Those who choose land for a country house or summer cottage often come across these abbreviations - this is how they denote different types of plots. It is important to know: you are not allowed to build a house on any plot, even if you bought it. On some, you can build cottages for year-round living, on others, only a summer cottage, and on some, you are only allowed to plant a vegetable garden and put up a shed for storing tools. It is better to understand all these nuances in advance. – Secondary housing – Houses in individual housing construction, SNT, private household plots and non-residential buildings. We explain what these letters are and where it is better to live
General concept
Each plot in the Russian Federation is assigned a certain category of land and the types of use permitted by law are indicated.
On a piece of land, citizens can work in accordance with the available view. To do this, this type of permitted use must be provided for this site. It can fall into one of two categories:
- settlement lands;
- agricultural land.
In the first case, such a plot is called a personal plot, in the second – a field plot.
According to statistics, in 2012, private farms produced more than 50% of the country’s total agricultural production. The total area of such sites at that time was 42 million hectares.
A private plot can be used not only for farming, but also for generating income. To do this, the following conditions must be met:
- No hired labor should be used on the site;
- Income can only be obtained by selling surpluses obtained as a result of economic activities, but cannot be the result of entrepreneurship.
Exemption from taxation is thus recorded in paragraph 13 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A residential building or outbuildings can be built on this site.
The site may contain a house, outbuildings, a small garden and a vegetable garden.
In most cases, a plot of private household plots belongs to municipal authorities, but it can be sold to citizens, leased out for a long term, or provided for indefinite use by citizens.
When the property has a private plot of private plots, this is what it means for its owner: such land is allowed to be used (based on Article 4 of the “Law on Personal Subsidiary Farming”, No. 112-FZ of July 7, 2003) for the production of agricultural products and for the construction of a residential building or auxiliary structures.
What else influences the development of LPH?
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the extension to private household plots of those state support measures that are provided at the expense of the federal budget to agricultural producers. Subjects of the Russian Federation are adopting programs for the socio-economic development of not only rural settlements, but also private household plots. Within the limits of their own powers, they determine in what form, size and order support will be provided for private household plots on their own territory together with the agricultural cooperatives and other organizations that serve them.
The right to enter into legal relations of compulsory pension insurance for leading private household plots is granted to citizens on a voluntary basis.
When does private household farming stop? This occurs in the event of termination of rights to the land plot where it is carried out.
What can be built
The buildings that can be erected on private plots are determined by local town planning regulations and rules of development and land use.
Typically this is:
- House;
- utility (utility, household) premises;
- non-permanent buildings.
Before starting construction, it is necessary to order an urban planning plan for the allotment (GPZU). This can be done in the architecture department at the place of registration of the site.
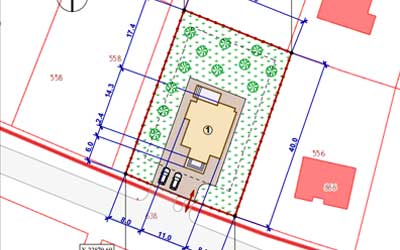
On its basis, a scheme of planning organization of the allotment (SPOZU) is drawn up, where it is necessary to indicate the location of all planned buildings, with the exception of non-permanent ones (buildings without a foundation).
A plot of private household plots implies the simultaneous presence of an additional type of permitted use , the concept of which includes the possibility of building objects such as a garage, bathhouse, barn, etc.
There is no need to take out a separate permit for the construction of these objects, but their presence must be indicated in the SPOSU.
It is important that all buildings do not violate SNiP, urban planning regulations, building and land use rules, fire regulations, etc.
These include:
- The location of the object is no closer than 5 meters from the road and no closer than 3 meters from the passage.
- The location of the object is no closer than 1 meter from the border of the site (fence).
- The location of the object at the required distance from buildings on the neighboring site, namely:
- no closer than 6 meters from each other stone (brick) buildings;
- no closer than 10 meters from each other stone and wooden buildings;
- wooden buildings no closer than 16 meters from each other.
In this case, the distance is measured from the most protruding part of the buildings .
These distances do not have to be maintained within the boundaries of one plot, but a wooden outbuilding adjacent to a brick house is not considered its continuation and the distance to the buildings of the neighboring plot must be maintained both from the brick house and from the wooden shed.
On a personal plot
On the private land of private household plots (located as part of the lands of settlements), you can build all, without exception, the objects listed above.
House
On a personal private plot, it is allowed to erect one residential building , not divided into separate apartments with a total number of floors of no more than three. Basement floors are not taken into account.
Read more in a separate article.
Standards for the construction of utility premises

Outbuildings should be understood as
buildings with no more than one floors, which are intended to serve a residential building and land plot
.
Information about them must be indicated in advance in the SOPSU, but there is no need to draw up a project for each object separately.
If the decision to build a garage, bathhouse, barn, etc. was accepted after the preparation of the SPOSU - there is nothing wrong.
There is also no need to take additional permission for the object, but when drawing up the next SPOZU (the document is valid for 10 years), it must be indicated there.
According to current legislation, the maximum area of such buildings on plots of more than 10 acres is 200 square meters in total .
On a plot of 6 to 10 acres, the construction of outbuildings with a total area of up to 100 square meters .
On a plot of less than 6 acres, the construction of outbuildings with a total area of up to 50 square meters .
These restrictions are advisory rather than mandatory and are not tested in practice. But at the same time, it is very important to comply with the standards of SNiP, PZZ and others.
Drilling of the wells
Without additional approvals, it is allowed to construct wells and drill wells into the first aquifer .
Otherwise, it is necessary to obtain a license for an artesian well.
On the field

Without restrictions and additional approvals
field private plots can be fenced off
, and
put a mobile trailer on it
(cabin), which can be picked up and taken away at any time.
Also, in agreement with the administration, non-permanent buildings can be erected on the field private plot, that is, buildings that do not have a foundation - greenhouses, chicken coops, etc.
There is also a controversial issue here about the possibility of erecting buildings on concrete slabs.
That is, by laying concrete slabs, large buildings, such as hangars, can be erected. They will not fall under the category of permanent buildings, since they do not have a foundation, and concrete slabs can be lifted and taken away. In practice, it is not a fact that such a building will be approved.
In resolving this issue, a lot depends on the local administration and its understanding of the current legislation.
Whatever building is erected on the field private plot, it will not be able to receive a postal address .
With regard to wells, the situation is exactly the same as in private household plots.
Private household plots as a business idea - is it worth spending time on implementation?
To answer this question, let’s analyze the pros and cons of this form of personal farming.
Pros:
- Ease of organization.
- Registration with government agencies is not required.
- The right to conduct an activity is valid as long as the land on which it is carried out is owned by the owner.
- Opportunity to implement your own project in the agricultural sector.
- It is not necessary to own the plot; it can be rented.
- The opportunity to involve local governments in the connection of communications on your personal or rented plot.
- There is a chance to receive subsidies to develop your business.
- If you wish, you can obtain a registration at the address of your farm.
- Tax reporting is not required for the sale of surplus production.
Minuses:
- You bear full responsibility for private household plots.
- You will need a lot of effort and manual labor to cultivate the land, raise poultry, or whatever type of work you choose.
- Limited land area.
- Relatively high tax rate on land within populated areas.
- Support from the authorities is provided in a smaller volume than stated by the state.
- You will not be able to engage in activities subject to certification, nor will you be able to construct permanent structures on the leased territory.
- The need to submit information to the “household book” of local governments.
Having opened a private household plot, you have the right to produce agricultural products for sale and sell them without providing any reporting documents to the tax service. Also, you are not afraid of sanitary inspections, since your activity is not considered a business.
But you should not think that this form of activity is a panacea for problems with the law. When you reach a certain level of income, regulatory authorities will probably have questions.
Read about how to register private household plots in a separate article.
Do I need a permit to build private household plots?

That is, after amendments to the law there is no need to obtain a construction permit. In order to start building, you need to notify the local administration. A positive response to your submitted documents will act as a permit. It is valid in the same way as a building permit - 10 years. Construction without permission is illegal. The house will be recognized as unauthorized construction. It is much more difficult to legitimize an already built OKS than to do everything according to the law. This will require more effort, time, and money. We recommend not to take risks, but to obtain permits before you begin work.
Despite the fact that the procedure for obtaining construction permits is well regulated, no two cases are absolutely identical. Sometimes additional approvals may be required. At a consultation with a Geomer Group specialist, you will learn how to quickly obtain a construction permit in your case.
What should be remembered by those wishing to organize private household plots?
As already stated, the law does not allow construction on agricultural land. That is, if you are planning to build a residential building or other structures, your private household plot must be within the boundaries of the settlement. It should be taken into account that rent per hectare of land within its borders costs an order of magnitude more than outside the settlement.
In the case of obtaining the status of a farmer (that is, the formation of a farm), a citizen is obliged to register as an entrepreneur with all the ensuing difficulties and consequences - maintaining a balance sheet, reporting, which greatly complicates the procedure for managing a plot of land and will scare many away from this activity.
Another option for those wishing to build on private household plot land is to seek transfer of the field plot to the category of settlement land. It must be remembered that land used for purposes other than its intended purpose may be legally seized.
Features and rules of running personal subsidiary farming
According to Federal Law No. 112, on these land plots you can engage in personal farming.
This means:
- breeding livestock, bees, poultry and other animals;
- growing garden and vegetable crops;
- floriculture;
- use of land for plowing and haymaking, etc.
A citizen (individual) has the right to engage in this activity alone or together with his family for his own, non-commercial purposes .
At the same time, it is possible to sell goods grown and created on this site. Moreover, under certain conditions it is not subject to tax.
Accounting for private household plots
All private household plots are recorded by the administrations of settlements and urban districts in their household books. These books are maintained according to the information provided on a voluntary basis by the leading citizen of the private household plot:
- Who runs it - full name, date of birth of the citizen to whom the plot was provided or who acquired it for the purpose of running private household plots.
- Data (full name, date of birth) of those who, together with him, participate in the management of private household plots (residents or simply family members).
- Area of land occupied by private household plots. On what lands are crops and crops planted, on what lands are there berry or fruit plantings?
- Number of livestock, farm animals, birds and bees.
- What property is available to private household plots? We are talking about equipment, agricultural machinery, vehicles that, by right of personal ownership or otherwise, belong to the leading citizen of the private household plot.
What area should such a plot have?
For personal subsidiary plots, only a plot of land whose area does not exceed the established limit can be provided.
The minimum and maximum amount of area that can be provided is established by the municipal authorities. These figures depend on the availability of such lands and their demand.
However, federal law sets the upper limit of the area provided at 0.5 hectares. At the same time, a reservation is made that the regional authorities have the right to increase this value. However, the maximum that cannot be violated in any way is 2.5 hectares.
Let's talk about selling private subsidiary farm products
Before you start selling products grown in your own private plot, you should obtain a certificate from the local administration (from the head of the rural settlement) stating that the products grown and sold by you were produced exactly there - in your private plot. This guarantees you tax exemption.
For example, you are taking your own vehicle to sell several slaughtered sheep or chickens to the city market. When stopped by a traffic police officer, questions may arise: where are you going and where is so much meat coming from? By presenting the specified certificate (that is, confirming that products grown in private household plots are being transported), you will get rid of unnecessary misunderstandings.
Another situation is that you plan to deliver this meat, for example, to a sausage shop. In this case, a trade and procurement act will be drawn up indicating your passport details and Taxpayer Identification Number (don’t forget to stock up on copies of these documents to provide the product to the buyer). The above-mentioned certificate of sale of products grown in your private household plot is a mandatory appendix to the trade and procurement act.

Permission
If you need to build a residential building, you must apply for permission from the local administration .
To do this, you must provide:
- a certificate confirming that the citizen owns the land plot;
- a copy of the civil passport of the specified citizen;
- SPOSU;
- GPZU;
- application addressed to the head of the local administration.
Additionally, other documents may be required, a full list of which is specified in the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation.
On a field private plot, it is necessary to obtain permission for all types of buildings (fences and mobile trailers are not considered such).
Advantages and disadvantages
To get a clear picture of which category is better between these two lands, it is important to consider their pros and cons.
Pros of private household plots:
- Simple organization (no need for legal registration).
- There is no need to register private household plots with the tax office, there are no tax reporting requirements (records are kept in special books on farms by local authorities, the owners of the plots only provide information).
- Availability of benefits (under certain conditions, exemption from personal income tax, preferential transport tax).
- The owner has the opportunity to independently decide on the payment of contributions to the Pension Fund.
Disadvantages of private household plots:
- Limitation of the area of the plot for private plots (its size should not exceed 0.5 hectares, but the local administration may decide to expand the land plot by 5 times).
- Lack of government support for preferential loans and subsidies.
- Certain types of activities that are subject to certification are prohibited; in this case, declarations of conformity are not issued.
If the size of the land plot is more than the permissible 0.5 hectares, then the excess part must be separated, otherwise it will be necessary to register an individual entrepreneur or farm.
Advantages of individual housing construction:
- A house registered as an individual housing construction is always assigned an address (you can easily obtain a registration).
- Local authorities are obliged to provide all necessary communications, as well as social services.
- The procedure for tax deduction of individual housing construction has been significantly simplified.
- You can provide land for individual housing construction as collateral if you need a loan from financial institutions.
Disadvantages of individual housing construction:
- Limitation on the area of a land plot (varies for different regions of the Russian Federation).
- Bureaucratic commissioning procedure (regulation of the construction of a residential building by many regulations).
Watch the video: Is it worth registering private household plots?

Why is it so difficult to register in SNT and DNP houses?
The law does not prohibit registration of houses on these sites, but this is not easy to do. To obtain registration you need an address, but small garden houses located outside the boundaries of populated areas simply do not have one. If you have an address, everything becomes simpler, otherwise you have to carry out an examination of the house and get a court decision on its suitability for living - this is the only way to register in it.
What to choose?
The choice depends on the purpose of using the land. Individual housing construction is the best option for the construction of a capital country house. Although it will cost more, it will be possible to sell it at a high price. If the main purpose of buying a plot is a summer house with a garden or vegetable garden, it is more profitable to choose DNP. Such land is cheaper, a house can be built for year-round living, but you most likely will not be able to register in it.
But the savings from purchasing land in DNP and SNT for permanent residence may be questionable. At individual housing construction sites, communications, roads and infrastructure are handled by the administration, but in garden and dacha communities all this will have to be done at their own expense.
Authors: Yandex.Real Estate team. Illustrator: Natasha Jola
Receive new materials by email
Personal subsidiary plot (LPH). Benefits for citizens of leading private household plots. Differences from farmers (peasant farms)
We can provide you with the service of developing a business plan for your farm for the bank or for receiving a subsidy , grant, or drawing up any other legal documentation. Cost of work here Contact us!
You have a small plot of land (vegetable garden) next to your house on which you grow vegetables, several units of livestock, and you do not plan to expand, but you cannot consume everything you grow yourself (most likely, you will sell this surplus, and if that doesn’t work out - just give it to someone - a treat for guests - no one has canceled hospitality yet).
Will the sale of surplus be considered business income ? Lawmakers think not . Such activities are regulated by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Personal Subsistence Farming” dated July 7, 2003 No. 112 Federal Law (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 112).
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 2 Federal Law No. 112 personal subsidiary farming is a form of non-entrepreneurial activity for the production and processing of agricultural products.
More on the topic: Grant 1.5 million rubles. under the “Beginner Farmer” program Grant 5 million rubles. under the “Family Livestock Farm” program
Personal subsidiary farming ( LPH ) is maintained by a citizen or a citizen and members of his family in order to satisfy personal needs on a land plot provided and (or) acquired for conducting personal subsidiary farming.
Agricultural products produced and processed while running a personal subsidiary plot are the property of citizens running a private subsidiary plot, and the sale of such products is not a business activity . plot itself is not registered in any way , and it is possible to carry out activities on a personal subsidiary plot from the moment of registration of rights to a land plot (either ownership rights or lease rights).
Citizens running personal subsidiary plots , in accordance with Federal Law of July 7, 2003 N 112-FZ “On Personal Subsidiary Farming,” are recognized as agricultural producers on an equal basis with farmers and agricultural enterprises.
We can provide you with the service of filling out application forms and drawing up any other legal documentation. Cost of work here Contact us!
1. What land plots can be used for personal farming?
There are two categories of land plots on which it is possible to organize personal subsidiary plots: these are land plots within the boundaries of settlements (household land plots) and land plots outside the boundaries of settlements (field land plots). Household land plots are used for the production of agricultural products, as well as for the construction of residential buildings, industrial, household and other buildings, structures and structures. Field land plots are used exclusively for the production of agricultural products without the right to erect buildings and structures on it.
2. Are there limits on the size of land plots that can be used for personal farming?
The maximum size of land plots provided to citizens from state-owned or municipally owned lands for running personal subsidiary plots is established by regulatory legal acts of local government bodies, and the maximum size of the total area of land plots that can be simultaneously owned and (or) other rights for citizens running personal subsidiary plots are established by the law of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
Part of the land plots, the area of which exceeds the specified maximum size, must be alienated by the citizens who own these land plots within a year from the date the rights to these land plots arise, or within this period the state registration of these citizens as individual entrepreneurs must be carried out or state registration of a peasant (farm) enterprise.
We can provide you with the service of calculating the amount of necessary taxes paid by a farm - LLC or individual entrepreneur-head of a peasant farm under different taxation systems , and draw up the required documentation. Cost of work here Contact us!
3. Can a citizen living in a city obtain land in a rural area to organize a personal subsidiary plot on it?
Yes maybe. But only citizens who are registered at their place of permanent residence in urban settlements are provided with state or municipally owned land plots for running personal subsidiary plots only if there are available land plots.
Accounting for personal subsidiary plots is carried out in household books by local government bodies of settlements and local government bodies of urban districts. Household books are maintained on the basis of information provided on a voluntary basis by citizens running private farms.
The household book contains the following basic information about personal subsidiary plots :
- Who runs the private household plot - last name, first name, patronymic, date of birth of the citizen who was granted and (or) acquired a plot of land for running a private household plot;
- Who else runs private household plots with him - last names, first names, patronymics, dates of birth of his family members living together with him and (or) jointly carrying out personal farming with him;
- On what land is the area of a private plot of land occupied by sowing and planting agricultural crops, fruit and berry plantings;
- How many livestock - the number of farm animals, poultry and bees;
- What is the property of private household plots - agricultural machinery, equipment, vehicles owned by right of ownership or other right to a citizen running a personal subsidiary plot.
Taxes of citizens running private household plots
According to Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation income of taxpayers received from the sale of livestock, rabbits, nutria, poultry, wild animals and birds grown on private farms located on the territory of the Russian Federation (both live and their slaughter products in raw or processed form ), livestock, crop, floriculture and beekeeping products, both in natural and processed forms, are not subject to personal income tax.
Organizing a personal subsidiary plot is a form of non-entrepreneurial activity.
Consequently, citizens who have organized personal subsidiary farming will not be payers of:
- VAT (since payers of this tax are only organizations and individual entrepreneurs),
- income tax,
- property tax (except for tax on real estate, equipment and vehicles),
- deductions from the salaries of employees (family members, in fact).
But land tax and citizen property tax (on real estate and equipment) will have to be paid .
Sales of products
Before selling your products grown on your personal plot, you need to stock up on a certificate from the local government ( head of the rural settlement ) stating that the products you are selling were grown on your personal plot . By presenting such a certificate, you are exempt from taxes .
You have slaughtered five sheep and are taking them to the city to sell in your vehicle. You are stopped by a traffic police officer. He may ask where you got so much meat and where you are going. Presenting a certificate stating that you are transporting products grown on your personal plot will save you from unnecessary explanations with the police.
You come, for example, to a sausage shop and want to sell this meat. They will draw up a sales and purchasing act with you, which will indicate your passport details and Taxpayer Identification Number (by the way, do not forget to make copies of these documents in order to give them to the buyer of your meat). And the trade and procurement act must be accompanied by the above-mentioned certificate stating that you are selling products grown by you on your personal plot.
According to the current tax legislation, the buyer does not have the right to withhold personal income tax and does not have to submit information against you to the tax office in Form 2-NDFL about the income you receive from the sale of products grown by you. But there are times when, due to ignorance of tax legislation, the buyer of your product will still file information against you with the tax office about the income received. What then? Then at the beginning of next year you will receive a notification from the tax authority that you received income based on the results of last year and did not pay tax. You will have to visit the tax office and give oral (or, as a last resort, written) explanations about the transaction. There is no need to submit any declarations, nor will you have to pay taxes.
If you decide to sell your products on the market you do not need to use cash register equipment (KKM, KKT) , since it is required for use only by organizations and individual entrepreneurs, which in this case you are not.
Conclusion : if you own or lease land plots of no more than the size established by law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, then perhaps this form of self-employment , such as organizing a personal subsidiary plot .
The undoubted advantages of such an organization are the absence of registration and the absence of taxation as such (except for land tax).
July 7, 2003 N 112-FZ Federal Law on Personal Subsidiary Farming (Adopted by the State Duma on June 21, 2003, Approved by the Federation Council on June 26, 2003)
Article 1. Legal regulation of relations arising in connection with the conduct by citizens of personal subsidiary plots
1. This Federal Law regulates relations arising in connection with the conduct of private farming by citizens.
2. Legal regulation of the conduct by citizens of personal subsidiary plots is carried out in accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, this Federal Law, other federal laws, other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, as well as laws and other regulatory legal acts of constituent entities of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them and regulatory legal acts of local governments.
Article 2. The concept of personal subsidiary plot
1. Personal subsidiary farming is a form of non-entrepreneurial activity for the production and processing of agricultural products.
2. Personal subsidiary farming is carried out by a citizen or a citizen and members of his family living together with him and (or) jointly carrying out personal subsidiary farming with him in order to satisfy personal needs on a land plot provided and (or) acquired for conducting personal subsidiary farming.
3. Agricultural products produced and processed during the management of personal subsidiary plots are the property of citizens conducting private subsidiary plots.
4. The sale by citizens running personal subsidiary plots of agricultural products produced and processed while running personal subsidiary plots is not entrepreneurial activity.
Article 3. The right of citizens to conduct personal subsidiary farming
1. The right to conduct personal subsidiary farming has the right to legally capable citizens who have been provided with land plots or who have acquired land plots for conducting personal subsidiary plots.
2. Citizens have the right to conduct personal subsidiary farming from the moment of state registration of rights to a land plot. Registration of personal subsidiary plots is not required.
3. Land plots in state or municipal ownership for personal subsidiary farming are provided to citizens who are registered at their place of permanent residence in rural settlements.
4. Citizens who are registered at their place of permanent residence in urban settlements are provided with state or municipally owned land plots for running personal subsidiary plots if there are available land plots.
5. When the lands of rural settlements are included within the boundaries of urban settlements, citizens conducting personal subsidiary farming retain the right to conduct personal subsidiary farming on land plots that were provided to them and (or) acquired by them for these purposes.
Article 4. Land plots for personal farming
1. A plot of land within the boundaries of settlements (household plot of land) and a plot of land outside the boundaries of settlements (field plot of land) can be used to conduct personal subsidiary farming.
2. A personal plot of land is used for the production of agricultural products, as well as for the construction of a residential building, industrial, domestic and other buildings, structures, structures in compliance with urban planning regulations, construction, environmental, sanitary and hygienic, fire safety and other rules and regulations.
3. The field land plot is used exclusively for the production of agricultural products without the right to erect buildings and structures on it.
4. The maximum (maximum and minimum) sizes of land plots provided to citizens from state-owned or municipally owned lands for private farming are established by regulatory legal acts of local government bodies. The provision of such lands is carried out in the manner established by land legislation.
5. The maximum size of the total area of land plots that can be simultaneously owned and (or) otherwise owned by citizens running private subsidiary plots is established by the law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation. Part of the land plots, the area of which exceeds the specified maximum size, must be alienated by the citizens who own these land plots within a year from the date the rights to these land plots arise, or within this period the state registration of these citizens as individual entrepreneurs must be carried out or state registration of a peasant (farm) enterprise.
6. The turnover of land plots provided to citizens and (or) acquired by them for running personal subsidiary plots is carried out in accordance with civil and land legislation.
Article 5. Relationships between citizens running private farms and state authorities and local governments
1. Intervention by state authorities and local self-government bodies in the activities of citizens running personal subsidiary plots is not allowed, except in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
2. Federal executive authorities, executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local self-government bodies, within the limits of their powers, exercise control over citizens’ compliance with the requirements of the law.
Article 6. Property used for running personal subsidiary plots To conduct personal subsidiary plots, a plot of land provided and (or) acquired for these purposes, a residential building, industrial, household and other buildings, structures and structures, including greenhouses, as well as farm animals, bees and poultry, agricultural machinery, implements, equipment, vehicles and other property owned by right of ownership or other right to citizens running personal subsidiary plots.
Article 7. State and other support for personal subsidiary plots
1. State authorities and local governments determine measures to support citizens running private farms in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
2. State support for citizens running private farming can be provided in the following areas:
- formation of service infrastructure (access roads, communications, water and energy supply, etc.) and ensuring the activities of private farms, promoting the creation of marketing (trading), processing, service and other agricultural consumer cooperatives;
- stimulating the development of personal subsidiary plots by creating organizational, legal, environmental and social conditions, including the provision of personal subsidiary plots and (or) agricultural cooperatives and other organizations serving them with state financial, material and technical resources on a repayable basis, as well as scientific and technical developments and technologies;
- carrying out measures to improve the quality of productive and breeding farm animals, organizing artificial insemination of farm animals;
- annual free veterinary examination of livestock, organization of veterinary care, and the fight against infectious animal diseases. ConsultantPlus: note. Clause 3 of Article 7 comes into force on January 1, 2004 (clause 2 of Article 11 of this document).
3. Personal subsidiary plots are subject to state support measures provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation for agricultural producers and carried out at the expense of the federal budget, budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local budgets.
4. State authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local self-government bodies, within the limits of their powers, develop and implement measures for the development of personal subsidiary plots and the socio-economic development of rural settlements, within the framework of relevant programs they determine the form, size and procedure for supporting personal subsidiary plots and those serving them agricultural cooperatives and other organizations.
Article 8. Accounting for personal subsidiary plots Accounting for personal subsidiary plots is carried out in non-economic books. The procedure for maintaining household books is determined by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Article 9. Entry into legal relations under compulsory pension insurance Citizens running personal subsidiary plots have the right to voluntarily enter into legal relations under compulsory pension insurance in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Article 10. Termination of personal subsidiary farming Maintenance of personal subsidiary farming is terminated in the event of termination of rights to the land plot on which personal subsidiary farming is carried out.
Article 11. The procedure for the entry into force of this Federal Law
1. This Federal Law comes into force on the date of its official publication, with the exception of paragraph 3 of Article 7 of this Federal Law.
2. Paragraph 3 of Article 7 of this Federal Law comes into force on January 1, 2004.
President of the Russian Federation V. PUTIN Moscow, Kremlin July 7, 2003 N 112-FZ
Comments: Andrey Dudkin
Many of you know. that this law has not existed since 1998 and by registering land under this category, one could vary its absence in one’s favor. Well, for example, the main thing is that it was possible to obtain permission to build on such a site...
This is where the main thing is hidden: THE STATE ORDERED EVERYONE TO LIVE ON EARTH IN A TENT FOR A LONG TIME!!! The new law clearly states that it is prohibited to BUILD ON AGRICULTURAL LAND FOR THE PURPOSE OF PERSONS EMPLOYED FOR PH. It turns out that if we want to build, then we need to ensure that private plots are located within the boundaries of the settlement, but then the payment for 1 hectare inside the settlement, as you know, is tens of times more than outside the settlement. And if now the cost of 1 hectare of private plot outside a settlement in Kuzbass is 600 rubles/ha, then what will happen if it suddenly becomes inside the settlement?
If you become Farmers (register not private household plots, but Farming Enterprises) - then everyone will have to register as entrepreneurs, which leads to reports, balance sheets and other accounting records. Which in itself will force people to give up land plots.
Thus, today in the Russian Federation there are no simple ways to obtain land plots for the creation of a Family Estate on it, except for one - obtaining such a huge plot within the boundaries of the settlement (which in itself is difficult to find). In total, there are three options left for construction on private plot lands:
1. Take land for private plots inside settlement lands
2. Turn field plots into settlement lands
3. Work with deputies and other authorities chosen by voters to defend their interests. After all, in the end, you can’t comb everyone with the same brush!!!”
It also follows from the new law that it is also forbidden to build on shares registered as a personal subsidiary plot (for example, Tula) - because These are field plots, not household plots. And those who have already bought a PAI may find themselves in a bad position if someone lays claim to their land; according to the law, they can now completely seize the land for non-intended use (construction is prohibited).
And if by some other means you managed to obtain a construction permit, then now you won’t have to challenge your case in court - the state has already decided for everyone.
What to do now - let's think together - this time the system gave us a “big surprise”.
We can provide you with high-quality consulting and information support and support for your project (including the development of competition and project documentation) when participating in state competitions for the award of grants and subsidies, as well as other types of support. Employees provide consulting services for entrepreneurs participating in this and other competitions, and advise on financial, economic, and legal issues.
Key competencies of the Company’s employees:
- The cost of possible packages of services and work can be found here. Contact us!
- consulting and information support for participants in state competitions for state support in the form of tax breaks, grants and subsidies, and other types of support,
- support of the applicant’s project in competitions of the Republic of Tatarstan and Russia,
- preparation of documentation for innovative projects,
- development of a development concept (strategy), business plan, feasibility study (feasibility study), memorandum, presentation, project passport, preparation of a package of project documentation,
- conducting market research (marketing),
- attracting investments, partners in a project, business,
- assistance from a financier, economist, lawyer, marketer.
Home construction
It is possible to build a residential building on a plot for personal farming. To do this, you need to complete paperwork.
You must have title documents for the land. They may vary depending on the specific situation:
- purchase and sale agreement, if the plot was purchased;
- if it was received as a gift, then the document of title is the deed of gift;
- the land could be inherited - in this case it will be necessary to rely on a will.
When constructing a house, a building permit must be issued.

You can build a house without a building permit, but this may cause problems in the future
It is important to consider that the final confirmation of ownership of real estate is the presence of a corresponding entry in the Unified Register of Property Rights. A mandatory requirement when entering data into it is the execution of cadastral documents.
In order for a house to be officially inhabited, a cadastral passport must be issued for it.
The final document in this case is the commissioning certificate. It can only be signed if the house is built taking into account all the necessary requirements and standards.
If a house was erected without a building permit, then in accordance with Article 9.5 of the Code of Administrative Offences, a fine in the amount of 2 to 5 thousand rubles is imposed.
In the video, the lawyer shares his experience of obtaining permission to build a house in private household plots:
Plot for private farms that can be built
Andrey, start by clarifying the permitted use of the land plot (see the cadastral passport for the land plot). According to Article 4 of the Federal Law “On Personal Subsistence Farming”, plots of private household plots are divided into two types: homestead and field. A plot of land is used for the production of agricultural products, as well as for the construction of a residential building, industrial, domestic and other buildings, structures, structures in compliance with urban planning regulations, construction, environmental, sanitary and hygienic, fire safety and other rules and regulations. A field plot of land is used exclusively for the production of agricultural products without the right to erect buildings and structures on it. If your land plot is located within the boundaries of a populated area, i.e. is a personal property, you can plan to build a residential building; if the land plot is located outside the populated area, i.e. field, it is impossible to build a residential building, its construction may end with a court decision on the demolition of the unauthorized building at the request of interested parties.
We recommend reading: Calculation of the average monthly tariff rate from the minimum wage in 2021
In other words, for the construction of a residential building on a private plot of land owned by private household plots, it is necessary to obtain a permit for the construction of a residential building, without official putting into operation until 03/01/2015, the house can be registered with the BTI and received a technical passport and registered in Rosreestr, ownership of an unfinished construction project.
Is it possible to transfer the plot to the intended purpose of private household plots?
The transfer of a land plot to private household plots is possible, but not always. Depending on the conditions:
- Territorial location of the allotment.
- General plan of the area.
In other words, if, according to the development project for a given area, the land plot belongs to territories with the type of individual housing construction or private subsidiary plots, then its transfer may be feasible. Otherwise, this is a completely futile exercise. In order to figure out what status your land has according to the master plan, you should find this plan. These are usually shown on local government websites. Find your plot using the cadastral number in the public cadastral map.
The law prohibits starting construction without permission from the district administration. But first of all, before contacting the municipal administration, establish an area for the upcoming construction that meets sanitary standards.
If you neglect the terms of the law and build housing without obtaining permission, in the future it will be possible to legalize it only through the judicial process. This will require extra expenses and is not always possible. If violations are discovered, the court will order the building to be destroyed.
What else should the owner of private household plot know?
If you sell the products you have grown on the market, the use of cash register equipment is not required - only an organization or individual entrepreneur, which you are not currently a member of, must have it.
Hence the conclusion - if the entire set of land plots in your ownership or lease does not exceed the size established according to the law of the subject of the Russian Federation, then this form of self-employment - in the form of organizing private household plots - can become the best option, since one of its undoubted advantages is the absence of registration and taxation .
At the same time, state bodies and local administrations are prohibited from interfering in the activities of the leading private household plot of the citizen, except in cases provided for by law. It is their authority to monitor the compliance of such citizens with legal norms.

How to get a subsidy for private household plots
Pursuing a social protection policy, the state supports low-income citizens by allocating them funds for development within the framework of a social contract for the development of personal subsidiary plots. If certain conditions are met (income per family member is less than the subsistence level, a legally allocated land plot and no debts to pay for it, the presence of three or more children), a citizen can apply to the social protection authorities with a request to allocate funds for the development of private household plots.
The size of the social contract is established by local authorities. Such subsidies can be allocated no more than once every three years and spent on the purchase of:
- Pets, poultry, bees or feed;
- fertilizers or planting material;
- equipment, equipment for cultivating land and caring for animals.
For its part, the participant in the social contract is obliged to:
- Develop and present a plan for the use of allocated funds;
- use the allocated money for its intended purpose, without deviating from the plan;
- insure property purchased using social contract funds;
- carry out plan activities and provide reports.
What can be done on the lands of private household plots - popular ideas for business
Personal subsidiary farming is an excellent start for a business, an opportunity to try your hand at the agricultural industry without large investments and significant losses if you realize that the chosen direction is not suitable for you.
So, for what types of agricultural production do our compatriots open this form of business?
Growing crops
Grow any type of vegetables, herbs, berries and fruits in your yard, or all of these at the same time, but in small quantities.
On your territory, you are free to make a greenhouse, grow mushrooms, cucumbers, onions, that is, what is in demand in your area and sells well.

Private household plots may not be very large; this is an excellent option for starting a business without the risk of major losses
Greenhouse installation
Greenhouse growing of vegetables, berries, and herbs is a way to generate income year-round. On your yard or rented area, you have the right to build one or more greenhouses for growing vegetables for sale and for personal consumption.
Poultry breeding
The local area will accommodate a spacious poultry yard for chickens, ducks, geese, and turkeys. Poultry is a source of fresh eggs, meat, and young animals for sale.
Animal keeping
A farmstead of 15 acres in size allows you to simultaneously keep 10-12 heads of cattle, 10 heads of pigs or a herd of sheep of 60 heads, up to 50 cages with rabbits, and there will still be room for a vegetable garden and garden. Such a barnyard will provide you with milk, fresh meat, young livestock for sale, wool, sheep and rabbit skins.
Organization of an apiary
According to the rules for organizing an apiary, no more than 10 bee families can be placed on 3 acres, therefore up to 30 families can be accommodated on 15 acres. This number of bees will provide you with honey, beeswax, beebread and other bee products.
According to Federal Law No. 112 of July 7, 2003, private household plots are classified as non-profit activities if only members of one family work in it.
Is it possible to build a house in the TSH-1 and TSH-2 zones
Let’s say you want to order a new plot of land for private household plots and rent it. The TSX-1 and TSX-2 zones are very convenient for me. I find on the Internet that in TSH-2 private household plots and the construction of residential buildings are allowed, but the Administration says that this is only possible in TSH-1, although nowhere is it written that residential buildings are allowed in TSH-1. Let's figure it out.
Private household plots are a form of non-entrepreneurial activity for the production and processing of agricultural products. VRI LPH involves the construction of an individual railway on such a site, taking into account the requirements of urban planning norms and rules. I am opening the PZZ of my district - The purpose of allocating the zone is to preserve and develop existing agricultural enterprises and the infrastructure that supports them, in order to prevent their use for other types of activities BEFORE CHANGING THE TYPE OF THEIR USE in accordance with the master plan of the settlement and the rules of land use and development. I open page 112 - Basic and conditionally permitted types of use of land plots and capital construction projects: The main types of permitted use are for the placement of personal subsidiary plots.
Thus, I believe that the Administration did not deceive me. However, I will warn you that in the absence of a well-functioning legal mechanism for regulating changes in such zones and their registration in Rosreestr, you may encounter certain difficulties associated with the work of the administrative body and delaying time.
What is a peasant farm?
Issues related to the activities of a peasant (farm) enterprise are spelled out in Federal Law No. 74-FZ dated June 11, 2003. This type of entrepreneurship includes associations of citizens who are related or have other relationships. They should be connected by the presence of common property, joint work on production, processing, and sale of farm products.
According to Part 2 of Article 3 of the Law, members of a peasant farm can be not only relatives of its head. He has the right to hire people who are not related to him, and there can be no more than five people.
The property of a farm is considered to be everything that is necessary for the implementation of its activities:
- land plot;
- buildings for various purposes;
- poultry, livestock;
- agricultural machinery;
- inventory, etc.
Property, as well as products and income from farming are common to all members of the peasant farm, i.e. belongs to them on the principle of shared ownership.
To carry out farming activities, plots for peasant farms are allocated. When using it, it should be taken into account that only those buildings that are necessary for farming can be erected, for example, household buildings for storing equipment, products, for housing poultry, livestock, etc. Residential construction on such sites is prohibited. Here you should also be guided by Art. 85 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, which allows residential development only on the lands of settlements and plots of peasant farms do not apply to them.