Pre-holiday day according to the Labor Code: concept
In accordance with the norms of the Labor Code, the pre-holiday working day is the day immediately preceding the official holiday. The duration of such a day (shift), in accordance with the norms of Article 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is legally reduced by 1 hour. When reducing employment time, it is necessary to take into account the following features of the nature of work:
- If the enterprise, by necessity, works continuously or the position of a specialist does not allow reducing the duration of employment, such stay is recognized as overtime and is subject to compensation in the form of an additional day off. Or the employee may be paid overtime (with the consent of the specialist).
- If an employee works a 6-day shift, the duration of the day of employment on the eve of official holidays can be a maximum of 5 hours.
- If the pre-holiday date falls not on a working day, but on a weekend (Sunday or Saturday), no reduction occurs on the previous date.
To understand what a short pre-holiday day is like, let us turn to the provisions of Article 91 of the Labor Code, which regulates the usual length of the working day. It says here that the weekly normal operating time is 40 hours maximum. And if an employee works under special conditions, for example, reduced hours (Article 92) or part-time (Article 93), or is a part-time employee, this does not in any way limit his right to go home an hour earlier on the eve of holidays.
What days are considered holidays?
Of course, not all holidays are recognized as official. For example, corporate parties, employee birthdays or professional dates cannot be considered holidays according to government regulations. The Labor Code defines the pre-holiday working day only in relation to those dates that precede those established in Art. 112 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, in Russia the following days are considered non-working days:
- New Year holidays - from January 1 to January 6 and 8;
- Christmas holiday – January 7;
- Feast of Defenders of Our Fatherland - February 23;
- International Women's Day - March 8;
- Labor and Spring Day – May 1;
- General Victory Day – May 9;
- Russian Federation Day – June 12;
- National Unity Day – November 4th.
This is also important to know:
Reducing the working week according to the Labor Code: payment features
All existing official holidays are marked in red on production calendars, and the day before the holiday is indicated especially with an asterisk *, so that personnel officers understand exactly when workers are entitled to relief.
How to make Friday short
If the employees of an enterprise belong to the general category of employees for whom the working week cannot exceed 40 hours, and the enterprise has a 5-day working week, then the length of the working day can be set, for example, as follows:
- 8 hours daily
- or on Friday the working day is reduced (for example, by 1 hour) due to the increase in working days from Monday to Thursday (for example, by 15 minutes, and in the end it is 8 hours 15 minutes on these days).
In this case, in any case, for all categories of employees, the duration of the working day or shift immediately preceding a non-working holiday is reduced by one hour.
For example
The company has a 40-hour work week, five days a week. Lunch break - 1 hour (not included in working hours). The working day begins at 9-00 and, taking into account 1 hour for lunch, ends at 18-00.
The employer decided to shorten Friday by 1 hour. Now employees work from Monday to Thursday from 9-00 to 18-15. And on Friday - from 9-00 to 17-00. At the same time, wages do not change, since the work norm of 40 hours a week remains.
What to consider when introducing pre-holiday days
When conducting personnel records on holidays and those preceding them, keep in mind that:
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
- If an officially approved holiday coincides with a day off, you should move Saturday or Sunday to the next day of work immediately after the holiday. The exception is the New Year holidays and Christmas, for which the Russian government has provided a special transfer procedure.
- If employees are not paid according to the salary system, such specialists are entitled to additional remuneration for non-working holidays. The mechanism for calculating and issuing payments is established in the enterprise’s LNA, for example, in a collective agreement.
- If an employee’s salary is paid according to the salary system, the employer does not have the right to reduce the total amount of remuneration if there are public holidays in the current period.
- By decision of the federal authorities, some days off may be rescheduled in order to increase overall labor productivity.
For example, January 1, 2021 is generally recognized as a holiday. The pre-holiday day is December 31, but in 2021 it falls on a day off, that is, Sunday. Since everyone doesn't work on Sunday, the next day before the holiday will be Friday. But the duration of employment on Friday will be, as usual, 8 hours and cannot be reduced according to Labor Code standards.
Nuances for paying for pre-holiday days
Key points related to payment:
- With an hourly wage system - in this case, the employee receives earnings based on the actual time worked. Therefore, a short hour will not be paid, and this is not considered a violation on the part of the employer.
- According to the salary system of remuneration - a short day before a holiday is subject to payment in full, without any reduction in the amount of earnings.
- With a piece-rate wage system, as well as an hourly system, this technique involves calculating earnings based on the actual volume of work or products produced. This means that a reduction in working hours on a pre-holiday day does not affect the amount of remuneration paid to piece workers.
- If you are employed on reduced terms or on a part-time basis, the salary for a short pre-holiday day is not subject to reduction.
Note! If the organization operates continuously and employees work as usual, that is, without shortening pre-holiday days, such time of employment is recognized as overtime and is subject to payment at a minimum of double the amount. The exact procedure for calculating compensation and the list of positions of persons who cannot be granted shortened days before holidays are approved by the manager in the internal document flow of the enterprise.
Pre-holiday day in continuously operating organizations
Not all enterprises can provide short working hours to all employees. If employees continue to work, then in this case they will have to pay one hour of overtime.
This is also important to know:
Overtime work of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2021: how it is paid, should not exceed...
According to the Labor Code, overtime work is paid for the first two hours no less than one and a half times the rate, for subsequent hours - no less than double. Payment for overtime hours at a particular enterprise must be prescribed by local regulations.
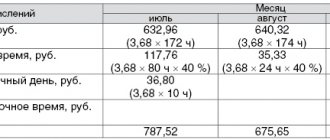
Example: mechanic Ivanov I.I., according to his employment contract, has an 11-hour shift (working time). His hourly wage is 150 rubles per hour. Ivanov I.I.’s work shift fell on 02/22/2017. It is not possible to provide him with a shortened work shift. The production process cannot be interrupted.
For ten hours of work, Ivanov I.I. was paid 1,500 rubles. (150 rubles/hour x 10 hours). Payment for one hour of overtime work is 225 rubles. (1 hour x 150 rubles/hour x 1.5). In total, for the work shift on February 22, Ivanov I. I. was accrued 1,725 rubles.
Payment for “shortened” time
A shortened holiday is not a reason to reduce wages.
There are some nuances:
- if an employee is paid according to a salary or a daily tariff rate under an employment contract, then the shortened pre-holiday day is paid in full (excluding the shortened hour);
- if an employee’s work is paid at an hourly rate, then for the pre-holiday day payment will be made for the time actually worked, the “reduced” hour is not paid;
- if an employee is paid on a piece-rate basis, then, regardless of the day of work, payment is made for the actual amount of work;
- If an employee works a shortened working day under an employment contract, then payment for a shortened working day is made according to general rules and depends on the type of payment (salary, daily rate, hourly rate or piecework payment).
Rules for registering work on a pre-holiday day
The pre-holiday working day provided under the Labor Code is noted in the timesheet according to special rules.
But many personnel workers do not know about this and continue to enter the usual number 8 on such days. However, on such dates, employees work less than the allotted time of employment. For example, an employee on a 40-hour work week works only 7 hours on the day before a holiday. Consequently, if this fact is not indicated on the report card, inspectors from the labor inspectorate may come to the conclusion that the person overworked and the employer violated the requirements of the law. Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Call: 8 800 511-39-66
Ask a Question
Should I draw up an order to reduce the working hours of the enterprise or not? In principle, since this requirement is regulated by labor law, there is no such need. But if the employer decides to issue such an order, this will not be considered a violation either. After all, it’s easier to remind employees that they can leave work early.
Is an order to reduce working hours before a holiday necessary?
Employers sometimes duplicate Labor Code norms in local acts or employment contracts. For example, the PVTR includes a clause stating that the working day before a holiday is shortened. However, there is no such obligation. The rule on reducing work on the eve of a holiday is fixed in the labor code and the employer is obliged to comply with it, regardless of whether it is prescribed in the LNA or not.
An order for a pre-holiday shortened working day may be needed if your enterprise has types of work in which shortening the working day is impossible, or if continuously operating enterprises have divisions with regular work schedules. The order will help separate workers who are entitled to short working hours from those who will subsequently receive compensation for overtime.
| We remind you If the work schedule cannot be reduced and the working day is reduced in accordance with the Labor Code, work during this hour is considered overtime and is compensated accordingly. |
Often, personnel officers play it safe and issue an order to shorten the pre-holiday day, so that during the GIT inspection it will serve as evidence of compliance with the instructions of the Labor Code.
We can conclude that it is advisable to issue an order to shorten the pre-holiday working day by an hour if there is a direct need for this by the organization. In other cases, such an order is not needed - the employee’s right to a short working day before a holiday is enshrined in the labor code, and it is not necessary to duplicate it in the LNA.
If the employer does not give a short pre-holiday day
In some organizations, shortening the working day on the eve of an official holiday is the norm, since such institutions are obliged to ensure continuous work. What an employer should do in this case is described above, but this will not be a violation of the labor legislation of the Russian Federation.
This is also important to know:
Reducing the working week according to the Labor Code: payment features
What should the employees of those companies do, whose administration does not want to hear anything about people going on vacation an hour earlier, and also does not pay overtime for overtime? First of all, remember that such actions are a violation of the requirements of the Labor Code, and therefore entail administrative liability under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offences. Punishment under this article is provided in the form of a fine of 1000-5000 rubles. per official, 30,000-50,000 rubles. to legal entities. Repeated offenses result in a fine of 10,000-20,000 rubles. per official, 50,000-70,000 rubles. to legal entities. The full list of sanctions is in Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offences.
Subscribe to the latest news