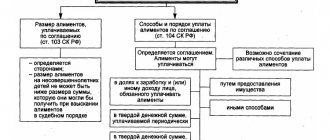
Amount of withholding from military personnel
Family law determines equivalent amounts of alimony for a military personnel and a civilian:
- 1/4 of income is allocated for 1 child;
- 1/3 is allocated for 2 children;
- For three or more children, 50% of the total income (in some cases the amount reaches 70%).
However, the concept of “military personnel” includes not only soldiers and officers of the Russian Army, but also those serving in other government services. These are the police, the FSB, the customs service. Each military man has his own accruals and additional payments, which are formed according to his service record. Let us note right away that it is possible to gain full access to data on the income of any military personnel only through an official request. This is due to the secrecy of personal data, and the rank of the employee does not matter.
How is child support paid if the father is a pensioner?
Child support is withheld from almost all existing types of income, including pensions (with the exception of survivors' pensions, which are not subject to this obligation). In general, alimony payments can occur in two ways:
- In a fixed amount (in a fixed amount) - in practice it is most often used if a citizen does not have an official income.
- Percentage from monthly income, established depending on the number of children:
- for one child - 1/4 of income;
- for two children - 1/3 of monthly earnings;
- for three or more children - half the payments.
Example
Citizen Svetlov N.A. pays alimony from an old-age pension for two children. The pension amount is 18,000 rubles. The amount of alimony payment for two children will be 18,000/3 = 6,000 rubles.
Since pensions to Russian citizens are paid regularly and in the established amount, and are also subject to annual indexation or recalculation (if the pensioner works and continues to receive wages), then most often alimony is paid as a percentage (i.e. in shares of income).
- If a pensioner agrees to voluntarily pay alimony from his income, including from his pension, then it can be paid by voluntary agreement. This method is the fastest to resolve all payment issues. To conclude such an agreement, it will be necessary to draw up a written document in two copies, which specifies all the conditions for the timing and amount of payments.
- Such an agreement must be notarized , since in the future, if the alimony payer stops making payments, it will be possible to collect alimony from him through the bailiff service without the need to go to court and obtain a writ of execution. It is enough for the bailiffs to provide only a notarial agreement, which has the force of an executive document.
- In the absence of a voluntary agreement in accordance with Art. 81 RF IC child support recovered in court in shares of income at the request of the parent living with the child. In this case, it is possible to consider the case in a simplified manner - by filing an application with the magistrate court about issuing a court order. If such a document is challenged by a pensioner, a case will be required by way of claim proceedings.
- After a court decision is made, the documents necessary to initiate enforcement proceedings ( court order, writ of execution ) must be submitted to the Federal Bailiff Service (FSSP) along with the corresponding application. After initiating the case, the bailiffs will transfer the necessary documents to the Pension Fund (PFR), which will independently withhold the amount established by the court from the pensioner who is obliged to pay alimony starting next month.
Alimony from a working pensioner
If a pensioner, in addition to the pension, continues to work and receives a salary, then alimony will be deducted equally from both the salary and the pension . Moreover, if, at the time of reaching retirement age, enforcement proceedings are already underway against the payer, he must independently inform the bailiff service about receiving additional income in the form of a monthly pension.
alimony debt may arise , for which a penalty of 0.5% . In addition, the recipient of alimony, as an interested party, has the right to independently contact the bailiffs or the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation with the necessary documents in order to withhold additional funds from a working pensioner for the maintenance of the child.
When the bailiff receives information that a citizen is hiding the fact of receiving a pension, he has the right to calculate the debt and penalty for unpaid funds, or to bring him to administrative responsibility.
From what income of military personnel is alimony deducted?
The Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation announced a list of approximate incomes from which alimony will be withheld without fail:
- For officers and privates of the Russian army, income is formed from: net salary, accruals for length of service and position, increase for rank, accruals for distance of service, monetary allowance (if it is regularly in material form);
- For police officers, firefighters and customs officers, income is formed from: salary, staff rank, position held, length of service;
- For privates and junior command personnel of all groups: salary, monthly allowance in the form of allowances (if issued regularly in the form of material resources).
Military personnel constantly have questions regarding accrual items. This is often due to the food that all military personnel receive each month. According to the law, allowances must be given in kind. However, the issuance of monetary compensation is not prohibited. It turns out that if a person receives compensation for food every month, then this is considered his income.
Collection procedure
To collect alimony, you must have a writ of execution provided by court decision. This sheet contains details, accounts and other information necessary for collection. The role of a writ of execution can be played by an ordinary agreement between spouses, signed voluntarily and notarized. The agreement has the same force in relation to the court decision.
It is necessary to indicate the place where the recipient will be given alimony. This can be a cash register or a simple transfer, if desired. But, given the secrecy of some units, it is better to receive transfers by mail. Simply because the territory of some military units is closed to civilians, so the path to the ticket office may not be possible.
Exemption from alimony
It depends on whether alimony was paid in court or by agreement. If according to the court, then the reasons for termination of alimony obligations may be:
- Death of one of the parties;
- The child reaches 18 years of age or is previously recognized as legally competent;
- If alimony is transferred to a disabled person, then upon recovery it stops;
- If the dependent has entered into a subsequent marriage;
- The minor child was adopted by another person.
If the payment of alimony is carried out by agreement of the parties, then termination may occur:
- When the child reaches a certain time date (for example, the child graduated from school);
- The agreement itself has lost force (for example, the document has expired);
- Death of either a soldier or a child.
Separately, the court considers options when a person cannot pay alimony due to disability or loss of legal capacity. However, not any disability group can cause termination of obligations. This usually applies to groups 1 and 2. In this case, the court has the right to reduce alimony or simply exempt from payments.
Procedure for issuing alimony
1. Voluntary.
Such payments are made by the employer in accordance with the employee’s application. The main feature of voluntary alimony is the absence of legal restrictions on its amount.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyen-GB
2. Charged by force of law.
The grounds for such a charge may be:
- availability of a court decision (and writ of execution) to collect alimony;
- agreement between the parties to a family relationship regarding the payment of alimony.
1. Paid by parents (brothers, sisters) for the maintenance of children (brothers, sisters) under 18 years of age.
Alimony to minor citizens is paid from the income named in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 18, 1996 No. 841. In particular, this list involves considering the average salary in various types (vacation pay, sick leave benefits, business trip salary) for calculating alimony.
In what cases alimony is withheld from sick leave, find out here.
2. Paid:
- parents for the maintenance of adult children who are recognized as disabled;
- adult children for the maintenance of parents recognized as disabled;
- one spouse in favor of the other;
- by adult citizens in favor of minor brothers and sisters;
- grandparents in favor of grandchildren (and vice versa);
- a pupil for the benefit of his teachers;
- a stepson or stepdaughter in favor of a stepfather or stepmother.
Such alimony is withheld from all income, unless otherwise provided by federal law. For example, Art. 101 of the Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” dated October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ contains a list of income from which alimony is not collected for the specified categories of persons.
At the request of the parent in whose favor the deduction was made, alimony amounts can be received either at the cash desk of the relevant institution where the military serviceman who is obligated to make alimony payments works, or transferred to a bank account, or sent by the accounting department by postal order.
To determine the procedure for receiving alimony payments, the parent-collector must submit to the accounting department of the military unit (or other institution where the military serviceman paying the alimony works) a corresponding application about where he will receive withheld alimony in the future. This application indicates the bank details or postal address of the alimony claimant.
All financial costs associated with bank or postal transfer of alimony payments are also deducted from the income of the military personnel paying alimony.
There are cases when the address of the recipient of alimony payments is unknown to the accounting department and the payer himself. In this situation, the employing institution must still withhold alimony, notify the bailiff about the current situation and transfer the withheld amounts to the deposit account of the court located at the location of the employing institution.
If alimony payments are made by agreement of the child’s parents, the serviceman is exempt from further alimony payments if:
- one of the parties has died (either the serviceman himself or the child in whose favor payments were made);
- the alimony agreement concluded by the parents has expired;
- there are grounds for termination of payments that are expressly provided for in the agreement itself (for example, a condition is stipulated that payments will stop when the child graduates from college).
Payments of alimony payments collected from a military serviceman in court must stop in the event of:
- the child of a military serviceman reaches the age of majority;
- children of a military serviceman acquire full legal capacity until adulthood;
- adoption of a child of a military man, for whose maintenance alimony payments were withheld, by another person;
- recognition by the courts of restoration of working capacity or lack of need for assistance from the citizen receiving alimony;
- the entry of a disabled ex-spouse who is the recipient of alimony payments into a new marriage;
- death of the recipient of alimony payments, or the death of a military serviceman obligated to pay alimony.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: The future of NPF and agreement on what is better
An official guilty of losing a writ of execution or a court order handed over to him for execution may be subject to a fine of up to 2,500 rubles. (Article 431 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
Violation by a person who is not a debtor of the legislation on enforcement proceedings, expressed in failure to comply with the legal requirements of the bailiff, provision of false information about the property status of the debtor, loss of the writ of execution, untimely dispatch of the writ of execution, entails the imposition of an administrative fine (Part 3 of Art. 17.14 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for citizens in the amount of 2,000 to 2,500 rubles;
- for officials in the amount of 15,000 to 20,000 rubles;
- for legal entities in the amount of 50,000 to 100,000 rubles.
In addition, malicious failure by an employee of a commercial or other organization to comply with a court decision or other judicial act, as well as obstruction of their execution, is punishable (Article 315 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation):
- or a fine of up to 200,000 rubles. or in the amount of wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of up to eighteen months;
- or deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for a period of up to five years;
- or compulsory work for up to 480 hours;
- or forced labor for up to two years;
- or arrest for up to six months;
- or imprisonment for a term of up to two years.