Accounting in examples
Subscribe Free Silver Newsletter
Subscribers 6,724 RSS
| November 2007 | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| 12 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
| 19 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | |
| 26 | 28 | 29 | 30 | |||
Haven't gone out once in the last 60 days
Mailing site: https://kcbux.ru/ Opened: 04/05/2006
Author Marina Ivanovna
Statistics
6,724 subscribers -1 per week
- Issues
- Statistics
All episodes
Payroll
Quick establishment of primary accounts, automatic payroll calculation, multi-user mode, free updates and technical support in the online service Kontur.Accounting!
Get free access for 14 days
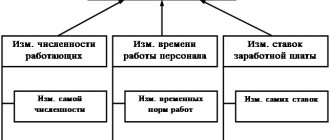
Wage expenses are written off against the cost of production or goods, therefore the following accounts correspond to account 70:
- for a manufacturing enterprise - 20 account “Main production” or 23 account “Auxiliary production”, 25 “General production expenses”, 26 “General (administrative) expenses”, 29 “Servicing production and facilities”;
- for a trading enterprise - account 44 “Sales expenses”.
The wiring looks like this:
D20 (44.26,…) K70
This posting is made for the total amount of accrued salary for the month, or for each employee, if accounting on account 70 is organized with analytics for employees.
The procedure for calculating the advance payment is similar. Its date depends on the payment method established in the organization:
1. If the advance is paid in a fixed amount from the employee’s monthly salary, then an entry for calculating the advance is not needed. Make only the monthly payroll entry on the last day of that month;
2. If the advance depends on the time that the employee actually worked in the first half of the month, then, as a rule, additional reserve deductions for personal income tax, alimony and other payments are made. Create an entry for accruing the advance at the end of the first half of the month for which it was accrued. For the same date, create a deduction entry.
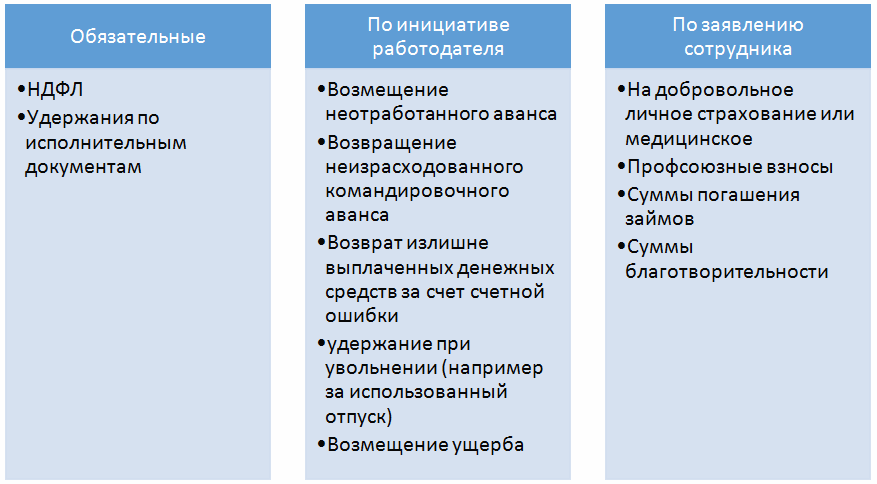
Grounds and procedure for deduction from wages
Types of possible deductions from an employee’s salary:
Income not subject to withholding
These types are established by Art. 101 of Law No. 229-FZ. The main types of such income:
- Compensation for damage caused to health or in connection with the death of the breadwinner;
- Compensation for injury to an employee and family members if they die;
- Compensation from the budget as a result of disasters (man-made or radiation);
- Alimony;
- Amounts of business travel, moving to a new place of residence;
- Financial assistance in connection with the birth of a child, marriage, etc.;
Deduction order
Deductions from an employee's salary are made in the following sequence:
- personal income tax;
- Writs of execution for alimony for minor children, for compensation for harm to health, death of the breadwinner, crime or moral harm;
- Other writs of execution in the order of receipt (other mandatory deductions);
- Retentions at the initiative of the manager.
Limiting the amount of deductions
The amount of mandatory deductions cannot exceed 50% of the wages due to the employee. In some cases, the amount of deductions may be increased. For example, deductions based on writs of execution. These deductions are subject to a 70% limit:
- On alimony for minor children;
- Compensation for damage caused to health, death of the breadwinner;
- Compensation for criminal damage.
Also, when calculating deductions, you should take into account:
- If the amount of mandatory deductions exceeds the limit (70%), then the amount of deductions is distributed in proportion to the mandatory deductions. No other deductions are made;
- The amount of limitation on deductions initiated by the employer is 20%;
- At the request of the employee, the amount of deductions is not limited.
Example of calculating salary deduction
In the name of employee Vasilkov A.A. 2 writs of execution were received: alimony for the maintenance of 3 minor children - 50% of earnings and compensation for damage to health in the amount of 5,000.00 rubles. The salary amount was 15,000.00 rubles. The personal income tax deduction for 3 children amounted to RUB 5,800.00.
We will calculate deductions based on writs of execution:
- Personal income tax tax base = 15,000.00 – 5,800.00 = 9,200.00 rubles;
- Personal income tax = RUB 1,196.00;
- Amount of earnings for calculating deductions = 15,000.00 – 1,196.00 = 13,804.00 rubles;
- Limit amount = RUB 9,662.80.
Deductions in the amount of =11,902.00 rubles, of which:
- For alimony = 6,902.00 rubles. (58% of the total withholding amount);
- Compensation for damage = 5,000, rub. (42% of the total withholding amount).
As a result, deductions are made according to writs of execution in the amount of:
- For alimony – 9,662.80 *0.58 = 5,604.42 rubles;
- Compensation for damage – 9,662.80 *0.42 = 4,058.38 rubles.
Salary deductions
Quick establishment of primary accounts, automatic payroll calculation, multi-user mode, free updates and technical support in the online service Kontur.Accounting! Get free access for 14 days
Deductions from salary reduce the amount of accruals and go through the debit of account 70. As a rule, all employees have one deduction - personal income tax. Here account 70 corresponds with account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, posting:
D70 K68
In postings for other deductions and reserve deductions for personal income tax, the loan account changes, depending on where it goes. For example, when withholding under a writ of execution in favor of a third party, account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” is used, posting:
D70 K76
The accrual and withholding of personal income tax and other payments is made by postings on the last day of the month for which the salary is accrued. Postings for personal income tax payment - on the day the money is written off from the account or issued from the cash register.
In the Kontur.Accounting web service it is easy to work with salaries: accruals and deductions, personal income tax and contributions. The system automatically makes the necessary transactions and generates payment orders.
What is unjust enrichment
Unjust enrichment is the acquisition or saving of property by one person at the expense of another without due legal basis.
A person who, without the grounds established by law, other legal acts or transaction, acquired or saved property at the expense of another person, is obliged to return this unreasonably acquired property to the latter.
This obligation is established by paragraph 1 of Article 1102 of the Civil Code.
However, it also provides for a number of exceptions.
For example, according to paragraph 3 of Article 1109 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, wages and equivalent payments, pensions, benefits, scholarships, compensation for harm caused to life or health, alimony and other sums of money provided to a citizen as a means to existence, if:
- the receipt of these funds was not associated with dishonest actions of the acquirer;
- receipt of funds is due to a counting error.
In this case, the good faith of the citizen - the recipient of the disputed funds is implied.
The party demanding the return of overpaid amounts must prove the opposite.
More on the topic:
The RF Armed Forces prohibited the selection of benefits paid by mistake
RF Armed Forces: why can’t a debt be recovered as unjust enrichment?
Calculation of insurance premiums
Account 70 is not included in postings for insurance premiums, because they are not accrued to employees and are not deducted from their salaries.
Insurance premiums are included in the cost of production, i.e. pass through the debit of accounts 20 (26, 29, ...) or 44 in correspondence with account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security”. 69 accounts usually have subaccounts for each contribution. Wiring:
Convenient online accounting
Quick establishment of a primary account, automatic payroll calculation, multi-user mode in Kontur.Accounting
Try it
D20 (44, 26, …) K69
Deduction from wages: postings and examples
Mandatory deductions
Personal income tax is withheld from each employee’s salary at the following rates:
- 13% - if the employee is a resident of the Russian Federation;
- 30% - if a non-resident of the Russian Federation;
- 35% - in case of winning, savings on interest, etc.;
- 15% - from dividends of a non-resident of the Russian Federation;
- 9% - from dividends until 2015; interest on mortgage-backed bonds until 2007, from the income of the founders of the trust management of the mortgage coverage.
It does not matter in what form the income was received, cash or in kind. Let's look at an example:
Employee Vasilkov A.A. wages of 30,000.00 rubles were accrued, personal income tax was withheld from it at a rate of 13%, since Vasilkov A.A. is a resident.
Postings for mandatory withholding of personal income tax:
| Dt | CT | Amount, rub. | Operation description |
| 26 | 70 | 30 000,00 | Salary accrued |
| 70 | 68 | 3 900,00 | Personal income tax withheld |
According to executive documents

The amount under the writ of execution is withheld from wages, taking into account personal income tax. The amount of additional expenses under the writ of execution (for example, transfer fees) is debited from the employee.
Let's look at an example:
Employee Vasilkov A.A. wages were accrued in the amount of 20,000.00 rubles, of which 25% was withheld according to the writ of execution. Amount of deduction under the writ of execution = (20,000.00 – 13%) * 25% = 4,350.00 rub.
Deduction from wages of Vasilkov A.A. according to the writ of execution is reflected by posting:
| Dt | CT | Amount, rub. | Operation description |
| 26 | 70 | 20 000,00 | Salary accrued |
| 70 | 68 | 2 600,00 | Personal income tax withheld |
| 70 | 76.41 | 4 350,00 | The amount under the writ of execution was withheld |
| 76.41 | 50 | 4 350,00 | The amount according to the writ of execution was transferred from the cash register |
At the initiative of the employer
Deductions for the purpose of debt repayment are regulated by the Labor Code and other federal laws. In this case, it is necessary to issue an order no later than a month from the date of payment and obtain written permission from the employee.
If upon dismissal the amount of deductions is not completely written off, then, by agreement with the employee, the amount can be repaid:
- Judicially;
- By depositing funds into the cash register;
- Gift to an employee (in this case, expenses are not taken into account when calculating income tax);
- At the request of the employee, write off 20% of the salary monthly.
Typical entries for deductions from wages at the initiative of the employer:
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| 26 | 70 | Salary accrued |
| 70 | 68 | Personal income tax withheld |
| 70 | 73.2 | The amount of compensation for the shortage is withheld |
| 70 | 71 | Unreturned accountable amount withheld |
| 70 | 73.1 | Repayment of the issued loan |
Let's look at an example:
From employee Vasilkov A.A. RUB 1,500.00 was deducted from wages to repay the loan. The salary amounted to 10,000.00 rubles. The limit amount is = 8,700.00 * 0.2 = 1,740.00 rubles.
Posting the deduction of a loan from the salary of Vasilkova A.A.:
| Dt | CT | Amount, rub. | Operation description |
| 26 | 70 | 10 000,00 | Salary accrued |
| 70 | 68 | 1 300,00 | Personal income tax withheld |
| 70 | 73.1 | 1 500,00 | Deduction for loan repayment |
Accounting entries in examples
Newsletter description:
- Newsletter for aspiring accountants and more.
- The newsletter contains examples of preparing accounting entries for all sections of accounting.
- The examples are compiled with explanations and taking into account the requirements of regulatory documents.
- By subscribing to this newsletter, you will receive one example of preparing accounting entries every week.
- You will be able to independently analyze the example, familiarize yourself with the regulations, and consolidate your knowledge.
Issue No. 77
Settlements with personnel
Payments to personnel regarding wages
Example 11
[/td] Accounting entries (When you hover the cursor over the account number, a tooltip appears)
| To summarize information on settlements with employees of an organization for wages (for all types of remuneration, bonuses, benefits, pensions for working pensioners and other payments), as well as for the payment of income on shares and other securities of this organization, account 70 “Settlements with personnel” is assigned on wages." In the credit of account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” the following amounts are reflected:
The debit of account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” reflects the paid amounts of wages, bonuses, benefits, pensions, etc., income from participation in the capital of the organization, as well as the amount of accrued taxes, payments under executive documents and other deductions ( Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts. Account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”). | |||
Wages were accrued in the amount of RUB 122,200. the following categories of workers:
Dividends accrued to shareholders - employees of the organization - 70,000 rubles. Vacation pay was accrued to the employee from the previously created reserve for vacation pay - 12,000 rubles. Personal income tax withheld - 18,000 rubles. Salaries and dividends are paid from the organization's cash register. | |||
| Debit | Credit | Amount (rub.) | Content |
| 67 500 | - the amount of wages of workers in primary production | ||
| 34 300 | — the amount of wages of workers in auxiliary production | ||
| 20 400 | - the amount of wages of management personnel | ||
| 70 000 | — amount of accrued dividends | ||
| 12 000 | - the amount of accrued vacation pay from the reserve for vacation pay | ||
| 18 000 | — amount of withheld tax on personal income | ||
| 186 200 (122 200 +70 000 +12 000 -18 000) | - amount given to employees of the organization |
Amounts accrued but not paid on time (due to the non-appearance of recipients) are recorded in the debit of account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” and the credit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” (sub-account “Settlements for deposited amounts”) (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts. Account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”).
When these amounts are paid to the recipient, an entry is made to the debit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” and the credit of cash accounting accounts (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts. Account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”).