The total utility debt of Russians to housing enterprises has grown in recent years to significant sizes. This is due to the economic instability that Russia is facing; citizens not only lose their jobs, but also cannot resolve issues with housing and health, since the price level in most regions, and especially in large cities, far exceeds monthly incomes.
The owner of the residential premises is responsible for paying for the provided utilities, but this does not mean that other adults registered in it should not take part.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
+7 (499) 938-81-90 (Moscow)
+7 (812) 467-32-77 (Saint Petersburg)
8 (800) 301-79-36 (Regions)
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
If the owner is the state or local municipality, then the responsibility rests with the main tenant of the premises. In the case of rent, by agreement of the parties, payment is made by the owner or tenant. Utilities provided to residents include the supply of gas, water, electricity, and heat to an apartment or private house.
Housing services, which are also paid by owners in 2020, consist of rent, fees for major repairs of the entire building, heating of the staircase, garbage removal, and others (video surveillance, intercom, antenna).
Receipts are generated and sent to the residential address on a monthly basis; by law, payment must be made by the 10th. But provided that an agreement is concluded between the owner (tenant, tenant) of the premises and the utility company, you can pay utility bills until the 15th-20th of each month.
If the payer does not pay on time, it is considered that he is late in payment, which means that he may be charged a penalty, and the payment amount becomes a debt. Russian legislation allows utility companies to collect debts pre-trial or peacefully. One method is debt restructuring.
What it is
In essence, restructuring should be understood as the signing of an agreement between the utility company and the consumer, when the existing debt is evenly distributed over a certain period, but for a maximum of 30-36 months.
From the moment the agreement is concluded, the debtor assumes the obligation to pay the debt according to the schedule, which is drawn up as an annex to the agreement. When concluding a contract, the level of income of the debtor must be taken into account.
It is generally believed that a citizen does not have the right to pay more than 25% of monthly income on debts. If the debtor is a pensioner or a disabled citizen, for example, a disabled person or a woman on maternity leave, then it is impossible to collect more than 20% from him. Therefore, the payment schedule is drawn up in each individual case individually.
To restructure the debt, it is important that payments are made strictly on schedule; this will help the payer avoid the accrual of penalties.
Rent compensation for large families is awarded after submitting an application.
How to remove the radio from the rent - read this article.
Is it possible to appeal a refusal to restructure utility debts?
Installment is not a mandatory procedure. Therefore, an application for its provision can be either approved or rejected. However, the debtor has the right to appeal the refusal to grant installment plans.
On what grounds can they refuse and what to do in this case?
The management company may refuse to restructure the debt if it considers the reasons for its occurrence to be unjustified. In this case, you can file a complaint with the following authorities:
- housing inspection;
- local administration;
- prosecutor's office
The following should be attached to the complaint:
- receipts for payment of housing and communal services;
- calculation of the amount of debt;
- an application for installment plan that was rejected;
- written response from the management company;
- documents confirming the low level of income of the debtor.
Reasons for additional agreements
A fine may be charged to the debtor in accordance with the Housing Code, Art. 155 for each overdue day, initially it is calculated at 1/300 of the Central Bank refinancing rate, then no more than 1/130. As a result, the amount of penalties can be significant if utility bills are not paid for several months.
A more severe penalty includes disconnection of the premises from services if there is a debt. Reconnection is carried out by housing and communal services only after full payment of the debt. In another case, the debtor is asked to enter into a rent debt restructuring agreement.
Article 155. Payment for residential premises and utilities
Disconnection from the service is possible only after prior notice, first 20 days, and then 3 days if payment has not been made. The reason for concluding a restructuring agreement is serious debt. Sometimes, intending to repay a debt or pay utility bills on time, a citizen may not have such an opportunity. He needs to conclude an agreement in order to repay the debt gradually.
Housing and communal services workers themselves can offer this option for settling the debt if they see that payment is systematically delayed, but mutual agreement is required to resolve the issue. The housing and communal services may refuse the debtor if it considers that the conclusion of the agreement will not resolve the issue.
Circumstances play an important role in this case; they must be really difficult for the debtor. He will need to provide evidence that he lost his ability to work due to a long-term illness, or the family lost its breadwinner, there was a dismissal, etc.
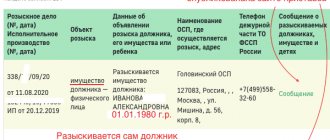
Sample certificate of state registration of rights
What is debt restructuring?
In cases where the court considers that the debtor is able to pay off creditors by changing the payment schedule, it appoints a debt restructuring procedure. It involves extending payment terms and reducing deposited amounts, based on an analysis of the borrower’s financial capabilities. The arbitration manager draws up a restructuring plan, which is approved by creditors and the court. The debtor transfers funds in accordance with the restructuring plan. In this case, penalties, penalties and other fines are not charged, but the debt cannot grow due to interest.
Debt restructuring involves a number of restrictions that are imposed on the debtor. Thus, he can carry out any transactions with property only with the written consent of the arbitration manager. This rule applies to any transactions involving the acquisition and alienation of property whose value exceeds 50,000 rubles, including real estate, transport, as well as transactions on loans, credits, etc.
Main conditions
The debtor has 2 ways out of the situation, contact:
- to the court so that he is allowed to restructure or the debt is written off;
- in housing and communal services and write an application for restructuring.
The agreement between the parties comes into force as soon as the contract is signed. Pre-trial proceedings are always preferable to additional financial expenses for legal fees.
At the same time, the court may reject the claim of the utility service against a citizen if the debt is exorbitant for him. Therefore, when voluntarily concluding an agreement, a citizen pays the amount of debt recognized by him, and in the case of judicial proceedings, the final amount of the debt is determined by the judge.
Paper requirements
An application must be submitted for restructuring and the conclusion of an agreement, and along with it you will have to present:
- passport;
- property documents for the owners, a lease or social tenancy agreement on the basis of which the residential premises are used;
- certificate of family composition;
- documentary evidence of valid reasons for which payments were delayed;
- documents on the income of working family members.
If a representative will act on behalf of the payer, then a power of attorney must be issued for him.
The application can be submitted in any form, it includes:
- the name of the company that provides utilities;
- personal data of the citizen;
- residential address;
- information about all citizens permanently registered in the premises;
- the reason why the debtor applies;
- an explanation of the situation, why the citizen wants to restructure, and on what basis the debt arose;
- information about the options for exiting the situation that the applicant offers, this could be installment plans (restructuring), cancellation of penalties.
The citizen's signature is affixed to the application. It is the basis for concluding a restructuring agreement. The sole owner or one of the co-owners can submit a petition. The application is considered within 10 days.
Requirements for the debtor
Federal Law No. 127-FZ dated October 26, 2002 prescribes a number of conditions under which debt restructuring may be prescribed, they are as follows:
- the borrower must receive regular income;
- the borrower must not have been declared bankrupt during the last five years preceding the procedure;
- over the past 8 years the borrower must not have gone through debt restructuring;
- the borrower must not have outstanding or unexpunged convictions for committing economic crimes;
- if the borrower was held administratively liable for petty theft, fictitious bankruptcy, intentional damage and destruction of property, then the penalty period should be considered expired.
Characteristics of the procedure
If a citizen signs a restructuring agreement, this does not mean that he cannot receive compensation or take advantage of benefits or receive a subsidy. In fact, the terms of the contract indicate the monthly payment amounts that may be feasible for the debtor, and the established terms must suit the company.
Conventionally, the restructuring procedure can be characterized by the following stages:
- preparation of necessary documents;
- filling out an application;
- visit to the territorial housing and communal services department;
- submission of papers for consideration;
- obtaining a decision from housing and communal services;
- concluding a restructuring agreement with the utility company.
How to ensure that a debtor is forgiven a debt that arose due to the fault of the company? He will need to submit an application for recalculation, to which supporting documents should be attached.
These may include:
- travel tickets or sick leave, indicating the citizen’s absence from the premises for a long time;
- act of checking the air temperature in the apartment;
- conclusion on the analysis of the composition of water entering the tap;
- other.
If, after concluding the contract, the debtor at some point stops fulfilling its obligations, the company has the right to terminate the contract unilaterally and collect the debt in full by force through the court.

Sample certificate of family composition
Contract overview
The executed agreement is considered valid until the debtor fulfills his obligations. A sample of such a document can be found on the Internet; it is drawn up in a standard form and should consist of a “header” and a main part.
It includes:
- information about the service provider company;
- information about the debtor;
- address of the residential premises for which the debt arose;
- the company’s rights to continue to provide the service to persons living in the premises, despite the presence of debt;
- the payer’s obligation is to repay the debt according to an individual schedule and, at the same time, make monthly payments;
- the amount of monthly contributions and the date of settlement of obligations, which are drawn up in the form of an individual schedule;
- other necessary information.
The agreement is signed by the parties to the agreement, and the company, for its part, is obliged to put a seal. The document is drawn up in 2 copies. A special form for drawing up an agreement is not provided, but according to legal norms, an analogy can be drawn with legal relations arising in other areas. Thus, the 83rd number of the law, issued in 2002, states that agricultural companies have the right to restructure debts on taxes and fees.
Regulations issued in various regions allow commercial organizations to repay debts to the budget gradually. Credit institutions use a restructuring agreement to recover funds from their borrowers.
The restructuring agreement is a civil law agreement, where the most important part is its subject matter. If it does not follow from the text of the agreement that it is of a restructuring nature, the deal cannot be recognized as concluded.
Such an agreement is concluded only on individual terms and depends on the amount of debt, the debtor’s income, and how accommodating the housing and communal services will be in relation to it.
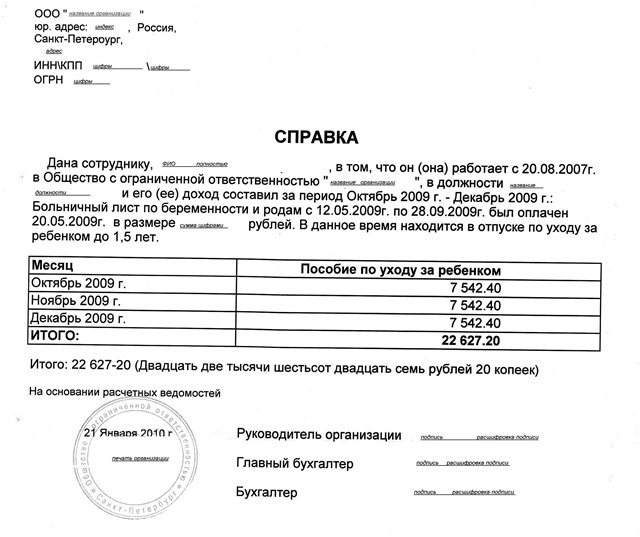
Sample income certificate
Is it possible to write off obligations?
In the Civil Code, art. 12, the legislator points to the concept of limitation of actions, that this is the period established by a regulatory act during which the injured party can defend its rights. For debts on utility bills, this period is in accordance with Art. 196 is 3 years.
It says that the statute of limitations is:
- determined in accordance with Art. 200;
- cannot be more than 10 years from the moment the plaintiff’s rights were violated.
The debtor must also remember the following:
- The statute of limitations can be taken into account if the defendant files an application; otherwise, the court will consider the claim in the general manner.
- If the debtor pays even a small part of his debt, this will be tantamount to recognition of obligations. The limitation period should be counted from the moment of partial repayment of the debt.
- Current payments cannot be made to pay off the debt. When making payments at the cash desk, you must accurately indicate the purpose of the payment - is it a current payment or is it necessary to pay a debt.
In judicial practice, to write off debts, they often resort to Art. 333 on reducing the penalty, but to apply it you will have to convincingly prove that the accrued fine is disproportionate to reality.
If the statute of limitations expires, this does not mean that the debtor’s obligations have automatically terminated. If the defendant files a motion to apply the statute of limitations, the utility company (plaintiff) may change the subject of the claim and request payment of a penalty.
How to write an application correctly?
By applying the statute of limitations, it is possible to win a dispute with housing services. But it will not be monitored either by the utility companies themselves (it is beneficial for them to collect the entire debt), or by the court (it stands up to protect the interests of the party whose interests are violated). Therefore, declaring the write-off of debts that are more than three years old is in the interests of only the debtor himself.
To do this, you must submit a free-form application to the court with the mandatory presence of the following details:
- Full name and address of the applicant;
- title – “statement on the application of the limitation period”;
- a request to consider a claim for debt, taking into account the time limit for collection;
- an indication that the statute of limitations for the utility debt has expired;
- list of supporting documents;
- date of application;
- applicant's signature with transcript.
The application may be accompanied by calculations for utility bills indicating the assignment period and amount, as well as documents explaining the reasons for non-fulfillment of requirements for payment for housing and communal services: lack of income, costs of expensive treatment, etc.
How rent debt is restructured
The utility company may well refuse the applicant to draw up a restructuring agreement; in fact, he resorts to concluding a deal with the debtor voluntarily in order to avoid litigation.
Design details
The application and copies of the necessary documents can be sent to the management company by mail. After the manager makes a decision with the original papers, you will have to come in person or send your representative to the department.
The housing and communal services management can, at its discretion, come to a solution to the issue in 2 ways, these are:
- increasing the deferment for monthly payments or for repaying the entire debt;
- cancellation of the entire amount of penalties for late payments.
The company can write off the debt completely if it reveals significant violations regarding the delivery of services on its part. In another case, she will be able to do this if there is an appropriate court decision.
From the moment an agreement is concluded between the parties, the penalty will stop accruing. But previously accrued penalties can only be written off in a special manner. All this will be valid until the debtor fulfills his obligations.
Debts for housing and communal services
A prerequisite for renting social housing, renting or private ownership is timely payment of utilities, which by law must be supplied to residents to ensure year-round living. Therefore, if a debt arises, the payer must know how to arrange a restructuring of the rent debt.
In the Housing Code, in Art. 156-157 indicate how utility bills are calculated and how to make payments. Deviation from the provisions of the law leads to the formation of debts, and ultimately can be grounds for eviction.
The rights that service providers and consumers may enjoy are specified in regulations. The supplier is assigned the right to influence the debtor independently using methods that will be chosen within the framework of the law. First of all, this is the imposition of penalties and disconnection from the service, and then the conclusion of a restructuring agreement.
If the first measure does not produce results, then the utility company resorts to the second, warning the resource user in advance. Separately, we can consider terminating the social rent agreement with the tenant if the utility service is not systematically paid for by him, and he will have large debts (LC, Art. 83).
Article 83. Termination and termination of a social tenancy agreement for residential premises
In this case, not only he, but also his family members whom he officially registered are subject to eviction. This decision can be made by the owner of the premises (landlord).
Issuing a subsidy
Some citizens, who understand in advance that their financial situation does not allow them to pay utility bills in full, seek to apply for a subsidy. Government Decree No. 761, issued in 2005, on the provision of subsidies for utility bills, regulates all issues of receiving benefits.
The main purpose of the state subsidy is to implement the standards of the Housing Code. Each region has the right to set payment tariffs separately, but there are maximum and minimum standards announced by the legislator.
Resolution No. 541 (08.29.05) states that paying off utilities should not take more than 22% of the total family income. The amount of the subsidy is set individually and monthly, based on the amount that the payer is required to pay for housing and utilities, but regional tariffs are applied.
To receive the benefit, documents must be submitted within the first 15 days of the month, and it will be assigned on the 1st of the next month. Typically, funds are transferred to the utility payer's bank account, and he can spend them only for their intended purpose. The application and other papers are submitted to the Social Security Administration at the place of residence.
What is housing and communal services debt restructuring?
Debt for housing and communal services arises if the subscriber does not pay his obligations on time or in full. A single violation of the payment procedure does not entail serious consequences for the consumer. But if the period of occurrence of the debt is several months, forced collection measures may be applied to the debtor. To avoid adverse consequences, it is recommended to enter into a debt restructuring agreement with the service provider.
What does debt restructuring for housing and communal services mean?
Debt restructuring is an agreement that is concluded between a utility consumer and a management company with the goal of repaying the debt in equal parts over a certain period (several months or years). This procedure exempts the debtor from accruing penalties for late payment.
Attention! The debtor may be provided with installment plans, an individual payment schedule, and comfortable conditions for repaying the debt.
If the terms of the agreement do not suit one of the parties to the agreement, he has the right to refuse to sign it.
Reasons why restructuring is necessary
Debt restructuring allows you to:
- reduce the financial burden on the debtor’s family budget;
- avoid cutting off the supply of utility resources;
- resolve the issue without litigation;
- retain the right to receive benefits and subsidies.
What laws govern installment payments for utilities?
The obligation to timely and fully pay for housing and communal services is determined by Article 153 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
Russian legislation does not provide for such a concept as “debt restructuring”. But a subscriber who has outstanding obligations for housing and communal services has the right to apply for their installment plan. After signing an agreement with the management company, the debtor is given the opportunity to repay the debt in stages (in equal parts at certain intervals).
The main documents regulating the restructuring of debt for payment of housing and communal services:
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation (regarding the procedure for concluding an agreement);
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2011 No. 354;
- other regulatory documents in force on the territory of a specific subject of the Russian Federation.