Last modified: February 2021
The presence of out-of-town suppliers and buyers, representative offices and branches without the status of legal entities, requires enterprises to periodically travel employees to the territory of other populated areas. With appropriate documentation and confirmation of the purpose related to the production activities of the organization, the trip is considered a business trip. Accountants will have to answer the questions: when and how is a business trip paid? How is salary calculated on a business trip?
The procedure for registering a business trip on a day off
To send an employee on a business trip on weekends or holidays, you must obtain his consent. The employer issues an order, to which the employee provides written consent. However, if the business trip lasts more than a week and includes days off for rest, written confirmation is not required.
There are the following cases when business trips include weekends and holidays:
- the business trip is long, more than a week, while the employee spends the weekend on a business trip and does not do work;
- the business trip is long, and on weekends the employee performs work duties;
- The time of departure or arrival from a business trip coincides with weekends or holidays.
Instructions
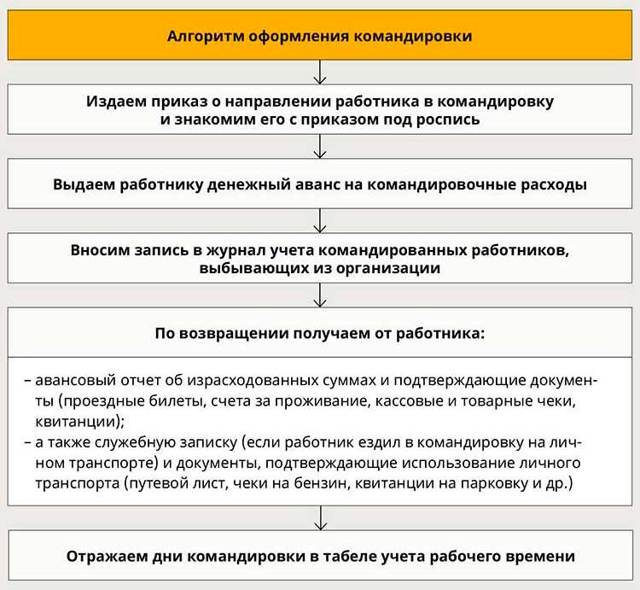
To arrange a business trip you need to follow the following steps:
- Indication of the purpose of the business trip (there is no need to issue a travel certificate).
- Indication of all necessary details in the business trip order.
- Creating a business trip order (who issues the order can be clarified with the chief accountant or general director).
- Filling out the accounting journal for business trips.
- Selecting a report form on the work done by the employee for the entire period of the business trip.
Each organization has its own internal rules for document flow, and despite the fact that the employee may not provide any reports on work performed (according to new changes in labor legislation), but still in many organizations (especially private ones), management still requires the provision of this type of reporting by the employee.
Features of calculating travel payment
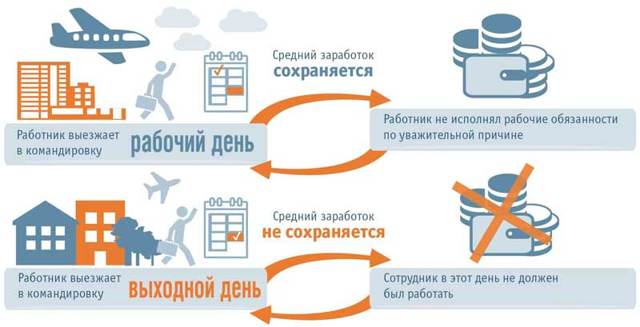
When sending an employee on a business trip, the employer is obliged to bear the costs of accommodation, travel, communications and other stipulated expenses. These are daily expenses, they are a fixed amount and are fixed in the local acts of the enterprise. The same amount of daily allowance is due for workdays and weekends. In addition, the employee is paid a salary for business travel days (travel allowance), including weekends and holidays.
Calculation of travel allowances on working days, weekends and holidays is done based on average earnings, not salary:
Average earnings = Actual accrued salary for 12 months. / Actual days worked for 12 months.
In some organizations, business trips are paid based on actual salary. This option is allowed if actual earnings are higher than average earnings, otherwise the employee’s rights will be violated. Days on the road and days of delay on a business trip are paid in the same way.
Employee business trips on weekdays
If an employee is sent on a business trip only on weekdays, then accordingly, travel allowances are accrued and paid to him based on the average daily income per day. Average daily income is calculated by dividing the actual income earned (wages) by the number of hours worked (number of days actually worked) over a specified period of time (usually two months).
The following types of compensation are included in the accounting of average monthly payments:
- various types of bonuses for civil servants;
- awards for memorable dates and anniversaries;
- compensation for unspent vacation;
- severance pay;
- other types of financial assistance.
All working days that the employee was away for work are displayed in the time sheet. In this case, the days of departure and arrival on secondment are considered working days and are paid according to the general scheme. You also need to take into account that the dates of departure and arrival recorded on the tickets must coincide with the dates in the order sending the employee on a business trip. Since the order itself is an important document in the organization’s internal document flow, and tickets serve only as the basis for recording working hours in the employee’s time sheet.
For unforeseen situations (for example, an employee fell ill on a business trip, an unexpected delay during a business trip, being sent on a part-time business trip, being sent on a business trip while the employee was incapacitated, the employee went on a business trip in a personal car or in a vehicle owned by the company and etc.) labor legislation provides for the use of additional schemes and calculations of material compensation for employees, and is also regulated by the internal labor regulations of the organization and, accordingly, additional supporting documents are required (waybills, checks recording fuel costs, etc.), and the preparation of additional memos for compensation of funds spent during a business trip.
Payment for a business trip on a day off
When a business trip falls on a weekend, the employee loses rest days. Lost weekends must be compensated in one of the following ways:
- double the payment for such days;
- provide the employee with an additional day off.
The first option is most often used, but the employee can receive an additional day off if he wishes. The employee will be provided with rest days for each working day off on a business trip. Then work on a business trip is paid at the standard rate, in a one-time amount.
An employee needs to be compensated only if it is known that he worked on weekends. If he used the weekend for rest and did not perform work duties, they do not need to be compensated. Similar rules apply for holidays.
Payment procedure for business trips
Business trips and material remuneration for them are discussed in Art. 167-168 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The regulation states that a specialist sent on a business trip retains the average salary and position held in the company. The employing company is obliged to compensate him for expenses associated with living away from home, i.e. daily expenses.
How are travel allowances paid? The calculation is based on the number of days spent on a business trip. It includes:
- days spent traveling both ways;
- days of forced downtime;
- weekends, holidays that fall within the travel period.
The resulting number of days is multiplied by the standard amount set forth in the company’s internal regulations. Daily allowances for business trips are determined by the employing company independently and are fixed in the internal documents of the organization. The law (Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) establishes their following maximum amount, which does not imply income tax:
- 700 rub. – for domestic Russian trips;
- 2.5 thousand rubles. – for foreigners.
If the company pays above the specified level, the difference must be subject to personal income tax.

The minimum daily allowance is regulated by law. It is a common practice that ordinary specialists are entitled to one level of compensation for business trips, while the management of the organization is entitled to increased amounts depending on their position. The gradation is fixed by orders and other internal acts of the company.
The transfer of daily allowances for a one-day business trip within the Russian Federation is not provided for by current legislation, but the employing company has the right to stipulate the payment of compensation and secure it by a collective agreement or by order of management.
What specialist expenses are reimbursed by the employer?
What is included in the daily travel allowance? The hiring company is obliged to reimburse the following expenses of specialists:
- purchasing round trip tickets;
- payment for housing (hotel, apartment, room, etc.);
- direct daily allowance – i.e. expenses incurred on food and accommodation away from home;
- other expenses (example: visa application, Aeroexpress to the airport, taxi from the station to the hotel, excess baggage, etc.).

The law regulates the calculation of travel allowances, but does not dictate what a specialist has the right to spend per diem on.
It is understood that he will use the funds received to eat during the trip and make other expenses necessary to create a comfortable stay outside the home.
The employee is not obliged to report on expenses: provide checks and receipts, and the administration of the enterprise does not have the right to control the appropriateness of using the money.
To confirm expenses other than daily allowance, the specialist submits an advance payment to the accounting department within three days after returning from the trip. Attached to it are ticket forms, checks confirming payment for the hotel and other expenses related to solving work issues.
The list of expenses subject to reimbursement by the employer is open. This means that the employee receives a refund for any expenses necessary for professional activities away from home, made with or without the consent of the employing company.

Are weekends spent away paid?
Paying for a business trip on a day off has a nuance: an employee receives a salary for the specified dates if work events are planned for them, and there is a trip home or to the place where work functions are performed.
To calculate the number of days for which a specialist must receive payment, you need to receive from the business traveler:
- Tickets confirming departure and return dates.
- An official note with notes from the receiving party is an analogue of tickets for employees who traveled in their own car or who lost their tickets.
Daily allowances for weekends are paid in any case. The accountant finds the total duration of the trip (in days) and multiplies it by the amount of allowance specified in the company's internal regulations.
In addition to travel allowances, the specialist is entitled to an average salary. For Saturdays, Sundays and holidays that fall during a trip and involve work events, payment is doubled or single, but with the employee subsequently being provided with the appropriate amount of paid time off.
How are overseas business trips paid?
Most organizations prescribe two daily allowance scales in internal orders:
- for domestic trips;
- for traveling outside the country.

It is recommended to pay for such business trips as follows:
- according to “foreign” standards - for days spent abroad;
- according to “intra-Russian” – for the day of entry into the territory of the Russian Federation.
The guideline for calculating days is the border service marks in the specialist’s international passport, which are affixed when leaving and entering the country.
A business trip abroad can be paid in rubles and in foreign currency, depending on the provisions of the internal documents of the employing company. Example: the daily allowance may be denominated in dollars or euros, but the employee is given an amount in rubles, calculated at the Central Bank exchange rate.
How to pay for days spent on a work trip?
According to the provisions of the law, travel allowances are paid based on the average income of a specialist calculated over a 12-month period. If a citizen has been employed in a company for less than a year, the calculation includes the entire period of his work until the last day of the month preceding the month of travel.
- Calculation of average earnings for a business trip is carried out using the formula:
- Sz = Z/Do* Dk, where
- Z – payments to the employee for the annual time interval included in the calculation (salary, bonuses and other income);
- To – the number of days actually worked during a 12-month period;
- Dk – number of days of business trip.
Income tax is withheld from payments due to a specialist who was on a trip. The employer's accounting department is obliged to calculate and pay insurance premiums for the specialist to the Federal Tax Service.
How to reflect payment for a business trip in the accounting records of an enterprise?
To reflect the payment of per diem, the accountant must make entries for travel expenses. He needs to calculate the compensation and show the result of the accounts:
- D 26 (20, 23, 25 – depending on the employee’s position) – K 71 – calculation of daily allowance.
- D 71 – K 51 (50) – payment of amounts due by bank transfer (cash).
- D 26 (20, 23, 25 - according to the employee’s position) - K 70 - salary calculation for days on the trip.
- D 70 – K 51 (50) – transfer of salary to a specialist’s card (handout from the cash register).
Weekends on the road
For hours of holidays and weekends spent by a posted worker on the road, double payment is also due. At the same time, daily allowances are also accrued.
To establish the employer's obligations to pay for a business trip, it is necessary to determine the time of its start and end. The start of the business trip falls on the day the transport departs from the place of work. The day of return is considered the day of arrival back to the place of permanent work. The journey from the office to the train station or airport is not included in the calculation, as is the waiting time for departure.
When traveling on weekends or holidays, the hours spent on the road are taken into account for payment. Even if the departure on a business trip took place at 23:00, this day cannot be considered free. Likewise, if you arrive on a weekend or holiday at 1 a.m., you will be charged double for that day. For incomplete business days, daily allowances are paid in full. This issue is not fully regulated by law, so we recommend establishing the procedure for paying for travel days in the local regulations of the organization.
Algorithm of actions when booking a business trip
1. Check whether the employee can be sent on a business trip.
You cannot send on a business trip:
- pregnant women;
- workers under 18 years of age (except for creative workers in the media, theaters, etc., as well as professional athletes).
Only with the written consent of the employee and in the absence of medical restrictions, you can send on a business trip (Article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- women with children under three years of age;
- workers with disabled children under 18 years of age;
- workers caring for sick family members in accordance with a medical report.
2. Issue a business trip order.
There are no restrictions on the duration of business trips, but this may determine whether the business traveler is entitled to daily allowance. For one-day business trips in Russia, daily allowances are not provided.
3. Issue daily allowances.
In order to give a posted employee cash for a business trip, you do not need to take an application for the issuance of accountable funds for travel expenses from him - an order from the manager is enough.
4. Mark the day of departure on a business trip on the working time sheet (forms No. T-12 and T-13). A day on a business trip is designated by code K.
There is no need to indicate the number of hours worked.
5. After the employee returns, receive an advance report from him (form No. AO-1).
All supporting documents (checks, hotel receipts, etc.) are attached to the report.
Accounting for travel expenses
According to the Federal Law “On Insurance Contributions” and the Tax Code, there is no need to make contributions to social funds and pay personal income tax on travel expenses if they meet the daily limit:
- for business trips to the Russian Federation the limit is 700 rubles;
- for business trips outside the Russian Federation - 2500 rubles.
For income tax purposes, you can take into account compensation provided to employees for weekends, holidays and travel days, if the rules of the organization provide for the possibility of working on weekends and holidays.
Reflection of travel expenses on weekends is no different from working days, and in accounting is carried out as follows:
| Debit | Credit | |
| Travel expenses paid | 71 | 50/51 |
| Payment of daily allowances, tickets, accommodation | 20,23,44, etc. | 71 |
| VAT reflected | 19 | 71 |
| VAT deductible | 68 | 19 |
| Other expenses taken into account | 20,44,10, etc. | 71 |
| Return the balance to the cash register | 50 | 71 |
| Overexpenditure reimbursed | 71 | 50 |
| Average earnings for business trip days or double for weekends | 20 (44, etc.) | 70 |
| Insurance premiums accrued | 20 (44, etc.) | 69 |
| Personal income tax is withheld from the amount of average earnings and daily allowances above the limit | 70 | 68 |
| Average salary paid | 70 | 51 |
| The amount of personal income tax transferred to the budget | 68 | 51 |
Calculation of travel allowances
Funds issued on account to an employee during business trips abroad can be either in Russian rubles or in the currency of the country where the employee is sent. After arrival, recalculation is made at the National Bank rate. There are also a number of nuances when traveling for different periods.
One day business trip
Since the minimum duration of a business trip is not established by law, the employer has the right to send an employee to another locality for one day. If the connection with economic activity is confirmed, such a trip is recognized as a business trip with payment for travel.
The nuances compared to the usual ones are that for a one-day business trip, daily allowances within Russia are not provided, and for an overseas trip - no more than 50% of the amounts established by local documents.
Formally, it turns out that the company cannot pay compensation without being subject to personal income tax and social contributions. The recommendation is to create a clause in internal documents that explains the employee’s lack of economic benefit, thereby avoiding personal income tax. Indirect confirmation in support of this position is the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 1, 2013 No. 03-04-07/6189.
Business trip exceeding daily allowance
An enterprise, by means of an internal administrative document, has the right to standardize the amount of daily allowance, both downward and upward. The specific amount is fixed in the employment contract with the employee and can be differentiated among employees.
For example, an employee left for a business trip on 10/05/2018 at 23.15, and arrived on 10/14/2018 at 00.45, the daily allowance according to the internal regulations is 900 rubles. Then:
- The number of days is 10, since 05.10 and 14.10 are included in the calculation.
- Daily allowance exceeding the limit: (900-700)*10=2000 rubles;
- Personal income tax: 2000*0.13=260 rubles.
In addition to personal income tax, it is necessary to accrue taxes on daily allowances in excess of the limit to social funds except for injuries, and not include them in expenses that form taxable profit.
To fully calculate travel allowances, you need to add documented expenses associated with financial and economic activities.
Rotating business trip
In practice, situations often arise when an employee goes on a business trip in one month and returns in another reporting period. If the trip goes to the next month, how to pay for the business trip, when and in what amount should it be included in expenses? Are there any restrictions on paying an advance? – questions that arise for accountants.
Example
For example, a production worker left on September 28, 2018 for a neighboring locality, and arrived on October 3, 2018 according to the order. He presented a transport ticket dated September 28 for departure in the amount of 1,500 rubles excluding VAT and dated October 3 for entry in the amount of 1,400 rubles, and a hotel bill for the amount of 5,000 rubles. On September 27, 2018, he was given an advance in the amount of 6,000 rubles in cash. The daily allowance is 500 rubles according to the employment contract. The report was submitted on October 4, 2018.
The accounting entries are shown in the table:
| date | Dt | CT | Sum | Operation |
| 27.09.2018 | 71 | 50 | 6000 rub. | An advance was issued for a business trip |
| 04.10.2018 | 20 | 71 | 500*6+1500+1400+5000=10900 rub. | Advance report approved |
| 04.10.2018 | 71 | 50 | 10900-6000=4900 rub. | Final calculation made |
Responsibility for non-payment of business trip on weekends
The law provides for administrative liability for violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation by organizations and officials. In order not to receive a fine, you must respect and know all the rights of the employee, pay in full for work on weekends and holidays and provide the employee with additional days of rest.
Having trouble keeping track of travel expenses? In the cloud service Kontur.Accounting it is convenient to keep track of expenses, pay salaries, calculate and pay taxes and send reports. Experience the benefits of the service for free with a 14-day trial period.
Try for free
Daily allowances for business trips in 2021 within the country and abroad
Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes the maximum amount of daily allowance.
Daily allowance amounts:
- For business trips in Russia - 700 rubles. in a day.
- For business trips abroad - 2,500 rubles. in a day.
The organization has the right to increase the amount of daily allowance
by your internal order. Moreover, daily allowances may be different for different positions, for different cities of Russia and for different countries, etc.
Most often, organizations set increased daily allowances for the director of the enterprise. This may be due to additional representation and other negotiation costs.
If you pay per diem in excess of the established amount,
from the excess amount you need to pay:
- personal income tax;
- insurance premiums (except for injuries).
Daily allowance in the amount established in your organization:
- are fully taken into account in expenses for income tax and under the simplified tax system (subparagraph 12, paragraph 1, article 264, subparagraph 13, paragraph 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- are not subject to contributions for injuries (clause 2 of article 20.2 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).







