A working citizen, whose relationship with the employer is secured by an employment contract, has legally guaranteed rights prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Constitution. One of the fundamental guarantees of the state for officially employed people is the right to rest.
This right is exercised in the form of vacations - time free from functional employment on weekdays, granted for a certain period. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for several varieties of this form of rest, each of which has its own characteristics in the provision, registration and payment. We will talk about them in this article.
The procedure for granting leave according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Annual basic paid leave (according to Article 114 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is free time that is provided:
- any employee for a certain number of days a year;
- without fail;
- with saving of working space;
- with payment based on the average salary in the previous year.
In order for an employee to go on vacation, some nuances must be observed:
- Vacation experience is the minimum time that an employee must work in an organization in order to gain the right to go on vacation.
The general requirements for calculating length of service are set out in Art. 121 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It includes:
- actual time worked;
- the time when an employee was absent from work, but his place was retained, including during forced absences and downtime;
- the time when the employee was suspended through no fault of his own;
- vacation time at your own expense up to 14 days a year.
And the time does not turn on:
- on parental leave until the appropriate age;
- downtime, absenteeism, suspensions due to the fault of the employee;
- vacations at your own expense in excess of 14 days.
According to the norms of the Labor Code (Article 122), the first opportunity for an employee to take basic leave arises after his work experience with a given employer is 6 months. Exceptions may be made:
- for pregnant women and women on maternity leave;
- minors;
- adoptive parents of newborns;
- other citizens in cases provided for by federal laws, for example, for Chernobyl victims (clause 5 of article 14 of the law of the Russian Federation of May 15, 1991 No. 1244-I), spouses of military personnel (clause 11 of article 11 of the law of May 27, 1998 No. 76-FZ ).
Further vacations are given in accordance with the vacation schedule approved by the employer for the next year.
- The procedure for granting vacations requires that they comply with the schedule. There are 2 options for compiling it:
- The schedule shows the exact vacation dates. Then the employer must remind (notify) the employee about the vacation against receipt no later than 2 weeks before it starts (Article 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The schedule shows only the month of vacation. Then the employee should write a statement indicating the start date of the vacation, and the employer should notify the employee about the start of the vacation from the specified date. The deadline remains the same (minimum 2 weeks).
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, vacation can be postponed due to serious production needs. It should be borne in mind that transferring vacation to the next year is possible only with the consent of the employee.
ConsultantPlus experts spoke in detail about the nuances of postponing vacation due to production needs. Get trial access to the K+ system and upgrade to the ready-made solution for free.
Unscheduled leave may be granted to the same categories of employees who are entitled to leave granted without completing the minimum required length of service.
Read more about drawing up a vacation schedule in the article “Vacation schedule - form and sample for filling out in 2021.”
- The leave is formalized by an order, which the employee reads against signature.
The form and example of the order are given in the material “Order for annual paid leave - sample and form” .
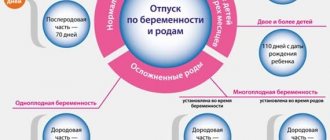
Maternity leave
This type of release from work associated with the birth of a child in the family consists of two parts:
- stay on sick leave due to pregnancy and childbirth;
- leave provided to care for a small child up to 1.5 or 3 years old (Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If the first type, for obvious reasons, is reserved only for mothers, then child care can also be provided by another family member, for example, the child’s father or grandmother. In this case, the mother must provide the place of work of the relative who is going on maternity leave with a certificate stating that she is not granted such leave. The law allows such leave to be divided into parts, with each part being used by different relatives. And further:
- While a parent or relative is on such leave, he has the right to state social security in established amounts, depending on his average salary.
- If the person caring for the baby expresses his desire in the form of an application, he can maintain state support while working part-time or remotely.
- This type of leave is fully counted towards the length of service and also guarantees the employee retention of his job and position.
How long is the vacation?
The duration of the main paid leave must be at least 28 calendar days per year (Article 115 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). A longer holiday can be set:
- federal legislation for certain categories of workers;
- internal regulations of the enterprise (for example, a collective agreement).
Important! By agreement between management and the employee, leave can be taken in parts, provided that at least one part lasts at least 14 days. Find out how you can split your vacation into parts here.
The duration does not include (vacation for these periods is extended):
- holidays;
- days of illness.
Vacation days are reflected separately in the working time sheet.
Read more about this in the article “Working time sheet - form T-13 (form)” .
Legislative regulation
According to the Labor Code, Article 115, the employer must pay at least 28 days per year. No matter what disputes this may cause, calendar days are paid and provided to the employee .
If the vacation falls on non-working holidays, then they are not included in its duration and are paid , which is regulated by Article 120 of the same Labor Code.
More information about holidays that fall on holidays can be found in this article.
Let's look at an example of how to calculate vacation:
- Manager Karpov decided to rest and wrote an application for leave from April 10 to April 17. During these 7 days there are 2 days off - Saturday and Sunday. Karpov is paid for all 7 days in a row and all of them are included in vacation.
- If Karpov writes an application for vacation for the period from May 7 to May 14, then only 7 days will be counted towards the vacation, since May 9 is a holiday .
The time that a vacationing employee spent on sick leave is not included in the calculation of vacation if he submits a sick leave certificate to the payroll department. The period of incapacity spent on vacation extends the duration of rest by the number of days of illness .
Watch a video about the nuances of granting leave:
When should vacation be paid?
As a general rule, vacation pay must be issued to the employee no later than 3 days before going on vacation.
See : “If vacation starts on Monday, you cannot issue vacation pay on Friday.”
In practice, exceptions are possible (for example, an employee is immediately given a part of paid leave, and the money is paid the day before), but the procedure for such situations is not established by law. That is, the inspection authorities may regard it as a violation.
See: “Emergency leave by an employee may result in a fine for the employer.”
Paid annually
This type of guaranteed rest is the main one and is provided annually for a certain period of time worked. The basic duration, without taking into account the specifics of the position held, for the specified type is 28 days.
Certain categories of citizens have the right to a longer period of paid annual rest. Among them:
- teachers and other educational workers - from forty-two to fifty-six calendar days, depending on the type of institution, its status and location. What other types of leave under labor legislation are provided for this category of citizens can be clarified in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- minor workers – 31 days;
- judges, prosecutors, civil servants, rescuers, researchers - from 30 to 48 days;
- disabled people – 30 days;
- persons engaged in specific production, including those associated with the creation of chemicals. weapons - 49 - 56 days.
All types of leave are provided after the relevant documents have been completed. So, for annual leave it is:
- schedule in form T-7;
- order (form T-6 and T-6a);
- note-calculation in form T-60.
Additional paid leave: cases of provision and payment
Additional leave is provided without fail in situations provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws:
- workers employed in hazardous and (or) hazardous industries;
- working in the Far North and similar places;
- minors;
- disabled people;
- workers with irregular hours;
- working in the fields of sports, education and medicine;
- for certain types of work of a special nature;
- employees of government agencies for military and regulatory purposes;
- a circle of people for whom leave is compensation (victims in Chernobyl, Semipalatinsk, etc.).
Additional holidays may also be established by internal regulations.
If there are additional vacation days, they are summed up in the year with the main vacation to calculate the total duration of annual vacation and the amount of payment for vacation.
Vacation without providing finance
“At one’s own expense”, “without payment”, “without pay”, “administrative leave” - this is the common name for the time that is provided to an employee in special situations with the consent of the employer.
Some of the situations are provided for by law, for example, a new addition to the family allows you to be legally absent for up to 5 days, a disabled employee can rest at his own expense for two months every year, etc. In cases not provided for by law, the duration and timing of such leave are decided depending on the specific situation.
Since approval is required, to grant this type of leave, a written application from the employee is required, if possible supported by supporting documents. Based on the application, a leave order is issued.
Results
Annual leave is mandatory for each employee after a certain period of work with the employer giving the leave. In some cases this period may be shortened. When employees go on vacation during each calendar year, it is regulated by the vacation schedule approved for that year.
The duration of full annual leave is 28 calendar days, but can be increased by additional days provided. Persons of certain categories are given additional leave without fail. Vacations may be split into parts.
Vacation pay is paid no later than 3 days before the start of the vacation. Their calculation is done for the actually used number of vacation days by multiplying them by the average daily earnings. The latter value is calculated from the income received by the employee at the place of receipt of leave for the 12 months preceding the month of going on leave, and taking into account the legally established average number of months per year. Vacation pay when the billing period is not fully worked out occurs according to a special formula.
Sources: Labor Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Short-term leave without pay
All employees in the Russian Federation have the ultimate right to receive short-term leave without pay when certain circumstances occur. This means that, subject to the conditions for granting such leave, after receiving the employee’s application and documents confirming the right to receive short-term leave, the employer cannot refuse the employee. Thus, compulsory leave of up to five days is granted in the following cases:
Birth of a child. Despite the fact that women are provided with compulsory maternity leave in case of pregnancy and childbirth, at the time of the birth of a child, fathers of children can also receive separate leave without pay.- Marriage registration. If an employee has a wedding, or even just a purely formal registration of the marriage relationship in the registry office, without celebration, this gives him the opportunity to receive unpaid short-term leave.
- Death of a close relative. Upon the death of a close relative, the employee is also provided with unpaid leave.
In all of the above situations, the employer has the right to demand from the employee documents confirming the existence of grounds for receiving short-term leave. In this case, the rest in question can be provided for each individual case, giving the right to receive such release from work.
The solution to this issue is different with other categories of workers. Thus, a number of persons have special social guarantees, expressed in the right to receive leave without pay due to the presence of a special legal status. For example, disabled people, WWII veterans, as well as a wide range of other categories of the population are entitled to such leave. You can read more about unpaid leave and who is entitled to it in a separate article.
In general, if a person has the right to receive leave without pay, he only needs to write an application and indicate the duration of the leave, which can be any period of time - from one day to the maximum period of unpaid leave provided by law. However, this does not mean that other workers cannot receive short-term leave without pay.
Thus, absolutely any employee has the right to write an application addressed to the employer and ask for short-term leave without pay. But if such an employee does not have the exclusive right to compulsorily provide him with leave, the decision on whether to allocate it or deny it to the employee is made by the employer himself. Thus, absolutely any employee can theoretically receive short-term leave without pay in any amount.
Grounds for refusal to provide
The Labor Code, which defines the types of leaves and the procedure for their provision, allows for the possibility of refusal in a limited number of cases. A refusal by the employer will be legal if:
- basic paid leave was requested for time worked that does not correspond to the minimum period required for its provision (6 months);
- you need a student leave, but without presenting a certificate of summons from the place of training;
- unpaid leave is required, but there are no reasons for providing it;
- Other reasons mentioned in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or the employment contract are also relevant.
An employer may not refuse to provide leave of any kind provided that all legal requirements are met. In cases of unlawful refusal, the employee has the right to seek justice and proper rest time through the court. Moreover, most of the lawsuits on the mentioned fact are resolved in favor of the employee.
Without content (save salary)
Temporary release from work without maintaining salary for the corresponding period is the right of a citizen who has good reasons for receiving it. Labor legislation does not regulate the duration of this type of leave. It is determined in contractual form between the employee and the employer.
Please note that some groups of people cannot be denied temporary leave from work without pay. This:
- disabled people – up to 60 days a year;
- relatives of military personnel or a number of categories of officials who died in the line of duty - up to 14 days a year;
- for pensioners – up to 14 days a year;
- workers registering a marriage, burying relatives or on the occasion of family expansion - up to 5 days a year
Features of the educational
Like all types of leave, labor legislation clearly defines the conditions and duration of release from work during study, dividing it into paid and unpaid.
1. With payment The average salary is maintained in cases where the employee goes to study at a university that operates in accordance with legal standards and has accreditation, for correspondence or evening (mixed) study, for:
- passing tests and exams - 40 days in the first and second years, 50 days in the following courses;
- up to four months to submit the final work and prepare for it.
Employees undergoing training at lower-level institutions (secondary colleges) have the right to be absent from the workplace upon completion of their studies for the duration of:
- 30 days for periodic certification in the first two courses and 40 days in the following courses;
- two months to submit the final work.
Workers studying in primary education institutions can count on 9 days and 22 days upon graduation
2. Without pay Study leave can be granted without pay:
1. university students:
- if necessary, leave for the entrance examination – 15 days;
- for submitting the final work – 15 days;
- Full-time students have 15 days to pass current exams and 4 months to defend their final work and prepare for it.
2. students studying at lower level institutions:
- for those taking entrance exams – 10 days;
- full-time students for passing current exams - 10 days and two months to defend the final work and prepare for it.
Basic principles for calculating vacation pay
Art. 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that average earnings are calculated for 12 calendar months preceding the period during which the employee retains the average salary. In this case, a calendar month is considered to be the period from the 1st to the 30th (31st) day of the corresponding month inclusive (in February - to the 28th (29th) day inclusive). Average daily earnings for vacation pay and compensation for unused vacations are calculated for the last 12 calendar months by dividing the amount of accrued wages by 12 and by 29.3 (the average monthly number of calendar days).
Average daily earnings = Actual accrued salary for the billing period: 12: 29.3
Another key document that clarifies this issue is Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2007 No. 922. Clause 6 clarifies that if the employee did not have actual accrued wages or actually worked days for the billing period or for a period exceeding the billing period , or this period consisted of time excluded from the calculation period in accordance with paragraph 5 of the Resolution, the average earnings are determined based on the amount of wages actually accrued for the previous period, equal to the calculation period.
Compensation for unused vacation
In accordance with Art. 126 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, part of the annual paid leave exceeding 28 calendar days, upon a written application from the employee, can be replaced by monetary compensation. We are talking about disabled people, minors, pelagic workers and other workers who are entitled to leave of more than 28 days.
As for all other employees, even if they have not taken vacation for several years, they cannot replace these vacations with compensation. In accordance with Art. 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, compensation is possible only upon dismissal of an employee. This topic is discussed in more detail in the article Vacation compensation: when can vacation be replaced with money?