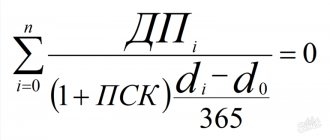What does the wage fund consist of?
The payroll consists of targeted financing, the cost of manufactured products or services provided and the profit of the organization. The indicator consists of three parts:
- Accruals for time worked or products produced. Payments are provided at tariffs and piece rates, compensation (for night hours, hazardous working conditions), incentive bonuses (for experience, qualifications), and production bonuses.
- Payments for unworked time. Includes payment for vacations (regular and additional), maternity benefits, sick leave, production downtime due to the fault of the employer.
- One-time payments. These include bonuses based on annual output or rewards for successfully completing an important task.
IMPORTANT! The structure of the fund does not include dividends, payment of financial assistance, purchase of vouchers and other targeted payments.
Pay statistics
We will help you write any paper on a similar topic.
- Essay
From 250 rub.
- Test
From 250 rub.
- Course work
From 700 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project
Find out the cost
The wage fund and its composition.
The wage fund is the total amount of money accrued by an enterprise to workers and employees for a certain period.
The wage fund includes the amount of funds accrued both for work performed and for time not worked, if provided for by law.
Types of wage funds.
There are the following wage funds for production workers:
1. Hourly wage fund;
2. Daily wage fund;
3. Monthly salary fund.
Hourly wage fund
— it includes remuneration for man-hours of actual work; it does not include payments for time not worked.
It includes:
1. Wages calculated at piece rates, tariff rates and salaries for hours worked.
2. Compensation payments related to working hours and working conditions.
3. Additional payments for night work.
4. Incentive additional payments to tariff rates and salaries.
Daily wage fund
wages - it is accrued for man-days worked and for hours not worked during the day, but paid.
It includes:
1. Hourly wage fund.
2. Payment for intra-shift downtime through no fault of the employee.
3. Payment for preferential hours for teenagers.
4. Payment for hours of performing state and public duties.
5. Overtime payment.
Monthly payroll
- includes daily wages and payments for unworked time during the month.
It includes:
1. Daily wage fund.
2. Payment for days not worked in connection with the performance of state and public duties.
3. Payment for all-day downtime.
4. Payment for regular and educational leaves.
5. Long service awards.
6. Cash compensation for unused vacation.
7. Other types of one-time incentive payments (one-time bonuses).
8. Payments for food, housing and fuel.
There is the following relationship between the indicators characterizing the average level of wages:
where Tdn is the average actual working day; Kdn - coefficient of increase in DFZP due to additional payments for unworked but paid time during the working day; fch
— average hourly wage.
where Tmes is the average actual duration of a working month; Kmes - the coefficient of increase in the minimum wage due to additional payments for unworked but paid time during the month; fday
- average daily wage.
Wage differentiation.
An important task of wage statistics is the analysis of wage differentiation.
It is carried out using the decile wage differentiation coefficient.
where D9 - shows 10% of employees who have wages higher than the obtained value; D1 - shows 10% of employees whose wages are lower than the obtained value.
Analysis of wage dynamics is carried out using the index method. For workers of certain categories, individual wage indices are calculated, and for a set of workers in various professions and industries, general indices are calculated. The most commonly used wage indices are variable, constant composition and structural changes.
Calculation of the rate of growth in labor productivity compared to the growth of average wages.
This coefficient shows by what percentage the growth rate of labor productivity exceeds the growth rate of wages.
Attention!
If you need help writing a paper, we recommend turning to professionals. More than 70,000 authors are ready to help you right now. Free adjustments and improvements. Find out the cost of your work.
Cost calculationGuaranteesReviews
Difference from payroll
The concept of wage fund is not synonymous with wage fund.
The wage fund (WF) consists of amounts assigned to employees for the actual performance of specific labor operations. It includes accruals for time worked or products manufactured, taking into account incentive additional payments and compensation.
ATTENTION! The salary package does not include payment for sick leave, travel expenses, or one-time bonuses.
The calculation of the wage fund includes the wages and salaries and all other accruals intended for employees.
What it is?
Salary is an employee's remuneration for work done. The salary depends on the employee’s qualifications, complexity and circumstances under which the work is performed.
The wage fund is the total indicator of all enterprise costs for remunerating employees in cash or in kind, without taking into account sources of financial resources.
Currently, there are no legislative acts defining the concept of the wage fund. These legislative acts have not yet been adopted in the Russian Federation.
But, in the Tax Code there is an article on labor costs (No. 255). Most lawyers believe that the terms spelled out in it can be used as a definition of the wage fund.
The wage fund is needed to make payments:
- on salary and tariff rate;
- additional payments and bonuses;
- additional payments for working in difficult conditions;
- for highly qualified labor;
- for excellent work results;
- for significant assistance in business development;
- bonuses for working at an enterprise for a long time.
The fund is replenished from the following sources : the cost of products or services provided, the employer’s own additional funds, targeted financing.
The size of the wage fund may change from year to year. Factors influencing changes in the value of the fund are presented in the diagram below.
Calculation periods
Depending on the time period that needs to be analyzed, the following types of payroll are distinguished:
- Hourly - these are accruals based on tariffs and piece rates, as well as additional payments associated with hours worked within a work shift (for example, for work at night). The indicator is used in enterprises with a time-based wage system, for example, when calculating the cost of products.
- Daily - calculated taking into account the hourly payroll, but it also includes accruals for unworked hours within a work shift (for example, payment of preferential hours for employees under 18 years of age or performance of government duties). Daily payroll is used for a more detailed analysis of the company’s costs.
- Monthly - consists of the previous payroll and accruals for unworked days (vacation, performance of government duties). The indicator is determined for monthly reports and analysis of the financial and economic activities of the organization.
- Annual – used for annual reports on the activities of the enterprise, as well as for analyzing the salary costs of the company’s staff for the year.
The calculated values can be used not only for reporting, but also during further planning of expenses for settlements with employees.
How to calculate annual payroll
There is no single rule for calculating this indicator, since each company has its own characteristics and formation procedure, depending on the form of payment used, internal and regional regulations.
To determine the amount of labor costs, you must have the following documents:
- Staffing schedule. The document contains information on the number of personnel, names of positions indicating qualifications, rates and salaries.
- Time sheet. The document records the actual number of hours worked by each employee.
- Salary sheet. The document indicates all amounts accrued to recipients.
The listed acts are filled out by personnel and accounting department employees. These documents are used by the organization’s specialists to make accurate calculations.
For an approximate calculation of the annual payroll volume, it is enough to know the average monthly salary and number of personnel. Formula for calculating the annual wage fund:
SMZ × PE × 12 , where:
SMZ – average monthly salary;
PE – number of personnel.
Calculation of wages based on salary
Time-based or time-bonus calculation systems can be based on the tariff rate or monthly salary. The tariff rate can be daily or hourly.
There is also an option when the salary corresponds to the number of working hours in a month. If an employee works only part of the time, he receives a salary in proportion to the share of days worked.
Formula for calculating wages at a fixed daily tariff rate:
Salary = Days × Rate
- Salary - the amount of wages accrued for the month.
- Days - the number of days actually worked according to the timesheet.
- Rate — daily tariff rate.
At the hourly rate, its value is multiplied by the monthly amount of time worked in hours.
Salaried employees (engineers, technicians, department heads) receive a fixed rate per month worked. If they work part of the month, the salary is calculated based on the number of days worked:
Salary = Salary / Norm × Actual
- The norm is the number of days in the past month according to the production calendar, and
- Fact - days actually worked.
The above formulas calculate wages without allowances and bonuses. 13% of personal income tax is withheld from the amount received, after which it is transferred to the employee’s bank card or issued at the cash desk.
Payroll planning
To form a payroll, the following activities are required:
- study the staffing table, the company’s regulations on wages, bonuses, as well as regulatory documents (Labor and Tax Codes);
- calculate the number of personnel in relation to the planned production volume;
- calculate payroll based on the data received.
ATTENTION! At enterprises, when forming a payroll, they are guided by the extrapolation rule, that is, they are guided by past production results and the amount of labor costs.
The extrapolation method involves the following steps:
- The actual size of the fund for the previous year is analyzed.
- Measures are being developed to optimize the indicator.
- Factors that can influence the volume of payroll are being studied.
- Based on the results of the research and calculations, the payroll amount for the planned year is calculated.