— Fixed payment (5686.25 rubles); — The number of pension points multiplied by their value (93 rubles). For example, if by the time of retirement a person has accumulated 100 pension points, then his pension will be 5,686.25 + 9,300 rubles = 14,986 rubles. In 2020, you can earn 9.57 points, and from 2021 the maximum amount will increase to 10 points. If we round up, now one point is given for a “white” income of 10 thousand rubles per month. If you earn 30 thousand rubles per month (360 thousand per year), you will be able to earn 3 points. And with a salary of 100 thousand - 10 points. This is the ceiling. Even if a person earns a million, his pension will not be higher.
USEFUL LINK
You can find out how much experience you have and how many points you have accumulated on the Pension Fund’s website in the “Personal Account of a Citizen.” To do this, you need to go there using the login and password from the government services portal. All information will be in the “Get information about generated pension rights” section. There is also a calculator for calculating your future pension.