Author of the article: Anastasia Ivanova Last modified: January 2021 28908
Whether it will be possible to open sick leave during maternity leave depends on the type of leave. Namely, the reasons why the woman temporarily interrupted her work activity. If there is a certificate of incapacity for work, compensation is paid by the employer according to standard regulations. The basis for the calculation is the employee’s average daily earnings.
The concept of maternity leave and sick leave for this period
According to current legislation, maternity leave will combine two concepts that are often confused with each other in everyday life. They have different grounds for temporary disability, and are also regulated by different legal documents.
For pregnancy and childbirth
The basis for going on maternity leave is a sick leave certificate filled out by a hospital employee, which is issued at the 30th week of pregnancy (if carrying more than 2 children at 28 weeks). In most cases, its duration is 140 days (70 days for preparation for childbirth, 70 days for the birth itself and caring for the baby in the first weeks of its life), which can be increased to 194 for the birth of 2 or more children. The legislation provides that a caesarean section for a pregnant woman is grounds for increasing the maternity period by 16 days, however, if at the birth of several children with complications during childbirth, such additional sick leave will not be taken into account (the period is extended only for large families by 194 days).
We recommend that you read about payments during maternity leave using the link.
The rules for issuing and the specifics of issuing sick leave under the labor code during pregnancy are regulated by clause 46 of Order No. 624-n of the Ministry of Health and Social Development. According to the law, it is possible to go on sick leave later than required. In this case, a certificate of temporary incapacity for work should be issued not at 30 or 28 weeks, but at any necessary time. Payment and calculation of sick leave benefits during maternity leave according to BiR occurs in accordance with established rules. For the entire duration of the maternity leave, the employee retains his place and position.
If complications arise during childbirth or an emergency or planned caesarean section is performed, the woman in labor has the right to receive a second sick leave, which will extend the maternity leave.
In some types of production, shortly before going on leave according to the BiR, a transfer to light labor conditions is provided (Part 1 of Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation; several SanPiN norms relating to hygienic labor standards for women) It normalizes the reduction of workload during work, and also bears a number of restrictions on lifting weights, using equipment, and other physical activities.
How to take maternity leave
To take leave to care for a child before his third birthday, you do not need to issue a certificate of temporary incapacity for work (according to Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In such a situation, the basis for maternity leave is a personal statement from the mother, father of the child or guardian. This period is included in the length of service as a non-insurance period. When applying for this type of maternity leave, a monthly social benefit is paid. The volume and frequency of payments are guaranteed by law, regardless of whether the mother in labor has official employment before pregnancy and childbirth.

Maternity leave can be taken several times and for any period until the child reaches 3 years of age. At all stages of maternity leave, the employee retains his place and position (according to Part 4 of Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Not only the woman giving birth, but also the father, official adoptive parent and guardian can receive parental leave if all the necessary confirmation is available. The basis for going on maternity leave is a personal statement from the employee addressed to the head of his organization.
What to do if an employee does not want to go on maternity leave
An employee of a private organization brought in “sick leave” for pregnancy and childbirth, but declared her desire to continue working until the birth. And two months after giving birth, she plans to go back to work and receive child care benefits. Does the employer have the right to satisfy such a request of the employee?
The situation was explained by Lenara KHIKMATOVA, Norma’s labor law expert:
– A certificate of incapacity for work for pregnancy and childbirth (or, as it is also informally called, “sick leave” or “sick leave”) is issued from the 30th week of pregnancy for 126 calendar days.
And even if a woman applied for “sick leave” after the 30th week of pregnancy, a certificate of incapacity for work is still issued for a full 126 days, regardless of the number of days remaining until childbirth.
Maternity leave, or as it is usually called in practice - “maternity” leave or “maternity leave”, is granted for a duration of 70 calendar days before childbirth and 56 (in the case of complicated childbirth or the birth of two or more children - 70) calendar days after childbirth with payment of benefits under state social insurance.
And the basis for the appointment and payment of such benefits is a certificate of incapacity for work. Accordingly, maternity leave is also issued on the basis of a certificate of incapacity for work. The provision of any other documents, in particular, an employee’s application for leave, reflecting her desire to go on maternity leave (as is the case with parental leave), is not provided for by law.
Attention All types of social leave, which includes maternity leave, are used in kind and cannot be replaced with monetary compensation.
It happens that an employee hides the duration of her pregnancy and does not bring sick leave until the last minute, continuing to work after the 30th week of pregnancy. Of course, in this case, the employer is not to blame and does not bear responsibility for late registration of leave under the BiR. He cannot “by eye” determine the duration of an employee’s pregnancy, therefore, until he has a sick leave certificate “in hand”, he will not be able to arrange maternity leave.
But after the employee has submitted “sick leave,” the employer is obliged to issue leave. Moreover, the leave is granted in full, regardless of the number of days actually used before the birth. Even if a pregnant woman brought sick leave literally on the eve of giving birth, she will still receive at least 126 days of leave (prenatal - 70 days and postnatal - 56 or 70 days).
Often private companies, not wanting to lose a valuable employee, allow her to work until she gives birth, even if she has sick leave.
But that’s why the certificate is called “due to incapacity for work,” since it confirms that the employee cannot work for a certain time due to health reasons, and accordingly, cannot receive a salary. And the benefit is precisely intended to provide financial support to the worker during such a period. In addition, the employer must remember that having a pregnant woman at work late in pregnancy has its own risks and may be unsafe for her. For allowing a pregnant woman to work in the presence of a certificate of incapacity for work, the head of the company may be held administratively liable under the Code of Administrative Offenses for violation of labor and labor protection legislation.
We would also like to remind you that before a pregnant woman goes on maternity leave, the employer must take measures to make her work easier. Based on a medical report, an employee who is “in trouble” is transferred to easier work, and production or service standards are reduced. Until the issue of transfer is decided, the pregnant woman is released from work while maintaining her average monthly earnings for all missed working days. Such an employee cannot be involved in working overtime and on weekends, or sent on business trips without her consent. And to work at night, in addition to consent, a positive medical report is also required.
Attention
Some unscrupulous companies do not want to pay financial and economic benefits, claiming that they have the right to dispose of their funds at their own discretion. Let us remind you especially for them that the Labor Code is mandatory for organizations of all forms of ownership. And evasion of the obligation to pay maternity benefits entails a fine of 10 to 15 BRV. The same offense, committed again within a year after the application of an administrative penalty, entails a fine of 15 to 30 BRV.
Is it possible to receive both a salary and child care benefits?
While on maternity leave, the employee can go to work at any time and begin her job duties, since she retains her place of work (position). And the employer does not have the right to prohibit the employee from interrupting her maternity leave, because taking such leave is her right, not her obligation.
Returning to your previous place of work can be in 2 options: full-time or part-time.
Attention
Pregnant women, as well as women who have a child under the age of 14, may demand the establishment of a part-time working week or part-time working day. And the employer is obliged to satisfy such a request.
If the employee returns to work full time, the maternity leave along with the payment of benefits ceases. If returning to work involves a part-time work schedule, benefits continue to be paid. At the request of a woman, while on maternity leave, she can work part-time or, by agreement with the employer, at home. At the same time, she retains the right to receive benefits.
Thus, an employee can return to work two months after giving birth. If she works part-time, she has the right to receive both a salary and child care benefits. When working a working day, no benefits are provided.
Working on parental leave on a part-time basis is documented in an agreement to the employment contract. Changes are made to it regarding working hours and wages. After signing the additional agreement, the corresponding agreement is issued.
Experts' explanations reflect their opinions and create an information basis for you to make independent decisions.
When should pregnant women apply?
It is recommended to have closed sick leave during maternity leave under two circumstances:
- If, at the end of the period of leave under the BiR, the woman in labor experienced complications, a painful condition was recorded (clause 22, order No. 624-n);
- If a citizen, during maternity leave, continues to work at home or at the workplace while employed part-time (clause 23, order No. 624-n).
According to paragraph 40 of Order No. 624-n, a sick leave certificate for caring for a sick child is not required to be issued if the employee is on maternity leave of any kind, but a temporary disability certificate due to the child’s illness can be issued in this case. The basis for this is that the woman in labor goes back to work at the end of her maternity leave under BiR. If an employee is on maternity leave to care for a small child, it is not necessary to take sick leave, and it is issued under standard conditions.
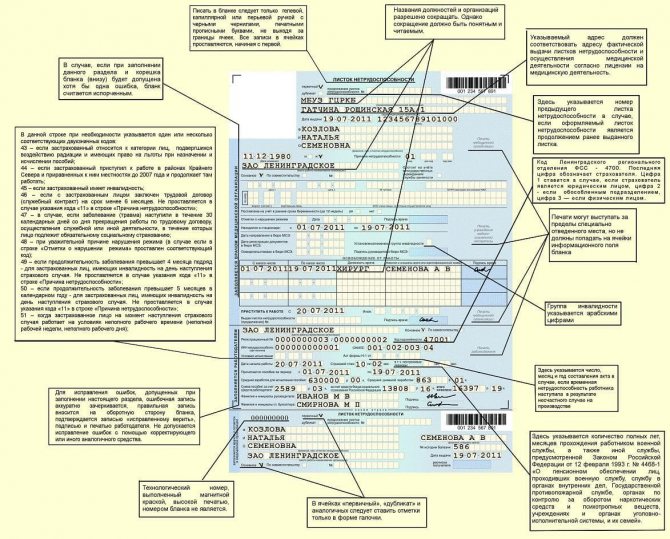
Payments during maternity leave
The legislation regulates the calculation and algorithm for paying benefits to employees during maternity leave, depending both on employment, on the type of leave, as well as on the characteristics of the work of the woman in labor.
Read about extending sick leave here.
When will they be produced
According to Order No. 624 and Federal Law No. 255 of the Russian Federation dated December 29, 2006, sick leave during maternity leave to care for a newborn child is paid if the employee continues to work in the organization part-time or works at home. Payment of sick leave is also acceptable in case of complications during childbirth or during a caesarean section. In such a situation, a second sheet of temporary disability is issued, which extends the paid period of maternity leave. The procedure is an extension of leave, so a personal application addressed to the manager, confirmed by a certificate of temporary incapacity for work, is required. Additional sick leave must be provided no later than 30 days after birth. This can be done independently or through a trusted person.
Read about sick leave payment in this material.
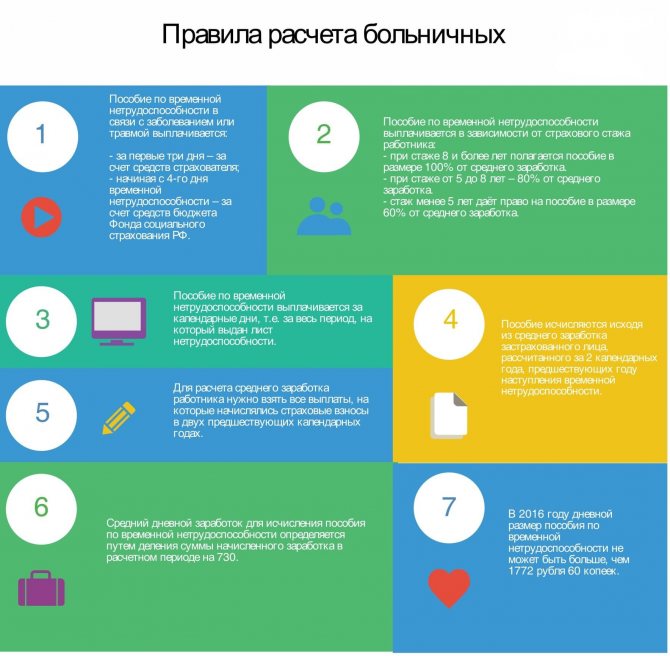
In all other circumstances, after the end of maternity leave, sick leave benefits may stop being paid.
The amount of sick leave is calculated according to the usual scheme and can be up to 100% of the average daily earnings for the last two working years.
When they won't get paid
If an employee does not go to work during the declared leave to care for a child under 3 years of age or does not continue to work at home, sick leave will not be accrued. This happens for the reason that during this period the woman in labor already receives social benefits guaranteed by the legislation of the Russian Federation. It can be of two types:
- Maternity benefit according to BiR. They are paid in the amount of 100% of the average income (clause 1, article 11 of Federal Law No. 255);
- If a citizen is on parental leave to care for a child up to 1.5 years old, they are paid a benefit in the amount of 40% of the average salary (Clause 1, Article 11.2 of Federal Law No. 255).
If a woman who is on leave to care for a small child experiences another pregnancy, she has the right to apply for any benefit she wishes.
Maternity leave, part-time work and sick leave...
This situation is discussed in the commented letter. The employee plans to go to work part-time while on maternity leave for up to one and a half years. Should an employer pay temporary disability benefits in the event of a child's illness?
Here's how the officials responded.
The benefit is also paid in case of illness of the employee’s family members. In this case, sick leave is issued to the employee who is actually caring for a sick family member.
A certificate of incapacity for work to care for a sick family member is not issued when the employee is on vacation:
- on regular paid leave;
- for pregnancy and childbirth;
- for child care until the child reaches the age of three, with the exception of part-time work or at home;
- without pay.
This is stated in paragraph 40 of the Procedure for issuing certificates of incapacity for work, approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated June 29, 2011 No. 624n.
Please note: in case of temporary disability of persons on parental leave before the child reaches the age of three and working part-time or at home, sick leave is issued on a general basis.
conclusions
According to the law, a woman has the full legislative right to issue sick leave during maternity leave when applying for part-time work or continuing to work at home. You can read the order on maternity leave to care for a child using the provided link. Parental leave is not mandatory from the point of view of the law; its registration is always of a declarative nature, and payment of sick leave during this period is carried out under the same conditions as during the period of maternity leave under the BiR for a woman. It is necessary to more accurately calculate the time of going on maternity leave, since there are factors that affect the amount of sick leave benefits at this significant stage of life.