Many articles, and even books, have been written about how an employee can leave their position. Layoffs occur everywhere, regardless of the level of staff turnover in the organization. Unlike a full-time employee of a company, the position of chief accountant involves some financial responsibility. In this regard, even more questions arise regarding his dismissal. Yandex statistics show that people are really interested in this topic, and among them there are quite a few of our clients. For example, the combination of the words “chief accountant” + “dismissal”, as well as “transfer of affairs” was requested by users about 30 thousand times in total during June 2017 (and this is not the season of layoffs, we would like to note). It is not at all surprising: it is important to understand on what basis the chief accountant resigns, whether it was the employer’s initiative or whether he himself made such a decision. We looked through the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, turned to accounting forums for help and collected some useful information that employees responsible for dismissal and hiring should know.
What are the features and difficulties of dismissing the chief accountant?
The smaller the enterprise, the more painful it is for the head of the accounting and tax department to leave.
If the chief accountant is preparing to resign at his own request, work within two weeks after filing the application is usually necessary for the employer. And there are many reasons for this. Let's look at them in more detail. In small businesses, an accountant performs many related functions. In such organizations, he combines the functions of a cashier, personnel officer, and secretary. They have access to trade secrets, know all counterparties, creditors and the real financial situation. The costs of re-issuing bank signatures, digital signatures and other documents can also become a significant problem.
Oddly enough, larger structures, especially budgetary and government ones, experience the process of changing the head of the accounting service more easily. There are several reasons for this:
- such enterprises (organizations) have good software;
- the chief accountant has deputies or executors who know the documentation and the established work procedure, as well as its shortcomings;
- the activities of such accounting departments, as a rule, are clearly regulated, and job descriptions are spelled out in detail;
- Inventory is carried out regularly;
- the personnel department has experience and knows how to fire the chief accountant at his own request;
- The organization has formed a personnel reserve for vacant positions.
Dismissal at the initiative of the employer
To dismiss a chief accountant at the initiative of the employer, grounds from the Labor Code are required. It will not be possible to fire an accountant due to personal hostility or dissimilarity of character.
Labor Code offers a large list of grounds for dismissal:
- failure to fulfill one's duties;
- absenteeism;
- appearing at the workplace under the influence of alcohol or drugs;
- violation of clauses of the employment contract;
- reduction of position or staff;
- inconsistency with the position, etc.
If you fired the chief accountant in violation of the law or internal company regulations, he may go to court. The court may side with the plaintiff, and then you will have to reinstate the former employee to the position he occupied.
How to properly arrange the departure of the chief accountant in 2021
The procedure for dismissing a chief accountant at his own request is regulated by the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and is no different from the termination of labor relations with other categories of employees. All basic requirements for this process are described in Article 80 of the code. A citizen who decides to terminate an employment relationship must inform the employer 14 days in advance. By mutual agreement of the parties, the contract can be terminated earlier, but such facts happen extremely rarely to chief accountants.
You can apply for resignation at any time after employment:
- during the test;
- on leave, including maternity leave;
- while on sick leave.
Within 14 days from the date the employee makes the decision to dismiss, the following occurs:
- The chief accountant submits his resignation. It is advisable to indicate in the application the exact date of completion of work;
- the application is properly registered;
- the working order is agreed upon;
- audit of accounting and transfer of cases is organized. A special order is issued, in which a person responsible for receiving documentation is appointed under signature;
- an audit is carried out - inventory, inventory of liabilities and assets, transfer of tax reporting documents, re-registration of financial liability (if such has been issued);
- based on the results of the inspection, an act of acceptance and transfer of cases is prepared and signed;
- a dismissal order is formed on the basis of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- the order is registered in the nomenclature of cases;
- the resigning employee reads the order and signs it;
- on the basis of the pay slip and calculation note, wages and due compensation are calculated;
- the employee is given documents (work book, income certificate, other documents from the personal file) and the final calculation is made.
Is it possible to fire the chief accountant when changing the head of the company?
A specific reason for terminating an employment relationship with such a company specialist as the chief accountant is a change of owner of this company (clause 4, part 1, article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
It is important to distinguish between dismissal when there is a change in the owner of the company and the dismissal of the chief accountant when there is a change in manager. A change in the ownership of a company (as opposed to a change in management) involves a transfer of ownership of the assets of that company from one person to another person(s). Clause 32 of Resolution No. 2 explains in what cases dismissal under clause 4, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is possible, and in which it is not allowed:
The new owner has the right to dismiss the chief accountant no later than 3 months from the date of his ownership rights (Part 1, Article 75 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If, after the specified period, the employee continues to work, then subsequently it is impossible to dismiss him on this basis.
If the employment contract is terminated on the grounds under consideration, the chief accountant has the right to receive compensation. The minimum amount of payments is 3 average monthly earnings (Article 181 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). By agreement between the parties it can be increased. The exception is the employees named in Art. 349.3 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For them, the amount of compensation cannot be higher than 3 average monthly earnings.
Case acceptance and transfer form
Upon dismissal, the following entry is made in the work book:
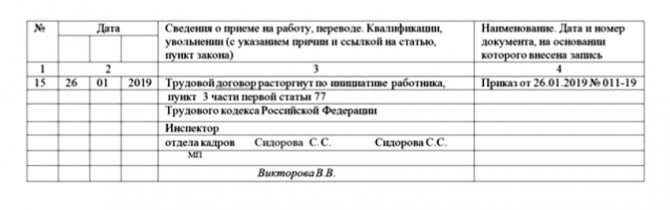
It is also worth noting that within 14 days of service, the employee has every right to change his decision and withdraw his resignation letter. The employer has no right to prevent this.
Dismissal by agreement of the parties
Dismissal by agreement of the parties is initiated by the employer or the accountant himself. The parties discuss the nuances of the process, agree on conditions, compensation, deadlines, payment and what will happen if the agreement is violated. For example, that the chief accountant works until he finds a replacement employee, and then transfers the cases to him within two days. The agreement is drawn up in free form - it will be useful if one of the parties violates the terms.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
Additional information about the working period
Strictly speaking, the Labor Code is not talking about the period of service, but about advance warning to the employer of dismissal. With this rule, the legislator protects the employer from spontaneous decisions of employees, thereby reducing risks for production processes. The employer retains the voluntary right to reduce the 2-week period.
There are cases when an employee is required to be fired on the day the application is submitted. (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 22 “b” of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2). In this case, dismissal is due to the impossibility of continuing work activity due to:
- admission to study at an educational organization;
- retirement;
- disease;
- transfer of a spouse to work abroad or a new place of duty;
- other valid reasons.
Sometimes, before dismissal, an employee may go on vacation or sick leave and then submit an application. This method of care is also available to the chief accountant. This is where professional ethics and career implications need to be kept in mind. Accountants, as a rule, try not to leave unfinished business and not abandon their employers during tax reporting period.
How to fire an accountant based on an article
An employee, including the chief accountant, who has already been brought to disciplinary liability, in case of repeated violation of labor discipline, may be dismissed on the basis specified in clause 5 of part 1 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (repeated failure to fulfill labor duties). You can be fired regardless of what the first punishment was (a reprimand or reprimand).
The procedure for applying a disciplinary sanction in the form of dismissal requires the employer to:
- record a violation;
- conduct an internal inspection, taking into account the severity of the act and accompanying circumstances (part 5 of article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 53 of resolution No. 2);
- comply with the deadlines for applying disciplinary sanctions set out in Part 3 and Part 4 of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (within a month after the discovery of the offense, but no more than 6 months from the date of its commission, and based on the results of an audit, inspection of financial and economic activities or an audit - no more than 2 years);
- complete all documents correctly.
The algorithm of actions is described in detail in the article “Dismissal for repeated failure to fulfill job duties.”
We transfer cases
It is worth noting that the transfer of affairs upon dismissal of the chief accountant is primarily useful to the outgoing specialist himself. This will allow the case to be completed completely and avoid disputes and unfounded claims later.
The acceptance certificate must be prepared in the quantity necessary for all interested parties. All documents for which the specialist is responsible must be submitted according to the inventory. According to Art. 29 Federal Law “On Accounting” No. 402-FZ dated December 6, 2011, accounting documentation is stored in the organization for at least 5 years. It is during this period that it makes sense to draw up an act (even if more time has been worked).
The new employee or the person designated to receive documents must receive the following documents from the outgoing head of the accounting service:
- Accounting policies (originals).
- Reporting with notes about submission to the tax office.
- Accounting and tax registers confirming reporting.
- Acts of reconciliation of settlements with tax authorities and funds.
- Current period working balance (monthly).
- Inventory records.
- Property that is in the custody of an accountant according to the inventory (stamps, keys to the safe, BSO, digital signature, originals of constituent documents and registration forms).
Transfer of cases when changing the chief accountant
The obligation of a resigning employee to submit files and draw up reports on the work done is not established by the labor legislation of the Russian Federation. Therefore, it is extremely important to formalize issues related to this procedure in the company’s local regulations. When developing such a document, as an example, you can use the “Instructions on the procedure for accepting and submitting cases by chief accountants (senior accountants with the rights of chief accountants) ...”, approved. Ministry of Health of the USSR 05.28.1979 No. 25-12/38.
It is also advisable to provide for the obligation to hand over and accept cases in the employment contract and job description of the chief accountant (see the article “Transfer of cases and other nuances upon dismissal of the chief accountant”).
The administrative document for the procedure for transferring cases when changing the chief accountant is the order of the manager. It states:
- the basis for issuing the order (dismissal of the chief accountant);
- employee accepting cases (new accountant, manager, other employee);
- other persons involved in the transfer of affairs (for example, auditors);
- timing of the procedure;
- the procedure for conducting and processing the procedure for submitting and accepting cases (if it is not established by a local act).
Is an inventory required when the chief accountant is dismissed?
A change in accounting management may be accompanied by an inventory and audit of the company's assets and liabilities. Inventory is carried out if:
- as determined by the employer (in a local act or order, paragraph 3 of Article 11 of Law No. 402-FZ);
- the chief accountant is assigned financial responsibility by a labor contract or agreement (Article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 4, paragraph 1.5 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory..., approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49).
Read even more details and a sample transfer document in the Consultant Plus system (ready-made solution “How to organize the transfer of affairs of the chief accountant”). If you do not yet have access to the ConsultantPlus system, you can obtain it free of charge for 2 days.
Responsibility of the chief accountant after dismissal
The chief accountant, who in accordance with all the rules transferred the affairs and resigned without claims from the employer, may, within the limitation period, be held criminally, administratively and financially liable for crimes or violations committed during the performance of his official duties.
Criminal liability may arise in accordance with Art. 199, 199.1, 199.2 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. For this case, it is important for the head of the enterprise to have in his hands an act of acceptance and transfer of the former employee’s affairs. This will make it easier to hold the former employee accountable.
An accountant who quits may also be brought to administrative liability (Chapter 15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for violation of procedures for working with cash and cash transactions;
- violation of accounting and tax reporting rules;
- violation of deadlines for filing tax and other reports;
- other administrative offenses related to improper performance of official duties.
Is it possible to fire a chief accountant for lack of trust?
Dismissal under clause 7, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is applicable only to an employee servicing monetary or commodity valuables: receiving, accounting, storing goods and money, transporting them, distributing them, etc. (clause 45 of Resolution No. 2). We are talking about financially responsible employees holding positions or performing work contained in the lists approved. Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 2002 No. 85.
The chief accountant is not an employee who directly works with monetary or commodity assets, therefore he cannot be dismissed on this basis. This point of view is set out in paragraph 4 of the Review of Legislation and Judicial Practice of the RF Armed Forces for the third quarter of 2006 (definition of the RF Armed Forces No. 78-B06-39).
Note! It is still possible to dismiss the chief accountant on the grounds under consideration, but only if he was entrusted with work (labor function) involving the direct servicing of monetary (commodity) assets (at present there is no ban on such a combination). Moreover, it is important that the fact of performing two different job functions is officially assigned to the employee (for example, in an employment contract or additional agreement).
Regarding dismissal under clause 7.1, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then it applies exclusively to employees whose positions are designated in the relevant regulations (for example, in the laws “On Anti-Corruption” dated December 25, 2008 No. 273-FZ, “On State ...” dated July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ ).
Read about the nuances of the procedure in the article “Dismissal due to loss of trust - features of the procedure.”
Difficult moments and their solutions
We list the most common difficulties when leaving an accountant:
- The accountant is responsible for maintaining personnel records. Here it is necessary to control both the transfer of personnel documentation and the correctness of the execution and final calculation of the employee himself;
- an employee who has decided to quit may not be motivated to submit reports on time and transfer cases clearly. In this situation, it makes sense for the manager to personally control this stage;
- the organization loses contact with the former chief accountant. It is necessary to agree with the resigning employee about the opportunity to contact him for some time for clarifications and questions regarding the transferred documentation.
Payments
In 2021, an accountant is entitled to standard payments in the form of compensation for unused vacation days, as well as wages.
In addition to them, there may be additional payments specified in local regulations or collective agreements of companies. Their presence may also be specified in the agreement of the parties.
It is possible to receive severance pay, but only in a few cases. These may include dismissal due to the liquidation of the company or due to a reduction in the number of its employees. In such cases, benefits will not go to only those who worked on the basis of a fixed-term contract.
Table: types of compensation payments provided for by law depending on the reason for dismissal
| Reason for dismissal | Compensation payment |
| Change of owner of the organization's property | Compensation in the amount of not less than three average monthly earnings - Art. 181 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Liquidation of an organization | Severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings and preservation of average monthly earnings for the period of employment, but not more than two months from the date of dismissal - Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Reduction in the number or staff of an organization's employees | Severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings and preservation of average monthly earnings for the period of employment, but not more than two months from the date of dismissal - Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Inconsistency of the employee with the position held or the work performed due to a health condition that prevents the continuation of this work (if the dismissal is initiated by the employer) | Severance pay in the amount of two weeks' average earnings - Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
This is also important to know:
Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employee
So, from the point of view of economic feasibility, a chief accountant who voluntarily resigns is much better than someone who is fired “without guilt.”
Peculiarities

The specifics of the chief accountant's dismissal are directly related to the specifics of the position. In any case of employee departure, it is necessary to organize the transfer of affairs to a successor. The absence of financial problems for the company depends on the timeliness and correctness of this procedure.
The chief accountant can delegate matters to:
- a specialist appointed to a vacated position;
- deputy or acting chief accountant, according to the order of management.
If these persons are absent or not appointed at the time of transfer of affairs, the documentation is accepted personally by the director of the company.
It is important to draw up an act confirming the acceptance of the cases by the other party, and a list of documents and reports received. The act reflects all the nuances of the process. If the chief accountant performed this part of the work improperly, which is recorded in the acceptance certificate, the resigned specialist may be held liable under Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Financial liability to the employer
The opportunity to recover material damage from an employee, provided for in Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, provides only for cases of direct calculable financial harm. The favorite topic of some employers about lost profits is completely excluded from the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Since Article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation limits the amount of liability to the average salary, and the chief accountant is not included in the list of positions with which a separate agreement on full financial liability can be concluded, the obligation to compensate for damage can only be prescribed in an employment contract (Article 243 of the Labor Code). But even then, the employee retains the right to refuse to deduct material damage from his salary. In such circumstances, the employer will be forced to prove the need for compensation and the amount of damage in court (Article 248 of the Labor Code).
If there is no one to delegate matters to
If the chief accountant’s own desire has become an unpleasant surprise for the employer, difficulties may arise with the search for a new specialist and the smooth transfer of affairs. The boss will simply sabotage the process by not appointing a successor and not signing the act himself. And although his actions can be indirectly regarded as an attempt to detain a specialist, it will be problematic to prove this in the same court. After all, the Labor Code does not say a word about how exactly this process should be organized; the enterprise is given complete freedom in this matter (Article 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
You can partially try to protect yourself with the help of your subordinates, because the position of chief accountant most often implies the presence of several more accountants in the company. Each of them is responsible for their own area of work, and, if these employees are loyal, you can try to sign with each of them your own copy of the act on the integrity of documents for the current and previous periods.
If the enterprise is large enough and has an archival service in its structure, then it is best to hand over the papers to the archivist. In any case, it is better to spend the two-week warning period for the chief accountant to check and put all the files in order, even if there is no one to hand them over to.
Unlike the retiring manager, it will be difficult for the chief accountant to transfer the archive for storage to a third-party organization or take the documents with him for self-storage.










