Personnel issues are regulated by a large number of legal acts: codes (Civil, Labor, Tax, Code of Administrative Offences), special laws, regulations and orders of the Government and ministries, many instructions and instructions from other government bodies, etc. In the variety of these documents, it can be difficult to understand how an employment relationship can be legally formalized in order to protect the interests of both the employer and the employee. In this article we will give a general idea of the possible options for the relationship between the person providing the work and the one who performs it.
How can you formalize your relationship with an employee?
Labor relations are only those relations between employer and employee that have the characteristics specified in Article 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation :
- work according to the position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications;
- the specific type of work assigned to the employee (labor function);
- subordination of the employee to internal labor regulations;
- provision by the employer of working conditions provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
But in addition to labor relations based on an employment contract, interaction with an employee can also be formalized within the framework of civil law relations, when the employer and employee act as a customer and performer. Such relationships are not subject to labor laws and relieve the customer of a significant share of responsibility for the working conditions of the contractor. At the same time, Article 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation emphasizes that the conclusion of civil contracts that actually regulate labor relations between an employee and an employer is not allowed.
The most frequent complaints from regulatory authorities are precisely the attempt to present real labor relations under the guise of civil law. What does the employer gain in this case? He not only has the opportunity not to pay insurance premiums for injuries and occupational diseases for the employee to the Social Insurance Fund, but also does not have to provide vacation, sick leave, maternity payments and dismissal benefits. But if the employer wins here, then the employee loses, therefore, from January 1, 2014, he has the right to demand that civil law relations be recognized as labor relations (Article 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), if there are real grounds for this.
We propose to take a closer look at how the interaction between employer and employee is structured within the framework of labor relations itself and within the framework of civil law, among which there is also the option of agency labor (staff leasing).
Payroll and personnel records
Preparation and registration of documents for an employee
After drawing up an employment contract for an employee, you must draw up:
The order of acceptance to work
The employment order is drawn up after the execution of the employment contract according to the unified form No. T-1 or No. T-1a. This document confirms the fact that the employee was hired and is also the basis for entering information into the work book and the employee’s personal card.
You can find out more about the procedure and samples for filling out an employment order here.
Employee personal card
One of the mandatory documents drawn up after concluding an employment contract is the employee’s personal card. Read more about filling out an employee’s personal card here.
Personal account
Personal account cards are compiled to monthly reflect information about wages paid during the year. The document is prepared by an accounting employee using forms T-54 and T-54a.
You can find out more about the procedure and example of filling out a personal account card here.
Card for individual accounting of accrued payments and insurance premiums.
This document is used to record the amounts of accrued payments and other remunerations, the amounts of insurance premiums related to them, in relation to each individual in whose favor the payments were made.
The new form of the card recommended by the Pension Fund of Russia and the Social Insurance Fund can be downloaded here.
A sample form for filling out the card can be downloaded here.
Note
: the form recommended by the FSS and the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation is not mandatory for use, and therefore the employer can develop a convenient form on its basis (taking into account the recommendations of these bodies).
Tax register for income and personal income tax
Employers who have entered into employment and civil law contracts are required to keep records of employee income and the amounts of personal income tax calculated and withheld from this income. This document does not have a mandatory unified form, and therefore the employer is obliged to independently develop its form.
The income and personal income tax register must contain the following mandatory information:
- Employee's full name.
- TIN or passport details.
- Taxpayer status (resident/non-resident).
- Amounts of income paid to the employee and tax deductions provided.
- Income payment dates.
- Amounts of calculated and withheld personal income tax.
- Dates of withholding and transfer of personal income tax.
- Details of payment orders for the transfer of income tax to the budget.
Sample of filling out the tax register for income and personal income tax (download).
Employment contract with the employee
Under an employment contract, the employer undertakes to provide the employee with work for a certain labor function, provide working conditions, pay wages on time and in full, and the employee undertakes to personally perform the labor function determined by this agreement and comply with the internal labor regulations of this employer (Article 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ).
An employment contract maximally protects the rights of the employee and, at the same time, places on the employer the maximum responsibility of all possible options for formalizing the employment relationship. We discussed how to conclude an employment contract and what conditions should be included in it in a separate article, because when concluding such an agreement, many nuances must be taken into account.
What else, besides concluding an employment contract, should an employer do when hiring and further interaction with an employee? The rights and obligations of the employee and the employer are prescribed in Articles 21 and 22 of the Labor Code. Let's briefly go through the points that an employer must provide to its employee:
- familiarize yourself with local regulations, such as internal labor regulations, regulations on remuneration, regulations on the protection of personal data;
- ensure safety and working conditions, as well as equipment, tools, technical documentation and other means necessary to perform labor duties;
- pay the employee wages in full, and payments must be made at least twice a month;
- pay monthly insurance premiums for the employee to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund at your own expense;
- provide for the everyday needs of employees related to the performance of their job duties;
- pay for non-working holidays and annual leave;
- compensate for harm caused to employees in connection with the performance of their labor duties;
- pay for maternity leave and child care benefits for up to one and a half years;
- pay for days of incapacity.
Dismissal of an employee without his actual consent is possible only for a number of reasons, and can sometimes create difficulties for the employer.
Where it all begins
Labor relations arise between an employee and an employer on the basis of a contract, and the following circumstances contribute to this:
- Selection for a specific position in the company.
- Appointment based on the results of a competition.
- Confirmation of position.
- Upon a court order.
- By decision of management, allow to work.
As already mentioned, all relationships between a newly hired employee and a boss are formalized by an employment contract, which in turn must necessarily contain a description of the conditions of the work provided and payment for it, as well as the procedure for accrual for overtime hours and other features caused by specific working conditions.
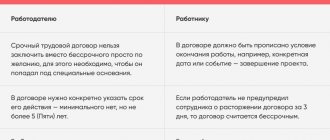
You can draw up an agreement:
- for a specified period, but not more than 5 years;
- indefinitely.
In cases where the document does not define its validity period, it is automatically issued for an indefinite period. Naturally, such transactions with future employees are drawn up in writing, and are valid from the moment the document is signed by both parties or from the actual start of work duties. The process of hiring employees occurs after submitting their personally drawn up and signed applications.
Civil contract with an employee - an individual
A civil law agreement (CLA) is a good opportunity for an employer to order a service (work) from a third-party contractor that cannot be performed by its full-time employees. Such an agreement is also suitable in cases where the volume of work is small and hiring an employee on staff would be unreasonable.
This could be repairing something, performing a translation, attracting a certain number of clients, developing technical documentation, etc. Such an agreement is drawn up not as an employment agreement, but in the form of a contract or service agreement. In addition, civil law contracts, on the basis of which an individual can be involved in execution, include contracts of carriage, transport expedition, assignment, agency, commission.
The subject of the GPC agreement will be the implementation of a specific task that has a measurable result. It is this result that will be paid for by the employer, who in this case acts as the customer. Labor legislation does not apply to persons performing work or providing services on the basis of GPC agreements.
In this type of work, the customer does not make entries in the contractor’s work book, but the period of work under a civil contract is included in the contractor’s length of service. Why? The fact is that although the GPC agreement is not an employment contract, the customer must, at his own expense, transfer insurance contributions to the Pension Fund for the contractor , based on the remuneration amounts paid. Contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases are not mandatory and can be provided on a voluntary basis. In addition, the customer, under a civil contract with the contractor - an individual, must fulfill the duty of a tax agent, that is, withhold and transfer personal income tax from the remuneration amount.
Let's compare the features of two types of contracts with an employee: labor and civil law.
| Employment contract | GPC agreement with an individual | |
| Subject of the agreement | Personal performance of a labor function by an employee | Measurable final result of work (service), accepted according to the act. The Contractor may involve third parties to complete the task, unless otherwise provided by the contract |
| Documenting | An employment contract is concluded, a hiring order is issued, a personal card is issued, and an entry is made in the employee’s work book. | A civil law contract is concluded and a task is agreed upon in the form of achieving a specific result of a service or work; an entry is not made in the work book. |
| Salary | The employee receives a monthly salary specified in the employment contract. Salaries are paid twice a month; for violation of payment deadlines, the employee is paid a penalty | The customer pays remuneration to the contractor after completing the scope of work or services. The customer is not obliged to make monthly payments, but stage-by-stage delivery of work or advance payments may be provided |
| Insurance premiums | Contributions to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund are required | Only contributions to the Pension Fund are required |
| Personal income tax | Held | Held |
| Social guarantees | The employee is provided with vacation, maternity leave, child care benefits, sick leave, and dismissal benefits at the employer's expense. | Social guarantees are not provided |
| Internal labor regulations | The employee must comply with the work schedule, obey officials, work occurs under the control of the employer | The contractor is not subject to the PVTR, the customer can check the progress of tasks, but does not have the right to give mandatory instructions |
| Work time | Recorded in the time sheet; work on weekends, non-working holidays and overtime work is paid additionally | The customer pays not for the time spent, but for the result. Working hours are not recorded, and no additional payment is made for overtime or work on weekends (non-working days). |
| Working conditions | The employer must equip the workplace, create material conditions for performing the work function, and provide safety instructions | The customer is not responsible for the creation and equipment of the workplace, safety precautions and labor protection. The contractor may use his own materials and tools (as determined by the terms of the contract) |
| Refusal to conclude a contract | Unreasonable refusal when concluding an employment contract is prohibited. Discrimination based on age, nationality, gender, language, etc. is not allowed | There is freedom of civil contract, so the customer can refuse to enter into a contract with a specific contractor |
| Contract time | The default is for an indefinite period. The conclusion of an employment contract indicating the term is permitted if there are grounds specified in Article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (for example, when temporarily replacing an absent employee) | The contract is concluded for the period of performance of work or provision of services |
| Prosecution | It is possible to bring the employee to disciplinary liability (reprimand, reprimand, dismissal for certain reasons). An employee's normal financial liability is limited to his monthly salary. An agreement on full financial liability can be concluded only with some employees | For violation of deadlines for completing work (services), the contractor may be required to pay a penalty. Causing material damage to the customer is compensated by the contractor in full. The contractor also bears the risk of accidental death or damage to the result of the work performed before its acceptance by the customer |
Mandatory data and terms of the employment contract
To determine the content of an employment contract, two main articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are used: 57 “Content of an employment contract” and 9 “Regulation of labor relations and other directly related relations in a contractual manner.”
If we structure Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then it can be divided into three blocks.
- Information about the employee, the employer, the date and place of conclusion of the employment contract.
- Required conditions. Their absence is an example of improper execution of an employment contract.
- Additional terms and conditions. The employer includes them in the employment contract at its discretion as necessary.
Particular attention should be paid to the first two blocks.
1. Information about the employer, the date and place of conclusion of the employment contract, and about the employee.
The employment contract must indicate:
- full name of the employing organization (as it appears in the constituent documents);
- an official who acts on behalf of the employer. Only an employee authorized to conclude it can sign an employment contract. The full name of this employee must be indicated in the header of the employment contract.
- the document on the basis of which this official acts: a power of attorney or other legal act.
- employer taxpayer identification number.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not require indicating the address or bank details of the employing organization, but if this data is included in the employment contract, this is not considered a violation of the law.
Information about the employee should include the person's full name and identification document, such as a passport or other document (this could be a military ID or driver's license).
2. Mandatory terms of the employment contract. There are nine of them in total.
1) Start date of work. This is a legally significant condition of the employment contract, because the same date is indicated in the hiring order, entered into the work book, the employee’s timesheet begins from this date, and the length of service and the working year are calculated from this date. However, the dates of starting work and concluding an employment contract may not coincide.
When drawing up a fixed-term employment contract, its duration and the reason for concluding a fixed-term contract must be indicated. In Art. 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains more than 20 grounds for concluding a fixed-term employment contract. The employer cannot go beyond this list. And if he does this, then it will be considered that the employment contract was drawn up improperly, and the employee will be able to challenge such a condition of the contract in court.
2) Place of work. Today, legislation does not oblige you to indicate a structural unit in an employment contract. But if a person is hired to work in a branch, representative office, or other separate structural unit located in another locality, then it is necessary to indicate, in addition, the name of the administrative-territorial facility in which the unit is located. It is also necessary to indicate the structural unit in cases where the employee receives some benefits associated with working there,
3) Labor function. This condition must be indicated in the employment contract: the name of the position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty, or specific type of work. Due to the introduction of professional standards for some professions, the name of the labor function may change. For example, if earlier the name of the labor function sounded like “labor safety engineer,” now it is “labor safety specialist.”
On the one hand, the legislator allows that the employer determines for himself the name of the labor function. Moreover, it must be exactly the same as in the staffing table.
But if some benefits, advantages, or restrictions are associated with the title of the position, then the legislator says: the title of the position must comply with qualification reference books or professional standards.
4) Remuneration. To formulate this condition, based on Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the requirements are as follows: the employment contract must indicate the amount of the main part of the salary: the amount of the official salary or tariff rate. It is not enough in the employment contract to refer to the staffing table when determining the amount of the official salary or tariff rate; it is necessary to indicate a specific amount in the contract itself.
But as for the above-tariff part of wages, including additional payments, allowances, incentive payments, then, judging by Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, commercial employer organizations can afford to simply list them, and the specific rules for their calculation (amounts, criteria, amounts) can be determined by local regulations. But if we are talking about state and municipal budgetary institutions in which the so-called effective contract is being introduced today, it must be taken into account that the employment contract itself must specify the employee’s job responsibilities, terms of remuneration, indicators, criteria for assessing the effectiveness of activities for assigning incentive payments in depending on the results of labor and the quality of government and municipal services provided.
Please note that not all mandatory conditions of an employment contract are listed in exhaustive form in Art. 57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. As can be seen from the Labor Code, other articles and sections also contain references to the employment contract as a mandatory source of information for the employee when determining certain conditions.
For example, Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the day of payment of wages is established by a collective agreement, internal labor regulations, and an employment contract. Since all three sources are listed there, this means that the employment contract must necessarily contain conditions on the days of payment of wages. In the same article. 136 states that salaries are paid at least every half month, and there must be equal intervals between payments. In addition, in its letter dated June 20, 2014, the Federal Service for Labor and Employment clarifies that all three mentioned sources must set specific dates for the payment of wages.
5) Work and rest schedule. This condition should be specified in the employment contract only if the working hours and rest periods differ from the usual ones specified in the internal labor regulations. When a person is hired, he gets acquainted with the PVTR under his signature, which means he agrees with this document. Accordingly, the work and rest schedule may not be specified in the employment contract.
The employer is obliged to indicate in the contract the following features of the employee’s working regime:
6) Compensation and benefits. The employment contract specifies compensation for work in harmful and dangerous working conditions and their characteristics.
As you remember, from January 1, 2014, the rules for determining the amount of compensation have changed. If previously the duration of working hours and additional leave was established centrally, now the Labor Code of the Russian Federation says that it is established by the employer himself. First, the conditions for the amount of compensation are fixed in the collective agreement and in industry agreements. And based on these documents, the amount of compensation is determined in a specific employment contract.
According to the new rules, reduced working hours are granted to those who work in places with a hazard class of 3.3 and higher, and additional leave of at least 7 calendar days - with a hazard class of 3.2. The duration of working hours and the specific number of days of additional leave in the employment contract are stated on the basis of a collective agreement or industry agreement. The amount of additional payment for work in harmful or dangerous working conditions is determined locally, either in a collective agreement or in local regulations.
The law today allows parties to contractually change the rules on compensation for work in harmful and dangerous conditions. For example, Art. 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation says that the employer and employee can agree and instead of a shortened working week (36 hours), the employee will be given 40 hours a week for an additional fee. But the legal possibility for such an agreement must be indicated in a collective agreement or in an industry agreement.
Characteristics of working conditions are taken from a special assessment card of working conditions or from a workplace certification card for working conditions.
7) Nature of work: mobile or traveling. Firstly, if working conditions differ from usual, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, compensation is due. Secondly, if an employee incurs costs to perform his job function, they must be compensated to the employee. Art. 168.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes compensation for the mobile and traveling nature of work.
The state does not centrally determine the amount of compensation. For such payments, the employer must adopt a local regulatory act, which will list professions, specialties, positions involving a traveling nature of work, and establish the amount of compensation. And on the basis of this local regulatory act, the employment contract states that such and such an employee has a traveling nature of work, in connection with which the employer pays compensation on the basis of Art. 168.1.
Please note that business trips, which provide compensation payments for the traveling and mobile nature of the work, are not considered business trips.


9) Condition on compulsory social insurance. It is necessary to indicate in the employment contract that the employer insures the employee and makes contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, Medical Fund, and Social Insurance Fund against accidents at work.
Notifying users about the end of the probationary period, temporary substitutions, and fixed-term employment contracts.
Try for free
Civil contract with an employee who is an individual entrepreneur
If the executor under the GPC agreement is an individual entrepreneur and provides services or performs work as part of his business activities, then this is a normal relationship between two business entities. In this case, the customer does not have to pay insurance premiums for the individual entrepreneur and withhold personal income tax from him. An individual entrepreneur himself pays tax on the amount of remuneration and pays his own insurance premiums.
This form of relationship benefits both the customer and the contractor: the first saves on the amount of contributions to the Pension Fund, and the second has the right to tax the income received not at the usual personal income tax rate of 13%, but, for example, at a rate of 6% if he works for the simplified tax system Income . However, this option is always especially controlled by tax authorities, because, in their opinion, it is a scheme created to evade taxes.
When concluding a civil law contract with an individual entrepreneur, just as when concluding a civil law contract with an ordinary individual, you must ensure that it does not contain any characteristics characteristic of labor relations.
- In civil law relations, the person performing the work is a third-party contractor, not an employee, therefore the contract cannot indicate the name of the position and the person to whom he reports.
- The performer or contractor under the GPC agreement must not be indicated in the staffing table and must comply with the internal labor regulations of the organization.
- Remuneration should be indicated based on the final result, which is accepted according to the act of acceptance of work or services. It is unacceptable to prescribe tariff rates, official salary, bonuses, compensation, incentive payments and allowances, because this is a sign of an employment relationship.
- The clause in the GPC agreement on the creation of working conditions and a social package for the contractor is also an indication of labor relations.
Rules for drawing up and executing an employment contract according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
There is no specific sample of this document in labor legislation, but it consists of a written form of an employment contract, submitted in 2 copies, each of which is signed by both parties.
Based on Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the clauses of the labor agreement contain:
- Name of the organization and full name of the employee with whom the employment relationship is concluded.
- Place of work.
- Type of work activity, main or part-time job.
- The start date of the employment relationship (when concluding a fixed-term employment contract, you must indicate the expiration date of the document).
- Responsibilities and rights of the employer and employee.
- Payment terms (tariff rate, salary, additional payments, etc.).
- Work and rest schedule.
- Compensation and guarantees.
- Additional conditions, if any (probationary period, business trips, part-time work, etc.).
Important!
The absence of one of the above clauses in the employment contract or the presence of errors in drafting determines the invalidity of the documentation and is considered grounds for its termination or annulment.
Distant work
Remote or remote work is an option that is perfect for performing those jobs or services that do not require constant presence in the employer’s office: IT specialists, designers, analysts, translators, call center specialists, marketers, sales managers, etc. Remote Work today is possible within the framework of both an employment and civil law contract, but this was not always the case.
Remote work under an employment contract was legalized only last year, by Law 04/05/2013 No. 60-FZ, which added Chapter 49.1 to the Labor Code. According to it, remote work is considered to be the performance of a labor function outside the location of the employer, subject to interaction with the employer through public information and telecommunication networks, including the Internet.
Before this chapter of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation came into force, remote work was in fact already carried out by many workers, but it was registered either as home work (which is incorrect, since home work involves the production of certain products), or as a GPC agreement, or the employee was registered under the agreement in office, but was not there. Now all these questions have been resolved, and if the employer and the remote worker want to conclude an employment contract, then this is possible. Such an employee is subject to all guarantees of labor legislation.
Requirements for a written contract
All employment contracts must contain the following information:
- information about the parties to the agreement;
- conditions of a contract;
- details and/or contacts.
The contract is drawn up in two copies, one of which is given to the employee, and the second remains with the manager. The employee must leave his signature on the manager’s copy, this will confirm that the second copy of the contract is with the employee. If the employee is under 14 years old at the time of concluding the contract, then the signature must be left by one of his legal representatives (parents, guardians).
According to the rules established in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employment contract must be concluded in writing.
If the manager does not have the status of an individual entrepreneur, then he needs to register an agreement with the employee with local authorities. This requirement is published in Article 303 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. But the consequences for the manager if this condition is not met are not described anywhere.
The employment contract is concluded in writing, but there are some differences in the sequence of registration of employment. Actual permission to work. An employee can begin to perform his duties with the knowledge of the manager. In this case, a special form of employment contract must be drawn up in writing no later than three days after the start of cooperation. In this case, the agreement may indicate the principle of starting activities “with the knowledge” or “on instructions”. “with the knowledge” means that the manager does not oppose the employee’s employment and acts as a passive party to the contract.
The wording “on instructions” implies an active position of the manager in relation to the employee.
The difference in these terms should be understood as follows: if an employee began work on behalf of a manager, then he can demand from the manager full payment for his work and the further conclusion of an employment contract precisely from the moment the work actually begins. If an employee started work with the knowledge of the manager, then he cannot demand any incentives from the manager, because He began working of his own free will, but with the notification of management. In this case, the manager can conclude an agreement “today”.
Official permission to work. This form of employment contract involves employment in the “correct” order: first the written employment contract, and then the start of work. That is, the manager enters into an employment contract with the employee, and only after that the employee begins to fulfill his duties. In this case, the employee can begin to perform his duties either the next day after the conclusion of the contract, or on the day specified in the contract.
Outsourcing (outstaffing) or agency labor
This type of registration of labor relations is the most controversial and most recently regulated in a legal sense. It would seem like a sound idea - a recruitment agency hires workers under an employment contract who have the same social guarantees as ordinary employees. At the same time, they perform their labor function not with a direct employer, but with another person who is a customer of a recruitment agency.
Here it is necessary to distinguish between two concepts: outsourcing of services and outstaffing as personnel rental. Outsourcing of services refers to the transfer to third-party services of non-key functions of the organization, such as personnel and accounting, legal, advertising, transport and translation services, call centers, cleaning services, security, computer network support, and the like. Employees of the performing organization can go to the customer’s office and carry out their work functions there, while they only provide services and are not subordinate to the customer as an employer. This method of providing services is absolutely legal, and we considered the option of outsourcing accounting services in the article on accounting support with tariffs for 2021.
But outstaffing as the provision of personnel, in which employees come under direct subordination and disposal to the customer without concluding an employment contract with him, is an illegal way of formalizing labor relations.
In May 2014, Article 56.1 was added to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which prohibits agency work carried out in the interests, under the management and control of an individual or legal entity that is not the employer of the employee. At the same time, Chapter 53.1 was added to the Labor Code, regulating the specifics of the labor of workers sent temporarily by the employer to other persons under a contract for the provision of labor.
Private employment agencies will have the opportunity to send their workers to perform work for other persons if the workers are sent:
- to an individual who is not an individual entrepreneur for the purpose of personal service and assistance with housekeeping;
- to a legal entity or individual entrepreneur to temporarily perform the duties of absent employees who retain their place of work;
- to a legal entity or individual entrepreneur to carry out work related to a deliberately temporary (up to 9 months) expansion of production or the volume of services provided.
These innovations in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation come into force on January 1, 2016.
Familiarization of the employee with local regulations
Before concluding an employment contract, the employee must be familiarized with local regulations. These documents are developed by the employer independently, taking into account the direction of his activities. Familiarization with some of them is mandatory, with others only if they are available in the organization.
Documents required for review:
- Internal labor regulations.
- Rules and instructions for labor protection.
- Regulations on remuneration (if the specified section is included in the internal labor regulations).
- Rules for storing and using personal data of employees.
Documents that are required to be reviewed only if they are available in the organization:
- Job description.
If the employment contract does not contain a list of the duties performed by the employee, they are specified in the job description, which is, in turn, an integral part of the contract. There is no unified form of this document - it is developed by the employer independently and is its internal local document.
Note
: if the job description is not signed by the employee, then penalties cannot be applied to him for failure to fulfill the duties specified in the instructions.
- Provision on financial liability.
- Regulations on document flow.
- Collective agreement.
- Regulations on social security of workers.
- Other documents developed by the organization.
After the employee has been familiarized with local regulations, he must sign the familiarization sheet, after which the sheet is stitched with the act, numbered and sealed and signed by the official.
note
, that a law will soon come into force that will simplify personnel records for micro-enterprises; in particular, these employers will be able not to adopt local regulations, and also not to enter information about work in the employee’s work book. Currently, the law has been signed by the President of the Russian Federation, and its official publication is expected (after which it will come into force 180 days later).
The right to choose the option of formalizing labor relations
We have considered all options for possible registration of labor relations:
- employment contract;
- civil contract with an employee - an individual;
- civil contract with an employee who is an individual entrepreneur;
- remote work on the basis of an employment contract or GPC agreement;
- outsourcing of services;
- temporary assignment of workers by the employer to other persons in cases specified by law (this possibility will appear from January 1, 2016).
Issues relating to the right of an employee to choose between concluding an employment contract or a civil-process agreement have more than once become the subject of disputes: tax, with the participation of extra-budgetary funds, the State Labor Inspectorate and the courts. Who has the right to choose an employment relationship that satisfies the interests of both the employee and the employer? It seems to us that these are, first of all, the aspects of labor relations themselves.
In fact, where is the line beyond which the good wishes of supervisory authorities to protect the interests of the employee violate his right to freely choose the option of formalizing labor relations? After all, often a GPC agreement, which inspectors unreasonably consider illegal, is precisely in the interests of the employee himself. Maybe it’s easier and more profitable for him to work as a performer than to be a full-time employee?
The freedom of the citizen to choose the contractual legal form of interaction with the person providing the work was indicated by the Constitutional Court in Ruling No. 597-О-О dated May 19, 2009: “Thus, contractual legal forms that mediate the performance of work (provision of services) , subject to payment (paid activity), under a paid contract, there can be both an employment contract and civil contracts (contracts, assignments, paid services, etc.), which are concluded on the basis of the free and voluntary expression of will of interested subjects - parties to the future agreement."
It would be great if government bodies, called upon to protect the labor interests of a citizen, would take into account his personal opinion and leave the right of choice to him, without unreasonably, in some cases, accusing the employer of trying to violate labor laws.
Receiving documents from an employee
When hiring a new employee, you must receive a package of documents from him. Depending on the position and the requirements for it, this list may change.
Required documents:
- Passport or a document replacing it (for example, temporary identity card in form No. 2P, birth certificate, document confirming the identity of a foreign citizen).
- Work book (details about maintaining, storing and entering data into the work book here).
- SNILS (insurance certificate of compulsory pension insurance).
- Military ID or certificate of a citizen subject to conscription for military service (if the employee being hired is liable for military service).
Note
: if the employee does not have a work book and SNILS (first place of work), then the employer is obliged to issue them. An exception is the hiring of remote employees, when the employment contract is concluded through the exchange of electronic documents. In this case, the employee himself receives SNILS at the Pension Fund branch and sends information about it to the employer.
Additional documents:
- Diploma or other document confirming education (certificate, etc.).
- Certificate of completion of a medical examination or medical record. Required in cases where the position requires a mandatory medical examination (see slider below);
- Certificate of presence (absence) of a criminal record (required for submission when applying for a position as a teacher, civil servant, bailiff, customs officer, etc.).
- Taxpayer Identification Number (if available). The absence of a TIN cannot be an obstacle to hiring an employee, since it is not included in the list of required documents and a refusal to hire due to the absence of the specified document is unfounded.
- International passport.
- Certificate 2-NDFL (required if the employee wants to receive tax deductions).
- Certificate of salary amount for the last 2 years (necessary for calculating sick leave benefits if the calculation will be made based on wages from previous employers).
- Work permit (patent) - for foreign citizens and stateless persons, if carrying out labor activities without the specified documents is impossible.
- Medical certificate confirming that there are no contraindications for working in the Far North (if the employee is hired in the specified region).
- Information about the income and property of the spouse and minor children. Providing this document is mandatory for civil servants, employees of the Central Bank (for a number of positions), and municipal employees.
- Application for a job. Drawing up an application for employment is not a
prerequisite for concluding an employment contract and its absence cannot be grounds for refusal to hire. The only exceptions are state and municipal employees who are required to draw up this application.
Who needs to undergo a medical examination when applying for a job?
The following categories of citizens are subject to a mandatory medical examination when concluding an employment contract:
- Minors.
- Workers in hazardous industries and industries with hazardous working conditions.
- Workers associated with traffic.
- Employees hired in the Far North and other equivalent areas.
- Workers hired for rotational work.
- Citizens employed in the field of catering, trade, water supply facilities, medical services, children's education (kindergartens, schools, etc.).
- Employees hired for underground work.
- Other employees whose mandatory medical examination is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Who signs the employment contract first - the employer or the employee?
The main thing is that everything is clearly stated in the contract.
If the documents don’t say anything about this, it means you were hired without any safety nets.
Then don’t expect your salary to be raised after 3 months. Nobody promised you this. Tricks of employers If your new job involves training at the expense of the employer, carefully read what is said in the employment contract about possible reimbursement of costs. “Usually the contract specifies how long you will have to work for the company after completing your training.
And if you quit early, you will have to reimburse the employer’s money,” says Elena Demina. “But many cunning bosses usually hide the fact that you are obliged to return not all the money, but only part of it.
If there is no such clarification in the contract, it is better to play it safe and ask for it to be included.”
And for an employee, this is a guarantee of receiving a salary on time, as well as all monetary payments required by law, safe working conditions and an additional social package (free food, travel, medical care, insurance, etc.) Conclusion algorithm To conclude a contract, the future The employee presents the necessary list of documents for employment:
Registration of labor relations with benefits for business | part 1
Labor relations begin with their proper registration.
Properly structured and formalized labor relations
– one of the key conditions for the stable and dynamic development of the company, labor efficiency and organization of work processes, allowing the employer to avoid financial and time losses in the event of labor disputes.

Labor relations are formalized by familiarizing the employee with signature with internal documentation, which includes: - the charter of the organization; - employment contract; — job descriptions; — internal labor regulations; — regulations on remuneration; — labor protection instructions and other local regulations. The employment contract and job descriptions will determine the range of rights and responsibilities of the employee.
For example, job descriptions can provide for a “dress code”, maintaining order in the workplace, which the employee is obliged to maintain, or compliance with labor safety standards.

It is recommended to periodically check personnel documentation for compliance with labor legislation.
When developing and drawing up personnel documents, it is necessary to be guided by the chapters of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as the “Qualification Directory of Positions of Managers, Specialists and Other Employees”, approved by the Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated August 21, 1998.
No. 37 and federal laws regulating the scope of the organization’s activities. However, the provisions of the employment contract will not be able to contain the entire scope of the employee’s labor responsibilities, therefore the employer must necessarily develop and implement the following local acts.

An employment contract is the main document of the employer.
Do not use an employment contract downloaded from the Internet.
The employer must remember that labor legislation prohibits requiring an employee to perform work not stipulated by the employment contract. Therefore, when registering an employee, you should not use a standard contract, which does not reflect the specifics of the relationship between the employee and the employer in a particular organization.
The employment contract must be signed within 3 days.
After the employee is allowed to work, the employment contract must be concluded within 3 days in writing and contain the entire list of rights and obligations of both parties to the employment relationship. If the employee does not start work after concluding an employment contract, the employer has the right to cancel the employment contract, after which it will be considered not concluded.
At the same time, cancellation does not deprive the employee of the right to receive compulsory social insurance benefits in the period from the date of conclusion of the employment contract.
An employer’s refusal to formalize an employment relationship must be motivated and must not violate the rights of the employee, otherwise he can appeal the refusal in court.

Allowing an employee to work entails the emergence of an employment relationship.
Actual admission to work is also a formalization of labor relations, but it leads to certain risks, for example, the regulation of the rights and obligations of the parties exclusively by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Actual admission to work by a person not authorized by the employer, if the employer or his authorized representative refuses to recognize the emergence of an employment relationship, entails the imposition of an administrative fine: - for citizens from 3,000 to 5,000 thousand rubles; - for officials from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles (part 3 of article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
It is also worth noting that hired labor - labor carried out by an employee at the order of the employer in the interests, under the management and control of an individual or legal entity that is not the employer of this employee, is prohibited.
Mandatory terms of the employment contract.
If, when concluding an employment contract, it did not include any information or conditions from those provided for in Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this is not a basis for recognizing the contract as not concluded or terminating it. In this case, the missing information must be entered directly into the text of the employment contract, and the missing conditions must be stated in the appendices to the employment contract or in separate agreements that are an integral part of it.

How not to enter into an employment relationship.
The conclusion of civil contracts that actually regulate labor relations is not allowed, since they are subject to civil law rather than labor law.
Moreover, in some cases, relations associated with the use of personal labor and arising on the basis of a civil contract may be recognized as labor relations by the employer himself or by a court decision.

Failure to comply with labor laws will result in fines.
Failure to comply with the requirements of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (evasion or improper execution of an employment contract, conclusion of a civil contract) may entail penalties: - for officials from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles; — for individual entrepreneurs from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles; - for legal entities from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles (part 4 of article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).

Properly developed documents minimize risks.
It is important to correctly spell out the provisions of the employment contract and other internal documentation in accordance with current legislation, the specifics of the organization, its goals and objectives.
Thus, the employer will have legal leverage over employees, and if they violate their official duties, they will be able to apply appropriate disciplinary action and dismiss the employee without negative consequences.

You can make an appointment by calling the office or sending a message on our website.
Office in Orel:
Maxim Gorky street 47d phone: +7 (800) 511-62-06
Office in Tula:
Lenin Avenue 57, office 115 phone: +7 (487) 244-05-20