Sliding work schedule
ATTENTION! An additional order, which is usually issued to attract employees to work on holidays, is not necessary in this case: its role is performed by a signed agreement on a sliding schedule or its establishment under an employment contract.
Some enterprises, for objective reasons, cannot organize their work in such a way as to provide employees with days off on the same days. Then you have to change the work schedule for the entire staff or specific employees. One option could be sliding mode.
What is rest time?
According to the Labor Code, all time a person is free from work is rest time. However, this is only true for working citizens. The duration of rest periods can vary - from a few minutes to a month .
Rest time according to the Labor Code is determined taking into account the provisions of Chapters 17 - 19. Moreover, in Art. 107 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation it is divided into:
- Breaks within the working day are short intervals that are provided to the worker for meals and other needs. Their duration ranges from half an hour to 2 hours. They can be included in working hours if the employee does not leave the organization due to objective reasons (technological process, distance from the city, specifics of the industry, etc.).
- Everyday rest - periods before and after work during the day. Does not have clear boundaries, depends on the operating mode. If the work is daily, there may be almost no work.
- Weekends are free days . By law, their duration is at least 42 hours. Usually provided on a contract basis. With a sliding schedule, they may include weekdays; in other cases, Sunday and the adjacent 1 day before or after it.
- Holidays - for most enterprises these are 14 days a year, which are established by the legislator. These include winter holidays (and Christmas), Defender's Day and Women's Day, May holidays, Russia Day in June and National Unity Day in November.
- Vacation time is usually 28 days or more, which can be taken consecutively or intermittently. Those who work in hazardous conditions, with heavy loads or in low temperatures are also given additional leave. Unlike the main one, it can be obtained not with time, but with money.
You can also take a vacation for personal reasons. However, it is not paid. The number of administrative days provided is established by agreement between management and the worker and cannot exceed the limit established in the collective agreement.
Additional agreement to the employment contract work schedule 2 through 2
Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If, due to the presence of vacancies in the organization, the employer needs additional labor, then labor legislation allows the use of workers on a part-time basis. In this case, one should be guided by the provisions provided for in Art. 98 and ch. 44 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Part-time work is understood as the performance by an employee of other regular paid work under the terms of an employment contract during free time from the main job with payment in proportion to the time worked with restrictions established by labor legislation. The introduction of summarized recording of working hours in the absence of a sufficient number of employees is unlikely to help solve the problem filling vacant places. This is due, for example, to the fact that shift schedules will have to be developed and approved taking into account normal working hours (i.e.
Financial issues The new provision will be in effect from the moment the additional agreement is signed. Accordingly, all calculations under the amended rule will be made from this date. Important nuances Remember that p Reflection in the time sheet The relevant changes must also be reflected in the work period sheet in order to determine how to correctly calculate wages.
Changes by agreement of the parties, if the working hours are established by the employment contract
The working hours can be changed in two ways: either by agreement with the employee ( Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ), or by the employer unilaterally if there are appropriate grounds ( Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ). Let's take a closer look at them.
By virtue of Art. 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, changes in the terms of an employment contract determined by the parties are allowed only by agreement of the parties, concluded in writing. This method is applicable when the working hours clause is included in the employment contract. Moreover, it does not matter whether the employee’s working hours differ from those established by the PVTR or not.
If employees agree to change the terms of the employment contract, an additional agreement must be concluded with each of them, in which the new working hours must be indicated. Here is an excerpt from the agreement.
| ... 1. State clause 1.4 of the employment contract in the following wording: “The employee is set working hours from 10.00 to 18.00 with a break for rest and food lasting 45 (forty-five) minutes from 13.00 to 13.45.” 2. This agreement comes into force on January 13, 2015. |
Additional agreement sliding schedule
3. The additional work assigned to the Employee will be carried out within ________ months by combining professions (positions) without exemption from the main work determined by the employment contract. 4. For additional work performed under this additional agreement, the Employee receives additional payment in the amount of ________ (________________________) rubles per month.
5. This additional agreement comes into force from the moment it is signed by both Parties and is an integral part of the employment contract No. _____ dated “__”________ ____. 6. This additional agreement is drawn up and signed in two copies having equal legal force, one of which is kept in the Employer’s files, the other is transferred to the Employee.
We recommend reading: Smartphone code for OKOF in 2021
Additional agreement on the transition to a rotating shift schedule
If employees cannot be provided with normal daily work hours, then in order to accurately account for working time, we recommend using summarized working time recording (). The working week with days off on a staggered schedule, as well as the use of summarized recording of working hours, must be recorded in the internal labor regulations.
Employer: __________________________________________________________, address: ___________________________________________________________________, INN/KPP ________________________/__________________________________________, r/s _____________________________ in _______________________________________, BIC ___________________________________.
A little theory
An example of a staggered work schedule is the organization of work for guards - on weekdays the premises only need a security guard at night, but on general weekends his presence is required 24 hours a day. Taking into account the existing standards for the ratio of working and free time, it is rational to schedule employees’ trips to work in advance and immediately for a long period of time (but not more than 1 year). What does flexible work schedule mean? This is a work regime in which floating weekends must be arranged in the calendar taking into account the mentioned standards, so that there is no overtime. The most commonly used schedule is 2 working days every 2 days off. This employment system is regulated by Articles 100 - 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and local regulations of the organization. It must be prescribed in the internal labor regulations of the organization (ILR).
How to include a staggered schedule in an employment contract
The employment contract should also describe the procedure for familiarizing the employee with the work schedule. For example, “ the employer is obliged to familiarize the employee with the work schedule for the next accounting period, against signature, 5 calendar days before the introduction of the schedule
».
The named operating mode is not shiftable. The fact is that during shift work, the same job duties are performed by different employees (a group of employees) in two, three or four shifts per day (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). With a “two in two” schedule, duties in a certain period are performed by the same employee (group of employees) during one working day (sample below). Moreover, the weekend falls on a different day of the week each time. That is, employees are set a work schedule that provides for a working week with the provision of days off on a sliding schedule (part one of Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, summarized recording of working hours is introduced.
Procedure for recording time worked
According to Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, with a flexible schedule, a summarized record of actually worked time is kept, for which one of the methods is selected:
- daily - standard hours of labor per calendar day;
- weekly - norm per week;
- monthly - number of hours of work per month.
Establishing an accounting period of more than 1 year is prohibited by the same article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
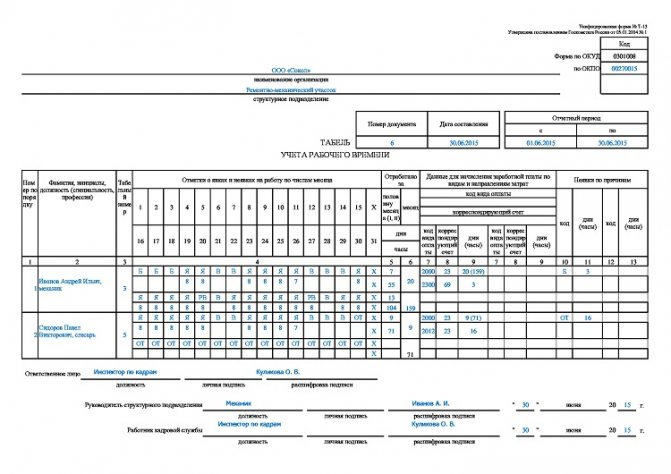
Recording and recording of each employee’s working time is carried out by specialists from the HR department or timekeeping service using the T-13 form based on the data received. The collection of information about the start and end times of employees’ working day is organized by the management of the enterprise in the form of:
entries of watchmen in the log of arrivals and departures;- electronic access system;
- video recording by surveillance cameras;
- submission of data by employees themselves.
The correctness of time recording during a flexible schedule is controlled by the head of the organization or the head of the personnel department.
Important! An employee with a flexible schedule can change the start and end dates of daily work, its mode, but the total number of payable hours in the accounting period used by the employer remains constant.
Below you can see the timesheet:
The picture shows the completed document:
Is it possible to specify the working hours in an additional agreement to an employment contract?
However, the schedule is drawn up once a month, it is approved by the employer, no changes are made to it,
changes are reflected
in the time sheet.
I made orders on the basis of memos from the head of a structural unit to transfer or change the work schedule depending on the need (this memo indicated the employee’s consent to change the schedule.)
Quote: The fulfillment by an employee of the duties of an absent employee, whose place of work is retained, can be formalized in various ways, while the parties to the employment relationship do not in all cases need to sign an additional agreement to the employment contract. Let's consider possible options for registering an employee performing duties for an absent employee.
Examples
To illustrate working on a sliding schedule, let’s give the following example: watchman Ivanov works on a variable schedule, and the organization has adopted quarterly cumulative accounting of hours worked. Ivanov worked: 110 hours in January, 100 hours in February and 237 hours in March. At the enterprise where the watchman works, a 40-hour work week has been introduced, that is, the norm for the quarter is 447 hours. From the summary calculations it is clear that the norm was not exceeded.
Wording in the employment contract
In the section of the employment contract “Working time and rest time” it is necessary to indicate that “the employee is given a sliding work schedule in accordance with the schedule approved by the employer.” If necessary, you can clarify that the employee is hired not only during the day, but also at night. The length of the work week, the total number of hours and duration of one shift, its start and end time, as well as the lunch break period are indicated.
IMPORTANT!
In addition to what is specified, the employment contract must specify the total type of calculation of time worked. If an employee needs to be transferred to a floating system, an additional agreement must be concluded to this effect to the existing employment contract.

Time sheet
The timesheet records the time worked according to standard rules, in accordance with the adopted work plan. The provision of days off on a sliding schedule is based on the production needs of the organization and is not focused on generally accepted days off.
Let's figure out how weekends are paid on a sliding schedule. If a working day falls on a public holiday, it must be paid at a double rate (Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Let's consider an example of a sliding work schedule according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
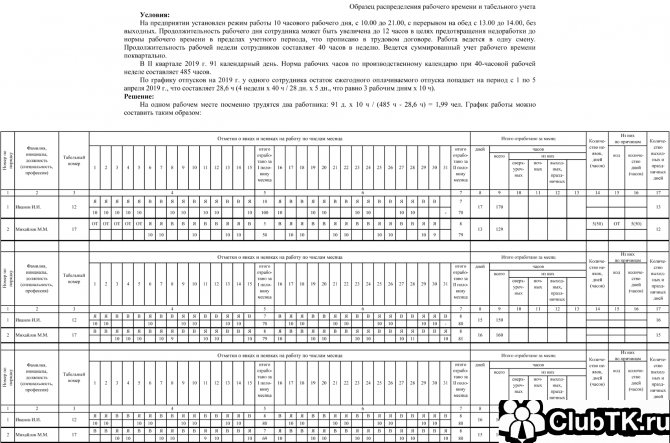
Sometimes rotating weekdays may fall on general weekends or holidays. If working days fall according to the schedule on Saturday and Sunday, then they are taken into account in the timesheet as normal weekdays. If a working day falls on a public holiday, it is paid at a double rate (Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Flexible working hours: how to create and maintain records
- Night time is defined as from 22.00 pm to 6.00 am.
- For work in the evening and night hours, increased pay is assigned: at least 20% for evening hours, at least 40% for night time.
- The exact amount of the premium is fixed in the local acts of the enterprise (Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
This is a work and rest schedule that involves moving days off and/or changing the length of the working day according to the needs of the employee and the enterprise. A flexible schedule is also called a sliding schedule. This schedule allows the employee to choose a convenient time for him to perform work duties.
We recommend reading: How long does it take to replace a passport if damaged?
Additional agreement with shift work schedule
Consequently, an employee’s work schedule can only be changed with his written consent. 2. If an employee is transferred to a position or job where a shift schedule is provided, the change in conditions does not require two months’ notice.
- the night shift is reduced by one hour without further work (part 2 of article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- work for two shifts in a row is prohibited (Part 5 of Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- weekly continuous rest should not be less than 42 hours (Article 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The concept and features of a sliding work schedule at an enterprise
- passport;
- employment history;
- documents on the education received;
- SNILS. Here you can find out how to fill out the insured person’s application form to receive SNILS;
- Military ID required for men;
- a certificate indicating the presence or absence of a criminal record. Where to get such a certificate and what documents are needed for this - find out here.
- young mothers can manage their time rationally to find time to communicate with their children;
- there is a lot of free time on weekdays;
- people can independently create a schedule for attending work that will be convenient for them depending on their health status or preferences;
- overtime work is reduced;
- the number of delays is reduced;
- When using teams, it is possible to change shifts if necessary.
Free legal assistance
At the same time, in a number of cases, the legal liability of the employer is due to the use of employee labor on a day off (non-working holiday) in violation of legal requirements. It is necessary to pay attention to a number of errors made in the advice given on the forum. Firstly, it should be remembered that the meaning Art.
Days off All employees are provided with days off (weekly uninterrupted rest). With a five-day work week, employees are given two days off per week, and with a six-day work week - one day off.
How to reflect a flexible work schedule in an employment contract, sample document
The employer is obliged to consider the application of the representative body of employees about the violation by the head of the organization, the head of the structural unit of the organization, their deputies of labor legislation and other acts containing labor law, the terms of the collective agreement, agreement and report the results of its consideration to the representative body of employees.
Lateness without a valid reason, absenteeism, violation by an employee of the flexible lunch break period specified in the employment contract are grounds for the application of these measures.
Rights and responsibilities of an employee
The rights and obligations of all workers in general, regardless of the schedule, are established by Article 21 of the Labor Code. In accordance with this standard, those working on a flexible schedule have the right to:
- conclude, terminate or change an employment contract;
- work in the place provided to them under the employment contract;
- the compliance of their workplace with sanitary and other requirements;
- to receive a salary corresponding to the functionality performed and existing qualifications. In this case, the salary must be paid in full and on time;
- for holidays and weekends;
- for professional retraining, training and additional education, if required by the work profile;
- to join a trade union to protect their rights;
- conclude collective agreements;
- protect your rights by any legal means;
- resolve labor disputes by legal means;
- receive compensation for damage and harm incurred;
- for compulsory social insurance (in legally established cases).
The latter must be established by federal legislation .
At the same time, a working citizen also has responsibilities that are inextricably linked with his rights:
- he must perform the job functions specified in the employment contract;
- obey the requirements of labor discipline;
- fulfill your time quota and the established amount of work;
- comply with occupational health and safety requirements;
- prevent damage to the property of the organization and the employer within their competence;
- inform the manager about all emerging or possible force majeure situations.
An employee with a flexible schedule, as can be seen from the above list of rights and responsibilities, has the same rights and responsibilities as everyone else. The only difference is that a person working in a flexible mode has the right to an unfixed start, end and duration of the workday .
Irregular working hours are also often used by employers. Read more about this in this article.
Additional agreement sliding schedule
1.8. For work in difficult, harmful and (or) dangerous conditions, the Employee is provided with the following compensations and benefits: _________________________ (this clause is included in the text of the contract if the work is carried out under the above conditions).
In order to correctly formulate a sliding work schedule, a sample of work shifts is presented below. Two groups of partners work one day in the morning shift from 7:00 to 14:00, the next - in the evening shift from 14:00 to 19:00. Thus, two teams have the opportunity to not work for two week-long weekends. In the event of a public holiday, the shift ends one hour earlier than scheduled.
We recommend reading: How to change gears on a gearbox with a divider and range-multiplier
Varieties
Varieties of flexible scheduling are:
- Sliding: means that the usual scheme for distributing working days and weekends (5/2) is used, but another (3/3, 3/2, etc.).
- Shift work: means that the working day does not last from 9.00 to 18.00, but, for example, from 7.00 to 15.00, from 15.00 to 23.00, from 23.00 to 7.00, and the employee is assigned to a specific shift.
- Free: involves the employee’s independent planning of his working time with a set amount of work and a certain time limit.
The main legal regulation of flexible schedule issues is carried out by the Labor Code (Article 102), and the following regulatory documents detail individual nuances:
- collective agreement;
- acts issued by the management of the organization (orders, instructions, etc.);
- employment contract.
The listed documents must include a clause on the employee’s flexible work schedule , after which this clause becomes an essential condition. So, for example, to change such conditions, a separate agreement or other legally established actions will be required in accordance with Art. 73 TK.
Sample entry on flexible hours in an employment contract:

Sliding schedule of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Sliding work schedule 5/2 - in this case, during the reporting period (week), the employee works the established standard hours in 5 days, and two days off can be sliding, moving to weekends or holidays.
- A 2/2 sliding schedule with a 7-day work week of 39 hours is an acceptable form of working time recording, in which the schedule resembles a shift schedule, but has sliding days off, which are agreed upon with management.
- Sliding schedule 6/1 - one day off is transferred to any day of the week, constantly moving depending on production needs.
A sliding work schedule involves “moving” weekends according to the calendar. Let's assume that this week the employee has days off - Wednesday, Thursday and Sunday, and next week - Monday, Tuesday, Friday, Saturday.
Differences between a sliding schedule and a flexible schedule
Since many employers often confuse a flexible work schedule with a sliding one, it is necessary to distinguish between these work modes in advance. However, they do have common features, which include the following features:
- Using summarized working time tracking. Both in the case of a flexible work schedule and in the case of a staggered schedule, the use of a legal framework is assumed to ensure the functioning of the summarized recording of working hours.
- General legal restrictions. The principles provided for by law prohibiting excess work volumes and requiring increased payment for overtime work have the same impact on these methods of organizing working time.
- Possibility of creating non-standard work schedules. Both flexible and rotating work schedules allow you to organize your working time within the limits of legal regulations in many different ways.
However, key differences between these methods of setting work schedules seriously distinguish them from each other. Some of the differences between a sliding work schedule and a flexible one include:
- One-sidedness. In the case of a staggered work schedule, the employee only needs to agree to the terms of the employment contract, after which the employer will have the right to use the methods provided for by it and local regulations to change it, which do not contradict the law. At the same time, a flexible work schedule implies a mandatory agreement between the parties to the contract for every possible change in the schedule, and such a change can be initiated not only by the employer, but also by the employee.
- Scope of application. Flexible work schedules are usually used in cases where the nature of the work makes it difficult to establish a fixed schedule, for example, for maintenance or utility workers, as well as senior staff. At the same time, a sliding work schedule is used when it is necessary to organize a stable, but non-standard working hours for ordinary employees.
- Fixation mechanisms. A sliding schedule implies the possibility of constant and advance planning of employees' schedule for going to work for any period of time up to one year, while a flexible work schedule usually changes much more often and involves fixing all working hours in fact.
Legal regulation
There are several regulations that provide important information regarding the rules and application of the rolling schedule. These documents include:
- Art. 100 Labor Code, which carefully describes how working hours are formed at different enterprises;
- Art. 101 of the Labor Code concerns irregular working days;
- Art. 102 of the Labor Code describes the concept of a sliding schedule, and also describes its nuances and features;
- Art. 103 TC talks about the shift schedule;
- Art. 104 of the Labor Code contains data on recording the working time of employees;
- Art. 105 of the Labor Code provides information on how employers are allowed to divide working time.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 100. Working hours
The working time regime should provide for the length of the working week (five-day with two days off, six-day with one day off, a working week with days off on a sliding schedule, part-time work), work with irregular working hours for certain categories of workers, the duration of daily work ( shifts), including part-time working days (shifts), start and end times of work, time of breaks in work, number of shifts per day, alternation of working and non-working days, which are established by internal labor regulations in accordance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreements, agreements, and for employees whose working hours differ from the general rules established by a given employer - an employment contract.
Features of the working hours and rest time for transport, communications and other workers with a special nature of work are determined in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Important! Violation of the basic provisions of the above acts leads to the need to pay fines.
Example of a moving chart
This solution is usually used if the enterprise operates without days off or breaks, so several shifts of workers are required. Often such a schedule is drawn up for 2 teams and two shifts.
For example, 2 teams work on the first day in the morning from 8 to 15 hours, and the next day from 15 to 20 hours.
Sliding work schedule
It is worth remembering that the employer is not obliged to draw up a schedule in such a way that employees’ work does not fall on officially established holidays. Although the law prohibits employment on holidays (Article 113 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), there are still exceptions. It is allowed to hire the following people to work on holidays on a flexible schedule:
- In the relevant section of the employment contract “work and rest schedule”, enter information about a staggered schedule. By signing a contract, a person accepts these terms.
- Draw up an additional agreement to the employment contract.
- Inform the employee before the start of the accounting period to avoid future conflicts.
Who is it suitable for?
Of course, a flexible work schedule is not suitable for everyone. However, this mode is popular in the IT sphere, as well as among various creative professionals - artists, designers and many others. The advantage is that the employee can work exactly when he is most focused on it . For example, for some people their peak performance occurs in the early morning, while for others it peaks in the afternoon. In addition, the transition to a flexible schedule is often associated with a person’s life circumstances. If the employer meets him halfway, both parties will only benefit from this.
Sliding work schedule
To comply with the established 40-hour duration, a summarized recording of working time is introduced on the basis of Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, where the recording period is equated not only to a month, but also to a quarter and a year.
The specifics of the activities of a number of enterprises, which require adherence to cyclicality, the absence of established days off for the staff “arsenal” at the same time due to production necessity, contributes to the creation of different organizational labor regimes. A sliding work schedule is a constructive option designed to ensure the interests of employers, hired personnel and third parties.