Article 81 of the Labor Code provides a complete and detailed list of reasons why an employment relationship with an employee can be terminated at the initiative of the employer (clauses 1-3, 5-6, 11-12 - suitable for all categories of workers, and clauses 4.7 -10.13 – in relation to certain groups of employees (management staff, chief accountant, teachers, educators, etc.)). Labor legislation also guarantees that no employee can be deprived of his job without reason.
In this article we will provide detailed step-by-step instructions for dismissing an employee.
The management of an organization is faced with a difficult task when the decision to dismiss has already been made - how, in fact, to remove an employee from his position painlessly and without consequences for both parties, because the number of legal appeals from dissenting dismissed employees is currently very large.
And most cases are resolved in favor of the employee, which results in additional financial losses for the company. Therefore, the employer will have to stock up on knowledge, patience and time in order to carry out the procedure for terminating the employment relationship as competently as possible.
Dismissal at your own request
Before dismissing an employee under the article, you need to advise him to separate “amicably”, namely, offer to write a statement of his own free will (clause 3 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is necessary to use all your art of persuasion so that the employee himself takes a pen and writes the required statement. It is best to push the employee to take this step by giving him the right motivation.
You can, for example, say that the company cares about his future and upon dismissal the best recommendations will be presented, and other employers will more favorably accept a new employee who is dismissed of his own free will rather than under an article. Some companies go further and even issue an additional bonus for an amicable separation. The main thing is not to incite conflict or start a quarrel, which, in the future, can work against you.
If an employee refuses to write a statement , then in this case you can push him to do so, but here you should be careful and not go beyond the bounds of decency, so that the actions are not subsequently qualified as bullying of the employee by the employer and forced dismissal. From this moment a very delicate game begins.
For example, to speed up the decision-making process, you can deprive an employee of a bonus, or catch him in a disciplinary violation and issue an order, warning him that a repeated violation will be entered into his personal file. Usually, after reading the first warning, the employee quickly writes a statement on his own.
Dismissal of an employee without working at his own request
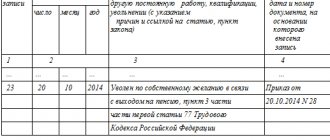
To dismiss an employee on your own, you need to issue an order. The order is based on the submitted application and includes its details. As the basis for dismissal, indicate - clause 3, part 1, art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Submit your dismissal order no later than your last day of work. But keep in mind that the accounting department must prepare for the dismissal of an employee and make all the necessary payments and calculations. Therefore, it is better to issue an order in advance. Together with the order, a note-calculation is drawn up. Familiarize the resigning employee with the order; if it is impossible to obtain his signature, make an appropriate note. Before issuing it, make a note of dismissal in your work book indicating the article.
Even if the employee has not worked the required period, he retains all rights. On the last working day, it must be calculated, wages, vacation pay and compensation, if any, must be issued, and all documents must be submitted. The employee also retains the right to appeal to the prosecutor's office or to court if management violates his rights.
For all days of delay in payment, management must pay the average salary. The work book must also be returned on time, otherwise you will have to compensate for material damage for each day the book is retained, because its absence does not allow you to get a new job. The date of dismissal is entered in the book as a number when the employee receives it. If the employee did not come for the book and refused to receive it by mail, the employer has no responsibility.
Dismissal of an employee
So, the hardest part is over and the paper is written. What's next?
- From the moment the application is written, the employee is given two more weeks to work, but by agreement he can leave earlier.
- An order to terminate the employment contract is issued, which is certified by the signature of the manager.
- The employee gets acquainted with the order, putting his signature on it.
- On the last day of work, a record of dismissal is made in the work book and on what basis it was made.
- Full payment is made to the employee.
- A copy of the work book is made for the archive (personal files are stored in the archive for 75 years).
- The book is issued to the employee on the day of dismissal.
- An entry is made in the Book of Movement of Labor Books.
The main rule of amicable termination of employment relationships is to give the employee the right to be the first to leave of his own free will, since all other methods can negatively affect the employee’s future work activity, as well as the reputation of the enterprise in the event of litigation.
What is the danger of dismissal without the employee’s consent?
It happens that an employee does not want to write a statement of his own free will and leave peacefully. The entrepreneur has to look for an article for dismissal. An entry in the work book becomes a stigma that makes it difficult to find a new job. And the person devotes himself to the showdown: he finds a lawyer, complains to the labor inspectorate, the prosecutor’s office and the court.
If the employee is dismissed due to mistakes, they will be returned. The employer will pay wages during the dispute under Art. 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and a fine to the state under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. And for the dismissal of a pregnant woman and a woman with children under three years of age, a criminal case is opened under Art. 145 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
It's safest to do this. Dismiss for a real reason and correctly draw up personnel documents.
Dismissal of an employee is legal and without consequences
If, contrary to belief or out of principle, the employee never wrote a statement, but it is necessary to part with him, then the following dismissal mechanism is activated. Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation takes into account the reasons why an employer can legally part with its specialist.
Let's consider cases that fit most categories of workers.
- The liquidation of a company on a voluntary or compulsory basis, or the termination of the enterprise’s activities occurs as a result of a bankruptcy procedure. The same applies to individual entrepreneurs.
- Staff reduction.
- Incompetence of an employee based on certification results or lack of qualified knowledge, illiteracy.
- Health status.
- Availability of disciplinary action; failure to fulfill labor obligations assigned to the employee.
- One-time gross violation of one’s labor functions.
- Loss of trust from management.
- Committing an immoral act that is contrary to the principles of the position held. As a rule, teachers, educators, and pedagogues are fired under this item.
- Actions of management and accounting that resulted in financial and property losses for the company.
- Providing knowingly false and forged documents when applying for a job.
Let's take a closer look at the most popular items.
Dismissal of an employee upon liquidation of a company
Liquidation of a company can be either voluntary or forced by decision of the relevant authorities. A company can also close because it is declared bankrupt.
In this case, the basis for dismissal is considered to be clause 1 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The process of terminating an employment relationship occurs as follows:
- Two months before the upcoming dismissal, the manager notifies employees of his decision . A notice or notice is drawn up and presented to employees under their signature. If the employee refuses to sign, then a corresponding note is made on the notice.
- At least two weeks before the first dismissal, the employer must notify the Employment Center.
- Then the corresponding reports are submitted to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Federal Insurance Service.
- All missing contributions for employees are paid within 15 days.
This clause allows the dismissal of all employees, including women on maternity leave, people with health problems, disabled people, and people with family burdens.
Calculation when leaving at your own request
Full payment of the employee is carried out on the last working day. All payments claimed by the former employee are calculated:
- monetary remuneration for the last month or period worked (depending on the internal policy of the organization);
- compensation for unused days of annual paid leave;
- additional payments provided for in the employment contract (severance pay, bonuses, etc.).
Payments must be made no later than the next day after dismissal.
Calculation procedure
Calculation upon termination of employment relations is carried out in accordance with Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The organization takes the following actions:
- an order is issued to remove the resigning employee from work;
- an entry is made in the work book (date of dismissal, reason for leaving, information about the contract that is being terminated);
- the employee is calculated.
ATTENTION! Entries are made with a blue ballpoint pen, legibly and without abbreviations.
Dismissal of an employee due to staff reduction
Forming a staff and normalizing the number of employees of an organization is the right of the manager. He recruits as many workers as he sees fit. In the event of a trial, the judge does not have the right to challenge the appropriateness of the manager’s decision, but is obliged to check whether the reduction was actually made or not.
When staffing is reduced, priority in preserving jobs is given to more experienced and highly qualified employees. Pregnant women, as well as women on maternity leave, cannot be fired.
The dismissal procedure is identical to that described in the previous paragraph.
Dismissal of an employee for health reasons
When hired for a position, an employee has the right to present to the employer a medical report on his state of health.
It seems that everything is clear with this point, but there are also pitfalls here, due to which the dismissal of an employee will be unlawful, namely:
- Temporary incapacity for work, for example, sick leave.
- Having a chronic disease.
- Disability.
If all this does not in any way affect the quality of the work he performs, then it is impossible to dismiss an employee on this basis. Otherwise, the employee’s calculation will be legitimate, for example, if a person’s existing disease poses a threat of harm to the health of other employees.
Dismissal of an employee based on certification results
Removal from work on this basis must be confirmed by the results of a previously conducted certification at the enterprise.
The following categories of employees are subject to mandatory verification:
- Scientific workers.
- Prosecutor's office employees.
- Customs officers.
- Heads of state unitary enterprises.
There is no required form for certification. This could be a test or an interview. Members of the certification commission must be competent in the issue being tested and be able to fairly assess the employee’s knowledge. Management is not required to be a member of the commission.
The result of the certification is issued in a separate order.
If an employee fails at the first certification, then it is worth giving him a second chance. If the second time is also negative, then it is best for management to offer the employee another, less paid and prestigious position. If a person refuses the offer, then he can be safely fired.
A person can challenge his dismissal in court – and even win in court! – in the event that the employer decided to conduct the exam suddenly, without familiarizing the employees with their plans. Then according to Art. 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the results are declared invalid.

Dismissal for violation of labor discipline
If the dismissal of an employee occurs under paragraph 5 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then one important condition must be met - the employment contract must specify the start and end times of service, otherwise it will be very difficult to record the employee’s lateness to his workplace.
- All tardiness must be accurately recorded on the Time Sheet.
- If delays become systematic, a disciplinary commission is convened.
- An act is drawn up.
- It is necessary to obtain an explanation from the latecomer. If it is not there, or the employee refuses to provide an explanation, then a statement of refusal is drawn up and certified by the signatures of members of a commission consisting of 3 independent persons, for example, a security guard, a cleaning lady and a secretary.
- Based on the report, a reprimand is issued to the late employee.
The only problem here is that a remark cannot be sufficient grounds for dismissal, so the remark should be turned into a reprimand. This is where you can use the golden rule - two comments and a reprimand followed by dismissal.
All documents (memos and comments) must be carefully selected and collected so that in the event of a trial, you do not lose face and prove the employee’s irresponsible attitude towards his duties. Witness testimony will also not be superfluous.
The opinion of the trade union committee should be taken into account if the dismissed employee was a member of it.
How to file a voluntary resignation

The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not regulate the termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employee. However, there is a certain algorithm:
- A free-form application is drawn up with the wording “dismissal of one’s own free will.” The document must be presented to the HR department or the head of the organization.
- The employee works for a two-week period. This time is legally provided to the company to find an employee for the vacant position.
- An order is issued to remove the employee from official duties in the unified form T-8.
- The employee is given a work book and a full payment, including the remaining salary, compensation for unused vacation days and other required payments.
When dismissing on his own initiative, a citizen has the right to request a copy of the enrollment order, a 2-NDFL certificate and other necessary documents.
Terms of dismissal
The law requires workers to give fourteen days' notice before leaving the workplace. This period is counted from the date of writing the relevant application.
The employer does not have the right to increase the period of compulsory service. However, by agreement of the parties, this period may be reduced or canceled.
ATTENTION! According to article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation No. 127, two weeks of work can be used by an employee as official leave or sick leave.
If a citizen is in an organization on an internship or probationary period, he must notify the manager of his resignation on his own initiative three days in advance. If the director resigns at his own request, he should be notified 1 month before leaving office.
Dismissal for a single gross violation
Clause 6 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation makes it very clear what can be considered such a violation:
- Absenteeism.
- An employee coming to work in a state of drug, alcohol or toxicological intoxication, and it does not matter whether he reached his workplace or not..
- Disclosure of trade secrets.
- Wasting, stealing or stealing, damaging or destroying business property.
- Violation of labor safety rules, which resulted in an accident, breakdown or catastrophe, or created a threat to their occurrence.
The most common reasons are the first two points.
You can dismiss an employee if he was absent from the workplace for 4 or more hours without a valid reason. A good reason is a subjective category, which is assessed and determined by the manager. Mostly this is a fire, illness of a close relative, accident, or broken down vehicle.
When starting dismissal due to absenteeism, it is better for the employer to have several memos and comments to the employee from management or colleagues. In the event of a trial, they will be very useful, because, as practice shows, the court is more likely to decide the case in favor of the employee if there have been no complaints against him from management before and everything is in order with his discipline.
It’s another matter when a violation of labor regulations is not committed for the first time, but there are many comments in the personal file.
An employee’s absence from work due to suspension from work or as a result of being prevented from working cannot be considered absenteeism. Also, absenteeism does not mean refusal to work by an employee who is at the workplace.
The relationship is terminated within one month from the date the offense was recorded.
It will be more difficult to prove that an employee is intoxicated, but even the appearance of an employee at the place of duty in this form is a valid reason for terminating the employment agreement with him.
The action algorithm in this case is as follows:
- The most reliable way to determine the state of drug, alcohol or toxicological intoxication is a medical examination by a narcologist. But not every employer can afford such conditions, so in the usual case, a report is drawn up recording the appearance of a drunk person at the workplace.
- The employer is obliged to remove a drunk employee from the production process on the same day, otherwise the employer loses the right to further dismiss the employee under clause 6 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- An order signed by the manager is issued to bring the employee to disciplinary liability.
- The employee gets acquainted with the order and signs it.
Next, you need to act as described in paragraphs 4-8 when resigning at your own request.
For absenteeism and alcohol - clause 6 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Violations of discipline can be serious. For one rude thing you can be fired immediately. This is also a disciplinary sanction. But there is no need to save the previous ones.
All gross violations are recorded in paragraph 6 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. These include absenteeism and alcohol or drug intoxication at work.
A gross violation is documented in the same way as a simple violation. A memo or act, explanation, order of dismissal no later than a month from discovery.
Absenteeism
Absenteeism is when a person does not come to work or is absent for four hours in a row.
There is no good reason for absenteeism: illness, accident, death of a relative. Time off and vacations without the request of the manager are also considered absenteeism. This is explained in paragraph 39 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2.
Example of absenteeism:
A specialist at a bank on the eve of a working day at 11:30 pm asked the director for a day off via a WhatsApp message. Silence was considered consent. When she returned to work, she was given absenteeism and fired.
The specialist appealed the absenteeism, but the court did not return the job.
The time off was not approved, which means it’s absenteeism. There is an absence from work report and a memo from the director, an explanation, an order. We met the deadlines. Dismissal for absenteeism is fair and documented correctly - case 33-12011/2019.
Intoxication
Alcohol and drug intoxication must be proven.
The act with witnesses is suitable. The court believed the witnesses that the store clerk was drunk behind the counter - case No. 33-5383/10.
The stronger option is a breathalyzer or a doctor’s report. For example, a breathalyzer helped in a dispute about the dismissal of a trolleybus driver - case No. 2-3639/2018. There is a possibility - take a test or call a doctor.
Dismissal due to loss of trust
The employer needs to take into account that under this clause, employees directly responsible for the storage of monetary and material assets serving them may be removed from their positions. Even when establishing the fact of extortion, bribery, theft and other illegal actions.
Therefore, employees under whose responsibility material, commodity and monetary values were not entrusted should be dismissed under clause 7 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is impossible. The employer must prove the fact of theft or other violation with documents, for example, provide photo, video or audio evidence, or witness testimony.
Dismissal at will without work if the employer violates the law
An employee who notices any violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on behalf of the manager, and also proves this, has the right to apply for dismissal of his own free will without working off. But here a small snag arises: how can you prove an illegal action on the part of an entrepreneur?
It is in this matter that you will be helped by the involvement of internal authorities for a thorough check in order to ensure the authenticity of the accusation. In this situation, paragraph 22 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation will help, where it is stated in clear language that it is a mandatory action to prove the charges already mentioned to the authorities, otherwise you can get punished for false information.
In what cases must an employee set the period of time worked?
- The head of a particular company violated the labor code of the Russian Federation.
- The employee is disabled (most often employees with some degree of disability).
For the first point, it is always worth remembering one thing , the meaning of which is that you first need to establish the found violation at the legislative level, otherwise nothing will work, since without evidence Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation cannot be confirmed.
The second point tells us that the employee is unable to continue his legal activities due to health reasons or the instructions of the attending physician; there is no other way. If your doctor has prescribed this, you should attach a copy of this document.
Dismissing an employee: solving the problem peacefully
Summarizing all of the above, we can draw one important conclusion: no matter how much you want to fire an employee, even if you have enough grounds in your hands, always keep a cool head and sober thinking. Emotions are your worst enemy in this matter.
- Always reserve the right for the employee to leave on his own and in every way encourage him to resign on his own initiative.
- Complying with all formalities, preparing and filing all documents correctly is not as easy as it might seem at first.
- A dismissed and offended employee can contact regulatory authorities, who will conduct an on-site inspection based on his statements. In addition, an employee may defect to competitors or divulge trade secrets.
- If the case goes to court, then for the duration of the trial (from six months to two years), the court may reinstate the plaintiff in his position so that he has the opportunity to earn money during this time. As a result, the staff will again have a person who undermines production and labor discipline.
- If you lose, you will be responsible for additional unplanned expenses, which can be quite significant. Salary for forced absence - once. Moral compensation - two. Legal costs - three. Services of lawyers and lawyers - four. Severance pay and compensation that could be paid upon dismissal on one’s own initiative are much less than the amount received.
Therefore, it is best for both parties not to bring the matter to court and resolve everything peacefully.