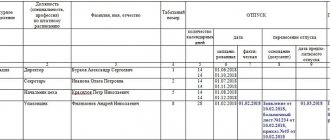
The vacation schedule is one of the most controversial documents of a legal entity. On the one hand, it is mandatory and is accepted no later than two weeks before the end of the calendar year. In case of its absence, the employer may be fined on the basis of Part 1 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
However, there are quite a lot of reasons to ignore the deadlines given in it. First of all, these include those generated by legislation that allows certain categories of workers to go on vacation whenever they wish.
Production necessity also plays a significant role, allowing management to issue an order to postpone the vacation of an individual employee for a particular period. Sometimes the life circumstances of the workers themselves change. Therefore, within the period established for the adoption of local regulations on the basis of Art. 372 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the vacation schedule is usually accepted at all enterprises, but later everything can be replayed several times.
Because of this, the vacation schedule becomes a rather formal local act.
Particular aspects of the practical application of the provisions of the Vacation Code
The mere fact that the deadline for going on scheduled leave is approaching does not mean that the employee can take it and not go to work. The Resolution of the RF Armed Forces dated March 17, 2004 No. 2 on the consequences of unauthorized leave is still relevant.
Although there is an opinion that, due to the fact that the employer must notify employees that the time for using vacation days according to the schedule is approaching, therefore, the employee does not need to write an application for vacation according to the schedule, but only an order that will be drawn up on based on the vacation schedule.
We note that there must be some kind of documentary evidence of the start of the vacation in any case.
If there is an order, then the employee does not need to write a leave application. If there is no order, but there is a statement that is approved by the leadership, then this is also a reason to walk boldly. If there is nothing, then there is a very high risk that this will become a reason for declaring absenteeism with subsequent dismissal.
Let’s not forget that the manager can issue a local legal act on the adoption of a certain procedure for going on vacation. Then this must be done strictly according to the order established by him.
The distribution of vacations relative to employees can be any. The law does not regulate this issue in any way. Most enterprises prefer that no more than two employees from a structural unit are on vacation at the same time. At the same time, one of the remaining ones is assigned to perform the duties of vacationers for a certain percentage of their salary.
But there are also enterprises where they prefer to go on vacation at the same time. During this period it suspends its work. This is due to the specifics in the organization of the production process.
Entry into force of the vacation schedule
This document is binding for both administration and staff. Deviations from the schedule for providing annual paid rest periods may be due to employee requests. If they are not related to preferential circumstances, then the conclusion of a primary trade union association (if any) is mandatory. In addition, the consent of the administration will be required.
Regardless of the availability of the schedule, the registration of the annual paid rest period is carried out by a special document. The procedure for its provision requires the adoption of an appropriate order.
Author of the article
Rights of certain categories of workers
Drawing up a vacation schedule should take into account the right of certain categories of employees to use vacation at a certain time. It arises on the basis of the provisions of the Code itself and individual Federal Laws.
Thus, employees whose wives are on maternity leave can go on leave at any time convenient for them based on the provisions of Part 4 of Art. 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and on the basis of Art. 11 of the Law “On the Status of Military Personnel”, military spouses have the same right.
There are 14 special categories of workers.
Of course, in combination with various types of business needs, it is very difficult to create a vacation schedule that respects the interests of all employees and takes into account the rights of all special categories. Especially in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, where in certain cases working parents of minors and persons equal to them in terms of rights have the right to receive annual paid leave out of turn.
Parents in these regions can even receive regular leave to accompany a child under 18 years of age entering an educational institution.
Vacation schedule and its approval
The current procedure provides for a number of basic rules for drawing up and approving schedules of annual paid rest periods. These include the following conditions:
- The document is approved by the employer. It becomes valid for all parties to the labor relationship from the moment the signature of the authorized person appears. This is the manager or another employee of the company to whom this authority is delegated.
- When drawing up the document, it is imperative to take into account the opinion of the primary trade union association. Currently, such organizations are not widespread. However, they can be found in various industries. It is assumed that a draft document planning the dates for granting leave is drawn up by the administration and submitted to the trade union for approval. The management body of this association has the corresponding right.
- The vacation schedule must be approved at least 2 weeks before the next calendar year begins. This limitation is dictated by the need to provide employees with the opportunity to decide in advance about their vacation. Often trips and tours are much cheaper if purchased several months before the trip.
Making a vacation schedule
The law does not establish rules on how an employer should collect the vacation dates they want from employees. Usually, all employees of a workshop or department are given a list of them, and opposite each name they themselves indicate the dates they want. If the collective agreement contains a provision that the leave is divided into two parts, then there are two stages.
Then the head of the department transmits the result to his immediate superior. Some institutions issue separate orders establishing regulations.
To draw up the schedule itself, the unified form T-7 is usually used, which was approved by the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation back in 2004. The law does not regulate how the schedule should be approved. In some enterprises, an executive visa is used for this, while in others an order is also issued.
All this makes the vacation schedule a mandatory document, which can be treated rather arbitrarily.
The controversial nature of the vacation schedule is confirmed by the fact that proposals to cancel it began to be voiced simultaneously with the proposal to cancel work books. However, the latter were transferred to electronic format, but they decided not to change the vacation schedules for now. Let us remind you that workers in the Russian Federation regularly recall their vacations, and some do not use them for several years.
Article 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The order of granting annual paid leave (current version)
1. The order of provision of annual paid leave is established by the schedule. The vacation schedule must be drawn up by the employer taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization for each calendar year and approved by it no later than two weeks before the start of the calendar year. For example, the vacation schedule for 2014 must be approved no later than December 18, 2013.
2. Vacations can be granted at any time during the year, but without disrupting the normal functioning of the organization. When drawing up the schedule, the wishes of workers and the features of the production process are taken into account.
An important condition that must be observed when drawing up a schedule: vacation should not begin earlier than the working year for which it is provided.
The approved vacation schedule is mandatory for both the employer and employees. This means that neither the employer nor the employee has the right to unilaterally change the scheduled time for going on vacation.
If an employee is not satisfied with the vacation time established in the schedule, he can ask the employer and the relevant elected body of the primary trade union organization to change it. With the consent of the employee, the time for going on vacation can be changed at the initiative of the employer.
A special procedure for providing paid leave has been established for employees of FIFA, FIFA subsidiaries, FIFA counterparties, confederations, national football associations, the Russian Football Union, the Russia 2018 Organizing Committee, its subsidiaries, whose labor activities are related to the implementation of activities for the preparation and conduct of Russian Federation of sports competitions - the 2021 FIFA World Cup and the 2021 FIFA Confederations Cup. The priority for the provision of vacations to these employees is determined annually in accordance with the vacation schedule approved by the employer, taking into account the action plans of the relevant organizations for the preparation and holding of sports competitions (see. Part 5, Article 11 of the Federal Law of June 7, 2013 N 108-FZ).
3. The approved vacation schedule is brought to the attention of all employees. Typically, vacation schedules are posted in departments of the organization or announced to employees against signature. However, this does not exclude the employer’s obligation to notify each employee of the start time of his vacation no later than two weeks in advance.
4. When drawing up a vacation schedule, it should be taken into account that for some categories of employees the laws provide for such a benefit as the right to use vacation at a time convenient for them. The number of persons entitled to such a benefit is currently quite significant. These include, in particular:
— workers under the age of 18 (Article 267 of the Labor Code);
- participants of the Great Patriotic War, war veterans, combat veterans, incl. and disabled people (Articles 14 - 19 of the Law on Veterans);
- Heroes of the Soviet Union, Heroes of the Russian Federation and full holders of the Order of Glory (clause 3 of Article 8 of the Law of the Russian Federation of January 15, 1993 N 4301-1 “On the status of Heroes of the Soviet Union, Heroes of the Russian Federation and full holders of the Order of Glory”);
- Heroes of Socialist Labor and full holders of the Order of Labor Glory (Article 6 of the Federal Law of 01/09/1997 N 5-FZ “On the provision of social guarantees to the Heroes of Socialist Labor and full holders of the Order of Labor Glory”);
— persons awarded the sign “Honorary Donor of Russia” (Article 23 of the Law on Donation);
- persons who received or suffered radiation sickness and other diseases associated with radiation exposure as a result of the Chernobyl disaster or with work to eliminate its consequences, disabled people as a result of the Chernobyl disaster, participants in the liquidation of the disaster, citizens evacuated from the exclusion zone and resettled (resettled) from the resettlement zone , and some other persons exposed to radiation as a result of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, other accidents at nuclear facilities for military and civilian purposes, tests, exercises and other work related to any types of nuclear installations (Articles 14 - 22 of the Chernobyl Law ).
When drawing up a vacation schedule, one should also take into account the right of a male employee to receive annual leave during the maternity leave of his wife, as well as the right of one of the parents (guardian, trustee) working in the Far North and equivalent areas to receive annual paid leave or part of it (at least 14 calendar days) to accompany a child under the age of 18 entering educational institutions of secondary vocational education or higher education located in another area (see commentary to Article 322). If there are two or more children, leave for this purpose is granted once for each child.
In cases where the employee has the right to choose, when drawing up a vacation schedule, it is advisable to invite him to write a statement about what time he would like to receive his vacation. If there is such an application and the employee’s wishes are taken into account when drawing up the schedule, subsequently changing the time of use of vacation can only be done by mutual agreement of the parties.
If an employer does not comply with the requirements of the law on providing leave to certain categories of employees at a time convenient for them or violates the approved leave schedule, employees have the right to seek protection from labor dispute resolution bodies (labor dispute commission, court).
Comment source:
Rep. ed. Yu.P. Orlovsky “COMMENTARY ON THE LABOR CODE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION”, 6th edition ACTUALIZATION
ORLOVSKY Y.P., CHIKANOVA L.A., NURTDINOVA A.F., KORSHUNOVA T.YU., SEREGINA L.V., GAVRILINA A.K., BOCHARNIKOVA M.A., VINOGRADOVA Z.D., 2014
Provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on vacations in judicial practice
The provisions of the article in question are quite simple. Usually, in the absence of a vacation schedule, if this is discovered by an inspection by the competent authorities, for example, a labor inspectorate, the employer simply pays a fine and the matter does not go to court.
The subject of consideration in the courts is often situations that are associated with the traditional erroneous understanding of the rules of law that is observed among employers. Thus, many of them believe that if some article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains provisions that leave can be divided into parts, then this gives them the right to divide leave without the employee’s consent.
On March 20, 2021, the Supreme Court of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania issued Decision No. 72-28/2020 in case No. 72-28/2020. It states that in violation of Art. 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee was given a notice of granting him part of the vacation, whereas in accordance with Art. 125 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, vacation can be divided into parts only by agreement of the parties. No agreement was reached between the employee and the employer at that time.
By the decision of the deputy prosecutor, a case was initiated against the director for an administrative offense under Part 1 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The above circumstances served as the basis for bringing the director to administrative liability by resolution of the State Transport Inspectorate.
This was challenged by the director, but in its decision, the Supreme Court of North Ossetia upheld the decision on the administrative penalty and the decision of the lower court on its legality without changes.
Rules for establishment and distribution
Some of this topic has already been stated above.
So, the priority of vacations is established on the basis of a schedule that each employer must draw up and approve two weeks before the end of the calendar year. The opinion of the trade union is taken into account.
In addition, you need to take into account that some categories of employees have the right to go on vacation whenever they wish. Or rather, they must inform the employer preparing the schedule when they want to go on vacation. What are these categories of workers? The answer is in the table:
| № | Category of workers | Law giving the right to choose vacation time |
| 1. | A husband whose wife is on maternity leave. | Art. 123 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. |
| 2. | Minor employees. | Art. 267 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. |
| 3. | Veterans and disabled people of wars and combat operations, including WWII. | Art. 14-19 of the Veterans Law. |
| 4. | Heroes of the USSR, Russian Federation, full holders of the Order of Glory. | Art. 8 of the Law “On Heroes of the Soviet Union...”. |
| 5. | Heroes of Socialist Labor, full holders of the Order of Labor Glory. | Art. 6 Federal Law “On the provision of social guarantees to Heroes of Socialist Labor...”. |
| 6. | Honorary donors. | Art. 23 of the Donation Law. |
| 7. | Chernobyl victims. | Article 14 of the relevant law. |
Thus, the right to choose the time of vacation is given to persons who have any merit to the state. The exception is husbands whose wives are preparing to become mothers. But here the principle of the Constitution of the Russian Federation on the special protection of motherhood and childhood is already in effect. During pregnancy, a woman needs the support and help of her beloved man.
It turns out that the employer must first ask the listed categories of employees when they want to rest, and then “scatter” the rest of the employees according to the calendar.
Part-timer's holiday
The rules for granting leave to this category of workers are established in Art. 286 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
They are:
- Part-time leave is granted at the time during which the vacation falls from the main job.
- If an employee has not worked for more than six months at an additional place of work, then leave is provided to him in advance.
- If at the second place of work the duration of vacation is not as long as at the main place, then the employee has the right to ask for days without pay.
In 2021, information appeared that some deputies of the State Duma of the Russian Federation are in favor of banning part-time work. Therefore, we do not exclude the possibility that this information will soon no longer be relevant.
If not used in the past year
What should you do in such a situation so as not to break the law? Art. 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that failure to provide annual paid leave for 2 years in a row is prohibited. Based on this provision and other norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, we can conclude that an employee who did not go on vacation last year must take all the time off this year.
Another conclusion suggests itself: if an employee does not want to go on vacation for the second year in a row, then the employer must “kick him out.” Otherwise, regulatory authorities may apply sanctions.
Registration
At the request of the employee, you are obliged to provide him with paid leave even earlier than six months. In particular, the following have the right to paid leave until the end of six months of continuous work (Article 122 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- women - before maternity leave or immediately after it;
- employees who have not yet turned 18 years of age;
- employees who adopted a child under three months of age.
An employee can receive early leave in other cases provided for by law.
For example, Article 123 of the Labor Code contains the following provision: at the request of the husband, he can be provided with annual paid leave for the period his wife is on maternity leave. It does not matter how long this person has worked for the company.
In addition, the issue of the possibility of providing vacation in advance can be regulated in a collective agreement or other local regulatory act of the company.
Although paying vacation pay for periods not worked can lead to negative consequences.
If at the time of dismissal an employee received vacation pay that had not yet been worked out, and there was nothing to keep them from, it is impossible to recover the overpaid amount through the court, according to the Supreme Court, after dismissal (Determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of February 5, 2021 No. 59-KG17- 19).
The employer (Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia) demanded to recover through the court from the former employee the amounts of payments for the period of vacation he had not worked. He was also paid his salary in advance.
The courts of the first two instances recognized the employer's demands as legal. They proceeded from the fact that the debt incurred by the employee, which was impossible to retain upon dismissal, constitutes material damage for the former employer. And material damage (direct actual damage) is subject to compensation in accordance with Article 238 of the Labor Code. The disputed payments, at first glance, fall within the definition of direct actual damage, since as a result the employer had a real decrease in available property.
However, the RF Supreme Court did not agree with this assessment. The financial liability of a party to an employment contract arises for damage caused by it to the other party to this contract as a result of its guilty unlawful behavior (Article 233 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In the case under consideration, the employee’s debt to the employer was not related to his illegal actions - neither when paying vacation pay, nor when paying wages.
There were no counting errors.
Thus, you need to remember: you can only withhold debt for unworked vacation days from the amounts due to the employee upon dismissal. There are no other grounds for recovery.
An unearned advance can be recovered through the court in two cases: a counting error or unlawful actions of an employee that resulted in excessive payment of wages.