Disability can be caused by various diseases, injuries or defects, the consequence of which is “limitation of life activity” - complete or partial loss of the ability to self-care, independent movement, orientation in space, control of behavior and speech functions. It is especially difficult for older people whose severe physical condition is complicated by age-related changes in the body and an unwillingness to understand and accept the changed circumstances of life.
People with disabilities need social protection and outside assistance. For this purpose, patronage for disabled people of group 1 has been established, which is understood as guardianship over a citizen who, due to existing physical disabilities, requires outside help.
The grounds for assigning 1st disability group are:
- inability to take care of yourself at home;
- partial or complete loss of motor functions;
- disorientation in space;
- inability to master basic skills and abilities;
- difficulties in communicating and controlling one’s behavior in society.
As statistical studies show, the most common cause of disability is diseases of the circulatory system.
To obtain the status of a disabled person, it is necessary to undergo a medical and social examination. It is carried out by specialists (members of the medical commission) based on a personal examination of the patient and the results of previously conducted examinations.
Legislative acts clearly define the circle of people who, for health reasons, can be assigned the status of group 1 disabled person. These include patients with such defects as:
- stumps of the upper and lower extremities;
- malignant tumors leading to relapses and metastases;
- mental disorders with persistent psychopathological syndromes;
- diseases of the peripheral and central nervous system;
- blindness in both eyes or complete deafness;
- vegetative state after stroke;
- paralysis of the musculoskeletal system.
When conducting a medical and social examination (MSE), legislative standards are used - Classifications and criteria approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated August 27, 2021 No. 585n. The document contains detailed clinical and functional characteristics of diseases that serve as the basis for assigning disability. It also adds rare diseases that were missing in previous versions of the document.
The status of a disabled person entitles a person to claim a number of benefits provided by the state: medicines, optimization of the home environment, provision of means of transportation.
Guardianship
First, let’s look at how guardianship differs from regular care for such a disabled person. Guardianship refers to more complete responsibility for a sick person. He must provide him not only with the necessary care, but also protect his rights. That is, the guardian is the official representative of the disabled person in all instances. You can obtain guardianship not only over a disabled person, but also over an incompetent person, including a child under 14 years of age.
The duties of guardians by law include the following:
- providing the necessary care for the ward (it does not say that this care should be provided by the guardian, but he must organize it properly);
- preservation and management of the ward's property , that is, the ward himself cannot always fully make decisions and manage all his property, therefore this responsibility is completely transferred to the management of the guardian, but alienation transactions are strictly controlled by the guardianship authorities;
- caring for the health of the ward , that is, the guardian must provide the necessary treatment, as well as create a good, calm atmosphere for his normal mental state.
The following aspects can also be identified as the main features of guardianship:
- It is established on the basis of a decision of the local administration , if its appointment is not related to the mental illness of the disabled person. In this case, a court decision will be required.
- It is allowed to appoint only one guardian for one patient.
- Monitoring of the performance of the duties of a guardian is mandatory.
Thus, a guardian is significantly different from a person who simply cares for a disabled person with the first category of disability.
Types of guardianship
Depending on the health status of the patient, care may vary:
- over an incompetent person who, due to mental disorders, cannot fully understand his actions;
- over a person who has only physical disabilities.
In addition, the age of the disabled person may also matter:
- adult ;
- minor child.
In addition, there are also differences in the types of guardianship depending on the payment of the guardian’s work:
- the guardian can carry out his actions for a fee , which will be carried out from the state budget;
- the guardian can provide his services absolutely free of charge and not require any funds for the performance of his duties.
Guardianship can only be obtained over the first or second category of disability, since these are the people who need the help of strangers or devices. The third group is considered partially functional, therefore such people do not require guardianship on these grounds.
Guardianship can be full or assigned in the form of patronage. This type means the signing of a special agreement in which the disabled person defines the list of duties and powers of the patronage assistant. Also, such an agreement may contain a condition on payment for its services by the disabled person himself.
Who can obtain guardianship
In most cases, a close relative of an incapacitated or limited citizen is appointed as a guardian. It is believed that it is easier for this person to obtain court approval. However, not every relative meets the established requirements:
- The guardian must be an adult with legal capacity.
- No criminal record.
- Have sincere intentions towards the mentee.
The court will also evaluate the applicant's financial capabilities and personal qualities. To do this you need:
- Have a permanent, official income.
- Have your own living space. If relatives live with the prospective guardian, it is necessary to provide the consent of these persons that they are not against cohabitation with an elderly person or a disabled person.
- Provide a reference from your place of work.
- Provide a certificate from a physician stating that the applicant does not have incurable diseases or acute viral infections.
In addition, the guardian must suffer from alcohol and drug addiction - this fact is confirmed by a certificate from a medical institution.
The status of a guardian gives the citizen certain responsibilities towards the ward:
- Caring for the elderly or disabled.
- Solving issues related to medicine (purchase of medicines, placement in a specialized medical institution, etc.).
- Representing the interests of the ward in all instances.
- Taking actions aimed at improving the quality of life of the ward.
- Disposal of his funds.
When making a decision, the court will take into account the person’s readiness to fulfill the established duties.
How much pay?
Due to such a great responsibility when receiving guardianship, this citizen has the right not to refuse payment for his services. If his ward has 1 group, then he has the right to count on the following amounts:
- if a person received his disability in childhood, then the amount of payments will be 5,500 rubles ;
- if the disability was acquired in subsequent years, then the amount of compensation for the guardian will be only 1200 rubles .
But when formalizing his obligations, the guardian must take the ward to live with him, or in extreme cases, with the permission of the guardianship authorities, move to live with him. Therefore, he will be able to enjoy some of the benefits of a disabled person:
- receive a discount or compensation for housing and communal services in the amount of 50%;
- arrange free vouchers and travel for one accompanying person to the sanatorium;
- receive housing tax exemption;
- receive discounts when paying transport and land taxes if the vehicle meets the established requirements and is used to transport a disabled person;
- receive labor benefits;
- get 50% discount on a landline phone
- when taxing received income; receive an increased tax deduction of 6,000 rubles
- ride free of charge on public transport as an accompanying person with a disability.
If a disabled person has only the second group, then payments to his guardian will not be assigned. However, he will be able to enjoy some benefits:
- You can receive social services free of charge.
- Travel as an accompanying person on public transport will be free.
- You can get a discount or compensation of 50% for housing and communal services.
- You can get some benefits when getting an education .
These benefits and payments apply to all guardians of disabled people.
But a group is not assigned to children, but rather the presence of a disability is simply determined. Therefore, the amount of payments for such a guardian will be 5,500 rubles until the child becomes an adult. But even after this, the payment will not change, since the same amount is provided for those who have been disabled from an early age.
In addition, guardians of children with disabilities have the right to claim the following benefits:
- to obtain housing or receive subsidies for its purchase;
- 50% discount or compensation on housing and communal services;
- apply for a plot of land for a garden or individual housing construction on a non-gratuitous basis;
- have all other benefits that are provided for guardians of sick people with group 1.
Please note that such payments are only available to non-working persons, and they must be able to work. If you are registered on the stock exchange and receive a corresponding benefit, you are not eligible to claim this payment.
But the ward himself can assign a reward to the person who takes care of him from his other income, for example, from renting an apartment or other property. You can learn more about this from the presented video.
Responsibilities of a guardian to the state
Benefits and payments for the maintenance of a disabled person
Social workers who receive an application for guardianship can check the candidate for a whole month. To ensure completeness of information, you may need a recommendation from the citizen’s previous places of work, an autobiography, a certificate of absence of debt on loans, alimony, housing and communal services and other payments. The district department of the Internal Affairs Directorate also provides a certificate of absence or presence of a criminal record of the candidate.
Social services inspect the place of residence of a potential guardian for compliance with sanitary standards. Living conditions can tell a lot about a person. After all, how he runs his household, cares for his own home, property and things will show his conscientiousness in the case of an immobile or limited-movement disabled person.
Such a responsible activity, sometimes requiring complete immersion and dedication, must be approved by the relatives of the person qualifying for the status of a guardian. Applications from a spouse, parents, siblings, adult children and other family members can sometimes play a decisive role and not give the right to custody.
Received benefits, privileges and payments for the maintenance of a disabled person are at the complete disposal of his legal guardian. However, the state imposes an obligation to regularly report on the expenditure of funds.
Every year, the officially appointed guardian must provide all receipts for purchases and services for which budget funds were spent. The Government Decree stipulates the rule on mandatory reporting. To do this, the citizen involved in guardianship fills out a form according to the established template.
Failure to comply with these instructions or failure to provide a complete report for all amounts will result in the violator being deprived of guardianship. If the state discovers misuse of funds, a fraud charge will be added.
Appointment of a guardian
It is important to understand that not every person can receive such responsibilities in order not only to take care of a person’s health, but also to represent his interests. Therefore, the following requirements are imposed on the applicant:
- He must be an adult . In exceptional cases, a teenager may request emancipation in order to gain full legal capacity at an earlier age.
- He must have legal capacity . That is, he must be fully aware of his actions and consequences.
- He should not have court decisions that would deprive him of parental rights or custody. There is no trust in such people, so they will not be trusted with the fate of another person again.
- The applicant must have a stable income. That is, even if he does not work, he must have his own source of funds, at least small, so that he has enough for his own maintenance.
- No criminal record under articles that provide punishment for causing harm to the health of other people. Otherwise, such a person will not be trusted.
- He should not have conflict situations with the relatives of the ward. That is, other people should not oppose the appointment of his candidacy, having significant evidence of their dissatisfaction.
When assessing an applicant, guardianship officers carefully study the moral aspects of the applicant, since it is important for them to transfer the fate of a disabled person into reliable hands. He must have normal health and psycho-emotional state in order to fully organize guardianship over a disabled person.
“receive an increased tax deduction of 6,000 rubles” is not true. Only up to 18 years old. The age of the ward citizen (incapacitated group I disabled person aged 26 years) exceeds the age established by paragraphs. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, therefore, the guardian taxpayer does not have the right to claim a standard tax deduction for personal income tax. Rationale: According to the general rule established by paragraph 1 of Art. 32 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, guardianship is established over minors, as well as over citizens recognized by the court as incompetent due to a mental disorder (regardless of their age). According to the general rule established by paragraphs. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the standard tax deduction for each month of the tax period applies to the parent, spouse of the parent, adoptive parent, guardian, custodian, foster parent, spouse of the foster parent, who is supporting the child. It is also determined that the tax deduction is provided in double amount to the only parent (adoptive parent), adoptive parent, guardian, trustee. Thus, a standard double tax deduction is provided to the guardian if he is the only guardian (this conclusion is confirmed by Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 14, 2015 N 03-04-05/72969). At the same time, par. 11 pp. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that a tax deduction is made for each child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24. At the same time, para. 18 pp. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation clarifies, in particular, that the tax base is reduced from the month in which guardianship (trusteeship) is established, or from the month of entry into force of the agreement on the transfer of the child (children) to be raised in a family until the end of the year in which the child (children) have reached the age specified in paragraph. 11 of this subparagraph. Since in the situation under consideration the age of the ward citizen exceeds the age established by paragraphs. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer-guardian does not have the right to claim a standard tax deduction.
“receive housing tax exemption” is not true. Only to the disabled person himself on his property. The guardian is not allowed. The list of preferential categories for paying property taxes is specified in Article 407 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Unfortunately, you do not fall into the preferential category. Therefore, you do not have any exemption.

Establishing guardianship for a person with a disability should be a meaningful decision. The issue is especially acute when a disability of the first group is assigned to a relative or loved one.
At the legislative level, there are no difficulties in the registration procedure, however, it is necessary that the applicant for the status of guardian has certain qualities and has the ability to provide such a service.
Who can be a guardian of a disabled person?
The candidate must meet a number of requirements, and the family connection between the ward and the potential guardian is of great importance. In general, the identity of the guardian must be subject to the following conditions:
- full legal capacity, that is, reaching the age of majority in order to fully legally bear responsibility for oneself (first of all);
- age up to 60 years (preferably), since pensioners often need help themselves and guardianship authorities are in no hurry to approve guardianship for them (there are no prohibitions in this regard in the law);
- absence of previous facts of deprivation of parental rights or cancellation of adoption, as well as offenses, addiction to alcohol or drugs, convictions for intentional crimes against health and life;
- non-involvement in same-sex relationships, that is, relationships can be, but only with a representative of the opposite sex;
— the presence of moral principles and qualities that will be welcomed by representatives of the guardianship authorities.
Plus, the health status of the guardian must be taken into account, who will have to undergo a medical examination before registering his new status. Experts, focusing on Government Decree No. 117 of February 14, 2013, do not allow, for example, citizens with:
- tuberculosis;
— disability of 1st group;
— substance abuse, drug addiction, alcoholism;
— oncology in stages 3 and 4 or stages 1 and 2 (if the candidate refuses treatment);
— behavioral and mental disorders until the termination of medical supervision;
- illnesses of a chronic and infectious nature, if complete recovery is not recorded.
Additionally, the future guardian must confirm that he has:
- owning a living space that meets sanitary and other standards (in any case, the new tenant should be comfortable in the space);
- a certain level of income that allows you to take care of the ward (certificates from work and other required documents are attached).
Important
! When considering a request, the guardianship and trusteeship authorities must take into account the opinion and desire of the potential ward, as well as his relationship with the guardian (for example, are they relatives or close friends, etc.).
Grounds for granting guardian status. Requirements for an assistant
A citizen who has been assigned disability group 1 is often completely deprived of the opportunity to serve himself independently. Therefore, the guardian needs to take personal responsibility for initiating an independent decision and providing the person in need with the necessary conditions for his life.
If the disability is not related to the presence of mental disorders, the disabled person has the right to choose his own assistant (Article 41 of the Civil Code of Russia).
The following legislative norms serve as the basis for the implementation of guardianship:
- Law No. 48 on guardianship of Russian citizens with disabilities, dated April 24, 2008;
- Federal Law on Social Protection of Disabled Persons in the Russian Federation No. 181/24.11.1995;
- Civil Code of Russia (Articles 32, 35, etc.) - about categories of citizens who vitally need a guardian, and the rights of such assistants;
- Family Code of the Russian Federation - Article 146, which reveals the requirements for the future guardian.
The above-mentioned regulations predetermine the qualities and conditions that a guardian should be endowed with:
- Age of majority and legal capacity;
- Availability of housing;
- Obtaining a permanent income;
- Good health;
- No addiction to alcohol or drugs.
Such qualities must be confirmed by characteristics from the place of residence and work.
Law No. 48 (Article 10, Part 2) provides that POiP has the right to request information about the applicant for the role of guardian from the following bodies:
- At the local department of internal affairs;
- Medical organizations;
- Civil registry departments.
Such serious selection is required to guarantee an honest relationship between the ward and the guardian, since the latter must not only care for a helpless disabled person of group 1, but also manage his household, look after his property, and make transactions necessary for the disabled person in his interests (Article 32 of the Civil Code , item 2). Most often, close relatives are appointed to the role of guardian: husband, wife, father, mother, brothers and sisters.
Important! Once a year, the disabled person’s assistant reports on expenses in performing his duties to the OOiP (guardianship and trusteeship authority) at the place of residence of the disabled person.
Guardianship can continue for as long as desired until it is terminated due to objective reasons, unworthy behavior of the assistant, or other subjective reasons. The appointment of the next guardian is subject to the approval of the candidate by the POiP.

If a guardian has taken on the responsibility of caring for a seriously ill citizen and for this reason cannot work, the state gives him the opportunity to receive compensation for guardianship. Regional legislative acts also provide for the possibility of guardians of group 1 disabled people receiving certain payments or benefits.
Features of guardianship
Some features of caring for disabled people should be clarified in advance so that later a large number of difficulties do not arise that may be beyond the capabilities of the person who has decided to formalize guardianship.
In a situation where a group 1 disabled person is deprived of legal capacity, a guardian must be appointed . If he is partially able to care for himself, he is assigned a caregiver. In a situation where a disabled person of group 1 is fully capable, he cannot be assigned guardianship or trusteeship. In such a situation, only patronage is possible.
If the disability is not caused by mental illness, then the person can choose his or her own guardian.
It is possible to obtain guardianship over a group 2 disabled person only due to the person’s loss of legal capacity. For example, the restriction was imposed by the court as a result of the manifestation of mental disorders that prevent the person from making important legal decisions. At the same time, disability does not have to be associated specifically with this disease.
When registering guardianship, you should be guided by the following regulatory documents:
- Family Code of the Russian Federation.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 343 of June 4, 2007.
- Federal Law No. 48 dated April 24, 2008.
When registering guardianship over disabled people of groups 1 and 2, the person will be given the opportunity to represent the interests of the incapacitated citizen. Property management and security impose certain requirements on the presence of certain qualities in the applicant for guardianship rights, therefore special authorities provide this opportunity only after a thorough check of the applicant.
The procedure for registering guardianship over a disabled person of group 1
In order to competently arrange guardianship of a disabled person of group 1, an applicant for this role must do the following:
1. Select documents certifying the need for third-party care for the life of a disabled person. This includes:
- His passport;
- Conclusion of a medical and social examination on assignment of disability group 1;
- Data on the availability of real estate and a copy of the certificate of ownership;
- A document from the Pension Fund confirming the amount of pension provision for a disabled person;
- The consent of the latter to be cared for by this particular citizen.
Amount of payments to trustees for custody
Payments to guardians of disabled and incapacitated people are small and amount to:
- 10,000 rubles – for citizens caring for disabled minors. An important condition for the provision of payment is the absence of official work for the guardian.
- 1200 rubles – for unemployed citizens caring for disabled people of group 1.
Guardians of disabled children can also count on a tax deduction of 6,000 rubles.
The benefit is paid regardless of whether the guardian and the disabled person live at the same or different addresses. Citizens who have received guardianship over disabled people of group 2 are deprived of financial support from the state, but they are provided with an additional 14 days of paid leave annually.
Payments for guardianship of disabled people of group 1 are terminated in the following cases:
- Death of the person being cared for.
- The guardian goes to work.
- The actual termination of care for the person under guardianship.
Termination of care services can be initiated by a disabled person. To do this, it is enough to submit an application to the state social service, which made the decision to appoint a guardian.
Attention! From January 1, 2021, guardians can apply for payments online.
Refusal to register guardianship: reasons and grounds
Citizens who have previously been deprived of parental (guardianship) rights or have a criminal record can receive an unequivocal refusal to assign guardian status. A previously committed crime must be one that is directed against the health or life of people (Article 35 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 2).

Grounds for refusal may also be:
- Provision by an applicant for the role of guardian of distorted information about himself;
- Presence of health problems (mental disorders, viral and other serious diseases), disability of group 1;
- Abuse of alcohol, narcotic or psychotropic substances;
- Lack of stable income and living space, and if it is available, the housing’s compliance with sanitary standards is taken into account.
If a Russian applying for the status of a guardian has not received approval of his candidacy, he has the right to appeal to the court and challenge the decision made by the OOiP.
Before filing a statement of claim, it would be more correct to contact the management of the body for an explanation of the reasons for the dissatisfaction of the application.
Filing a claim becomes possible within a month and is carried out to the authority at the location of the plaintiff (interested person) or defendant (OOiP).
Patronage and care for disabled people of group 1: features of the organization
Modern professional work is based on an understanding of the condition of a person with disabilities. His activity decreases as a result of disturbances in physique or body functions, making it difficult for him to perform household and social activities.
The task of the guardian is to compensate as much as possible for limited capabilities and to help the ward live life to the fullest. This is not an easy task, since group 1 disability is associated with severe functional disorders in the body. To perform his duties efficiently, the guardian must:
- know medical standards for first aid;
- have the skills to serve immobilized and limited mobility patients;
- have good communication skills;
- be attentive, patient, physically resilient;
- have basic knowledge of the psychology of people with disabilities.
Patronizing a disabled person of group 1 requires the caregiver to mobilize all mental and physical strength. In order to organize quality care and ensure a decent quality of life for a loved one, a caregiver often has to sacrifice personal life, study, and work. At the same time, the lack of basic care skills can worsen the health of both the ward and the guardian.
Termination of guardianship
One of the reasons for terminating the services of a guardian is his personal decision. The release of a guardian can occur when a disabled person (a disabled child or an elderly person) is placed in a specialized medical or educational institution.
OOiP may deprive an assistant of his duties if the following circumstances occur:
- Inadequate performance of duties to care for a person with a disability (leaving a helpless citizen unattended, using the guardian’s capabilities for personal gain). If the assistant’s guilt is proven, he may be brought to administrative responsibility (Article 39 of the Civil Code of Russia, paragraph 3);
- Illegal actions of a disabled person's assistant or failure to fulfill assigned duties will entail criminal liability in accordance with Article 26 (Part 4) of Law No. 48, dated April 24, 2008;
- Lack of mutual understanding between the ward and the assistant, which the disabled person reported to the guardianship authority.
Both the disabled person himself and his relatives, close people, and neighbors can file a complaint with the guardianship authority.
Legislative regulation of various legal acts and bringing them to a unified interpretation is carried out by the institution of guardianship and trusteeship. Correct implementation of the provisions and norms of legal acts will improve the legal situation of the physically and socially unprotected category of Russian disabled people.
Hello dear reader. In this material we will talk about how guardianship is established over a disabled person of group 1. Is this opportunity the will of a limited person or is it forced upon him? What rights does the ward have in this case? What requirements are imposed on the candidate, and what preferences does he receive if his credentials are approved? We will try to sort out all these questions within the framework of this material.

Promotion. Legal consultation 2500 rubles FREE until October 11
Payment amount
How much do they pay for guardianship? The amount and forms of payments depend on who is the guardian:
| Reasons | Types, forms |
| Parent doesn't work | Monthly payment in the amount of 60% of the minimum wage (Presidential Decree No. 551) |
| Disability pension | Since childhood – 11445 Acquired disease – 9538 |
| Monthly allowance | 3357 (Presidential Decree No. 175) |
| One-time payment when transferring a citizen to a guardian | 14497,80 |
Children with disabilities of group 1 can be brought up; adults can live in foster families. The RF IC establishes that a disabled person can be placed in a foster family. A corresponding agreement is concluded between guardianship and adoptive parents. Payments to guardians are determined at the regional level (in one region they may be more, in another - a little less). For example, in the Moscow region payments are as follows:
- the ward is classified as health group 1 or 2 due to health reasons - 12,650 for a child under three years old, 9,200 - after three years;
- the ward is assigned to groups 3-5 due to health reasons, then 25,000.
Guardianship payments are intended for the disabled person. They are spent exclusively on his needs, maintenance, payment for food, purchase of vital things.
The concept of guardianship and its types
Registration of guardianship is a certain procedure that assigns certain rights and responsibilities to the person who accepted it. Their list depends on the form of care. The powers listed in the law are assigned only to the person whose candidacy is approved by the guardianship authorities.
Guardianship is a type of protection of the rights of a citizen who is unable to work due to age, physical limitations or mental disorders. Depending on the type of restriction, one of the following forms of care may be prescribed:
- Full custody. With it, the guardian is responsible for the health and well-being of the incapacitated citizen. He is authorized to make decisions in the interests of the ward, manage his income and property.
- Patronage. This is partial guardianship over a person who is incapacitated but still retains legal capacity. The representative in this case only helps his ward in the implementation of legal rights, provides assistance and other types of assistance at the initiative of the disabled person.
Patronage or full guardianship will be established depending on what restrictions caused the limitation. If the ability for self-care and movement is lost due to the presence of physical abnormalities, then patronage assistance is issued. To officially confirm the powers of the guardian, consent will be required from the person whose disabled status is officially confirmed.
Incapacity recognized by the court is confirmation that, due to the presence of a mental illness or disorder, the person is not able to adequately assess the situation and make informed decisions. Then a guardian is forcibly appointed, who will act in the interests of the ward and will receive a wide range of powers and obligations.
Attention!
Guardianship can be either voluntary or compulsory.
Understanding guardianship and its types
Guardianship in simple words is when one capable citizen represents the interests of another person who, due to limited capabilities, is recognized as incompetent and in need of comprehensive assistance.
In general, guardianship is much broader and involves not only caring for a disabled person who is practically incapable of any independent actions. In fact, the guardian still has to protect his interests, if necessary.
Guardianship consists of:
— providing care for those in need of group 1;
— management of property belonging to a disabled person, as well as ensuring its safety;
— organizing conditions and everything that may be needed to maintain the health of a person under care in group 1.
As for the forms (types) of guardianship, there are not many of them. This is patronage, guardianship and full guardianship. Let's look briefly at each type.
1) Patronage
most often implemented if the case concerns a legally competent adult citizen, and the parties enter into an agreement. But this form of guardianship is not excluded in relation to disabled people with group 1, if they are unable to fulfill their duties and represent their rights.
2) Guardianship
can establish if the fact of limited legal capacity of a person is recognized in court. Or persons aged 14-18 years are considered. It is worth considering an important point: guardians have the right to give consent to the execution of transactions in which a disabled person is involved, but they should not carry out transactions on behalf of the ward. Simply put, the guardian only approves the fulfillment of the duties and rights of the ward.
3) Guardianship
is fully applicable if a person is incompetent (this is recognized by the court) or is in fact such, that is, the age of the ward plays a role here - up to 14 years.
Important
! The guardian of a disabled person of group 1, as the legal representative of his interests, is provided with a full set of duties and rights of the person under guardianship.
Legislative regulation of the issue
To understand the essence of guardianship, the rights and obligations of the parties and to become familiar with the procedure for obtaining benefits, you need to refer to some legislative acts. Let's consider projects that will reveal the issue in full.
| Legislative acts regulating the issue | ||
| № | Name, date of adoption | Issues that are regulated |
| 181 | On the protection of disabled people, dated November 24, 1995 | Defines the concept of disability |
| Stipulates social guarantees for limited persons | ||
| 197 | Labor Code of the Russian Federation, dated December 30, 2001 | Indicates benefits that are provided to a working caregiver |
| Establishes requirements for candidates, legal and mandatory parameters of the parties | ||
| 51 | Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Part 1), dated November 30, 1994 | In part of Art. 35 defines the concept of guardianship and guardianship |
| 48 | Federal Law on guardianship and guardianship, dated April 24, 2008 | Determines the types and features of the purpose |
| Specifies the procedure | ||
| 1013-n | Order of the Ministry of Social Development | Establishes criteria for determining disability |
| № 423 | Government Decree | Defines the rules and order of procedure |
Features of guardianship over a disabled person of group 1
The main feature of establishing care for a disabled person of the first category is the right to financial assistance. If a caregiver cannot find a job due to the need for constant presence in the life of the ward, then he is assigned a monetary allowance. Let's consider the main features of establishing guardianship:
- A guardian cannot be appointed for a person who is in the custody of a state institution. For example, the administration of this institution is responsible for the well-being of residents from nursing homes.
- Only one legal representative can be appointed.
- Guardianship is established compulsorily if the fact of incapacity is confirmed.
- The candidate must express a voluntary desire to become responsible for the welfare of a disabled person.
- With full guardianship, the candidate is responsible for the health and life of his ward and for his property.
- For foster care, the consent of the disabled person is required.
Article 32 of the Civil Code determines that a guardian is a legal representative who, acting in the interests of a ward, can make all transactions on his behalf, including those of a property nature.
How to obtain guardianship over a disabled person of group 1
Guardianship, which entails certain rights and obligations, is not established automatically. A relative who actually cares for a disabled person is not a legal guardian. The appointment must be initiated or you will not be eligible for benefits.
- Passing the ITU to confirm disability.
- Medical examination of a candidate for trustee.
- Collection of documents.
- Filing an application to guardianship or court.
- Making a decision.
- Becoming a candidate for rights.
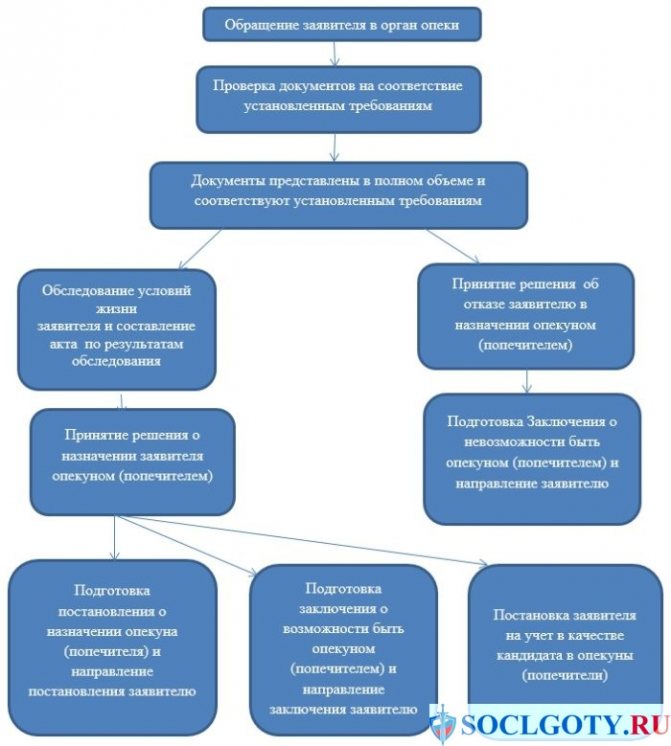
Where to contact
Which authority to contact for appointment depends on the legal capacity of the ward. If there are no mental health problems, then you need to act through the guardianship authorities. Persistent mental disorders are grounds for going to court. Once a person is declared incompetent, a legal representative must be appointed.
Attention!
Guardianship authorities agree on the candidacy of a guardian and monitor his commitment in the process of caring for a sick person.
Required documents
- First package from a disabled person:
- ITU conclusion;
- passport;
- court order of incapacity (if any);
- certificate from the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation on the amount of benefits;
- property data.
- Second set from the applicant:
- original passport + copies;
- characteristics from the employer;
- income certificate;
- autobiography;
- extract from the house register;
- a medical report confirming the absence of persistent diseases;
- report on the quality of living conditions (provided the disabled person lives with a guardian);
- certificate of good conduct;
- an extract from the dispensary stating that the candidate is not registered.
For reference!
Medical certificates are valid for 3 months.
Application for guardianship
It is submitted by an applicant who plans to take responsibility for a disabled person. This is a special form containing a number of mandatory information, which is filled out by the candidate at the guardianship authorities.
What documents need to be prepared to register guardianship?
In order to confirm your desire to become a guardian, you must provide the following documents to the guardianship and trusteeship authority:
- Statement.
- Autobiography.
- Passport or other identity document.
- Medical certificate of health.
- Certificate of employment or other document reflecting income level.
- Certificate of no criminal record.
- Certificate from a narcologist.
- A document confirming the availability of living space.
- Consent of persons living with the applicant in the same living space.
- MSEC conclusion on assignment of a disability group.
- A court decision declaring a person incompetent.
This is a general package of documents. It should be noted that in each specific case the applicant may need additional information.
Payment of benefits and allowances to guardians of group 1 disabled people
Financial support for caregivers is one of the popular types of benefits. Caring for a disabled person from childhood, you can receive 5,500 rubles; for other applicants in the first group, they pay 1,200 rubles monthly. At the regional level, additional monetary support can be provided.
- reduction of work shifts;
- 14 days towards the main vacation;
- ban on hiring on weekends and holidays;
- early retirement;
- 4 additional days off per month.
Popular questions and answers
Question:
What other benefits are offered when caring for a disabled person?
Answer:
At the federal level, other than monthly benefits and labor preferences, there is no provision. Some regions offer applicants a discount on utility bills, free trips to a sanatorium and travel on public transport.
Question:
In what time frame do authorized bodies make a decision on an application?
Answer:
On average, the review process takes 10-15, maximum 30 days.
A disabled person has the right to decide whether he needs a guardian or not, if he is not limited in his legal capacity. Otherwise, a legal representative will be assigned to him. Official status allows the trustee to represent the interests of the ward and forces him to take care of him.
What are the responsibilities of the person providing patronage?
Each person's needs and requirements are different. Some people cannot imagine life without a manicure, while others cannot imagine life without regular visits to the gym. How to determine the mandatory minimum of actions when caring for a disabled person?
There is a fairly clear definition of the term “continuous care” - this is the assistance of outsiders in meeting the basic needs of a person, including:
- personal hygiene;
- dressing;
- nutrition;
- fulfillment of natural physiological needs.
The law does not regulate the amount of time that a guardian must spend with his ward, nor does it specify a specific list of work that is required to be performed within the framework of patronage.








