Yulia Zhizherina, business consultant on personnel management and labor law, tells how to prepare salary documents to avoid fines.
Employers often make mistakes when describing wage conditions, which can lead to unpleasant consequences.
For incorrectly indicating the terms of remuneration in an employment contract, the employer may face administrative liability under Part 4 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the form of a fine on officials in the amount of 5,000 to 10,000 rubles; for legal entities - from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles.
If the employer incorrectly prescribed wage standards in local regulations, he may be held liable under Part 1 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the form of a fine on officials in the amount of 1,000 to 5,000 rubles; for legal entities - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
If working conditions are incorrectly reflected in the employment contract or local regulations, there is also a risk of a dispute with the employee, who, to protect his rights, can appeal to both supervisory authorities and the court.
If an employee contacts supervisory authorities, the employer will in any case face an inspection. If the employee goes to court, then if a decision is made in his favor, he can also recover moral damages from the employer.
To avoid these risks, spell out the terms of remuneration correctly in all documents.
In local regulations
Labor laws governing wages are few in number. Art. 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that wages are established by an employment contract in accordance with the current employer’s remuneration systems, described in local regulations. Thus, local regulations are the main documents regulating wages. Based on these documents, the terms of remuneration are reflected in the employment contract.
The only requirement for local regulations is that they do not worsen the situation of workers in comparison with the legislation.
For whom will the new minimum wage be established (hourly)
Employee salaries must correspond to the minimum hourly rate if two conditions are met simultaneously:
- working part-time;
- the employment contract is fixed-term and concluded for a period of up to 3 months.
The use of the indicator in other situations is unacceptable.
It turns out that the accountant will now monitor the compliance of salaries not only with the monthly minimum wage, but also with the minimum wage for individual employees.
In the internal labor regulations
According to current practice, the internal labor regulations must necessarily reflect the timing of payment of wages (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, specific dates should be specified.
To avoid errors in determining payment dates, keep in mind that wages must be paid at least every half month, and no later than 16 days after the end of the period for which they were accrued (ILO Recommendation No. 85):
“The official salary is paid to the Employee every half month for the time actually worked based on the time sheet: for the first half of the month - on the 16th day, for the second half - on the 1st day of the next month.”
As for the amount of wages for the first part of the month (the so-called advance), the rules need to stipulate that it is paid according to the time actually worked (Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated May 23, 1957 No. 566; Letter of Rostrud dated 09/08/2006 No. 1557- 6) in accordance with the report card. Setting the first part of the salary at a specific amount, for example 40%, is illegal.
In the terms of remuneration, it will be illegal to establish that the employee is obliged to receive wages from a certain bank, for example, as part of a salary project (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Please note that to change the bank, the employee must inform in writing about the change in the details for the transfer of wages no later than five working days before the day of payment of wages. This condition can be fixed in a local act. The employer has the right to establish a special procedure for an employee to submit an application to change a credit institution.
According to Art. 134 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the company must establish conditions for wage indexation (see also Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated June 17, 2010 No. 913-О-О). The provisions of the current labor legislation do not directly indicate the frequency of wage indexation; it is determined by the employer. This is usually done once a year:
“The Employer indexes the wages of employees, as a rule, by 3% annually in the second quarter of the current year based on the financial capabilities of the Employer and the approved budget.”
Write down all the guarantees and compensations provided to employees by law (allowances, additional payments, compensation), and also secure other payments established by the employer (for example, the possibility of bonuses).
New changes to the minimum wage: prerequisites
The minimum wage is set annually and is equal to the subsistence level of the working-age population for the 2nd quarter of last year. In 2020, this figure is 12,130 rubles. (Federal Law dated December 27, 2019 No. 463-FZ). Regions can set their own minimum wage, which cannot be lower than the federal one, i.e. 12,130 rubles.
The minimum wage arose in connection with the need to evaluate the work of the lowest paid workers. Thus, the state is trying to ensure a minimum threshold of fair wages and control employers.
Control is carried out as follows:
- The Federal Tax Service pays attention to understated incomes in forms 6-NDFL, “Calculation of insurance premiums” (special control ratios have been developed for this purpose, comparing indicators with the minimum wage and industry average wages in the region);
- inspectors will send a demand to the employer to explain the low salary figures;
- tax officials send information about violations to the labor inspectorate, so employers who underestimate wages may be called to the labor commission;
- the payer also risks being included in the plan of on-site tax audits (clause 5 of Appendix 2 to the Federal Tax Service order No. MM-3-06/333 dated May 30, 2007).
Unscrupulous employers often pay workers below the minimum wage, arguing their position with part-time work. It is for such a case that the Government will establish a new minimum wage - hourly.
In the wage regulations
Be sure to establish a wage system, a system of additional payments and allowances, and a bonus system (Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If different categories of employees have different remuneration systems, the remuneration regulations must describe them all.
The section on the remuneration system or systems describes its elements: time-based, time-based-bonus, piece-rate, piece-rate-bonus, commission, etc. If the system includes salaries, you can specify how they are set. If the company has a grading system, it can be included in the salary regulations as an appendix.
In light of the requirements of Art. 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicate that wages cannot be lower than the minimum wage established by law.
To discipline employees, state that “wages are calculated based on the working time worked by the employee according to the working time sheet. The employee’s absence from the workplace without good reason is not paid.”
The amount of additional payments for combining duties, performing the duties of an absent employee, or expanding the scope of work can be stated as a specific percentage of the salary or it can be indicated that their amount is provided for by agreement of the parties.
Indicate the procedure and terms for paying wages, whether wages are paid in cash through the organization’s cash desk or transferred to bank accounts, in what parts wages are paid, on what dates. This section also specifies the guarantees provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (payment of vacation no later than 3 days in advance, payment of wages when the payment day coincides with a weekend or holiday, etc.).
If the company employs employees who work in the Far North, indicate that the company pays percentage bonuses and regional coefficients and their size (Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
"3.1.3. To the actual accrued wages, including bonuses related to the performance of labor duties, a regional coefficient of 30% is applied to wages for work in areas equated to the regions of the Far North.
3.1.4. To the actual accrued wages, including bonuses related to the performance of labor duties, a percentage increase of 50% is applied to wages for work in areas equated to the regions of the Far North.”
The employer also needs to provide guarantees and compensation for employees working in harmful and/or dangerous working conditions, compensation or allowances for the traveling nature of the work, for working on a rotational basis.
Describe what allowances and additional payments are due to certain categories of employees. For example, the wage regulations stipulate guarantees of increased payment to employees for overtime work and work on days off and non-working holidays.
A whole section of the remuneration regulations can be devoted to a description of the terms of bonuses. When compiling this section, you can specify the conditions for bonuses in detail, down to KPI, or you can limit yourself to the phrase: “Employees for effective work and conscientious work, by decision of the manager, may be paid a bonus.” At the request of the employer, the terms of bonuses can be formalized in a separate local regulatory act, for example, by approving the regulations on bonuses.
Kinds
Simple time-based
The amount of simple time payment is calculated based on the amount of time worked and is not determined by the amount of work done . This form of payroll is divided into three types:
- hourly;
- daily;
- monthly.
Disadvantages of such payment:
- insufficient motivation of the employee to perform a large amount of work and improve the quality of work;
- there is no connection between wages and work performed.
The advantages include the employee’s confidence that he will be paid - this is also good for the employer, because it means that staff turnover will decrease.
Formula:
Zp = C * Ev.
C - rate, Ev - unit of time.
An example of calculating hourly wages:
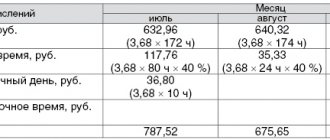
The hourly rate is 100 rubles. A company worker worked 20 days, 8 hours each, in a month. This means that the number of hours worked per month will be 20 * 8 = 160 hours. We receive a salary of 16,000 rubles.
Time-based bonus payment
The time-based bonus payment includes the tariff rate or official salary, and the employee is also awarded a bonus for fulfilling the employer’s requirements (high quality, positive personal qualities: responsibility, erudition).
Advantages of such payment:
- employee incentive to improve the quality and volume of work;
- When distributing bonus payments, the results of each employee are taken into account.
Flaws:
- strict management oversight is needed to keep track of the best employees;
- Management's assessment of the work performed is not always objective.
Formula:
Zp = O + Pop * Sp.
O - salary, Pop - percentage of production, Sp - amount of production.
Example of calculating time-based bonus payment:
The employee's salary is 50,000 rubles. In one month, the employee sold products worth 200,000 rubles. The percentage paid to the employee is 5. This means that the employee’s bonus will be 10,000 rubles. The total salary is 60 thousand rubles.
Time-based with a standardized task
With such a system, the work plan completed by the employee in a certain time is taken into account, while maintaining the quality standard. Time-based wages with a standardized task include a time-based share and an additional payment for the completed plan.
Advantages:
- the employee has motivation to fulfill a certain work plan;
- the employer keeps track of those doing the work.
The disadvantages of time-based payment with a standardized task include the fact that the worker will not receive additional payment for exceeding the plan .
Formula:
Zp = O + O * Poo.
O - salary, Poo - percentage of salary.
Example:
The employee's salary is 20,000 rubles. He must produce 200 units of goods in a month. For fulfilling the plan, the employee will receive 20% of the salary. A worker produces 205 units of goods. This means that his salary increase will be 4,000 rubles.
Mixed
This type of payroll combines piecework and time-based payment. An employee's salary is calculated depending on the percentage of proceeds or the rate of the labor function.
Flaws:
- factors that are not determined by the efforts of the worker are not considered (if the products sold have become irrelevant);
- It is not always possible to accurately measure an employee's contribution.
Advantages include the employee’s desire to complete more work.
Formula:
Zp = Of / Sk * Ks.
Of - general fund, Sk - sum of coefficients, Ks - employee coefficient.
Example:
The general fund of the organization is 50 thousand rubles. For the first employee the coefficient is set to 1.25, and for the second - 0.75. The total sum of the coefficients of two workers is equal to two. This means that the first employee will receive 50,000 / 2 * 1.25 = 31,250 rubles from the organization’s fund.
Watch a video on how to calculate time wages:
In the bonus regulations
Providing bonuses to employees is a right, not an obligation, of the employer. If the employer decides to approve the bonus provision, this document can reflect:
- bonus indicators;
- bonus conditions;
- circle of employees receiving bonuses;
- amounts of bonus payments;
- procedure for calculating bonuses;
- frequency of bonuses;
- sources of bonuses;
- a list of circumstances in the presence of which the bonus is paid less than the base amount or is not paid at all;
- list of payments for which the bonus is calculated.
When drafting the text of the bonus regulations, do not allow a situation where the bonus may be considered mandatory.