Interview
When hiring a driver, certain requirements are imposed and tests are carried out and questions are asked.
The purpose is to check whether the driver’s qualifications correspond to the position. The driver must have a certificate of completion of a medical examination and a driver's license of the appropriate category .
Pay attention to the driving experience (it can be easily tracked using the work book): if an employee is hired for this position for the first time or is transferred to another type of vehicle, and also has a break in this work activity for more than a year, he needs to undergo an internship in the organization.
An example of a driver application form can be downloaded here.
Starting from 2021, according to the law, the results of the conversation must be entered into interview sheets, which the employer is required to keep for 5 years. The interview sheets are filled out in free form. You can invite the chief mechanic to a conversation with a potential employee - he will ask more specific questions to the driver.
Also, at the request of the employer, the driver can undergo testing (theoretical or practical), which will assess his knowledge and skills. Perhaps these will be tests on knowledge of traffic rules and the technical parts of the car. But most often the driver is asked to demonstrate his ability to drive a car.
From 2021, the driver must meet the professional standard. Read more about this here.
Filling out an employment contract with a driver
- The start date of the contract is a mandatory requirement. This is the date when the employee begins to perform his work duties with this employer.
- The details of the employer and the citizen hired as a driver are indicated.
- Labor function and place of work.
Art. 57 of the Labor Code defines the general requirement for a number of conditions that must be reflected in a standard employment contract, applicable to all employees of the organization. But for special categories, drivers, there are conditions that must be specified based on what the driver’s work involves.
Besides what we call:
- job title;
- structural unit of the organization;
- indicate the job function;
- we prescribe the operating mode if it differs from the generally established one within the organization;
we are obliged to prescribe special conditions regarding the direct performance of his official duties. These are the conditions that determine the nature of the work.
By nature, the work in relation to the driver can be classified (Article 57 of the Labor Code):
- to normal (without features);
- traveling;
- on my way.
For the convenience of documenting trips, it is better to establish a traveling nature and secure it with an employment contract. Then the employer will not need to arrange business trips when traveling for a long time or distance. Your presence on the road is confirmed by waybills.
On-the-go jobs are usually indicated for truckers. It implies the inability to return home at the end of the work shift and a long stay on the road.
Guarantees and compensation for work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions are applied if the organization has the results of a special assessment of workplaces. If it is carried out, then you should look at what is provided as guarantees and compensation for the driver. Most often, when passing certification, the driver’s workplace receives a hazard class of 3.1 or 3.2.
If the workplace belongs to a certain hazard class, additional annual paid leave, increased wages, and reduced working hours are usually provided. All of them are reflected in the employment contract.
- Operating mode.
There are two articles in the legislation regarding the operating mode: 57 and 189 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. All regimes for any category of employees must be prescribed in the internal regulations of the organization. However, for a number of drivers, special conditions may be established; then these will be individual work parameters and they must be reflected in the employment contract.
Indicated:
- mode name;
- start and end times of the work shift;
- working days and weekends are determined;
- It is also recommended to prescribe the standard hours that the employee will work.
If this is a standard working day, then you can be guided by the production calendar for a certain category of employee (for example, for harmful and dangerous conditions, the norm should not exceed 36 hours per week). The contract must also stipulate breaks for rest and food: their number, duration (in accordance with labor legislation and Order of the Ministry of Transport No. 15), and the procedure for provision.
- Internship.
Legislation limits the ability to begin full-time work without an internship for a number of categories of drivers:
- those who have started working as a driver for the first time or have no experience working on the type of vehicle on which work will be carried out in this organization;
- if there is a break of more than one year as a driver.
- Salary. A mandatory condition of labor relations is the establishment of remuneration for the employee. The contract must specify the system for calculating remuneration, as well as additional payments in the form of allowances and surcharges.
- The condition of full financial responsibility. In the case of transportation of goods or money, the employer has the right to enter into an agreement with the driver, within the framework of which he will be responsible for their safety.
Contracts can be fixed-term or indefinite, main or part-time. The Labor Code sets certain restrictions for drivers. And when concluding an employment contract, it is important to take into account the requirements of Article 329 of the Labor Code, which prohibits the establishment of part-time work for the driver who drives the vehicle. You cannot be a driver at your main place of work and a part-time driver.
Cargo transportation can be carried out both over relatively short distances and long distances. In any case, it is advisable to conclude an agreement with the driver on financial liability for the entrusted cargo in the event of its complete or partial loss as a result of circumstances related to its movement.
We invite you to read: Greenhouse rental agreement between individuals
In the case of a truck driver, it is necessary to stipulate in the employment contract an individual work schedule, terms of payment for irregular hours of work, as well as compensation related to maintaining the vehicle in working condition.
When hiring a driver for organizations involved in the transportation of large and (or) heavy cargo, it is necessary to pay attention to his driving experience. It must be more than 5 years, with the condition that the last year has been worked in transport of the corresponding category. Drivers who do not have a penalty in the form of deprivation of their license in the coming year are allowed to transport dangerous goods.
Art. 188 of the Labor Code obliges to pay attention to the situation when an employee uses his personal transport for work purposes. In this case, the employer can agree with the driver on compensation for expenses associated with depreciation of the vehicle. The amount of such compensation is determined solely by agreement of the parties to the employment contract and is formalized in an additional agreement to it. It is also recommended to enshrine the list of payments in a collective agreement. This may include: payment for fuel and lubricants, vehicle repair and maintenance.
We also accept the option when the employer also signs a vehicle rental agreement with the driver. It stipulates all the operating conditions of the car and the associated costs.
When registering an employment relationship with a bus driver, it should be taken into account that the candidate must have a driver’s license confirming the right to drive such a vehicle (category D). In cases of long-distance passenger transportation, it is necessary to provide for a work and rest schedule in accordance with the requirements of Order of the Ministry of Transport No. 15.
With a taxi driver
A citizen can be hired as a taxi driver:
- with personal transport;
- for a car owned by the employing company.
In the first case, the employer must conclude not only an employment contract with the driver, but also a rental agreement for a car, which is the personal property of the employee.
The employment contract with the taxi driver should also provide for an irregular work schedule and the possibility of night shifts.
A distinctive feature of this position is that in addition to driving functions, it also performs additional functions:
- receiving goods from the warehouse and transferring them to the warehouse;
- external inspection of the cargo packaging for its integrity;
- functions for monitoring loading and unloading operations;
- work with documents for cargo escort.
In this regard, the forwarding driver is financially responsible for the entrusted cargo. To do this, a financial liability agreement is concluded with the employee.
Required documents
If the interview is successful, the driver must present the following documents to the employer:
- passport;
- insurance certificate (SNILS);
- work book;
- certificate of completion of a medical examination;
- military ID (if you are liable for military service);
- a document that confirms education/qualification (certificate, certificate, diploma);
- driver's license with categories B, C, CE, C1, C1E (depending on the type of transport).
In addition, the driver must have a driver's card to operate a tachograph . If it is missing, then a person will be able to start work only after receiving it.
Driving a car without a card is punishable by a fine for both parties, so it is better for the employer to know what documents need to be completed when hiring a driver.
Insurance premiums and personal income tax are not paid on compensation
Compensation for the traveling nature of work is not subject to either insurance contributions or personal income tax on the basis of subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 20.2 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ “On compulsory social insurance against accidents in production and occupational diseases.”
Like any other expense in tax accounting, compensation expenses must be documented.
The Russian Ministry of Finance wrote exactly the same thing in letter dated January 17, 2019 No. 03-15-05/1909. The main idea of which is that the amounts of compensation paid to employees in connection with the traveling nature of the work are not subject to insurance premiums and personal income tax, provided that such expenses are documented.
If we follow the position of the Russian Ministry of Finance, an employee’s expenses for business trips do not need to be subject to insurance premiums and personal income tax if such expenses are provided for in the company’s documents. Firstly, the condition regarding the traveling nature of the work must necessarily be provided for in a collective agreement, agreement, local regulation or employment contract. Secondly, each expense must be supported by a document.
If the company does not have the necessary local acts or the employee does not provide supporting documents, the accountant will not be able to take these expenses into account. The Federal Tax Service does not recognize these expenses and will assess additional taxes and, accordingly, fines and penalties. According to officials, which is quite logical, there are no documents confirming the expenses of employees - there is no compensatory nature of these payments.
Expenses for payment of compensation to employees whose work is traveling in nature are recognized as expenses for ordinary activities as of the date of approval of the advance report. This is provided for in paragraphs 5 and 16 of the Accounting Regulations “Expenses of the Organization” PBU 10/99, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n.
Until the employee submits an advance report and it is approved by the director, the funds issued to the employee are considered an advance. These amounts must be reflected in accounting as an employee’s receivables according to the rules of paragraphs 3 and 16 of PBU 10/99 “Organizational Expenses”.
Travel by employees whose permanent work is traveling in nature is not considered business trips. This is stated in Part 1 of Article 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Accordingly, daily allowance standards cannot be applied to this work.
The order of acceptance to work
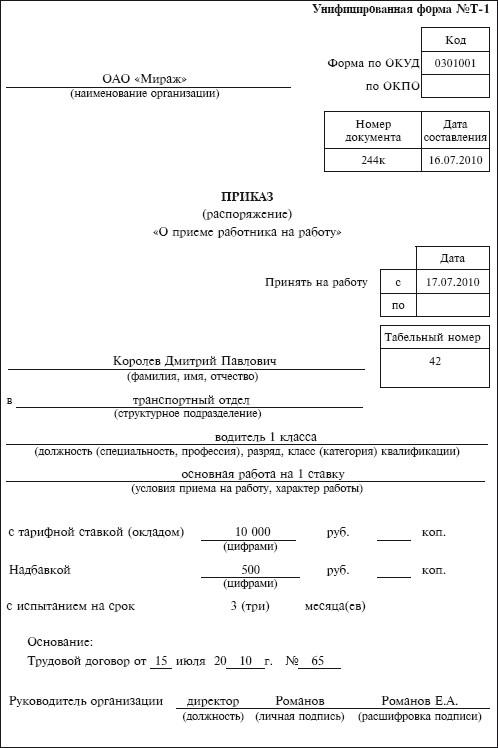
An employer can issue an order to hire a driver using a special T1 form, but has the right to use an order of its own form .
In the latter case, it is necessary to include in the order such information as: last name, first name, patronymic of the employee, name of the department, position, probationary period (if any), salary amount, date/number of the employment contract on the basis of which this order is drawn up.
Then the order is signed by the director, and within 3 days the new employee must be familiarized with it. At the end of the order the driver must put his signature.
Sample order:
The HR specialist must familiarize the employee, against signature, with the instructions on labor protection, internal labor regulations, regulations on material incentives for employees and the use of his personal data, etc.
Signs of a traveling character and suitable professions
Work functions are performed outside the workplace. For example, when an employee, in order to fulfill his duties, must move from place to place within one or several localities. This could be setting up equipment, installing equipment, delivery, installing windows, insurance, etc.
The place of direct work is located quite remote from the place of registration of the company.
The employee is in no way tied to a specific workplace. He performs his duties in different places. For example, courier, delivery driver, media correspondent.
The employee is constantly traveling by order of management or in accordance with the job description. For example, a traveling salesman or sales representative, an affiliate network manager, a retail outlet controller, etc.
The workplace itself often changes location. For example, this happens when building roads. Or, when a company provides services to partners directly in their offices, which are located at different addresses.
Professions in which work is of a traveling nature include the following:
- workers of all professions engaged in the construction, repair and maintenance of highways;
- couriers or delivery managers;
- manager-consultants for installation and configuration of equipment or software;
- Affiliate network managers serving and monitoring retail outlets;
- insurance and sales agents;
- service employees;
- fitters and shipping track technicians;
- traveling crew workers;
- divers;
- blasting instructors;
- car drivers, forwarders;
- media correspondents, etc.
Thus, the employee's main responsibilities must involve constant travel. Almost every company has couriers. And all companies involved in trade have managers for working with retail stores. There may also be a lot of traveling workers in companies that provide consulting, legal, insurance, accounting, information, maintenance, and IT services.
Material liability
It is impossible to conclude agreements on full financial liability with drivers, because this profession is not indicated in the list of jobs and categories of workers with whom such agreements can be concluded (List, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 2002 N 85). The conclusion of such an agreement is possible only if the driver is simultaneously assigned the functions of freight forwarding. However, even in this situation, he will bear full financial responsibility only in relation to the duties of the forwarder (decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated November 19, 2009 N 18-B09-72). At the same time, the driver is obliged to compensate the employer for direct actual damage caused to the latter (Part 1 of Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, lost income (lost profits) is not subject to recovery.
Full financial responsibility rests with the driver in situations provided for in Art. 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in particular, in the following cases:
the valuables were entrusted on the basis of a special written agreement or received by the driver using a one-time document;
the damage was caused intentionally;
the damage was caused while intoxicated (alcohol, drugs or other toxic);
the employee has committed a crime (established by a court) or an administrative offense (established by the relevant government agency);
the damage was not caused while the employee was performing his job duties.
Recovery of damages is a right, not an obligation of the employer; he can fully or partially exempt the employee from his compensation (Article 240 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the amount of damage does not exceed the average monthly salary, then it can be recovered by written order of the employer (Article 241, Part 1 of Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the amount of damage exceeds the average monthly salary, then it can be compensated either by the employee voluntarily or by court decision (Parts 2 and 4 of Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The damage caused can be recovered regardless of whether the employee is brought to disciplinary, administrative or criminal liability (Part 6 of Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Is the driver's consent required to change cars?
A common situation in practice is when the driver’s employment contract specifies that his workplace is a car of a certain brand and with certain license plates. At the same time, employers often explain the inclusion of this information in the employment contract as a requirement of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on the mandatory indication of the place of work in the employment contract. In fact, in the contract with the employee it is enough to write the name of the organization, and, if necessary, indicate the name and location of the branch, representative office or other separate structural unit. Including information about a specific vehicle in an employment contract will lead to the fact that in the event of its breakdown, sale, or if there is another need to transfer the driver to another car, the employer will be forced to enter into an additional agreement to the employment contract (Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If there is no reference to a specific car in the employment contract, then in order to transfer the driver to another car, his consent is not required (clause 3 of Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).