Home / Labor Law / Employment / Employment contract
Back
Published: 07/07/2016
Reading time: 10 min
0
5316
Official labor relations between the employer (tenant) and the employee are regulated by a special agreement that establishes the rights and obligations of both interested parties. Traditionally, employment contracts are concluded between individuals and legal entities (enterprises, organizations, institutions).
The employee assumes certain obligations, such as subordination to the internal regulations of the organization or enterprise, as well as the performance of labor duties within the framework of his position and in accordance with his existing specialization (qualification). The employer’s responsibilities include familiarizing subordinates with current local documents (for example, collective agreements), if any, in the organization or enterprise.
But the legislation requires the conclusion of contracts regulating labor relations also between ordinary citizens or individuals.
- When are such agreements used?
- Structure and pattern
- Design nuances
- Differences from an employment contract concluded with a legal entity
- Civil contracts
Employment contract between individuals
Any citizen can hire another person and register his work officially, without being an individual entrepreneur. The rules for drawing up such an employment contract and the working conditions under it are regulated separately by the Labor Code.
All details regarding the execution of a rental agreement between two citizens, neither of whom is registered as an individual entrepreneur, are regulated by legislative acts:
- Chapter 48 of the Labor Code - determines the basic procedure for formalizing and implementing business relations with an employer who is an individual;
- Article 303 of the Labor Code – regulates the conditions for registering a job with an individual.
ATTENTION! In the matter described, the term “employment contract”, as well as the conditions and rules for its execution, do not differ from standard situations. The legal aspects of this issue are also determined by the provisions of Article 56 of the Labor Code.
Civil legal relations formalized in an agreement
If the work performed or services provided do not require consistency, but are one-time in nature, the payer is interested in a specific result within a certain period of time, and not a constant work process, then it makes sense not to draw up an employment contract with the provision of vacations and sick leave to the employee, but to draw up a civil law contract .
- Piece wages in an employment contract
For comparison, as an example: it is more profitable to formalize the services of a nanny or housekeeper with an employment agreement, since the time of arrival and departure and the validity of the reason in case of absence are important. It is more profitable to formalize the services of a team for carrying out repairs through a contract related to civil law agreements, since the specific time of the work process does not matter, the result and the deadline for receipt are of paramount importance.
If the total transaction amount exceeds 10,000 rubles, a civil contract between individuals must be drawn up “on paper” based on the requirements of Article 161 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The following are required to be reflected:
- description of the service provided or work performed, including deadlines;
- price and calculation procedure, reimbursement of expenses incurred in the event of force majeure circumstances;
- responsibility of the parties, the procedure for satisfying claims regarding quality, failure to meet deadlines for the provision of services and calculations, the mechanism for calculating penalties and financial sanctions in case of dissatisfaction of participants;
- procedure for early termination of relations and coverage of losses.
Representatives of the parties can be both individuals with the status of individual entrepreneurs and citizens without the appropriate status. But if services are provided on a paid basis systematically, a citizen who is not registered as a business entity faces an administrative fine in the amount of 2,000 rubles in accordance with Article 14.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Which individuals can hire
The following citizens can become employers:
- officially registered as individual entrepreneurs;
- working as lawyers and notaries;
- hiring people to provide services in their personal household (cleaners, nannies, butlers, etc.).
There is an important condition: hiring employees is only available to adults.
Individual entrepreneurs
In this regard, individual entrepreneurs are practically no different from legal entities. The rules for maintaining personnel documentation at individual enterprises allow their owners to:
- draw up rental agreements;
- fill out personnel work books;
- determine the conditions and requirements of the organization’s internal regulations.
The main difference between individual entrepreneurs and legal entities in the matter of hiring employees is that the former do not necessarily need to register concluded contracts with the municipality of the locality.
ATTENTION! A citizen registered as an entrepreneur is not deprived of his right to act as an employer of individuals to receive services in his personal household as an individual.
Lawyers and notaries
Lawyers or notaries are registered as a lawyer's office or a notary office, respectively. The algorithm for hiring citizens for permanent employment is similar to hiring employees as personal assistants.
Employers of personal assistants and domestic staff
Individuals who are not registered as entrepreneurs have the right to hire citizens for their own needs. For example:
- driving a personal vehicle;
- property protection;
- management of the estate;
- creative activity;
- help around the house, etc.
According to the provisions of the Civil Code, a person, when hiring an employee for personal needs, is obliged to make pension contributions in respect of his employee. To do this, he must register with the Pension Fund as an employer within a thirty-day period from the date of execution of the contract.
Advantages of the agreement
Any contract, including an employment contract, establishes the rights and obligations of counterparties. The absence of a written contract makes it impossible to file claims related to non-fulfillment of the agreed terms. For example:
- accidental or intentional destruction of the employer's property by an employee will not entail compensation for damage, since the fact of the employee's access to this property will not be confirmed by anything;
- the dismissal of an employee cannot be appealed due to the absence of an employment contract;
- dismissal of an employee will not be accompanied by payment of severance pay;
- an employee working without a contract is not entitled to paid leave, etc.
That is, neither the employer nor the employee will have access to the procedure for protecting their rights related to labor relations. But, in our case, the lack of opportunities to protect rights is fully compensated by the lack of responsibilities, which means that we can hardly expect a boom in the conclusion of employment contracts between individuals in the near future.
Payment of taxes and contributions under such an agreement
The employer is obliged to pay his employee wages at least twice a month (advance payment and the basic amount of remuneration). From these funds he must pay taxes and insurance premiums for the employee in the amount of:
- personal income tax – 13%;
- to the federal budget – 20%;
- social insurance – 2.9%;
- medical insurance - 3.1% (2% - to the territorial body, 1.1% - to the federal body);
- pension contributions - 14% (8% - insurance part, 6% - funded).
All specified contributions, with the exception of personal income tax, are paid from the personal funds of the employer. Only 13% income tax is withheld from the employee’s remuneration.
The provisions of Article 243 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allow individual employers to reduce contributions under the Unified Social Tax by the amount of contributions to the employee’s pension insurance by issuing a tax deduction.
A sample employment contract with an individual can be downloaded from this link.
If you decide to enter into an agreement
The legislation does not impose any special requirements for an employment contract between individuals, which means that it will include a standard set of structural elements characteristic of any employment contract.
So, the main structural elements will include:
- date and place of conclusion of the contract;
- Full name, addresses and passport details of counterparties;
- the subject of the contract, that is, the actual fact of establishing labor relations between the employer and the employee;
- the employee’s place of work, that is, the address of the premises (area) in which he will perform his functions;
- work start date;
- information about the employee’s functions, that is, the job for which he is employed. For example, child care, care for the elderly, gardening, etc. There can be many options, the main thing is that they do not include even a hint of the employer’s entrepreneurial activity. Thus, an employee can take care of the garden and pick flowers, but the employer has no right to oblige him to sell these flowers at the market;
- information about the employee’s qualifications. This may be required when the employer requires education or relevant experience. For example, the contract must stipulate that the employee has a driver’s license, a certificate of completion of massage therapist courses, or a diploma in pedagogical education;
- work schedule and rest schedule;
- duration of the contract, conditions of the probationary period;
- salary amount, method and procedure of payment;
- other conditions that the parties may agree on. For example, an additional condition may include the employer’s obligation to provide the employee with a place to live at the place of work;
- signatures of counterparties.

We have already said above that by concluding an employment contract as an employer, an individual assumes the obligation to comply with the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in relations with an employee. Thus, the employer is obliged:
- provide the employee with annual paid leave of at least 28 days;
- provide the employee with weekly uninterrupted rest of at least 48 hours;
- do not exceed the 40-hour working week;
- pay all statutory insurance premiums for the employee.
An individual employer is obliged to transfer personal income tax from the employee’s income only if he is an individual entrepreneur. Individuals who are not entrepreneurs are required to pay only mandatory insurance contributions for their employees.
An employer who is not an entrepreneur must register an employment contract concluded with an employee with local executive authorities.
Features of the contract for hiring an employee without paying taxes
An employee performs actions for a specific result. This is what is valuable to the customer. The performing worker receives payment for the result. The concept of a contract for paid services is disclosed, as an agreement under which one party must provide services and the other must pay for them. Unlike contracting, what is valuable here is not the result, but the process.
The employer guarantees payment of remuneration for work, payment of insurance premiums, except for contributions to the Social Insurance Fund. As a tax agent, an individual entrepreneur must withhold personal income tax from income paid to an individual. Any work activity must be formalized in accordance with the requirements of the legislator. Compliance with this rule allows you to avoid many problems when regulating relations between the parties - the employee and the employer. Please note that according to the Constitution of the Russian Federation, a person has the right to freely dispose of his work. He can draw up an employment contract or enter into an employment agreement.
Temporary employment contract with an employee for individual entrepreneurs without paying taxes
New on the topic New from 03/30/2018: The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation in letter dated 03/21/2018 No. 14-2/B-191 clarifies whether numbering of employment contracts in a commercial organization is mandatory, and what numbering system can be used. New from 03/19/2018: The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, in letter dated 03/05/2018 No. 14-2/B-148, clarified how the personnel registration of workers involved in work for which various restrictions are defined by law is carried out.
Otherwise, he risks being accused of illegal business activities. Advice: it is important not to use labor law terms in the employment agreement. This is considered a violation of the structure of the agreement. What must be included in an employee employment contract? First of all, it is worth noting that the contract itself is concluded between the employee, contractor, author and customer, who will subsequently be obliged to make cash payments.
Individual entrepreneur hiring workers under an employment contract taxes
Unregistered employees of individual entrepreneurs also violate the procedure for providing information about individual taxpayers by the tax agent (employer). And finally, the Criminal Code comes into play, which provides for liability for intentional evasion of taxes and mandatory payments.
In addition to the preparation and timely submission of reports, payments of all fees and taxes must be made within the deadlines established by law. Fines for unregistered employees Can an individual entrepreneur hire workers under an employment contract? Maybe, but he must register them officially.
Contract disputes: where to go if rights are violated
In some cases, a person may seek protection of violated rights from the labor inspectorate - for example, if wages are not paid or leave is not given.
Labor Dispute Commission. It is convened at the initiative of the employee or employer. It includes an equal number of representatives of the parties. Not all companies have such a commission, and at the first request of an employee who has complaints, it will not be convened. Therefore, most often, employees immediately go to court to protect their rights.
As a general rule, a claim is filed in court at the place of residence of the defendant, if the defendant is an individual entrepreneur or individual, or at the location of the organization, if the defendant is a legal entity. If an employee works in a branch or representative office of a company, he can choose the court at the location of his workplace.
When the claim concerns a contract, it can also be filed in court at the place where the contract is performed. For example, an employment contract may be signed in Moscow, but it states that the employee will perform his duties in Tver. If the parties have a dispute under such an agreement, it can be considered in both Moscow and Tver.
What is an employment contract?
- indicate the full details of both parties to the agreement;
- subject of the contract – employment;
- the terms of the agreement are specified;
- describe the responsibilities of the customer and the contractor;
- indicate salary, other payments or compensation, possible benefits;
- grounds for termination of an employment contract.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
Each party's data
Since the employer is an individual, he does not have the same details as an enterprise or entrepreneur. Therefore, the parties must provide the same information about themselves:
- full name;
- passport data;
- address where they actually live;
- contact information – current mobile phone numbers and current email addresses;
- INN, SNILS.
Labor contract
– a bilateral agreement, therefore must be signed by both parties. This is how they seal their agreements and confirm the accuracy of the data provided.
A labor contract concluded between citizens is drawn up according to the rules prescribed in Art. 303 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
How the contract is terminated or amended
The main reasons for the breakdown of labor relations are specified in Art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. These include:
- the desire of the employee himself;
- agreement of the parties;
- employer's desire. Here you can focus on the points prescribed in Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. But not all of them are related to citizens - employers. For example, liquidation or reduction cannot happen to an individual.
Therefore, the rupture of labor relations occurs, as a rule, in the presence of guilty actions on the part of the employee himself.
For example , absenteeism, that is, absence from work without good reason. But, just like a legal entity, an employer-citizen must correctly document the misconduct of his employee. For example, a state of intoxication can only be recorded by a doctor.
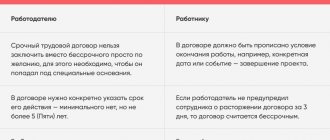
Changing the terms of the contract is possible by agreement of the parties. If the employer decides to make changes to the clauses, he must notify his employee at least 2 weeks in advance. Notification occurs in writing. If a person does not agree to work under new conditions, the parties terminate their cooperation.
Tax-free employee employment agreement sample
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the mandatory entry of a corresponding entry into the work book if he has worked in one place for more than five working days, but there are exceptions that apply specifically to hiring a customer who is also an employer.
- is a civil document without concluding an employment relationship between the employer and employee;
- absence of any guarantees provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- the work is carried out according to clearly defined results;
- the employee does not obey the internal rules, performing clearly specified actions specified in the employment contract;
- equal rights from a legal point of view;
- remuneration by mutual agreement;
- clearly defined deadlines.