What is it and how is it different from a workplace?
An employment contract must contain mandatory information in accordance with Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and one of the points is the place of work. It is not entirely clear how it differs from a worker.
In order not to confuse the concepts, we remember: the first is the company in which the employee works, the second is the workshop, site, office, office, and so on, that is, a specific indication where job responsibilities are performed.
Here is an example of how to indicate the place of work in an employment contract:
“The Employee’s place of work is Fakel LLC.”
Remote work: features and types
In its letter, the Moscow State Technical University notes that in the situation under consideration, the work may be remote. The specifics of regulating the work of remote workers are established in Chapter 49.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It defines how to conclude an employment contract for remote work, organize interaction between the employee and the employer, and on what basis a “remote” employee can be fired.
A feature of remote work is that the labor duties established by the employment contract are performed outside the location of the employer, as well as the territory or facility controlled by him and the stationary workplace. Interaction with the employer and resolution of work issues occurs via the Internet or mobile networks.
Important
Individual entrepreneurs and legal entities will be given a subsidy for employing unemployed people
Otherwise, the concept of remote work corresponds to the usual norms of labor legislation. An employer, when employing a specialist under a remote work agreement, must provide work within the framework of the responsibilities agreed upon with him and pay wages in full on time. It cannot be reduced only on the grounds that the employee does not work in the office, but remotely.
The employer is also obliged to provide remote workers with safe conditions and labor protection. In particular, he needs to familiarize them with the relevant requirements when working with equipment recommended or provided by the organization, as well as provide OSS for remote employees against industrial accidents and occupational diseases.
Healthy
On imposing a fine for an incorrect SNILS in the SZV-M form
Remote work can be provided on a permanent basis, that is, during the entire term of the contract, as well as temporarily, with the consent of the employee or on the initiative of the employer. In the latter case, an LNA is adopted on the temporary transfer of employees to remote work. This occurs in exceptional cases in which the life or health of the entire population of the country or part of it is endangered.
Is it possible not to write a specific address?
The Labor Code does not oblige you to indicate the location of the workspace, and what a place of work is cannot be immediately defined in an employment contract. Confusion ensues. But it is enough to enter the name of the organization. This is an indication of where the employee works. But the address is an additional condition, which means it is not necessary to write it. But difficulties arise if it is necessary to confirm the fact of absenteeism - it is difficult to prove where exactly the employee should have been.
The address is a specification of the work location, but is the place of work required in the employment contract? Yes, this condition must be present in the document.
What is a place of work
The concept of place of work is not contained in the Labor Code, which causes confusion when specifying this clause in contracts with an employee. Place of work is the employer’s address and name. In judicial practice, there are also decisions according to which the place of work is understood as the specific locality where the work was carried out, or the address where work duties were performed.
The place of work is a mandatory condition of the employment contract (based on paragraph 2, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code). It is often included in the “Subject of the Agreement” section. Correctly indicating the place of work helps the employer:
- Relocate or transfer an employee.
- Determine jurisdiction in labor disputes.
- Avoid penalties when inspected by the state labor inspectorate.
- Resolve a controversial situation regarding dismissal for absenteeism.
- Provide the employee with the guarantees and compensation due to him.
HR specialists often make mistakes when indicating the place of work in the contract, especially in cases when we are talking about shift workers, builders, drivers, etc.
The Supreme Court emphasized that the place of work is an organization located in a certain area, its representative office or branch. To avoid potential disputes in the contract, the place of work should be specified, such as the name of the employer and the location where the employee will work.
The place of work and the workplace may not coincide - and this situation occurs quite often in practice.
Formulations when an employee works remotely
Remote work has become especially popular recently. And questions immediately began to arise: is an employment contract drawn up without a place of work, if a person himself chooses where to perform his duties? At home, in the country, even in the park - the presence of a laptop and the Internet has opened up new opportunities for remote or remote work.
The following formula applies in this case:
How to prescribe working conditions in the workplace without SOUTH
Until the letter from the Ministry of Labor came out, which, by the way, also did not add clarity, but at least lifted the veil of uncertainty, many personnel specialists indicated in their employment contracts working conditions, who is good at what (working conditions are normal, working conditions will be determined after a special assessment (before such dates), etc.).
How can one prescribe working conditions at an employee’s new workplace when a period of one year is given for this? But Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation requires this, without any exceptions.
The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, in its letter No. 5-1/OOG-2516 dated July 14, 2016, advises that if an employee is accepted into a newly organized workplace where an assessment of working conditions has not previously been carried out, then before conducting a special assessment of working conditions in the workplace A contract with an employee hired for such a workplace may indicate the general characteristics of the workplace (description of the workplace, equipment used and features of working with it).
The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation did not provide any, at least approximate, formulation. And what will you write? Use your imagination again?
The Labor Inspectorate, in its online responses after the release of this letter, began to refer specifically to it, also without providing any wording. Although, you can still come across answers that until a special assessment of working conditions is carried out, nothing needs to be specified in the employment contract.
Question: A mandatory condition of an employment contract is working conditions in accordance with the results of a special assessment (optimal, acceptable, harmful, dangerous). What should be indicated in the contract if an employee is hired for a position that has just been added to the staffing table, for which a special assessment has not yet been carried out and must be carried out within 12 months?
Answer: If a special assessment of working conditions (SAL) was not carried out in relation to the newly introduced workplace, then nothing needs to be specified in the employment contract with the employee regarding working conditions at his workplace. In such a situation, it is necessary to immediately conduct a special assessment and, based on its results, conclude an additional agreement to the employment contract indicating information about the working conditions at the employee’s workplace.
Information portal of Rostrud “Online inspection of the Russian Federation”, April 2017
It is also worth mentioning the letter of Rostrud dated November 20, 2015 No. 2628-6-1, which also asked a question about working conditions when there is no special assessment. In the said letter, the department noted that Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for any temporary deferrals in the fulfillment of this obligation of the employer, therefore, in order to avoid violations of labor legislation, in the absence of valid results of certification of workplaces for working conditions, a special assessment of working conditions must be carried out as soon as possible.
In fact, working conditions need to be spelled out in an employee’s employment contract. Indicate in the contract everything that the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation advises, namely, describe the employee’s workplace, the equipment he uses and the features of working with it (at the end of the article I provided an approximate example). Because the judicial system has not yet come to a common denominator on this issue .
The employer lost
The employer indicated in the employees’ employment contracts that “working conditions in the workplace will be determined after carrying out the special labor assessment,” which he was obliged to carry out within 12 months, because these were newly organized workplaces. There were no violations on his part; he still had time.
The Samara Regional Court, in its decision of October 2021, did not agree .
The court referred to Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as to the above-mentioned letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated July 14, 2016 No. 5-1 / OOG-2516, based on which, the employment contracts of employees must indicate the general characteristics of the workplace (description of the worker places, equipment used and features of working with it).
In addition, the court noted that failure to inform workers about the working conditions at their workplaces violates the labor rights of workers and creates a threat of harm to their life and health, since those dangerous and (or) harmful production factors that may affect workers in the process of their work.
Thus, the employer received the minimum possible administrative fine in the amount of 50,000 rubles under Part 4 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (maximum 100,000 rubles), but there was still no indication of the working hours in the part-time worker’s employment contract, which is also mandatory for inclusion in the contract.
But a judge in the Arkhangelsk region decided that the absence of working conditions in an employee’s employment contract (without conducting a special labor assessment) is not a violation of the law.
The employer won
The employment contract of the new HR director stated that working conditions in the workplace were normal. The employer had another whole year to conduct a special assessment of working conditions.
The labor inspectorate inspected the organization in May 2021 and brought the employer under Part 1 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (fine from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles), although it should have been under Part 4, as for improper execution of an employment contract, well, that’s not the point.
The court did not agree with the position of the State Labor Inspectorate, noting that this was a newly organized workplace, so the employer still had time to conduct a special assessment.
The court also referred to the fact that the position of “HR Director” does not belong to the category of workplaces containing potentially harmful and (or) hazardous production factors (Part 6 of Article 10 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ) , namely:
- workers' workplaces, professions, positions, specialties of which are included in the lists of relevant works, industries, professions, positions, specialties and institutions (organizations), taking into account which the early assignment of an old-age insurance pension is carried out;
- workplaces in connection with work in which employees, in accordance with legislative and other regulatory legal acts, are provided with guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions;
- workplaces in which, based on the results of previously conducted certification of workplaces for working conditions or a special assessment of working conditions, harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions were established.
Consequently, the absence of working conditions at the workplace in the employment contract concluded with the employee is not a violation of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Working conditions in the workplace without SOUTH (sample)

The stated wording of working conditions is approximate! The main thing is to remember that what you write down in the employment contract can only be changed by agreement of the parties . Therefore, if your furniture and office equipment are constantly changing, then try to write general phrases, do not write about types of monitor screens (liquid crystal, based on a cathode ray tube), do not list all types of peripheral devices that an employee can use (such as an external hard drive , flash drive, uninterruptible power supply, projector, etc.). Prescribe only those things that you are 100% sure will be consistent. Also, you cannot write that working conditions are safe (optimal, acceptable), because... you don’t know about it yet (there are no special assessment results). The fact that working conditions comply with labor protection requirements. So this is the responsibility of the employer (Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)...
Regarding the timing of the special assessment. I wrote a general phrase, although many indicate a specific date by which a special assessment will be carried out (in the case of a newly organized workplace, this is 12 months). As I wrote above, Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not make any exceptions, therefore, in order to comply with the law, a special assessment of working conditions must be carried out as soon as possible .
By the way, you can take some phrases from the sanitary rules (just don’t overdo it), at the same time you will emphasize a lot:
— SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization”; — SanPiN 2.2.2.1332-03 “Hygienic requirements for organizing work on copying equipment”; — SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96 “Hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises”; — SanPiN 2.2.4.3359-16 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for physical factors in the workplace”; — SanPiN 2.2.0.555-96 “Hygienic requirements for working conditions for women”; - Set of rules. Administrative and domestic buildings. Updated version of SNiP 2.09.04-87.
Formulation for a shift worker
Shift work is usually associated with remote regions, where it is not so easy to get to, the location of the facility often changes. It is important to indicate the region, especially if it is located in the Far North or equivalent regions, since labor in these conditions requires certain guarantees.
Here is an example of how to register a workplace in an employment contract so that the document complies with the requirements of the law:
“The Employee’s place of work is the construction sites of Stroy-Vector LLC in the Krasnoyarsk Territory.”
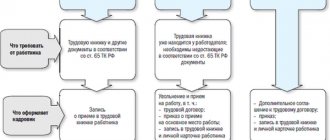
Mandatory (material) conditions of the employment contract
All terms of the employment contract must comply with the requirements of current labor legislation.
1) place of work (i.e. name of the employer) (paragraph 2, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
2) position according to the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications. Also here the specific type of work entrusted to the employee must be indicated (paragraph 3, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
3) start date of work. If a fixed-term employment contract is concluded, then the validity period of this contract and the circumstances (reasons) according to which this fixed-term employment contract is concluded (paragraph 4, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) are also indicated here.
That is, it is indicated that the employee is hired to work under a fixed-term agreement for a certain period, indicating the date of dismissal. If, after the completion of a fixed-term employment contract, the employee continues to work, then such a fixed-term employment contract will be reclassified as an open-ended employment contract.
4) terms of remuneration (including the size of the tariff rate or salary (official salary) of the employee, additional payments, allowances and incentive payments) (paragraph 5, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
5) working hours and hours (paragraph 6, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
6) guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions. In this case, the characteristics of working conditions in the workplace must be indicated (paragraph 7, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
7) working conditions in the workplace (paragraph 9, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
conditions that, if necessary, determine the nature of the work (for example, the nature of the work may be traveling or on the road) (paragraph 8, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
We suggest you read: What documents for divorce if there is a child?
9) the condition on compulsory social insurance of the employee (paragraph 10, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
10) other conditions in cases provided for by labor legislation (paragraph 11, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Entries in the employment contract for drivers (traveling nature of work)
How to determine a place of work for those who never sit still? Train drivers, drivers, couriers - all these and many other workers sign a contract with the condition of traveling work. Along with this condition, determine in which city or region your employee works.
For example:
“The Employee’s place of work is Vympel LLC, St. Petersburg. The work is of a traveling nature, trips are carried out within the Leningrad region.”
What it is?
According to Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in an agreement concluded by the parties: a certain organization and an individual - an employee, the place of work must be indicated (what should be contained in the employment contract is written here).
This information must be written down in the document not in every case, but only in those specified in the law, namely:
- if you have to work in a branch;
- at the representative office;
- in a structural unit.
It is important that such a place of work is remote - located in a different area than the main office of the organization.
A simple example: a company operates in Moscow, but has a production workshop in Voronezh, which acts as a branch. In this case, the employment contract must indicate that the employee is hired to work in the “capital of the Black Earth Region”, and not in the main city of the country.
Important! When considering the issue of place of work, you should know that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation has rules regulating the remote activities of hired employees.
So, in Art. 312.1 there are provisions that indicate that an employee can conduct his activities not in a representative office or branch, but in another territory that is in one way or another controlled by the employer.
Example: a company is engaged in advertising activities in St. Petersburg. Every day the company needs to produce new models. She was unable to find a talented designer in the city. But such a person was discovered in Volgograd. He copes with the job quite well: he communicates with management via video conference - via the Internet, and sends the results of his work by e-mail. Thus, the place of work of such an employee will not be St. Petersburg, but Volgograd.
Opinions differ in legal science about what exactly is considered a place of work. The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation and Rostrud are trying to clarify the issue. And, in general, they succeed. Taking into account the existing clarifications, we can come to the conclusion that it is enough to indicate in the employment contract:
- name of the structural unit;
- his location.
It is more difficult to resolve the issue in cases where an employee needs to work in an area where there is no branch or representative office. But this will be discussed later in the article.
Differences in wording
There is serious confusion about these two concepts. If the place of work is mentioned in Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and in some other articles, then the definition of a workplace must be sought in Art. 209 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It says the following location:
- where the employee should be or where he should arrive;
- being, to one degree or another, under the control of the employer.
At first glance, the difference is small, or not at all. Is it so? For a better understanding of the differences, you should refer to Art. 81, where, among other things, we are talking about dismissal for absenteeism. It says that absenteeism is considered to be the absence of an employee from the workplace for more than 4 hours during a work shift , unless there are good reasons for this.
Thus, based on logic, it can be noted that the workplace is a more specific concept.
For example: place of work - Kursk branch of Brothers-Mechanics LLC. And the workplace is workshop number 1, located at the address: Kursk, Lenin Street, building 52. However, this position is not true for everyone. The issue remains debatable.
But it seems that in order to ensure legality in the field of labor relations, it is necessary to issue local regulations , which would specifically indicate to which, say, machine a turner is “assigned”, to which department a store employee is assigned.
As for the place of work, which must be specified in the contract in the cases specified in the article, then here too the position of the “personnel officers” is not established. Some believe that it is enough to indicate the name of the branch or separate division. Others say that this information is not enough.
Attention! When it comes to documents and legal requirements, it is better not to neglect the details.
It is recommended to indicate in the contract:
- name of the branch or division;
- his exact address.
If this is done, then there will be fewer disagreements and disputes in specific situations.
Place of work in a separate department
When the organization is both the head office and the place of work of the hired employee, it is not necessary to include specifications regarding the location in the clause of the contract. But if the hired person performs his duties in another department, workshop, warehouse or office, then clarification on his location will be required in any case. This is clearly stated in Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.

Despite the fact that labor legislation requires specifying the structural unit into which the employee is hired and where he will directly perform his work duties, there is no reference in the article to the fact that it is necessary to indicate the address of the building. Only the need to clarify the location is specified.
When registering an employee in one of the structural divisions, it is recommended to follow the following procedure for describing his affiliation:
- The name of the employer's organization itself.
- Name of the structural unit.
- Location.
This information may look like this:
LLC LUKOIL-ENERGOSETI, Astrakhanenergoneft, Astrakhan.
Representative office and branch
When sending an employee to one of the branches of a company or its representative office, it is understood that he will work in the company, but its location is different from the location of the head office. Large companies may have branches and representative offices both on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad. This case requires mandatory clarification in the contract, as it may cause misunderstanding, and is interpreted as withholding information from the hired person. When signing an agreement, a citizen must clearly understand what obligations he is taking on and where he will fulfill them.
If the representative office is located in another federal district or even outside the country, then its location should be specified as accurately as possible.

It is recommended to present information in the following sequence:
- Company name.
- Name of the branch or representative office.
- Federal district of the Russian Federation or country (if we are talking about another state).
- City.
A specific address may or may not be provided as desired.
Difference between place of work and workplace
Article 57 of the Labor Code lists all the mandatory and additional conditions that must be specified in the contract concluded between the employer and the new employee. One of the mandatory conditions is to indicate the place of work. At the same time, the same article provides extremely sparse explanations of this point, and there are no explanations at all about what should be understood by this concept. However, based on the wording and further explanatory definitions, one circumstance becomes absolutely clear - this concept has nothing to do with the expression “workplace”.

Article 209 of the Labor Code provides an explanation of the expression “workplace”. It is defined as a certain point where the employee is obliged to regularly arrive to perform his immediate duties. Moreover, this item must be controlled by the employer with whom the cooperation agreement was concluded. In fact, a working space is considered to be the space where an employee works day after day, has his own tools, a table, a chair or other objects that are transferred to him for the duration of his work.
The work place is a less individualized space. It also employs other people who have also entered into contracts with the organization. The place of work always has a postal address.
“Place of work” from the point of view of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation
Until 2014, there were several interpretations of this concept in the information available to practicing lawyers.
The legislative authority represented by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation brought certainty to the issue under consideration. According to the judicial body of federal jurisdiction, an MR should be considered an organization, its representative office, branch, or other separate structural unit located in a certain locality (settlement).
However, legal practice shows that misunderstanding of this term is still the cause of various problems. The court's definition did not indicate the difference between “place of work” and “workplace.” Today, legal experts agree on only one thing – we are talking about different concepts.
Note ! This opinion was expressed in decisions of a number of court hearings: Sverdlovsk Regional Court from 2012 under number 33-11596/2012, Tula Regional Court from 2012 under number 33-380, Amur Regional Court from 2011 under number 33-281/11.

It is not entirely clear what constitutes a “place of work”
The Labor Code in parts two and four of Article 57 summarizes that the workplace condition is considered as additional. It can be included in the contract by agreement of the parties.
The ambiguity lies in the fact that the legislator understands as a workplace the place in which the employee must be present during working hours and arrive at a specifically designated time. A prerequisite is control by the employer: indirect or direct. This means that the place of work should be characterized by other categories. It’s just not clear exactly which ones. There is no unanimity on this issue either among lawyers or among employers.
Note ! The thesis proposed by the Supreme Court is included in the “Practice of consideration by courts of cases related to the implementation of labor activities by citizens in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas.” And this suggests that the concept has a legal basis and is a precedent for other decisions.

Place of work and workplace are different things
Taking into account the position of the supreme court, the concept of “place of work” should include the following elements:
- information about the name of the organization, employer;
- geographical indications about the area where the organization is located.
The concept of locality has administrative implications. It is understood as a populated area located in accordance with the existing administrative-territorial division.
Note ! A similar view (decision) was expressed earlier, in 2013, in connection with the trial of the Central District Court of Novosibirsk under number 2-2091/2013.

The place of work must include information about the organization, its location