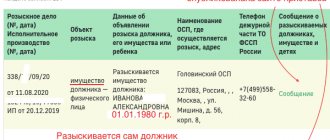
A writ of execution is a document issued by a judicial authority after the judge’s decision has entered into force. The initiator of its issuance is usually the plaintiff in the case. In some cases, for example, when collecting funds from the budget, the document is sent directly to the judicial authority for further execution.
A writ of execution is the basis for FSSP employees to initiate enforcement proceedings, within the framework of which debt collection is carried out. Current legislation provides bailiffs with an extensive range of powers, which is constantly expanding. Therefore, there is nothing surprising in the relevance of the question of whether it is possible to challenge a writ of execution before or already during the work of the bailiffs? The answer is contained in the article.
Grounds for challenging a writ of execution
Current Russian legislation gives a clearly negative answer to the question of whether it is possible to appeal a court's writ of execution. The fact is that it is not the executive document that needs to be challenged, but the court decision on the basis of which it was issued.
It is important to understand that there must be serious reasons for this. In relation to civil cases, they are listed in the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, adopted after the signing of No. 138-FZ of November 14, 2002. The version of the document approved on April 24 of this year is currently in effect.
In accordance with the provisions of the Code of Civil Procedure, the grounds for challenging a writ of execution in court are divided into three categories. The first includes the following:
- incorrect interpretation by the judge of the circumstances of the case;
- lack of factual evidence;
- obvious discrepancy between the decision and the circumstances of the case;
- incorrect application of the provisions of domestic legislation.
The second category includes grounds relating to the use of substantive or proprietary law. These include the application of laws that are inappropriate for the particular circumstances of the case or that were misinterpreted by the judge.
The third group of grounds for challenging a court decision includes:
- illegal composition of the court;
- failure to notify the parties of the appointment of the trial;
- violation of the rules for conducting a court hearing, for example, in terms of presenting the circumstances of the case in a language understandable to the defendant;
- incorrect execution of the protocol or lack of a timely completed document;
- violation of the procedure for making a court decision.
It should be noted that it is almost impossible to independently answer the question of whether it is possible to challenge the receipt of a writ of execution and what are the prospects for the case. This is due to the complexity of the legal framework on the topic under consideration and the need to take into account many factors. Therefore, you should entrust the study of the circumstances of the case to professionals who have both a sufficient level of knowledge and extensive practical experience in such work.
What the law says
It is necessary to distinguish between the statute of limitations for presenting writs of execution for collection and the period during which bailiffs are obliged to ensure repayment of the debt. Here are the procedural points contained in Law No. 229-FZ:
- the deadline for submitting a writ of execution for forced collection is 3 years from the date of entry into force of the judicial act;
- bailiffs are obliged to initiate enforcement proceedings within 3 days at the request of the claimant;
- 2 months are given to carry out enforcement actions, during which the FSSP specialist is obliged to seize accounts and property, begin to withhold and sell.
In practice, everything works much more complicated. The deadline for execution almost never falls within the 2 months required by law. However, the bailiff is required to ensure payments under the writ of execution if a one-time deduction is not possible. for this purpose, documents will be sent to the debtor’s place of work or service for regular deductions from earnings, or forced sale of assets will begin.
The procedure for challenging a writ of execution in court
The procedure for appealing a court decision involves the sequential implementation of the following actions:
- Establishing the grounds for challenging the judge's verdict. In this case, the peculiarities of a particular proceeding and whether the case is classified under civil, arbitration or criminal law are taken into account.
- Drawing up a statement of claim and filing it with a higher court. An appeal is sent directly to the judicial body that made the contested decision, and a cassation complaint is sent to a higher organization.
- Confirmation of the applicant’s position with a set of documentary evidence.
- Participation in proceedings ordered by a higher court.
Payment term
According to the general terms, debts with individuals and legal entities (LLC, JSC, KPC, etc.) will be executed. This includes debt on loans, payment of compensation from an insurance company, and repayment of debt for housing and communal services. There is a special deadline for receiving money:
- in disputes with a budgetary institution, since the money will be transferred by the Treasury (3 months are given for settlement with the claimant);
- according to administrative decisions, including the repayment of a traffic police fine (the statute of limitations will be 2 years, and the debtor is given 60 days to voluntarily pay the sanction);
- in cases related to the bankruptcy of an organization (the period for receiving funds will depend on the actions of the manager and the volume of creditors’ claims).
When making a decision, the bailiff is obliged to indicate the deadline for payment on a voluntary basis. It can be up to 5 days, during which FSSP specialists have the right only to seize property and accounts. As soon as 5 days have passed, interim measures may be introduced and forced debits from bank accounts.
The timing of collection under a writ of execution by bailiffs also depends on the actions of the claimant. If, when submitting an application to the FSSP, you provide the most detailed information about the debtor, his place of work, and the availability of property, then the process of seizure and sale of assets will go much faster. Our lawyers will provide assistance in correctly preparing documents for the FSSP.
Concept
This document is understood as an official standard form with special watermarks and seals, containing information about the court decision, details of the court document and the name of the court.

Based on this sheet, the claimant receives the right to demand from the debtor the fulfillment of the obligations imposed by the court. The writ of execution is drawn up in the same court where the decision was made. It is issued only after the court decision has entered into legal force. Since after a decision is made, the parties always have the opportunity to challenge it. And if an appeal is filed, the case is sent back for re-examination by a higher court. In this case, after the decision is made by another court, a new writ of execution will be drawn up.
However, there are cases when this document is issued immediately. Such cases usually include lawsuits regarding decisions on alimony, reinstatement, and other matters that are usually not contested.
The right to receive a writ of execution belongs to the claimant himself, as well as to his authorized representative if he has a notarized power of attorney.
Deadlines for issuing a writ of execution
In order to receive this document, several conditions imposed by law must be met:
- Wait until the court makes a decision in favor of the plaintiff or until both parties approve the relevant agreement.
- Wait until the deadlines set by law for the defendant to file a corresponding complaint with the court have passed or until he is officially denied the right to file a complaint.
- After all this, you need to go to court with a request to issue a writ of execution.
Important fact -
A writ of execution is issued by court decision. But not only based on the results of the work of arbitration or even civil. It can also be obtained if the plaintiff applies to arbitration. Also, the right to receive such a document is available as a result of acts and agreements that are drawn up and signed by foreign organizations or international associations.
How to obtain a writ of execution based on a court decision in a civil case: procedure and deadline for issuance
After considering the case, the appeal and cassation returns its materials to the court that considered it at first instance. Application for the issuance of a writ of execution According to the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, on the basis of Article 428, you can obtain a writ of execution from the court immediately after a court decision is made, if this decision requires immediate implementation. Judicial acts of arbitration courts are enforced after they enter into legal force, with the exception of cases of immediate execution, in the manner established by the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws regulating issues of enforcement proceedings.
Return of the writ of execution and enforcement fee
After the writ of execution is executed, it is returned to the claimant.
If the debtor, in fulfilling his obligations under the writ of execution, has committed a delay, then in this case the claimant can demand payment for the use of someone else’s funds, which increases the amount of his obligations.

The debtor will have to pay the enforcement fee
The debtor pays under the writ of execution not only the amount of debt to the collector, but also the amount of the enforcement fee, i.e. duties in the amount of 7% of the debt amount.
In this case, the amount of the fee cannot be less than 1 thousand rubles. The court may reduce the amount of the fee, taking into account the financial situation of the debtor.
Until the execution fee is paid, the obligation will not be considered completed.
Some writs of execution are returned to the claimant unexecuted
For example, in cases where the bailiffs cannot identify any material and monetary assets belonging to the debtor.
This does not mean that the collector does not have the right to turn to the bailiffs again, but in this case, you need to wait 6 months and try to collect the debt again.
When can a writ of execution be returned to the court office?
There are cases when bailiffs return the writ of execution to the court without opening a case on enforcement proceedings. This happens in the following cases:
- If the debtor has no source of income;
- If the debtor has no property and no bank accounts are opened.
Bailiffs can return received documents within 3 days from the date of their receipt. Repeated contact with the bailiff service is possible after 6 months from the date of return of the package of documents. The duration of the suspension is subtracted from the validity period, i.e. the validity period is counted again.
It should be remembered that the number of repeated applications is unlimited and the validity period of the writ of execution is not counted.
How to present a writ of execution to the bailiffs?
There are times when there is no need to contact bailiffs. This usually occurs when the debtor voluntarily decides to pay the debt. However, if this does not happen, then the plaintiff can file the document during the entire period of its validity.
Initially, the plaintiff should submit an application to initiate enforcement proceedings to the bailiff service. It is also necessary to present documents obtained during the trial.
Bailiffs must make a decision on opening an enforcement case within 3 days, and only from this moment the validity period of the writ of execution begins to be calculated.
The bailiff has the right to refuse to reopen the case. This may happen for the following reasons:
- If errors, typos or inaccuracies in facts are found in the received documents. In this case, the plaintiff must again go to court for new papers and only after the judge makes a decision to contact the bailiff again.
The validity period of the writ of execution begins 3 days after the bailiffs receive a new package of documents.
The production process itself can last about 2 months. However, there are cases where the deadline may be changed. This happens in the following cases:
- If the validity period of the writ of execution is fixed on the document itself;
- If one of the bailiffs instructed the other to perform a number of enforcement actions. Thus, it is given about 15 days to complete. In this case, the period begins to be fixed from the moment the instructions are transmitted.
In addition, upon receipt of the writ of execution, the bailiff must make a decision to reinstate the debtor to his previous place of work. This must be done the next day after the bailiff receives the writ of execution. Also, if a writ of execution is received on the basis of a claim, then all demands must be fulfilled the next day.