Salary is an amount that is clearly stated in the employment contract (without taking into account bonuses, allowances or disability benefits) and it is this amount that the employer is obliged to pay the employee for his work duties. Salary is the amount that is used to calculate the employee’s salary. The salary amount is indicated both in the employment contract and in the employment order. From the above, we conclude: salary is the main figure that is used for wage calculations.
Let's figure out how salary differs from wages . As mentioned above, the salary amount is indicated in the employment contract when applying for a job, the salary is calculated after the new employee has worked at the company for a month or upon his dismissal from his position. It is the salary that is used to calculate wages, and not vice versa.
Salary is the amount of money that an employee receives after calculating all allowances, bonuses or benefits, as well as withholding personal income tax. persons To calculate wages, the salary fixed in the employment contract is used, to which bonuses and compensations are summed up, including for harmful production, and personal income tax is withheld.
Tariff salary.
Tariff salary (official salary) is the amount of money that is included in wages. Labor salary is calculated for the employee’s fulfillment of work standards, completed work plans (for a certain time), without taking into account compensation, incentives or social payments. This payment is fixed and is the minimum guarantee of remuneration for an employee, below which he cannot receive, subject to the performance of job duties.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the tariff salary (tariff rate) must be reflected in the employee’s employment contract, together with other mandatory terms of the employment contract.
Tariff Rate Functions
The use of a tariff payment system for calculating remuneration in monetary form for the performance of labor functions has a number of advantages over other forms of payment.
The tariff rate as a unit of payroll calculation performs a number of important functions:
- makes wages and maintenance commensurate;
- divides the minimum part of payment depending on the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of labor;
- organizes labor incentives in the prescribed conditions (for example, in hazardous production, with significant work experience, overwork, etc.);
- helps to adequately calculate payment for different labor organization systems and work schedules.
NOTE! The main principle of applying tariff rates is equal remuneration for an equal amount of work.
Labor salary.
The salary is a figure that is fixed in the employment contract; the salary consists of the salary and those percentages, bonuses and deductions that are provided for by law and the terms of the employee’s employment contract.
The salary with all allowances and bonuses will be the employee’s wages, that is, the amount of money that he will receive after the end of the calendar month or upon his dismissal. The salary must be indicated in the employment contract, while the salary is a calculated indicator and is not indicated in any documents other than the salary payment sheet.
Minimum salary.
The minimum salary is the minimum, legally approved amount of money that the employer is obliged to pay to the employee after the end of the calendar month or upon his dismissal. As a rule, changes in the law on the minimum wage occur once a year, but in 2021 this indicator was changed twice: From January 1, 2021, the minimum wage was 6 thousand 204 rubles. From July 1, 2021, the minimum wage was 7 thousand 500 rubles.
The date from which the minimum wage was introduced.
What is the tariff rate
This is the amount of money that an employee will receive if he fulfills a certain labor standard. The rate depends on several factors:
- level of qualification of a particular specialist;
- working conditions, workplace equipment;
- duration of the time period (1 hour, day or month);
- provided equipment and tools.
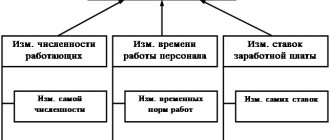
What does remuneration consist of?
The overall level of remuneration for work depends on many factors. Of course, the lion's share of the remuneration comes from the size of the established official salary, which will then be used to supplement other money due to the employee. The final level of income of a citizen will be influenced by:
- presence of harmful and dangerous working conditions;
- the need to work at night or overtime;
- long period of work in one place;
- exceeding established production plans or other indicators by which the company makes a profit;
- actual time worked (salary is paid for the monthly standard of working hours, if they are not worked, payment will be made proportionally);
- the presence of legislative or regulatory documents regulating the conditions of remuneration (for military personnel, civil servants, employees of internal affairs bodies, and other officials).
Difference between concepts
You can understand how a tariff rate differs from a salary by comparing these concepts according to a number of parameters:
- For the item that is being paid for. The salary is set if the amount of work, the time it takes to complete it and the complexity are difficult to calculate. The tariff rate is approved for the performance of strictly defined work. This can be the production of a given number of parts in accordance with technological conditions.
- By area of use. The salary is typical for the service industry. It is installed for economists, lawyers, managers, marketers, etc. Tariff rates are used to calculate income in the production sector - they are set for turners, mechanics, millers, etc.
- In most cases, the salary includes incentive payments for doing a good job. To receive more than the approved rate, the employee must exceed the norm.
- The salary is set for a calendar month. The rate can be hourly, daily or monthly.
- To size. The salary depends on how valuable the employee is to the company. If remuneration is calculated at the tariff rate, then payment is proportional to the work performed.
- The difference between salary and rate also lies in the procedure for establishing the amount of remuneration for an employee. The salary is fixed in the employment contract - the employee knows how much he will receive at the end of the month.
- Salary increase. If the organization uses tariff rates, then the indexation of payments affects all employees. An increase in salary is possible if the employee individually agrees with the head of the organization.
In most cases, the employee does not know the difference between the tariff rate and the salary. The employee is obliged to work in accordance with established standards throughout the entire working day. If the employer's demands are not met, the employee may be fired.

What is the wage rate
The tariff rate is a documented amount of remuneration for achieving a labor standard or other degree of difficulty per unit of time. The basic principle of applying tariff rates is to pay the same remuneration for the same amount of work.
The tariff rate is necessarily fixed in the employment contract, which is signed with employees. The employee will not receive less than the amount specified in the contract, provided that all job functions are performed.
According to Art. 143 of the Labor Code, the tariff system of remuneration involves a certain differentiation of rates depending on the categories assigned to employees. The wage differentiation consists of:
- From tariff rates (the amount that is paid to employees for fulfilling labor standards, depending on their qualifications and the complexity of the tasks performed).
- From tariff schedules (a system consisting of tariff rates and including the ratio of the complexity of the work performed and the level of his salary).
- From the coefficients.
- From salaries.
To determine the tariff rate, you need to multiply the rate for the first category by the increasing tariff coefficient.
The tariff rate as a unit for calculating earnings performs several important functions: it makes payment and labor content commensurate, denotes a minimum depending on quantitative and qualitative characteristics, stimulates work in given conditions (during processing, hazardous work, etc.), adequately calculates wages .
The time period for which the tariff rate is determined can be any: hour, day or month. Hourly rates are usually set if the company has a shift work schedule or if the company employs hourly employees.
The hourly tariff rate is used in the process of calculating pay on weekends, night shifts, in excess of standards, in dangerous, harmful and difficult conditions.
The hourly rate can be determined in several ways : by dividing the monthly rate by the number of working hours according to the calendar. In the second method, the hourly rate is calculated by dividing the salary by the average monthly number of hours during the calendar year. The exact calculation algorithm used by the employer must be recorded in a local regulatory act (for example, in a collective agreement).
For work at night (from 22 to 6), the employee is paid a salary of no less than 20% more than the standard tariff rate. Work on weekends and holidays is paid at double rate.
Day rates apply if work is completed during the day. At the same time, the number of working hours in a day is the same, but differs from the norm under the Labor Code. That is, it is advisable to use daily rates if the number of working days differs from the standard 5 days.
Monthly rates are valid subject to the process of standardization of working hours : if workers have firm, fixed days off and a stable schedule. In this case, the time sheet must be closed regardless of the number of hours actually worked: after working out the monthly quota, the employee earns a salary.
Payment options
Small commercial organizations set salaries for employees. When hiring, the applicant for the position and the company representative agree on the salary level and fix it in the contract. There is no single system for organization.
Large manufacturing companies introduce tariff schedules. The base rate is approved, the salary of workers in various professions and positions is several of these values, as coefficients are applied. For example, a worker can receive up to 6 tariff rates, a leading specialist - up to 15, and an enterprise director - up to 30. Wage differentiation is achieved through bonuses and personal allowances.
For some professions, piecework wages are introduced - remuneration depends solely on the results of work that can be physically measured.
The concepts considered do not include:
- bonuses;
- compensation payments (for example, for the use of your own equipment and tools);
- remuneration based on the results of the quarter or year;
- bonuses for working on weekends;
- compensation for harmful working conditions.
The amount of remuneration depends on the amount of remuneration fixed in the contract with the employer. A person should not focus on the salaries or tariff rates approved by the company, since such nuances concern accountants and managers more.
What payments are included in the calculation of the minimum wage?
If you look at the 2002 edition of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, you will see that earlier in Art. 133 it was clearly stated that the minimum wage does not include compensation and incentive payments. They go above the minimum wage. There are no such instructions in the latest Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It only says that the monthly salary of an employee who has fully worked his normal working hours cannot be lower than the minimum wage.
When such an edition appeared, questions began to arise. “After all, here the monthly salary is meant, and, in accordance with Art. 129 of the Labor Code, wages are remuneration for labor depending on the quantity, quality, conditions of the work performed, as well as compensation and incentive payments.” It turns out that the salary seems to include both compensation and incentive parts. Some people think that then they can make a salary, for example, 10 thousand rubles, and with compensation and incentive payments bring it up to the minimum wage. On the one hand, yes, it could be interpreted that way. But all these issues were settled by the Constitutional Court. Let us remind you that its decisions are binding on all employers.
You can figure out how to correctly calculate your salary, average earnings and withhold personal income tax at Kontur.School. Upon completion of the course you will receive a training document.
Sign up
So, what payments should go above the minimum wage:
- Payments of a compensatory nature, such as additional payment for overtime work, for work at night, for work on weekends and non-working holidays (Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated April 11, 2019 No. 17-P).
- Additional payment for replacing a temporarily absent employee, combining a profession or expanding service areas (Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of December 16, 2019 No. 40-P).
- Regional coefficient and percentage bonus for work in the regions of the Far North (Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated December 7, 2017 No. 38-P).
Note!
Regional and industry agreements may introduce special conditions for additional payments and allowances. For example, in Moscow the minimum wage does not include additional payment for work in hazardous conditions.
In 2021, a resolution of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation was issued, where the court indicates that incentive payments (such as bonuses) should also go in excess of the minimum wage (Resolution of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated February 10, 2020 No. 65-AD20-1).
It turns out that the minimum wage does not include compensation and incentive payments, regional coefficients, and bonuses for work in the Far North. They come from above.
Be sure to check that it doesn’t turn out that your employment contracts with employees indicate, say, a salary of 10 thousand, and you bring everything else up to the minimum wage with compensation and incentive payments. This order is currently incorrect.
Definition
The salary represents the amount of money that the employer initially offers to calculate the final amount. This indicator is reflected in the employee’s employment contract and is indicated in the order upon admission to work. Salary is the basic characteristic for the subsequent calculation of other indicators.
Salary is the amount of money that an employee receives after calculating the necessary allowances and withholding personal income tax. To calculate it, the salary amount is used, to which interest stipulated by the contract, bonuses and compensation, for example, for hazardous production, are added, and personal income tax is withheld.
Comparison
The most significant difference between them is that one indicator is calculated based on the other. In other words, there is an established base salary for a certain position according to the staffing table, to which all interest and bonuses for quality work done are added and from which personal income tax, deductions for property damage or compensation for material damage caused are deducted.

The salary with all the “pros” and “cons” will be the employee’s salary, that is, the amount of money that the employee will receive after the end of the calendar month or upon his dismissal. The salary, according to current legislation, must be indicated in the employment contract, while wages are a calculated indicator that is not written down in any documents other than the salary payment sheet.
What does the tariff salary consist of and how does it differ from the official salary?
The official salary (tariff rate) of employees of organizations is determined by multiplying the corresponding coefficients approved for calculating their official salary (tariff rate) depending on the assignment of positions to functional blocks and length of service in the specialty, assigned qualification categories (for workers), by the size of the BDO in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated December 31, 2015 No. 1193 “On the system of remuneration of civil servants, employees of organizations supported by the state budget, employees of state-owned enterprises.”
Hourly wages are regulated by Art. 106 Labor Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan. With reduced working hours for certain categories of workers provided for by the Labor Code, hourly wages are established. Situations often occur in organizations when there is a need to establish part-time work, flexible forms of employment, as well as to perform temporary or one-time work. In such cases, this rule allows the employee to pay hourly wages for work actually performed. In addition, the legislation, Art. 69 of the Labor Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, certain categories of workers are provided with reduced working hours, which also establishes hourly wages. The use of such payment must be regulated in labor and (or) collective agreements, as well as by acts of the employer.
Remuneration for summarized recording of working time Remuneration for summarized recording of working time is made for the number of working hours actually worked according to the shift schedule (watch schedule). In this case, wages are calculated at an hourly tariff rate, calculated on the basis of the tariff rate (official salary) and the monthly standard of working time in accordance with the balance of working time for the corresponding calendar year. In continuously operating production facilities, workshops, sections and in certain types of work where, due to production (work) conditions, the daily or weekly working hours established for a given category of workers cannot be observed, summarized working time recording is used. When recording working time in aggregate, payment is made for hours actually worked according to the shift schedule (watch schedule). In this case, wages are calculated at an hourly tariff rate, calculated on the basis of the tariff rate (official salary) and the monthly standard of working time in accordance with the balance of working time for the corresponding calendar year.
The hourly tariff rate is calculated by dividing the tariff rate (official salary) by the number of working hours in the current month, with a five-day or six-day working week, according to the working time balance for the corresponding calendar year. In organizations where summarized working time records are kept, overtime hours (if any) are calculated based on the results of the accounting period. The accounting period for the summary recording of working time is the period within which the average daily and (or) weekly working hours established for a given category of employees must be observed.
What is salary and wages
Wages represent an employee's remuneration for work activities. When carrying out any work, a person, in one way or another, expects monetary compensation for the expended physical and time resources. At the same time, the salary must be no less than the subsistence minimum, regulated by the Constitution of the Russian Federation.

When applying for a job, a person must be aware of all the details related to this topic so that he cannot be deceived, and he receives everything that is due by law.
What is a salary and how is it different from a salary? The answer to this question will appear as we study the presented material.
What is official salary
The concept of official salary
For work performed, each employee receives a monetary reward. At the legislative level, it is determined that wages consist of at least three main components:
- the main part, formed on the basis of the salary (rate);
- compensation payments due to an employee for performing actions under certain conditions;
- incentive part, which is awarded as various additional cash bonuses in order to increase interest in the work performed.
As a rule, the most “weighty” part of the remuneration is the official salary (tariff rate), which, depending on the employee’s field of activity, ranges from 40 to 90% of the total level of all remuneration due.
Official salaries are displayed in the company's remuneration system. Their formation is carried out taking into account the hierarchy of positions, the complexity of the work performed in a certain area, the specifics of the functions assigned to the employee, the necessary skills and qualifications.
As a rule, the remuneration system provides for a range of official salaries for each position in order to be able to set the level of basic income for a new specialist, taking into account his professionalism.
Remember, an official salary is a fixed amount of remuneration for work activity, which is established for an employee upon hiring and is reflected in the employment contract.
Considering that the range of official salaries usually provides a gap of 5 to 20% between the upper and lower levels, you should be interested in the size of the basic remuneration during the job interview process.
Concept in labor law
Wages (wages) in our country are regulated by a number of legislative acts and laws:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Constitution of the Russian Federation.
- Specially prescribed individual laws.
The legal basis for this issue determines the minimum wage rate, the terms of payment of wages, the procedure for monetary penalties and incentives, special measures for failure by the employer to fulfill its obligations to pay wages, and the like.

Salary elements
Salary is a combination of three elements:
- The fixed part is the salary (we will touch on this concept a little later).
- The variable part is modified in relation to the actions of a particular employee, the type and class of enterprise, and even geographic location. For example, residents of the northern regions must receive a special allowance due to the harsh living conditions. The variable part represents a certain portion of the salary (from 15 to 100%) based on their residence in a particular region.
- Additional payments are related to the season, production characteristics or performance of work that is not specified in the employee’s employment contract.
For example, employees of some enterprises are paid monetary compensation for food. Covering the cost of travel to your vacation destination is also an additional payment, because this happens extremely rarely.
Differences from salary
So what is salary? Let's try to understand in more detail the concept that interests us.
The salary is the so-called base from which one starts when calculating wages.
What is the difference between salary and salary? First, tax deductions are primarily based on salary. Secondly, appropriate increases can be accrued in case of processing. From there, penalties for damage to property or other fines are deducted, and incentives or bonuses are added.
This is interesting! Posadovy salary in Ukrainian is an official salary.
As a result, the salary is what the employee receives in his hands. It can be either less or more than the salary. As a rule, the salary amount is agreed upon in advance for a certain amount of hours of work, but if during the process the employee exceeded the norm at the request of his superiors by working overtime, then he should be compensated for this.
What salary size is clearly regulated by the legislation of the Russian Federation? It is a fixed amount, which must be prescribed when drawing up an employment contract with an employee, and changing the salary is hardly possible. In order for the concept under consideration to change its size, a number of conditions are necessary. One of them is the Order. In this case, the salary, or rather, changing it, would be advisable. But the salary is a calculated amount, so it is not written down anywhere in advance.

An employee should carefully monitor the amount of his salary, because sometimes the employer writes off damage to materials or equipment as a deduction for the employee’s monetary compensation, although the latter is not actually to blame for anything (indirectly or directly).
For such a gross violation of laws, you can sue the employer.
The work of counselors at a summer camp can serve as the most striking example of such a case. Some property damage is deducted from new caregivers' pay when management does not verify that the previous shift was completed.
The employee has every right to be informed of all deductions of his wages.
So, what is salary in an employment contract? After all, everyone knows that for some important reasons and in some cases, drawing up this type of agreement is simply necessary. Whether the concept itself and the size and other characteristics are indicated in it, we will consider further.
The employment contract must specify the salary of an employee of the enterprise, the procedure for calculating it and increasing it.
As a rule, the salary is calculated based on the remuneration system, which is:
- tariff-free – wages are calculated based on the company’s final profit;
- tariff - the employer evaluates the employee’s work results based on the agreed norm and production time;
- mixed - the employer takes into account the total profit of the company and the contribution of a specific employee to it.

The main differences between salary and salary
The salary contains only the salary component when a “bare” tariff system of remuneration is established; in other cases, the salary component will only be a component in the total amount of remuneration. The difference between salary and wages according to specific defining criteria is presented in the table:
| Criteria | Salary | Salary |
| Indication in an individual contract | Fixed if the remuneration has a salary part or a salary is established - this is payment at a standard monthly rate | Must be reflected, including the system and mechanism for forming a specific size |
| Setting the minimum wage below the federal or regional level | Not prohibited, subject to additional payment up to the minimum wage due to other components | It is prohibited to set it below when the time limit is fully worked out and the labor function is performed (Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) |
| Additional payments | Not included, since the definition contains the adjective “fixed” (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) | Includes additional payments, allowances and bonuses |
| Change in value | Not allowed without agreement with the employee; if working for less than a full month, it is adjusted by the time worked | Occurs automatically, by changing the bonus or compensation component |
The fixed component, which means the salary in the salary, is payable based on the time worked. If the period is not fully worked out, an adjustment is made for the time spent. In addition to the fixed part, the salary includes a variable component, consisting of additional payments, allowances and bonus payments.
If the employee did not carry out production activities without good reason, then the remuneration in monetary terms will be accrued lower than the established salary.
Some nuances of an employment contract
In Russia, salaries are most often calculated according to the tariff system. In this case, the employee’s experience and qualifications, which are prescribed in the employment contract, must be taken into account.
It is worth remembering that this written document indicates only the established salary of the employee, but the final salary may differ significantly from it, both up and down.
Some employers stipulate in the contract a mixed system for calculating wages, which is very relevant for the sales sector, when the salary depends on the results of the work of a talented specialist.
Bet concept
The wage rate is a certain fixed amount calculated when paying wages to an employee per unit of time.
Usually the rate is indicated in the staffing table and is equal to one.

It does not depend on the employee’s qualification level, work experience, education or age, whereas the question of what salary is would be answered with precisely these criteria.
But these concepts also have something in common: both values cannot be less than the minimum amount specified by the state.
What is a time-based wage system?
Interpretation of the basics of the time-based method - payment to a specialist for time worked (day, hour), based on a fixed rate.
The time-based system presupposes the qualifications of the employee. The higher his level and professional skills, the higher the salary or rate of the specialist.
Based on these principles, employees strive to constantly improve their skills and attend additional courses, the completion of which is confirmed by issued certificates.
To use a time-based system, a company needs to take a number of steps:
- assessment of personnel and the time worked system from the point of view of the feasibility of its application in practice;
- maintaining time sheets;
- displaying in local acts the values of tariffs, rates or salaries, additional payments, allowances, incentive payments.
All personnel working on a time-based basis must undergo tariffication.
We recommend : What is lump sum payment?
How is it different from the piecework form?
Today, for entrepreneurs, piecework and time-based forms of the tariff system of remuneration are the main ones.
The main difference is the dependence on the time worked; quality does not play a role. With time-based payment, the specialist will receive the salary due to him, regardless of whether he worked or was only present at the workplace.
Piece payments are made for the number of products produced and operations. The use of working time is not taken into account.
The primary criterion is volume; payment is made for the final result. Compliance with increased standards contributes to additional earnings, which is of direct interest to the employee.
Article 150 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that when performing work of various qualifications, time payment is carried out according to the highest category.
A similar situation in a transaction involves payment at established rates for work performed. If a specialist is assigned work related to tariff categories (qualifications) below those assigned, then the employer pays the difference between them.
The piecework system is beneficial to the employer and specialist; earnings are paid in proportion to the volume of production of products and services.
This method also has a number of disadvantages:
- the difficulty of taking into account factors independent of personnel;
- emphasis on quantity of goods rather than quality;
- accounting for the work of an individual specialist, and not the entire team as a whole;
- excessive consumption of raw materials, defective products;
- difficulties in determining production standards.
The use of a time-based system does not involve unnecessary costs for quality control of manufactured products. A specialist is part of a team, the close-knit work of a group of professionals. But there are also disadvantages here: lower remuneration, unstable performance.
Kinds
Time payment occurs both in its pure form and with its individual additions. There are 4 variations:
- Simple - payment is made for the time spent at work, performing official duties. Paid time is defined as hours, working days in a month, a whole month, or a year. The range of work does not affect earnings, the final result does not depend on the employee’s activities.
- Time-based bonus - in addition to the simple scheme, reward in the form of incentives is added. The use of this form is advisable when qualitative and quantitative achievements are realized in the performance of labor tasks.
- With standardized tasks - a work plan of appropriate quality is fixed for a certain period of time. The salary consists of payment for a unit of time worked and an additional payment for the implementation of the plan (it is not a bonus; exceeding the norm is not taken into account).
- Time-based piecework (mixed) - eliminates the negative aspects of each of the systems separately. The basic production rate is established for the monthly standard of hours, which is paid in proportion to the time worked. Also, during the allotted period, the employee can increase the production of goods and count on additional remuneration.
The flexibility of implementing a reward system allows you to more quickly respond to the wishes of employees and the company, market changes, which immediately affects the speed, quality, and novelty of the product produced.
The entire team should be interested in improving the performance of the enterprise.
How to calculate wages?
All calculations are based on the tariff rate (daily, hourly) or salary. There is an option that the salary is comparable to the number of work shifts in 1 month. When an employee does not work for a full month, he receives a salary in proportion to the days worked.
Calculation formula for a fixed tariff (daily rate):
Salary = D × St, where
- D - actual days worked;
- St - tariff rate for 1 day.
When setting the hourly rate, the value is multiplied by the amount of time worked per month in hours.
Specialists with a fixed salary receive a stable payment for any month; if the employee was on vacation or sick leave, the salary is reduced.
Salary = O/N × Fact, where
- O - salary;
- N - number of days according to the production calendar;
- Actual - the number of days actually worked.
This formula is applicable to calculate earnings without allowances and bonuses. Personal income tax (13%) is deducted from the amount received; the result is transferred to the employee’s bank account or issued through the cash register.
Salary calculation examples
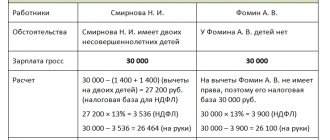
Example 1:
The beauty salon has approved a time-based bonus payment system.
In accordance with the Bonus Regulations, employees are entitled to a 20% increase in income if the company’s total monthly revenue reaches or exceeds a certain figure.
The hairdresser worked 20 out of 22 working days, his salary is 10,000.
The salon's revenue for the past month reached good levels, allowing it to issue bonuses to employees.
Calculation:
- Time-based salary = 10,000 / 22 * 20 = 9,090.90.
- Premium = 10,000 * 20% = 2,000.
- Total salary for the month = 2,000 + 9,090.9 = 11,090.90.
Example 2:
The store's opening hours are from 10 a.m. to 10 p.m., salespeople's work schedule is 2 every 2, work shift is 10 hours. There are only 31 days in a month; the first and second employees will work 16 shifts according to the schedule.
The price for one shift is 1500 rubles.
Salaries of salespeople for this month = 15 shifts * 1,500 = 22,500.
Salary functions
Payroll carries out the following functions:
- Motivational is the main function for an employee, because wages make it possible to satisfy needs. People would not waste their time working without monetary reward.
- Reproductive – closely related to the stimulating function, but contributes to the benefit of the enterprise: the employee must be in good physical shape and have normal nutrition. His family members should also not need anything so that he can fully concentrate on his work responsibilities. Decent financial reward increases employee productivity and ensures smooth operation of the enterprise.
- Stimulating - an employee must understand when going to work that his salary directly depends on his work performance. For such purposes, the employer provides the employee with work instructions, identifies achievements and stimulates the employee for exceeding them, for example, with a bonus.
- Status – the salary amount is determined by the employee’s qualifications, experience and knowledge. The amount of material remuneration reflects a person’s place in a certain social group.
- Production and business – the employer takes into account the contribution of each employee to the final production costs.
- Regulatory – employees and subordinates must interact effectively.
Remuneration system
The procedure for remuneration is all activities that financially reward the employee for his work.

In this case, it is necessary to take into account all the hours spent and the final results, as well as the quality of work. The organization of wages in our country depends on:
- payment systems;
- forms of remuneration;
- rationing of labor activity.
Piece wages
Such remuneration is quite common; an employee’s earnings are determined not by the time worked, but by certain indicators. Such indicators include the number of parts produced per shift, articles written, etc. Such remuneration is applicable both to large industrial enterprises and to employees working from home.
With such remuneration of labor, a working time schedule must be maintained; the employee’s working time under such a system should not exceed forty hours per week. In the case where the employer is not able to control the work process (employees working from home), the director of the enterprise or other responsible person must issue an order that the employee has the right to independently draw up the schedule and duration of the working day, but the working week should not exceed forty hours per week.