By Sergey Mashkov / 1st June, 2021 / Labor Law / No Comments
The employee worked full time, then switched to 0.5 rates. Since Regulation No. 922 does not require excluding from the calculation period time not worked during part-time work, it follows that the month is considered fully worked (despite the fact that the time sheet is marked for example, only three days worked out of five possible on a regular schedule, as well as weekends and holidays). And the calculation takes into account the earnings accrued for this month and the average monthly number of calendar days (29.3). The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the GlavAccountant System 1. Article. Vacation of an employee working at 0 5 rates 286 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for persons working part-time, annual paid leave is provided simultaneously with the main job. If an employee has not worked for a part-time job for six months, then leave is provided in advance.
Part-time hiring - what is it?
If a boss needs to apply for a part-time job at his main place of work, then he needs to be guided by the principles of labor legislation. Information about such a process is contained in Articles 93 and 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It talks about two main features of the requirements if you need to arrange a part-time job:
- Working at half the rate can be fixed in different ways. It can be noted that the employee works in production part-time or, if more convenient, part-time.
- If full agreement is reached between the employer and the employee, then in this case it is possible to establish a part-time working day for him not only at the time of signing the employment contract, but also if he has been working in production for some time.
The employee also has the opportunity to write an application for transfer to part-time work. And in some cases, the employer is obliged to satisfy the employee’s request by placing him on a part-time basis:
- If the application is written by an employee who is expecting a child;
- If the application is written by an employee who has children under the age of fourteen. A similar statement can also be written by a parent or guardian of a child with a disability. If he has not reached the age of eighteen, then the employer must also transfer this employee to part-time work;
- If the employee who wrote the application is currently caring for a sick relative. Such an application must be accompanied by a medical certificate confirming the fact of the disease.
All the reasons mentioned above make it mandatory for the employer to comply with the employee’s request to renew the employment contract for part-time work. If he refuses to do this, then the worker has the right to first appeal to a special commission, and if, as a result of the labor dispute, an agreement is not reached, then to the court.
It must be remembered that an employee who works part-time is subject to all laws prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. And they apply to the employee in full. This applies to both vacation and other rights and privileges that are guaranteed to the employee by law.
Legal regulation of working hours for athletes and coaches
Legal regulation of working hours is provided by a special chapter. 16 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter also referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Code). These legal norms form the legal institution of working time. It is based on the Constitution of the Russian Federation, in particular Art. 37, which stipulates that a person working under an employment contract is guaranteed the length of working hours established by federal law, weekends and holidays, and paid annual leave.
The Institute of Working Time makes a significant contribution to solving the problems defined in Art. 1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: protection of the rights and interests of employees and employers.
The norms of the working day and working week established by the legislator are a measure of the duration of participation of each employee in social labor and form the basis for the distribution of time over various segments with the aim of its rational use. Such periods of time can be a calendar day, week, month, quarter, year and other accounting periods. The choice of calendar period during which the legally established working hours are distributed depends on the specifics of the employer and the work schedule. Organizations can work discontinuously, that is, when there is a stoppage of work for one or two days off (this is typical for most organizations in the modern period of time), and continuously - when the main production operates on all days of the calendar week, as well as with a single-shift and multi-shift production cycle.
Based on these circumstances, working hours standards should be distributed in such a way as to ensure favorable conditions for the organization to carry out its functions, full use of equipment, coordinated work of departments, as well as compliance with labor legislation in order to protect the health of workers and provide them with rest time.
What is part-time work?
When an employee is hired, his working hours are set. This is the number of hours and mode of operation.
Normal working hours are 40 hours per week according to Art. 91 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This is the familiar five-day shift in the office or a rotating shift schedule in catering and retail.
An advertising company hired an illustrator. He paints in the office from Monday to Friday from 9 am to 6 pm. These are normal working hours.
Part-time work rate - when an employee works less than 40 hours a week under Art. 93 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Working hours can be cut as needed. Then we get:
- part time,
- part shift,
- less than a week
- dividing the working day into parts.
There is no point in calling an illustrator for the whole day. The employee's work hours in the office were set from 9 a.m. to 1 p.m. This is part time work.
The hours worked are monitored by the employer. The hours are recorded on the time sheet. Then the salary is calculated according to the timesheet.
Article: how to fill out a time sheet
Working hours are reduced at the request of the employee, by agreement or by order of the company. You can't just cut time like that. For every reason there are vital reasons. We'll talk about them further.
Working hours 0.5 rate
Info
N 588, which approved the Procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain periods, is calculated only for full-time workers (40 hours per week), and the norm of hours for part-time workers is determined by simply multiplying the full-time norm by 0.75, or 0.5, etc. .d.With this calculation, the pre-holiday day was reduced not by one hour, but in proportion to the occupied rate, i.e.
for those who work 0.75 the pre-holiday rate was reduced by only 45 minutes, for those who work 0.5 the pre-holiday rate was reduced by only 30 minutes. Motivation is the new standard of working time according to the new calculation.
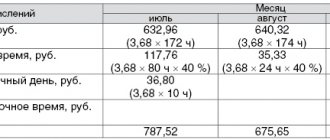
In numbers it looks like this: standard work time for full time (40 hours) for February 2021.
Part-time agreement
Let’s make a reservation right away: we are talking about a situation where part-time work is introduced by agreement between the employee and the employer. According to Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such an agreement can be concluded for any period and even for an indefinite period. Employees who agree to work part-time are entitled to leave of the same duration as if they were working full-time. Their length of service is calculated in exactly the same way as if the working hours were full-time.
In practice, there are different schedule options for part-time work. Sometimes an employee works the whole week, that is, from Monday to Friday, but less than eight hours (for example, two, three or four hours daily). In other cases, the number of working hours varies depending on the day of the week: Monday two hours, Wednesday three hours, etc. It is also common to have a schedule in which an employee works a full day, but not a full week: for example, he works eight hours from Monday to Thursday and rests on Friday.
Compose HR documents using ready-made templates for free
Methods of administration
Part-time working hours may provide (in accordance with by-laws and law enforcement practice):
- reducing the day shift by several hours on all days of the work week;
- reduction of working days while maintaining normal working hours;
- reducing the number of working hours per day and the number of working days per week at the same time.
In addition, flexible working hours may be introduced under Art. 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when the beginning, end and duration of the working day are determined by the parties.
For what reasons can you dismiss an employee without his consent under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2020-2021?
Employment contract for part-time employment
If the head of an enterprise needs to arrange a part-time job at the main place of work, an entry in the work book is carried out on a general basis, as with any other full-time employment. A different procedure is provided for part-time work, which in itself cannot imply full-time work.
When an employee is hired part-time, there are no restrictions on, for example, the duration of paid leave. The employee still retains the right to rest, regardless of the fact that such a person works fewer hours than required. It is also prohibited to restrict an employee from receiving
length of service
, as stated in Art. 93 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In order to register a person for part-time work, it is necessary to conclude a special employment contract with him. When writing it, a free form is used, which, however, must include the following points:
- General concepts of employment contract and part-time work;
- The rights that an employee who takes over a shift receives. This paragraph also indicates the duties that must be performed by the employee at the workplace;
- Subject of the employment contract;
- The schedule according to which the employee will work and rest;
- The conditions under which the employee will be paid for his work. It is also necessary to indicate the remuneration system there;
- Characteristics of the conditions in which the employee will have to work. The hazard class of the workplace must also be indicated there, and what harmful factors will affect human health;
- Details of the parties who entered into the agreement.
It is worth noting that the points indicated above are mandatory, but not final. If the parties agree that the terms of the employment contract require additional clauses, then they can be easily introduced there. There are no restrictions here. The main thing is that these clauses correspond to the specifics of work activity and add additional details to the terms of the contract without violating the fundamental rights and obligations of the parties regulated by labor legislation.
A person who gets a part-time job at his main place of work still has the right to take advantage of a shortened working day. It must be assumed in the conditions of the production calendar. And if an employee is hired for a part-time job, then it is necessary to stipulate working time standards. This is done so that the employee can count on overtime and all the payments that come with it. This is stated in Art. 99 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Part-time work shifts must be established in the employment contract, which is concluded between the employee and management. There you can indicate both part-time and part-time work.
- In the first case, the employee will work 4 hours a day with a five-day working week.
- The second concept is somewhat more complex, and in this case the employee can work on different schedules.
For example - four days a week and five hours a day - the main thing is that his working time is actually half of the standard working hours. And it is very important in the text of the contract to accurately reflect the number of hours that the employee will have to spend on shift.
If an employment contract is concluded with an employee for full shifts, then working hours may not be specified, but only the number of such full shifts per week or month in accordance with the half-working schedule.
Also, in addition to clear hours of rest, there is another part of the schedule that must be prescribed without fail. This is the period during which the employee can count on rest. In addition, it is necessary to separately stipulate such a clause of the employment agreement as the subject of the contract, in which it is necessary to describe the general functions that the employee will have to perform.
This paragraph also indicates the duration of the probationary period and the place where the employee will work. If the contract is fixed-term, then it is necessary to clarify the period during which the employee will be at his workplace. At this point, it is important to indicate that working in this part-time position is the main one for the employee.
Salary accrual at 0.5 rate
Therefore, one should agree with the opinion expressed in the literature46 that in society the distribution of working time pursues two main goals:
- apply the established working hours in such a way that intervals of working and non-working time alternate in an optimal way from the point of view of protecting the employee’s health, his participation in family life and in various areas of social activity;
- ensure that hours of work are allocated per unit of time in such a way that it meets the interests of society, both for the better organization of work and for the better use of equipment and other facilities of the employer.
All this characterizes the working time regime, which is the distribution of working time for the proper flow of the labor process and ensuring free time for workers. Establishing a rational regime of work and rest is a means of increasing the efficiency of working time, as it allows you to produce the same or more quantity of products or provide services with less effort on the part of the person performing the work.
In Art. 348.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that the specifics of the working hours of athletes and coaches, their involvement in overtime work, work at night, on weekends and non-working holidays, as well as the specifics of remuneration for athletes and coaches at night, on weekends and non-working holidays can be established by collective agreements, agreements, local regulations.
Meaning of Art. 348.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is difficult to overestimate, since the work schedule of athletes and coaches, as a rule, differs significantly from the work schedule of other employees.
For example, the working hours of athletes and coaches include:
- time of training and participation in competitions;
- time of medical examination;
- rest time before competition;
- the time of traveling to the place of training sessions or competitions and returning back.
Although the above-mentioned features of the work of athletes and coaches do exist, the provisions of Art. 348.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not establish for them any specific legal regulation that differs from the general rules.
Thus, in accordance with the general provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on working hours (Chapter 16), employment contracts with athletes and coaches may provide for the following working hours: irregular working hours, work in flexible working hours, shift work, division of the working day into parts.
Athletes and coaches are fully subject to the requirements of the Labor Code regarding normal working hours, which should not exceed 40 hours per week (Part 2 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation; at the same time, according to Part 3 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the sports club as an employer is obliged keep records of the time actually worked by each employee), reduced working hours (Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), part-time work (Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), overtime work (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), etc.
For athletes and coaches whose work involves participation in competitions, it is impossible to establish a day off on Sunday, which, in accordance with Part 2 of Art. 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is a general day off. Therefore, days off are provided to them on other days of the week alternately (Part 3 of Article 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Based on the above, we can draw the following conclusion. Physical culture and sports organizations have the right to independently determine in the internal labor regulations (Part 4 of Article 189 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) the working hours of their employees, based on the regime of preparation and participation in competitions, determined not only by the local regulations of the employer, but also by the calendar plans of physical education events and sporting events, observing the general rules of the law on working hours.
It is obvious that the working time of athletes and coaches is difficult to strictly account for and regulate. Athletes participate in training camps, compete on weekends and holidays, and work beyond the established working hours. The fact is that athletes and coaches, as a rule, receive higher remuneration for their work compared to other categories of workers. Therefore, they agree to exceed the limits of the established working hours.
At the same time, it is important for the employer to correctly document the specifics of the working hours of athletes and coaches.
Firstly, in local regulations, for example, in the Internal Labor Regulations, the employer must establish the specifics of the working hours of athletes and coaches, involving them in overtime work, work at night, on weekends and non-working holidays.
Secondly, it is possible to establish irregular working hours for athletes and coaches. Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines irregular working hours as a special regime. It provides that an employee, by order of the employer, if necessary, occasionally performs his labor functions outside the established working hours. At the same time, you need to remember about the episodic nature of such work and the guarantee provided to the employee in this case (additional leave - at least three days a year).
The Code imposes an obligation on the employer to keep records of the working hours actually worked by each athlete. Not only wages, but also other labor rights of athletes and coaches depend on correct accounting.
Since, according to the working conditions of athletes and coaches, the established weekly working hours cannot be observed, sports clubs use summarized recording of working hours (Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The duration of the accounting period is a month, quarter or year.
Please note that the Code does not define the specifics of the regime and recording of working time for athletes and coaches. Therefore, the procedure for maintaining records must be established by the employer’s internal labor regulations.
Thus, in order to comply with the rules of legislative technology, we consider it possible to exclude Part 5 of Art. 348.1.
46See: Ginzburg L.Ya.
Regulation of working time in the USSR.
- M.: Nauka, 1966. - 304 p.; Ivankina T.V.
General and special issues of legal regulation of working time in the USSR.
Author's abstract. dis. ...cand. legal Sciences - L., 1963. - 19 p. and etc.; Korshunova E.N.
Legal regulation of working time of workers and employees in the USSR.
Author's abstract. dis. ...cand. legal Sci. - M., 1950. - 22 p.; Protsevsky A.I.
Legal regulation of working time of workers and employees in the USSR. Author's abstract. dis. ...cand. legal Sci. - M., 1961. - 18 p.
Tags: legal regulation, working hours, conference, development, conference materials, collection of scientific articles, Scientific and Practical Conference.
Postgraduate students portal > General > Teaching > Work at 0.5 associate professor rate. How much time should you spend in the department every day?
View full version: Work at 0.5 associate professor rate. How much time should you spend in the department every day?
The question is this. If a person works for 0.5 assistant professor at a university, how much time per week should he spend at the department? It is clear that this also depends on the number of classroom sessions that such a person will be given on a schedule. Well, besides classes, how much time should you spend at work?
Apart from classes, you don’t need anything at all :).
Well, besides classes, how much time should you spend at work? necessary - not at all, must - depending on the traditions of the hut
SHOULD - depending on the traditions of the hut, and even more significantly on how interested they are in you.
If they value you at least a little, calmly move on to everything except, in fact, classes.
Thanks for answers. I have one more question on this topic. Please tell me how to correctly fill out an individual work plan for the year? Previously, when a person worked full time, his workload was about 900 hours, the rest of the time was the so-called “afternoon” (about 648 hours), i.e. methodological, scientific, educational, organizational and other work of the teacher. At the end of the year, it was necessary to reach 1548 hours; if less was achieved, then the person did not fulfill the plan; if it was much more, it was also not advisable. What about a person working at 0.5 rate? It turns out that his ped.load will be about 450 hours, and then how much is allocated for the “second half of the day”? I ask knowledgeable people to answer. Many people at our department are now asking this question, and opinions differ.
? It turns out that his ped.load will be about 450 hours, and then how much is allocated for the “second half of the day”? exactly half)) so, if the bet is 0 648, then half the bet is 648/2 or 50% of the bet for 2 half days
Added after 1 minute We already have many years of proven technology. X (total number of hours) - load = 2 half days (rate) for o.5, 0.75, 0.25 - respectively - percentage
exactly half)) so, if the bet is 0 648, then half the bet is 648/2 or 50% of the bet for 2 half days
Added after 1 minute We already have many years of proven technology.
X (total number of hours) - load = 2 half days (rate) for o.5, 0.75, 0.25 - respectively - percentage
Thank you! Now I’ll give my colleagues a link to this topic, let them read it