Employers must withhold personal income tax (PIT) from their employees' paychecks. Therefore, if an employee has a salary of 30,000 rubles, he will receive only 26,100 rubles in cash minus personal income tax of 13%, if without any difficulties.
In order for some groups of employees to receive more, tax deductions were invented. The deduction works like this: they take the employee’s income, reduce it by the amount of the deduction, and calculate the tax from this amount. That is, they reduce the tax base, and not the tax itself.
Example
Florist Katya has a salary of 30,000 ₽ and a deduction of 1,400 ₽ for her daughter, which means they will deduct from her salary:
- in January: (30,000 - 1,400) × 0.13 = 3,718 ₽
- in February: (60,000 - 2,800) × 0.13 - 3,718 = 3,718 ₽ and so on.
Remember, personal income tax is always considered an accrual total from the beginning of the year as in the example.
Deductions for personal income tax are different: standard, property, social and professional. Most often, employees come with standard tax deductions: for themselves or for a child.
Standard tax deductions reduce income, which is subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%. Standard deductions are not applied to income at other rates and dividends. Non-residents cannot use deductions either. Let us remind you that a non-resident is an individual who stays on the territory of the Russian Federation for less than 183 days within one year.
Child deduction
Parents are entitled to a deduction for each child under 18 years of age. If the child is a graduate student, resident, intern, student or cadet and is studying full-time, then the age limit is increased to 24 years.
The following may receive a deduction:
- each of the parents - no matter whether they are married, divorced or never married;
- husband or wife of a parent;
- each of the adoptive parents, guardians, trustees, when there are several of them;
- each of the adoptive parents, if there are two of them.
If the only parent or the second parent refused the deduction, you can count on a double deduction. Moreover, only a working parent can refuse the deduction: if the parent does not work, then he does not have the right to the deduction, which means there is nothing to refuse.
Amounts of deductions for children
The deduction amounts are currently as follows:
— for the first and second child — 1,400 ₽
— for the third and each subsequent — 3,000 ₽
Children are counted regardless of age. For example, an employee has three children. Two are already adults: 25 years old and 23 years old, and the third is 16 years old. An employee is entitled to one deduction for a third child - 3,000 rubles.
There are more deductions for disabled children:
— for parents and adoptive parents — 12,000 ₽
— for guardians, trustees, foster parents — 6,000 ₽
It does not matter what type of disabled child is in the family. You can also add general deductions for children. For example, for an only disabled child, the deduction will be 13,400 rubles. After all, parents are entitled to a deduction for their first child - 1,400 rubles and for a disabled child - 12,000 rubles.
Important: provide a standard tax deduction for a child until the month in which the employee’s income from the beginning of the year exceeds 350,000 rubles.
Interesting fact
If a child grows up quickly and gets married, then you can no longer get a deduction for him - now he provides for himself. But if he decides to try his hand at work, then his parents still have the right to a deduction. In general, marriage is a responsible matter :)
Let's sum it up
Families are looking to save on income taxes, especially those raising children with disabilities. Such offspring need to purchase not only the standard set in the form of clothing, food, school supplies, but also undergo expensive treatment and buy various medications. It is unlikely that the state will be able to ease the financial burden of citizens by lowering prices for the services and products they seek, so tax deductions are provided to reduce tax collections, increasing the funds earned by parents.
Receiving a deduction allows you to improve your family’s well-being
Documents for child support
First, the employee needs to write a free-form deduction application and attach supporting documents to it: a birth certificate or a certificate from an educational institution.
Deduction application template
If an employee has not been working since the beginning of the year or works part-time in another organization, ask him for a certificate in form 2-NDFL from other places of work. She will confirm that income since the beginning of the year has not exceeded 350,000 rubles.
Important: do not provide an employee with standard tax deductions that he did not receive from his previous employer or did not receive in full.
In some cases, other documents will be needed. For example, from a spouse who is not the child's parent or guardian, ask for a statement from the child's mother or father stating that the spouse is providing for the child.
Some documents need to be updated every year. The general rule: if a document confirms the right to deduction only in one period, then it needs to be updated in the next. For example, request a certificate from the university every year, because the situation may change next year.
For what period
The Tax Code clearly states that “children’s” deductions are provided until the month in which the employee’s income, calculated cumulatively from the beginning of the year, exceeded 350,000 rubles. Please note that income does not include dividends, as well as payments exempt from personal income tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 21, 2013 No. 03-04-06/8872). Starting from the month in which this milestone is passed, deductions for the child are canceled.
Standard deduction for a disabled child
Read more…
Another reason for canceling the deduction is when the child reaches the age of 18. For older children in full-time education, there are two reasons: either completing their studies or reaching the age of 24. Experts from the Ministry of Finance explained: the right to deduction remains until the end of the year in which the child turns 18 years old. For full-time students, the same rule sounds like this: the right to deduction remains until the end of the year in which the child turns 24 years old, if training has not yet been completed. As soon as studies are completed, regardless of age, deductions stop (letter dated October 22, 2014 No. 03-04-05/53291).
Mid-year deduction
The question may also arise: for what period should a child deduction be provided if the employee applies for it in the middle of the year? Simply put, is it necessary to give a deduction for January and February if the employee applied for a deduction in March? In Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It says that the deduction is due from the month of birth of the child, or from the month in which the adoption took place, guardianship (trusteeship) was established, or the child was placed in foster care. There are no additional conditions regarding the moment of applying for a deduction in the Code. Therefore, in case of a late application, the accountant must give a deduction retroactively. The Federal Tax Service for Moscow also agrees with this approach (letter dated December 26, 2017 No. 20-15/ [email protected] ).
What about the “no income” months?
There is no clear answer to the question of whether a “children’s” deduction should be provided for months in which the employee did not have income subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%. The Russian Ministry of Finance believes that everything depends on whether income has resumed this year. If resumed, then deductions for “non-income” months can be provided. If there is no income up to December 31 inclusive, then there will be no deductions this year (letter dated October 22, 2014 No. 03-04-06/53186).
However, the Federal Tax Service of Russia thinks differently - that deductions for a child for months in which there was no income are due in any case (letter dated May 29, 2015 No. BS-19-11/112). A similar point of view is stated in the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 14, 2009 No. 4431/09. In our opinion, this approach is correct, and thanks to the court’s position, it is completely safe.
What documents must the employee provide?
Deductions for children are provided on the basis of a written application and documents confirming the right to deduction (Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But legislators did not provide a list of specific documents and did not indicate how often the employee must write a statement. Specialists from the Russian Ministry of Finance reported: it is enough to submit the application once, there is no need to update the application annually (letter dated 02/26/13 No. 03-04-05/8-131). A repeated application will be needed only if the employee’s circumstances for receiving the deduction have changed (letter from the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated December 26, 2017 No. 20-15/ [email protected] ).
Now we will try to make a rating of the necessary papers based on the explanations of officials of the Ministry of Finance - for various situations.
In general, the employee needs to provide a copy of the birth certificate and a copy of the passport with a mark on the registration of the marriage between the parents or a copy of the marriage certificate (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 18, 2013 No. 03-04-05/38670).
If the parents are divorced, you need a copy of the divorce certificate, a notarized agreement on the payment of alimony or a writ of execution (court order) to transfer alimony in favor of the other parent and documents confirming the transfer of alimony (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 30, 2011 No. 03-04- 06/1-125).
If a parent lives with the child, but is registered at a different address, a certificate from the housing and communal services about the joint residence of the child with the parent is needed (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 18, 2013 No. 03-04-05/38670).
If a child under the age of 24 is studying full-time (including at a paid university), a certificate confirming this fact is needed (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 2, 2015 No. 03-04-05/56445). If the training takes place abroad (again, full-time) - a certificate from the educational institution, translated into Russian (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 27, 2011 No. 03-04-06/8-289).
Anything can happen in life. If the wife’s children from her first marriage live with their mother and her new husband, who did not adopt them, you will need a statement from the mother that the children are jointly dependent on the spouses (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 5, 2012 No. 03-04-05/8-1064 ).
If the child is being raised by adoptive parents, you need a copy of the agreement on the transfer of the child to be raised in a family and a copy of the adoptive parent’s certificate (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04/06/2012 No. 03-04-05/8-465).
note
If the employee has not written an application and brought supporting documents, the employer cannot provide him with a “children’s” deduction. But this does not mean that the right to deduction is lost forever. At the end of the year, the employee should submit a declaration to the Federal Tax Service in Form 3-NDFL and attach the necessary documents to it. Then the inspectors will recalculate the taxable base for personal income tax and transfer the money to the employee’s account (letter from the Ministry of Finance of Russia in letter dated December 23, 2011 No. 03-04-08/8-230).
Child benefit period
Provide a deduction from the month in which the employee confirms that he has a child. If the employee submitted an application in the current year, then provide deductions from the beginning of the year. Even if he declared his right to a deduction in the middle or end of the year.
Example
Alice has been working in the organization since the beginning of the year, but she only remembered that she had the right to a deduction in May, and then she submitted an application. Alisa is a mother and has two minor sons. This means that from January to May, deductions amounted to 14,000 rubles (1,400 × 2 × 5).
Alice has a salary of 40,000 ₽, in total, from January to April, Alice was credited 160,000 ₽ (40,000 × 4) and withheld personal income tax - 20,800 ₽.
In May, the accountant will calculate all unaccounted deductions and only personal income tax will be withheld from the salary in the amount of 3,380 ₽ ((200,000 - 14,000) × 0.13 - 20,800), instead of 5,200 ₽ (200,000 × 0.13 - 20,800). This means that Alice will receive 36,620 ₽ (40,000 - 3,380), instead of 34,800 ₽ (40,000 - 5,200).
But if an employee had the right to a deduction last year and forgot to declare it, then he can only receive this deduction on his own through the tax office.
Deduction for yourself
Some adults are entitled to a deduction of 500 ₽ or 3,000 ₽. The amount depends on which benefit category the employee belongs to. Among them are disabled people who suffered from the Chernobyl disaster, participants in military operations, heroes of Russia and many others. All categories can be viewed in paragraphs. 1 and 2 paragraphs 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
To receive a deduction, the employee brings an application and documents confirming his right to the deduction.
Such deductions cannot be added and used at the same time. If an employee is entitled to several standard deductions, provide one of them - the maximum. But there is no income limit - provide deductions for yourself regardless of the amount of income received.
What does the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation say about this deduction?
Starting from 2021, the department agrees that the deduction for a disabled child and the regular children’s deduction should be summed up (letters dated 03/20/2017 No. 03-04-06/15803, dated 08/09/2017 No. 03-04-05/51063, etc. ). The Federal Tax Service took a similar position.
For an example of such a calculation in numbers, see the material “Personal Income Tax Deduction for a Disabled Child: The Ministry of Finance has changed its position.”
However, until that time, the officially existing position regarding the provision of a deduction for a child with a disability was as follows: a deduction for such a child can be issued only in the amount of the deduction specified in Art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for a disabled child. The size of the deduction did not change depending on the circumstances of the child’s account, that is, it could not be added to the standard “children’s” deduction (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 14, 2013 No. 03-04-05/8-214, dated April 18. 2013 No. 03-04-05/13403).
Deduction for individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system and patent
If you are an individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system or a patent and you have a child, then you will not be able to get a deduction. Your income is not subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%, so a deduction cannot be applied to it.
But if there is an individual entrepreneur, for example, who simultaneously works for hire, he will receive a deduction from the employer, but this no longer has anything to do with the individual entrepreneur.
Submit reports in three clicks
Elba will calculate taxes and prepare business reports based on the simplified tax system and patent. It will also help you create invoices, acts and invoices.
Try 30 days free Gift for new entrepreneurs A year on “Premium” for individual entrepreneurs under 3 months
How to fill out form 3-NDFL to receive tax benefits and deductions.
The form of the document and the procedure for filling out the declaration are established in the order of the tax service dated December 24, 2014 No. МММВ-7-11/ [email protected] (as amended according to the order of the Federal Tax Service No. МММВ-7-11/ [email protected] ). The unified KND form 1151020 can be downloaded from the resources of specialized institutions and on helper sites.
In the current year 2021, by declaring to the tax service their intention to receive a deduction for paying for their children’s education in 2021, the parent also has the right to return the tax for both 2021 and 2021. You need to prepare a separate declaration for each year. To correctly fill out the fields, you must use the 2-NDFL certificate.
To complete the declaration you need to fill out:
- Personal data of the declarant. This includes information from the passport - full name, registration address, as well as codes - the local tax authority and an eleven-digit code - according to OKTMO. You can find out these digital values by calling the tax office. After completing each page, you must save it;
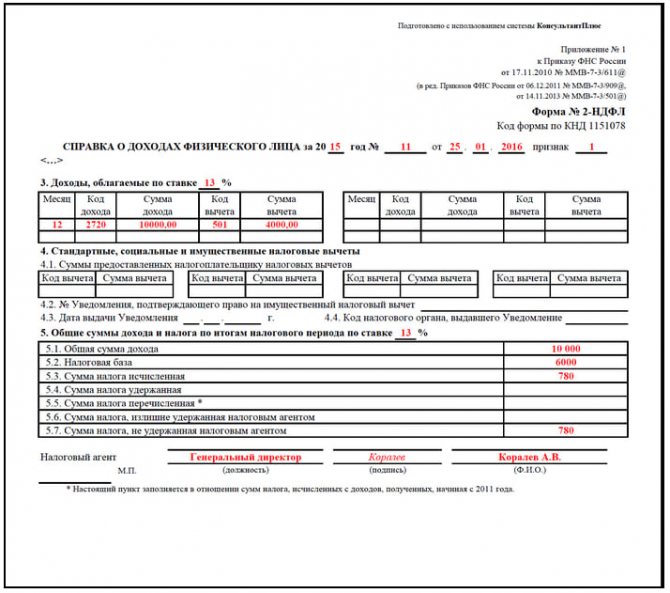
- Next, fill in information about the type of income, most often it is salary. Its size is taken from the 2-NDFL certificate provided by the employer’s accounting department. The name of the company, its tax identification number, checkpoint and OKTMO code are also taken from this certificate and entered in the appropriate field;
- In the line “Total amount of income for the year” the figure from clause 5.1 of form 2-NDFL is entered;
- Line “Total amount of income for the year” - this data must be taken from paragraph 5.1 of the 2-NDFL certificate;
- Data on the taxable amount of income is entered in the next line, and is also taken from certificate 2-NDFL (clause 5.2);
- The withheld tax amount is transferred from clause 5. 4 of the certificate to the next declaration period.
After filling out the section of the declaration containing information about income, you must enter the requested information in the section on standard and social deductions.
Here you need to select the appropriate item “Children’s education expenses” and indicate their amount.
Completing each sheet of the declaration with a personal signature indicates the completeness and accuracy of the information.
Where should the declaration be submitted and within what time frame?
You can receive a social tax deduction from your employer if you paid for your training in the current year. If a parent wants to return part of their income for a year or several years, they need to contact the tax authority. In this case, the deduction can be provided to the parent for a period not exceeding 3 years.
It is necessary to apply for a deduction for the education of children at the tax office at the place of residence by April 30 following the reporting year.

To apply to the tax authority for a refund of part (13%) of the funds spent on training, you must submit to the inspector:
- Statement;
- Original and copy of passport;
- Declaration 3-NDFL for the year in which the payment was made;
- A certificate from the employer confirming the amount of taxes withheld;
- Agreement with the university on the provision of paid educational services;
- A certificate confirming that the child is studying at a specific university;
- A copy of the license of the university, academy, institute.
Confirmation of the fact of payment are the original payment documents. Copies of these are also provided. The declaration and scanned copies of documents can be delivered in person, using the Internet or postal services.
Ways to compensate for deductions
When applying for a deduction for training from an employer, previously paid income tax is not returned through the company cash desk directly to the mother or father.
Having received a notification from the tax office, a parent’s application and payment documents confirming the expenses incurred for their children’s education, the accounting department will withhold a monthly reduced amount of tax from current earnings, taking into account the required deduction.