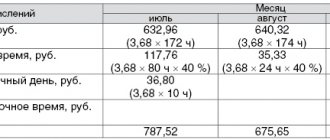
What is a work schedule
Labor legislation provides for standardized or irregular working hours for employees. It is established by internal labor regulations, collective agreements, agreements, and employment contracts.
Normal working hours include the following work schedule:
- 5-day week with 2 days off;
- 6 days with 1 day off;
- a week with days off on a rotating schedule or a part-time work week.
Labor standards specify what employee work schedules are. The main types are:
- single shift;
- weekly;
- sliding;
- removable;
- shift worker, etc.
In case of irregular working hours, a shift schedule is established for some categories of employees. This is a document that is established in accordance with Art. 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and is introduced when the duration of the production process exceeds the working time of the employee.
In production, groups of employees replace each other, and in order to ensure continuity of the process, it becomes necessary to work or provide services around the clock. To keep their working hours within the norm, shift schedules are introduced. Usually they are annexed to the collective agreement, and when approved, the opinion of the representative body of workers is taken into account.
IMPORTANT!
Micro-enterprises have the right to include a shift schedule in the employment contract with the employee. Write down the work schedule and rest time in this format (part 2 of article 57, part 1 of article 100, part 1 of article 104, article 107, 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- length of the working week;
- beginning, end and duration of work shifts, number of shifts per day;
- alternating working days and weekends;
- time of breaks, their duration;
- accounting period, if summarized working time accounting is maintained.
ConsultantPlus experts discussed how to create a work schedule during shift work. Use these instructions for free.
to read.
NTVP "Kedr - Consultant"
LLC "NTVP "Kedr - Consultant" » Services » Legal consultations » Labor disputes » How to specify in an employment contract working conditions for a part-time employee with piecework wages
The organization plans to hire an employee part-time with piecework wages. The work is performed in free time from the main work, as needed.
Question:
How to specify and whether it is necessary to specify working hours in an employment contract?
Lawyer's answer
The following conditions are mandatory for inclusion in an employment contract:
working hours and rest hours (if for a given employee it differs from the general rules in force for a given employer);
Art. 57, “Labor Code of the Russian Federation” dated December 30, 2001 N 197-FZ (as amended on December 16, 2019) {ConsultantPlus}
Who can apply for flexible working hours?
It can be installed by one employee or several. Including if the employee works part-time or reduced working hours. There are no legal restrictions on the establishment of flexible working hours.
Often this regime is established for those whose work does not require constant presence at the workplace; work can begin (end) at different times. For example, real estate agents, journalists, some communications workers. Or it is installed for those who, for personal reasons, find it difficult to start (finish) work every day at the same time. For example, women with children, workers who are undergoing rehabilitation or training in their free time.
The fact is that under this regime, the employee’s working hours may not be fixed, but vary from day to day. The specific working conditions for flexible working hours are not defined by law. Agree with the employee what flexible work hours they will have - start time, end time or the total length of the working day. Write this down in the employment contract. This follows from Part 2 of Art. 57, part 1 art. 100, part 1 art. 102 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For example, an employee may come to work either at 8 or 11 o’clock. Or, for example, work 7 hours one day, 9 hours the other.
Attention! There is an opinion that flexible working hours cannot be established if the employee does not have a separate workplace or, for example, has a traveling nature of work. The argument is that it is impossible for such an employee to keep track of working hours. However, this is not so - according to the law there is no prohibition. There are no risks if you give such an employee a flexible work schedule. In addition, it is necessary to keep records of the working hours of all employees (Part 4 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). And it doesn’t matter whether the employee works in the office, on the road, remotely or in some other way. Therefore, we recommend fixing the procedure for recording working hours for an employee with a flexible schedule, for example, in an employment contract.
Ready-made solution: How to set an employee’s working hours with a flexible work schedule (ConsultantPlus, 2020) {ConsultantPlus}
How to include flexible working hours in an employment contract
To prescribe a flexible working time regime in an employment contract, you need to indicate, in particular (part 2 of article 57, part 1 of article 100, article 102, part 1 - 3 of article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
• working hours, which can be flexible (start, end or total length of the working day). If you have agreed with the employee that you will specify a flexible work schedule in the internal labor regulations, make a reference to them in the employment contract. And if you plan to draw up flexible work schedules (separately from the employment contract), still write down all the elements of the work schedule in it, and specify the work for certain periods with schedules. We'll talk more about this below;
• working conditions at night (from 10 pm to 6 am). Or set a ban on it. This way, in particular, you will avoid additional expenses, since it is paid at an increased rate. Or, if you are not against such work, clarify all the nuances of working at night, including, if necessary, obtaining the employee’s consent to it;
• accounting period. Usually it can be from one working day to a year. An exception is, in particular, workers with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions. Their accounting period, as a rule, should not be more than three months. If the accounting period is longer than a day or a week it is not possible to comply with the standard working time, it is also advisable to establish a summarized accounting of working time and, accordingly, indicate this in the employment contract;
• the period for which you establish such a regime. It can be anything, since there are no restrictions in the law.
If you make changes to an existing employment contract, then document all the conditions in an additional agreement to the employment contract.
Ready-made solution: How to set an employee’s working hours with a flexible work schedule (ConsultantPlus, 2020) {ConsultantPlus}
Sample employment contract with a flexible work schedule
4.1. The employee is provided with a flexible working time regime:
• 40-hour, five-day work week with two days off;
• working days: Monday to Friday;
• days off: Saturday, Sunday;
• duration of daily work - 8 hours;
• start time from 8:00 am. until 11:00 am, which is determined by the employee in agreement with his immediate supervisor;
• closing time from 17:00. until 20:00 The specific end time of work is determined by summing the start time of work, the break for rest and food and the duration of daily work;
• break for rest and food - one hour from 12:00 p.m. until 15:00, which is not included during working hours and is not subject to payment. The employee coordinates the specific break time daily with the manager;
• accounting period – one working day.
{Form: Employment contract with a flexible work schedule (sample filling) (ConsultantPlus, 2020) {ConsultantPlus}}
Thus, the regime of working time and rest time (if for a given employee it differs from the general rules in force for a given employer) is a mandatory condition for inclusion in the employment contract. In this case, the employee may be given a flexible work schedule. An approximate formulation of the flexible working time regime is given above in the sample employment contract.
The explanation was given by Igor Borisovich Makshakov, legal consultant of LLC NTVP Kedr-Consultant, February 2020.
When preparing the answer, SPS ConsultantPlus was used
What are the differences from a time sheet?
It is necessary to distinguish the document recording the working hours from the timesheet of hours worked, which is maintained by the employer in accordance with the requirements of Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and is a kind of document recording working hours for the month. The norm is 40 working hours per week. The employer is obligated to keep records of actual time worked for each employee.
There are no special requirements for familiarization with the report card within a certain period and there is no need to coordinate it with the representative body of employees. The employer can only not exceed the established duration of the working day and provide workers with rest in accordance with the requirements of Art. 110 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Keeping timesheets is mandatory for any organization. But with a continuous flow, when people work in shifts, a working time schedule is required. In both cases, it is necessary to specify in the employment contract all the specifics in the section that concerns the working hours.
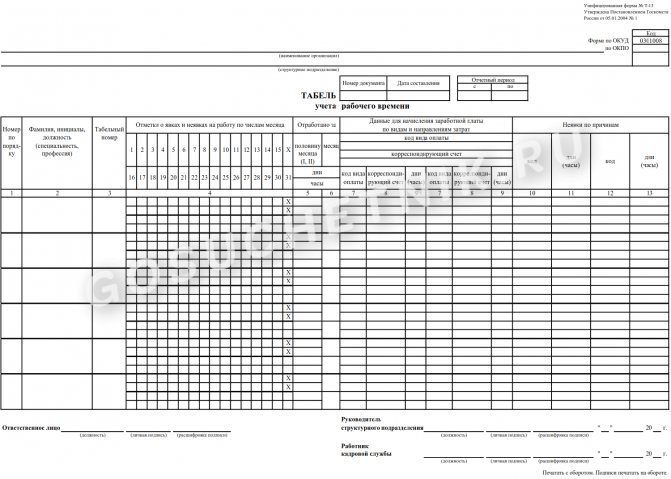
How to correctly write the RV in the contract?
According to Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the TD must contain a clause on the employee’s working hours. But this condition must be specified if the work schedule of a particular employee differs from the others.
If internal regulations specify in detail the work and rest schedule of employees, and the hired employee undertakes to comply with the established rules, then there is no need to indicate additional information in the TD.
If the organization has established a standard 8-hour work day, and the standard hours per week is 40 hours, and the employee is hired on a shift schedule, then the contract must necessarily contain a clause on the time of work and rest established for a specific employee.
The following information is included in the contract:
- link to the established shift schedule;
- duration of one shift;
- start and end times of the work shift;
- time for rest and lunch.
Important! If rest time cannot be allocated separately due to the nature of production, then it is included in working hours.
Data on non-standard work hours must be contained both in the local regulations of the enterprise and in the TD.
Features that require priority attention
Every organization must have an accurate record of time worked for each employee. Regardless of the established schedule, each employee holding a certain position must know how many hours he must work. In addition, the amount of remuneration is determined depending on the number of hours worked.
If an employee fulfills his obligations beyond the norm specified in the employment contract, then such work is considered overtime, and the employer must pay additional remuneration for it.
Not only wages and the number of working hours, but also rest time depend on the work regime established in the organization. Weekend days are calculated based on the schedule.
How to reflect summarized accounting?
To transfer employees to summarized working time tracking, the employer must perform several actions:
- issue an order to apply summarized accounting;
- set a work schedule;
- make changes to internal regulatory documents.
To change the conditions for the performance of labor functions by an existing employee, the parties enter into an agreement between themselves, which specifies the changes. If a trade agreement is concluded with a new employee, then the following points must be included in it:
- job title;
- job responsibilities;
- shift schedule and how long they last;
- wages (hourly rate);
- the amount and conditions for receiving bonuses and other remuneration;
- processing on holidays and weekends;
- details of both parties;
- duration of the employment relationship.
For more information about the typical contents of a TD, about the clauses that it may contain and the conditions of conclusion, read this material.
Why do you need a work schedule?
Its functions are quite diverse. It is required for:
- streamlining employee work time;
- calculating wages when fulfilling specific obligations;
- calculating average earnings;
- benefit calculations;
- determining the employee’s insurance length;
- absence of errors in determining earnings and compensation for vacation (together with the working time sheet, it is the basis for calculating wages and other payments);
- identifying overtime overtime and determining additional payments.
After approval, the team is introduced to the schedule for signature one month before commissioning. If a signature is refused, a special act is drawn up with the signatures of two witnesses. Failure to comply with the established regime is a serious disciplinary offense.
Shift working hours
Shift work - working in shifts throughout the day. In this case, workers work different shifts for a certain period of time, for example, three days.
Such work is used for the purposes of production efficiency and business activity. For example, in order to increase the volume of services provided or products produced. When the production process exceeds the permissible operating time.
Under this regime, each group of workers works according to a shift schedule.
Workers are provided with continuous rest - 42 hours per week and between-shift rest - double the duration of the shift.
There are day, evening and night shifts. If 50% of the shift duration falls on the time period from 22.00 to 06.00, then such a shift is considered a night shift.
Is there a required form?
There is no unified form: each employer has the right to independently develop its own document form or use a ready-made template. Instructions on how to make a work schedule for a month in Excel or any other editor:
- Prepare a database to fill out: indicate the name and registration information of the organization.
- List all employees and their positions.
- Mark the days on which each employee comes to work.
Develop the document in such a way as to prevent shortcomings or rework beyond normal working hours and ensure optimal workload on the team and on production processes. The schedule is most often developed for a month.
Normal working hours
The following working hours can be distinguished:
- daily five-day work, including two days off
- daily six-day work, including one day off
- working week with days off provided according to a variable schedule
- summarized work time tracking
This schedule is called a single-shift work schedule.
In cases of daily recording of work time, any work beyond the norm is overtime.
The summarized time recording used in this mode (the point is that the time worked in one day on average is equal to the standard working day for the corresponding accounting period) serves to measure working time. How long should it be taken into account? Set by the employer, but not more than a year in advance. It turns out that the amount of time worked by such an employee cannot exceed the number of working hours determined by the norm.
Filling procedure
The general rules for creating a schedule are simple. Here's how to create a duty schedule for a month in the form of a table without errors:
- Fill out the document taking into account the working hours in accordance with the internal labor regulations in force in the organization. Indicate the beginning and end, duration of the working day, breaks, number of shifts, alternation of work and rest.
- Keep track of the length of the working day. The duration is regulated by internal regulations, taking into account the working time regime established by the employment contract.
- If necessary, provide for a shorter working day, as, for example, in industries with harmful and dangerous conditions (Part 4 of Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) or when the work of disabled people and minors takes place (Parts 1, 3 of Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) .
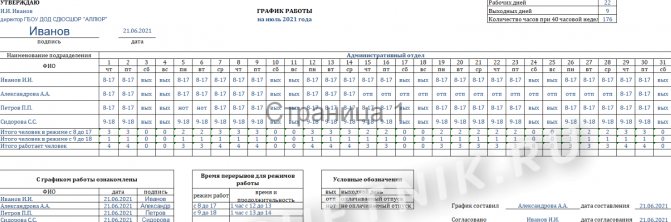
Work schedule as a document regulating daily individual work schedule
The work schedule is one of the most important documents for organizing the work of those employees who do not work according to the general (production) calendar. Thus, the daily schedule regulates the time of coming to work, leaving work, break times, and even the workplace assigned to the employee.
The schedule is usually drawn up for one month, but this period is not regulated by law. Therefore, depending on the circumstances and characteristics of the production process, the document can be drawn up for a week, a quarter, or a year.
The schedule, as a document, can be drawn up:
- simultaneously for all employees of the enterprise;
- for employees of one structural unit;
- for a certain group of employees from different structural divisions;
- separately for one employee.
Form and symbols
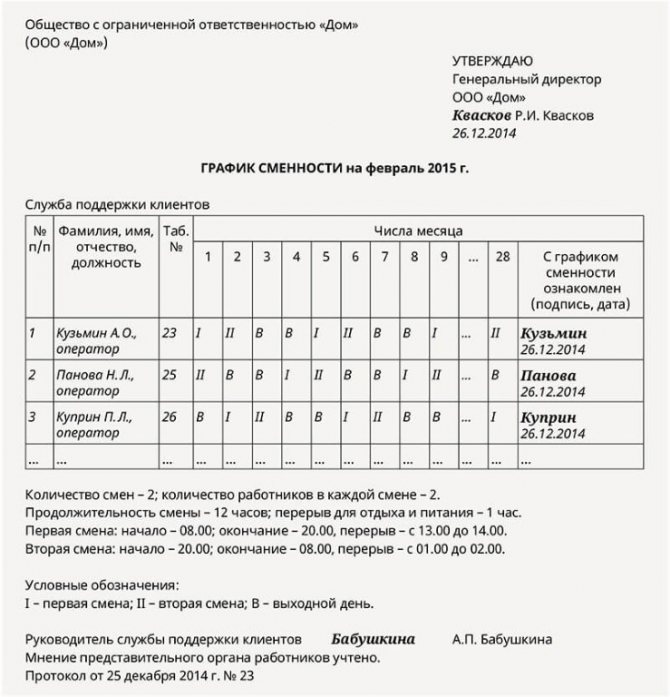
In the shift schedule it is enough to indicate only the shift designation

looks like a table, each row of which is assigned to an individual employee, and the columns correspond to the calendar days of the period chosen to determine the work regime (for example, a calendar month).
The legislation does not oblige employers to use any standard unified form or adhere to any unified system of symbols when drawing up a work schedule. This means that each employer has the right to develop its own rules for drawing up this document, taking into account the specifics of the work of its organization, guided by the maximum ease of using the schedule in work.
You can include any information in the schedule:
- in the shift schedule, when the direct work schedule of the shift is already fixed in some legal regulation (for example, in the PVTR), it is convenient to include only an indication of the shift number for the employee on a specific day;
- a sliding schedule will inevitably have to include all possible elements of working time - the start and end time of the working day, the time of breaks, the total number of hours of work per day, information about the assigned place of work (if necessary).
Since any schedule is an employee’s work plan in accordance, first of all, with his individual work standard for the accounting period (month, quarter, etc.), the final column of the document always displays the amount of planned hours. If a month is selected as the accounting period, the resulting column will be one - the monthly norm. If the accounting period is a quarter, it is recommended to include two columns in the form - the monthly rate and the quarterly rate (the latter will be displayed “with a cumulative total” throughout the entire quarter).
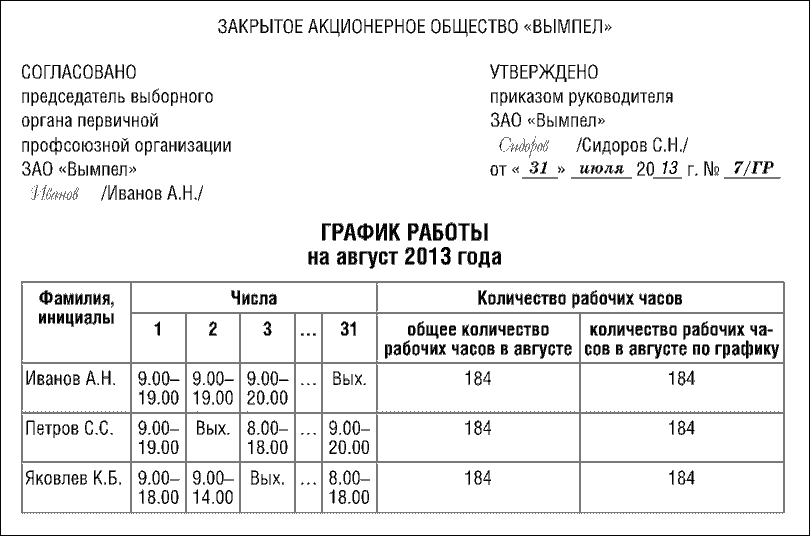
When summarizing accounting, the schedule must contain columns reflecting the amount of hours per month, per quarter (depending on the accounting period)
The process of drawing up and approving the schedule
The procedure for drawing up and approving a schedule in an organization can be regulated either by a local regulatory legal act or by order of the manager. Persons responsible for maintaining, approving and approving documents are determined by designation in these documents and the inclusion of a corresponding item in the job description.
As a rule, the schedule is drawn up by the person responsible for this in the structural unit (department, service), endorsed by the head of the structural unit, a representative of the personnel department and the trade union, approved by the head of the enterprise or his deputy in charge of the relevant area of activity.
The schedule can be drawn up either manually (using standard Office tools with output on paper) or in specialized software packages (for example, 1C: HR and Salary, SAP, etc.).
Schedule requirements
When drawing up a work schedule, the employer is in a situation where it is necessary to comply with a lot of rules, requirements and interests. First of all, these are the requirements of labor legislation that protects the rights, interests and even health of the employee:
- The duration of daily work should not exceed those established by Art. 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation limits (special limits are established for minor employees, disabled people, workers in harmful unsafe conditions).
- The number of working hours per week should not exceed the norm according to the production calendar (40 hours as a general rule). For those who have been assigned summarized accounting for an accounting period, it is mandatory to comply with the standard hours for this accounting period (quarter, month, etc.).
- Shifts that primarily occur at night should be reduced by 1 hour.
- After a shift lasting more than 24 hours, an equal or greater rest period is provided.
- If the employee does not have a condition for dividing the working day into parts, his lunch break (or the sum of several during the day) should not last more than two hours.
- The minimum lunch break is 30 minutes. It is obligatory to establish daily, if the agreement of the parties and the PVTR does not provide for the employee to eat food in parallel with work. Lunch break is not paid.
- It is prohibited to work during two shifts following one another.
- Hours that fall during an employee's illness or vacation are also included in his monthly (quarterly) rate. In other words, the employee is not required to make up the hours actually missed to normal.
- The limits established by Art. 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for overtime work (no more than four hours in a two-day working period, no more than one hundred and twenty hours per year), etc.
Of course, when creating a schedule, the operating mode of the enterprise, workload standards, and the interests of the employee himself are taken into account.
Employee familiarization
The employer is obliged to familiarize employees with the work schedule no later than one month before the day it comes into effect - this is a direct requirement of Art. 103 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Violation of this deadline may result in administrative liability.
To avoid violating the requirements of the law, you should start drawing up a schedule no later than one and a half months before the start of the accounting period. For example, the schedule for December should be drawn up before October 15 in order to have time to coordinate, approve and familiarize all employees with it (after all, some of them at the time of familiarization may be on vacation or on sick leave, but this circumstance is not an excuse in case of violation of the deadlines for familiarization ).
Where and how long is it stored?
Order No. 236 of Rosarkhiv dated December 20, 2019 established the storage periods for personnel documentation. Clause 8.1 of Section II of the order states that books, journals, accounting cards and databases are stored for 5 years. When working with difficult, harmful and dangerous working conditions, the shelf life is set at 75 years or 50 years if the document was completed after 01/01/2003.
There is no specific reference in the order regarding how long to keep the work schedule. Still, some employers prefer to store such documents for a year in the human resources or accounting department in case of a labor dispute with an employee regarding the issue of standardization of working hours or payroll.
Irregular working hours
Irregular working hours are a work regime in which certain employees, by order of the employer, are involved in the performance of assigned functions outside the working day. A popular mode of operation for managers. That is, the employee also works during normal working hours. But there is still a possibility of working beyond your shift.
An irregular day is established for certain employees included in a special list attached to the collective agreement (internal regulations).
It should be noted that the employer is not required to obtain the consent of the employee or the representative body to engage an employee in this type of work. This right of the employer is regulated by the employment contract.
An employee’s refusal to perform this type of work is not allowed. Otherwise, this is a violation of labor discipline. This regime involves overtime, so labor legislation provides for the provision of additional leave.
Split working hours
The working hours with the division of the working day into certain parts are determined by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For work of a special nature or for work with unequal intensity during a shift, the working day must be divided into parts.
As a rule, such work is related to serving the population: passenger transport, communications, trade. In any case, the time worked should not exceed the duration of daily work. The legislation does not determine the number of parts into which a working day can be divided. This mode of work provides an additional payment to the employee’s basic salary.
Reference
A certificate of working hours may be needed under certain circumstances:
- First case. Such a certificate is required from a woman applying for a special work schedule due to the presence of a small child. Then the worker’s husband must provide a certificate from his place of service to confirm the need for a special regime.
- Second case. If you are fired or laid off, you can apply to the employment service for unemployment benefits. Under these circumstances, it is necessary to provide a certificate of working hours in order to calculate the average wage of the worker.
Example of a certificate about working hours:
At the moment, the labor sphere is characterized by a large abundance of work schedules. When choosing one mode or another, be guided by the specifics of your profession, family circumstances and characteristics of physical and mental health .
The well-being of not only the employee, who makes a choice in favor of one or another schedule, but also the employer, whose well-being is directly determined by the labor productivity of his subordinates, depends on the working mode chosen by the worker .
Watch the video about working hours:
Shift working hours
Shift working hours are a form of labor process not at the place of residence of workers, when the possibility of their daily return to their place of residence is excluded.
A shift is a period consisting of time spent performing work and rest time between shifts.
The duration of the shift cannot exceed one month, but in exceptional cases it can be extended to three months. In this case, the shift can last 12 hours daily.
With this working time regime, summarized time tracking is established. Including travel time to the place of work, vacation time falling within this calendar period of time.
Labor legislation prohibits the involvement of minors in work of this nature. The work of women and persons with medical contraindications is separately regulated.