Single mothers law
, the exact concept of “single mother” is still . Understanding who is the only parent, the requirements for him, as well as the procedure for recognition depend on the scope of the regulatory document. Thus, the most important laws defining the term “single mother” are:
- Resolution of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 1 of January 28, 2014 (for labor relations).
- Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-05/78050 dated October 30, 2018 (tax area).
- Regional regulations (social benefits).
- Art. 17 of Law No. 143-FZ of October 22, 1997 and the Family Code (the basis for local legislation regulating benefits and payments).
What benefits are available to a single mother?
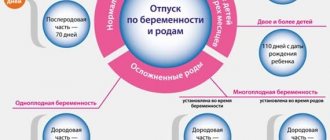
A single mother receives all the same benefits as women from two-parent families, but usually in larger amounts:
- One-time benefit for women registered before 12 weeks of pregnancy - in 2021 - 649.84 rubles.
- Maternity benefit. From January 1, 2021, the procedure for calculating this benefit has changed (according to Federal Law No. 21-FZ dated February 25, 2011, now certain periods will be excluded when calculating average daily earnings).
- A one-time benefit for the birth of a child in accordance with Federal Law No. 81-FZ of May 19, 1995 “On state benefits for citizens with children.” Its size in 2021 is 16,759 rubles. (RUB 110,775 when adopting several children who are brothers and/or sisters, a disabled child or a child over 7 years old).
- The monthly benefit for the period of parental leave for up to one and a half years - from 01/01/2019 is calculated based on the earnings of the insured person for the previous 2 years. In 2021, the minimum amount is 3277.45 rubles. at the birth of the first child and 6584.89 rub. at the birth of a second child.
- Maternity capital in the event of the birth of a woman’s second child. Its size does not depend on whether the mother is raising the child alone or together with the father.
Other types of benefits for single mothers and their amounts depend on the federal subject in which the family lives. For example, in Moscow, a mother has the right to:
- Monthly allowance for children under 1.5 years of age and from 3 to 18 years of age.
- Monthly allowance for children from 1.5 to 3 years old.
- A monthly compensation payment to reimburse expenses for the increase in the cost of living for children under the age of 16 (or 18 for students of general education institutions where government programs are implemented).
- A monthly compensation payment to compensate for the increase in the cost of food for single mothers, as well as families in which one of the parents evades paying child support, for children under 3 years of age.
- Providing assistance in kind (including free sets of baby linen for newborns; free baby milk food with a doctor’s prescription, issued in medical institutions for children under 2 years of age).
- Monthly compensation payment for caring for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a disabled person from childhood under the age of 23 (disabled people of group I or II who do not work). Benefits for children under 3 years old.
The amount of benefits depends on whether the income a single mother receives is above or below the subsistence level. For example, in Moscow in 2021 the cost of living will be 18,781 rubles.
That is why it is better to submit an application for benefits for single mothers in a period other than the last months of sick leave payments and payments in connection with pregnancy and childbirth, since the income according to the certificate will be overestimated. If a woman gets married, but her husband does not adopt her child, his income is not taken into account when calculating and assigning benefits.
To clarify the amount of payments and benefits for single mothers, you need to contact the social protection authorities at your place of residence.
Who is eligible to receive the status?
The clear concept of “single mother” is not fixed by law. When determining who has the right to count on acquiring such status, it is worth focusing on the requirements provided for acquiring benefits in a particular area.
In order to receive the benefits provided by labor legislation, the mother must meet the requirements provided for in paragraph 2 of clause 28 of the Resolution of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation No. 1 of January 28, 2014. In particular, a single parent is obliged to raise and provide for the child independently, without the participation of the father . The father may be absent due to:
- Death.
- Deprivation or restriction of rights to education.
- Official declaration of missing persons.
- The presence of incapacity.
- Serious health problems that do not allow him to take responsibility for financial support and participation in the life of his daughter/son.
- Convictions of stay in correctional institutions.
- Evasion (refusal) from paying financial resources for the maintenance of a minor.
At the same time, labor legal acts do not consider it mandatory for the father to be absent from the birth certificate. A parent may be included in the certificate, but avoid paying child support, or do not have the physical ability to do so.
To receive tax benefits, a woman will need to meet the requirements described in Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-05/78050 dated October 30, 2018. According to the criteria specified in the regulatory act, a mother can receive single status if:
- The father is not included in the birth document.
- The parent died or was officially declared dead.
- The pope is missing in action, about which there is a court order.
For tax benefits, therefore, the criteria are stricter than for labor benefits.
Divorce and failure to fulfill parental responsibilities are not considered grounds for recognizing a mother as single.
Allowances and other social compensations and benefits are established by regional legislative acts. Therefore, the requirements for a mother to obtain single status may vary significantly. However, most laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are guided in determining the mandatory criteria of Art. 17 of Law No. 143-FZ of October 22, 1997 and the Family Code.
In particular, social benefits will be provided if the father is not identified and there is a dash in the corresponding metric column. It is also considered acceptable to indicate the father from the words of the mother. In this case, it is legally considered that the father does not exist and has no rights or obligations in relation to the child. This entry is made if:
- The marriage has not been officially concluded, the parents have not submitted a joint application to indicate paternity, and there is no decision from the judicial authorities.
- There is an appeal from an unmarried woman about the need to include the pope in the documents from her words, the man himself did not show any initiative to establish kinship.
- The mother was married, but the marriage was dissolved more than 300 days before the birth of the baby; other candidates did not file applications to indicate paternity.
- The woman’s husband passed away (died, died, was declared missing) more than 300 days before the birth of the child.
Svetlana Anokhina
Family lawyer, website expert
In the social sphere, the mother will be recognized as the only parent only if the father is not legally established. Divorce, incapacity, conviction or failure to pay alimony are not grounds for establishing status!
To begin with, who is considered a single mother?
The law still does not define the concept of “single mother” or “single parent”. But there is Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2014 No. 1, which explains the concept of “single mother”. We are interested in paragraph 28, according to which:
“A single mother may be classified as a woman who is the only person who actually carries out parental responsibilities for the upbringing and development of her children (natural or adopted) in accordance with family and other legislation, that is, raising them without a father, in particular in cases where the child's father died, was deprived of parental rights, had limited parental rights, was recognized as missing, incompetent (limitedly capable), due to health reasons cannot personally raise and support the child, is serving a sentence in institutions that carry out a prison sentence, evades raising children or from protecting their rights and interests in other situations"
Simply put, a single mother is a woman who has child-rearing responsibilities and cares for the child alone. In this case, the child’s father died, lost parental rights, was declared missing, or was considered incompetent.
You can obtain the status of “Single Mother” in the following cases:
- If there is no information about the father on the birth certificate
- If a man has proven that he is not the father of the child
- If a woman gives birth to a child 300 days after the divorce
- If a woman adopted a child without being officially married
Important: if a woman is divorced from the child’s father, she cannot be recognized as a single mother, even if the father does not pay child support
It turns out that a single mother cannot count on alimony - it means that there is simply no one to pay it to. But it is worth noting that she can alone make decisions that usually require the consent of both parents - for example, about leaving a child abroad.

How to get status?
In order to obtain single parent status, you must contact the organization responsible for providing a specific benefit. For example, to use labor or tax breaks, you must:
- Prepare a set of documents ( your passport, birth certificate of the baby, paper confirming your right to receive benefits ).
The basis may be: the father’s death certificate, certificate of form No. 2 (formerly No. 25), a court decision on deprivation of parenting rights, his conviction, recognition as absent, or a certificate confirming that the ex-spouse is evading payment of alimony.
- Contact the HR department (or accounting department) at your place of work.
- Write an application indicating the type of benefit, the legislative basis for receiving it, your and your child’s details, and the date from which the relief is required to be established.
- Attach the necessary documents.
To receive compensation and benefits, as well as various benefits of the non-labor plan, you will need to contact the local social protection authority, the MFC or the State Services website. Algorithm for performing steps to assign status in this area:
- Prepare a package of documents.
You will need, depending on the instructions of regional laws: the mother’s passport with a registration mark, a birth or adoption certificate of the baby, a certificate of form No. 2 (formerly No. 25), an extract about cohabitation with the child, a document confirming that the father has died or the marriage has been dissolved before the expiration of 300 days by the time the baby is born. Sometimes a copy of a work permit, a certificate of income, living conditions, absence of arrears in housing and communal services payments and other documents are requested.
- Make an appointment with the social protection authority or MFC.
- Fill out the application according to the established form. You can also submit it through the State Services portal.
- Present a package of documents.
- Wait for a decision ( up to 10 days from the date of application).
One of the main documents for registration of the status of a single mother is a certificate in form No. 2, established by Order of the Ministry of Justice No. 200 dated 01.10.18. It replaced form No. 25, approved by Order of the Ministry of Justice No. 144 of 10.08.17, after as a normative document ceased to be valid.
The certificate is issued simultaneously with the issuance of a birth certificate after applying to the civil registry office at the place of residence of the mother or the place of birth of the child. It is also permissible to submit a petition through the MFC or State Services. To obtain a certificate in form No. 2, you must send an application no later than one month from the date of birth (clause 6, article 16 of Law No. 143-FZ of October 22, 1997)
Papers required to purchase a document:
- Mom's ID.
- Document in form No. 103/u , issued by a medical institution and confirming the birth of the baby (can be replaced by a court decision or witness testimony proving this fact).
- An act recording the death of a spouse or divorce more than 300 days before the birth of a newborn (if this took place).
- Application from the mother for the issuance of certificate No. 2 and the entry of information about the father from her words.
In some cases, the mother's application to be recognized as a single parent will be rejected . The reasons depend on the scope of the benefit (labor, social, etc.). This can be done by:
- Presence of a registered marriage at the time of the birth of the baby.
- A court decision to identify the father, as well as a statement from both parents recognizing this fact.
- Divorce or death of a spouse before 300 days before the birth of the newborn.
- Availability of official paternity in the absence of assistance from a parent (for social and tax benefits).
Also, the status will not be assigned if the mother applied with an incomplete set of documents, provided false or inaccurate data, or the child is older than the legal age.
Single mother - today this expression does not cause former condemnation. Single-parent families, where, as a rule, there are not enough fathers, are becoming more and more common. Moreover, there are many successful single mothers. Russian legislation provides for them a number of benefits, subsidies and payments. But not all single-parent families can count on state support. Let's figure it out.
Lonely or only
It is generally accepted that a single mother is a woman who raises a child (or several children) alone, but the law interprets this concept differently. According to current legislation, a single mother is a woman who gave birth to a child out of wedlock (or after 300 days after divorce), and if it is not properly established who the father of the child is (voluntarily or in court). If a child was born in marriage or 300 days have not passed since the divorce, but the ex-husband has challenged paternity and there is a corresponding court decision certifying that the man is not the father, then in this case the woman is considered a single mother.
This status is also acquired by a woman who has not entered into marriage and has adopted a child. In other cases, the legal status of “single mother” is not assigned to a woman, which means she does not enjoy benefits and payments. And, oddly enough, a widow is also not considered a single mother, although in this case the family is granted benefits due to the loss of one breadwinner. If the child’s father has been deprived of parental rights, then in this case the mother is not considered single, and the father, deprived of rights, is still required to pay child support.
Simply put, a mother is not considered single if the child has an official father, whether he is alive or not. Thus, in the child’s birth certificate, the “father” column should be empty, or this column should be filled in with unofficial data with the clarification “recorded from the words of the mother”
Our laws do not contain the concepts of “single mother”, “single parent” or “single parent”. The application of one or another concept depends on the purposes of their use in different laws.
So, for example, in labor relations, a “single mother” is a woman who is the only person exercising parental responsibilities, that is, raising a child without a father. In particular, in cases where the child’s father has died, is deprived of parental rights, has limited parental rights, as well as in other situations.
For the purposes of receiving social benefits and guarantees in Khakassia, a woman is considered a single mother when there is no entry on the child’s birth certificate about the child’s father or the entry was made in the prescribed manner at the direction of the mother. Moreover, if a single mother gets married, she retains the right to receive an increased monthly benefit for children born before marriage.
An increased monthly child benefit is not assigned or paid to a single mother if the person from whom the woman gave birth to the child is recognized in the prescribed manner as the father of the child or if the child is adopted upon the mother’s marriage.
The Tax Code also establishes its own concept for the purpose of providing tax benefits. It calls a single mother a “single parent.”
Dash on the birth certificate
A dash in the birth certificate in the “father” column or an entry about the father “according to the mother” has its advantages and disadvantages.
For example, for a mother and child to travel abroad, a notarized permission from the father is required. If the father's place on the birth certificate is vacant, the mother will not need to prove to customs officers that the father entered in her words is not legally real.
So the main advantage of a dash in the “father” column is the absence of bureaucratic problems and the need to spend money on a notary every time.
However, there is one caveat to this state of affairs. According to the Civil Code, children are considered first-priority heirs, so a child will not be able to inherit property from the actual father if there is no official record of paternity.
Loneliness Guide
The legislation provides a number of benefits and benefits for single mothers. There are few of them, and frankly speaking, their size is tiny. This may be due to the fact that benefits for families with children also apply to single mothers. In any case, if a mother, regardless of her status, wants to find out everything in detail, then she should contact the social protection committee at her place of residence. Here you must be told about all the procedures, benefits and payments in force in the republic.
Let's look at some of them.
In our republic, a monthly child benefit is assigned and paid to one of the parents (adoptive parents, guardians, trustees) for each child born, adopted, taken under guardianship (trusteeship) and living with him until he reaches the age of sixteen (for a student of a general education institution - until he completes his studies, but no more than until he reaches the age of eighteen) in families with an average per capita income, the size of which does not exceed the subsistence level established in the Republic of Khakassia. Let me remind you that in Khakassia the cost of living for the second quarter of 2021 is 11,139 rubles.
State child benefit in the Republic of Khakassia
Size – 266.84 rub.
The increased size is set for a child:
❶ single mother – 533.68 rubles;
❷ whose parents evade paying alimony, or in other cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, when collection of alimony is impossible - 400.27 rubles;
❸ a soldier undergoing military service upon conscription – 400.27 rubles.
Payment frequency is monthly.
Guarantees in the field of labor relations
The Labor Code does not allow termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer with a single mother raising a disabled child under the age of 18 or a child under the age of 14, as well as with another person raising such children without a mother (except for dismissal on certain grounds, in particular, in the event of liquidation of an organization, gross violation of labor duties by an employee, or submission of false documents to the employer when concluding an employment contract).
In addition, a single mother raising a child under the age of 14, or a father raising such a child without a mother, may be granted annual additional leave without pay at a time convenient for them by a collective agreement for up to 14 calendar days. At the same time, fathers raising children without a mother are also subject to guarantees and benefits provided to women in connection with motherhood, in particular, restrictions on night work and overtime work, involvement in work on weekends and non-working holidays, sending on business trips, provision of additional leaves, establishment of preferential labor regimes.
In addition, a working single parent with three or more children under the age of 12 is granted annual paid leave at his request at a time convenient for him.
You can apply for payments and benefits:
- directly to social security authorities;
- through the MFC or the Unified Portal of State Services.
After submitting the application and all necessary documents, the authorized body is obliged to prepare a response within 10 days and assign payments and benefits or refuse to assign them, indicating the reasons.
We will talk about such a benefit for single mothers as a personal income tax deduction next time. Do not miss.
Call the Chance Public Reception and share your experience or talk about your problems. We will analyze your situation, offer solutions and hold negligent performers accountable. Appointment by phone: 8-902-996-88-91, Tatyana Vitalievna Cherednichenko.
Advantages of obtaining status
Acquiring the status of a single parent greatly simplifies the life of a mother raising her children (child) on her own. It gives the right to receive various benefits, benefits, compensation and other assistance, which greatly simplifies the maintenance of a daughter/son. In particular, the advantages of this situation are:
- The opportunity to improve the financial condition of the family through various monthly and one-time benefits.
- Receiving compensation for utility bills, visiting preschool educational institutions, clubs, and cultural institutions.
- The possibility of adopting a child by a new spouse without going through the procedure of refusal of the biological father.
- Providing a place in a preschool educational institution in a special manner.
- Obtaining the right to reject employers' requests to go on business trips, work at night and overtime, and thus be able to spend more time with the child.
- Reducing the tax burden.
- The right to travel with the child, including traveling abroad, freely, without the consent of the father;
- No obligation of the child to support the biological father in the future.
Is it possible to be married and be a single mother?
Yes, it is possible, if a woman has a child in whose certificate there is a dash in the “father” column or he (the father) is written down from her words, and she got married, then she does not lose the status of a single mother in relation to this child and remains with her the right to receive an increased monthly allowance for a child.
However, if the spouse adopts a child after registering the marriage, the woman ceases to be a single mother and loses the right to receive additional benefits.
Negative aspects in acquiring status
Despite all the positive aspects of acquiring status, after it is assigned, negative consequences are also possible. Negative situations that may follow after recognition as a single parent:
- The obligation to provide for the baby independently, including all possible financial costs for food, clothing, education, medical procedures and treatment.
- Inability to petition the court to establish alimony. Payment of child support from the father will follow only after he is recognized as a parent, which will entail the removal of the status of a single mother and all assigned benefits and allowances.
- There is no chance of receiving the inheritance left from dad in the future. This will become possible only after an examination to establish kinship, a court decision, or a will of the parent himself.
- The inability to force the father to raise the child.
Before registering the status of a single parent caring for a baby, the mother needs to weigh the pros and cons of such an event. Perhaps going to court to determine paternity will be more beneficial for both her and the newborn.
Do you consider all the disadvantages listed above to be a sufficient reason not to receive the status of a single mother?
Yes
27.18%
No
72.82%
Voted: 206
Who is recognized as a single mother?
| Granted the status of “single mother” | Not recognized as single mothers |
| A woman who gave birth to a child (children) out of wedlock, and provided that the paternity of the child has not been established (when registering the child with the registry office, a joint statement of the parents is not presented or there is no court decision to establish paternity). | A woman raising a child (children) in a single-parent family as a result of divorce or widowhood. |
| A woman who gave birth to a child during marriage or within 300 days after divorce, if the child’s father is registered as the spouse (former spouse), but paternity was successfully challenged in court. | A woman who gave birth to a child within 300 days after the divorce, annulment, or death of the spouse. In this case, the former spouse is recognized as the father of the child, even if he is not the biological father of the child. |
| A woman, without being married, adopted a child. | An unmarried woman raising a child whose paternity has been established (voluntarily or in court). |
| A woman raising a child whose father was deprived of parental rights. |
If, for example, a woman’s husband died, then officially she is not a single mother, she becomes a widow. Unfortunately, for some reason such situations are not taken into account, and a woman who actually has to raise a child alone is not entitled to the corresponding benefits.
When is the status revoked?
In some cases, the status of a single mother may be removed. This occurs in connection with various events, often depending on the type of benefit or allowance that is established for the mother.
After removal of the status, the payment of any monetary compensation, the provision of concessions and special benefits ceases.
The most common reasons for this event:
- Paternity has been officially established (by a court decision, a joint agreement and filing an application with government agencies, etc.).
- The mother was deprived or limited in her rights to raise.
- The child has reached the maximum permissible age ( 18 years , or 23 if he was in full-time education).
- It has been proven that false information was provided in documents for obtaining status and benefits.
- The baby was seized and transferred to state care;
- The mother or child herself died.
- The woman got married.
- The baby is adopted by another man.
Video: Talks about who has the right to receive the status of a single mother, what benefits and concessions are provided for by Russian legislation.
To determine who is considered a single mother by law, it is necessary to establish in which area the woman plans to receive benefits. This is due to the fact that there is no single concept of the term, and for help in the tax, social or labor areas, various requirements are presented to the mother.
To assign status and receive benefits and concessions, you must contact the social security authority or your place of work, having previously completed a package of mandatory documents.
How to establish paternity voluntarily
To establish paternity out of court, it is advisable to use the following algorithm.
Step No. 1. Drawing up an application
Usually the application is written by both parents together. It can also be submitted during the mother’s pregnancy if there is a possibility of difficulties in doing so in the future, for example, when the father is seriously ill. Such a document expresses the consent of the parents of the unborn child for him to take the surname of one of them and the first name, in accordance with his gender. This is stated in Art. 48 RF IC and Art. 50 of the Law “On Acts of Civil Status” No. 143-FZ of November 15, 1997.
In accordance with Art. 48 RF IC and Art. 52 of Law No. 143-FZ, when a child reaches the age of majority on the day of filing an application, his consent to the procedure is required. It is usually stated in the text of the statement. In case of incapacity of the child, the consent of the guardian or the guardianship and trusteeship authority is provided.
Step No. 2. Preparing a set of documentation
The application must be accompanied by:
- Parents' passports.
- The child’s birth certificate (if it has already been issued) or a certificate from a medical institution or from a private doctor about pregnancy.
- Consent of a child who has reached the age of eighteen (if it is not in the text of the application).
- Consent of guardianship if the child is incapacitated.
- A receipt confirming payment of a fee in the amount of 350 rubles, in accordance with Art. 333.26 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
paternity claim
Step No. 3. Contact the registry office
The application must be submitted to the civil registry office located at the place of residence of the father, mother or at the place where the child’s birth was registered. Documents are delivered in person or through the Unified Portal in electronic form.
If the parents cannot write a statement together, everyone has the right to draw it up on their own behalf. The signature of a person who cannot be present when submitting papers in person must be confirmed by a notary.
Typically, a certificate is issued on the day the application is made. If the application is submitted while the woman is pregnant, registration can be carried out after the birth of the new citizen. In this case, there will be no need to re-send documents if they were not withdrawn before registration.
Note! In accordance with Art. 53 of Law No. 143-FZ, registration of paternity establishment will be refused if the records already contain information about the child’s father, except for the case when they are entered from the words of the mother.
What other benefits are available to a single mother?
A single mother has the right to a monthly child benefit in a larger amount than others, regardless of the mother’s level of financial security and her living conditions:
- an additional amount is paid for up to 1.5 years;
- every single mother has the legal right to receive annual additional financial assistance from the state;
- A single mother cannot be dismissed from work on the initiative of the administration when the child reaches 14 years of age, except in cases of liquidation of the organization, when dismissal with mandatory employment is allowed. Mandatory employment of these workers is carried out by the employer also in cases of their dismissal at the end of a fixed-term employment agreement (contract). For the period of employment, they retain the average salary, but not more than three months from the date of expiration of the fixed-term employment agreement (contract);
- single mothers are entitled to 100% sick pay for caring for a child under 14 years of age for a longer period than other women;
- they also have the right to annual leave without pay, attached to the main leave or separate from it for a period of up to 14 days at a time convenient for them;
- It is prohibited to refuse employment and reduce wages of employees for reasons related to the presence of children. When refusing to hire a single mother with a child under the age of fourteen, the employer is obliged to provide the reason for the refusal in writing. Refusal to hire may be appealed in court;
- in case of need, she has the right to priority housing;
- a single mother has the right to unhindered placement of a minor child in a child care institution with full state support;
- A schoolchild of a single mother can count on free meals in the school canteen - the decision on this is made by the school director. The same goes for free textbooks;
- in territorial departments, in order of priority, free (or with partial additional payments) vouchers to sanatoriums and health camps are issued at least once every two years (you need to check with prefectural employees);
- benefits are also provided for the purchase of certain medications, a list of which should be available in every children's clinic. There is a 50% discount on some medications.
An important help for a single working mother is the double personal income tax deduction provided in accordance with paragraph. 7 subp. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, in 2021, for single mothers, the standard deduction for the first child is 1.4 thousand rubles, for the second – 2.8 thousand, for the third and subsequent ones – 3 thousand rubles. For a disabled child of groups I and II under 18 years of age or full-time education students under 24 years of age, 24 thousand rubles are allocated.
Unfortunately, single mothers should not count on serious government assistance, especially financially. Not to mention the fact that if a woman is actually raising a child alone, but his father exists somewhere, she cannot be called a single mother, but officially goes into the category of “incomplete family.”
Accrual

As mentioned above, the registry office is responsible for issuing papers confirming the grounds for applying benefits. But all responsibilities for checking the provided papers, as well as for assigning the status of a single mother, are handled by the social service. Regardless of whether the family was single-parent initially, or the need for financial assistance arose later, the woman will have to contact the social service.
So, immediately after the birth of the baby, mothers begin to prepare documents for the accrual of child benefits. At the same time, additional papers are submitted for the assignment of benefits due to the sole upbringing of the child. The main papers that need to be collected include:
- mother's personal passport;
- the baby’s birth certificate (which is proof of the father’s absence);
- a copy of the identification code;
- certificate of family composition;
- extract from the migration service regarding registration.
It is also required to open a separate financial account, into which payments will be made. As a rule, money begins to be transferred from the next month after submitting the application. At the same time, the Law requires that all months except the one in which the child was born are counted.
If the benefit is issued a little later, then the package of documents will be the same, but in addition you need to attach an official document by virtue of which paternity was canceled. Help will also arrive starting next month.