The rental of residential premises, regardless of the rental period, must be formalized by an appropriate agreement. According to Russian law, the tenant is responsible to the landlord for the safety of the property transferred to him under the lease agreement. Moreover, such property means not only the real estate itself, which was transferred under a lease agreement, but also things located within the residential premises.
In order to avoid possible disputes between the parties regarding the fact of transfer of property located in the apartment, it is necessary to draw up an appropriate inventory or an acceptance certificate. This document will reflect all the property to be transferred to the tenant along with the apartment for temporary use. Thus, an apartment rental agreement with an inventory of the property is an additional guarantee for the parties that the counterparty will conscientiously fulfill its obligations and is necessary in all cases when the property located in it is transferred along with the real estate itself.
Concept
This action is carried out by the bailiff on the basis of a writ of execution. It is he who notifies the accused about the action being performed, as well as its time and place. He has the right not to clarify the fact of receipt of the document. Sending it is considered the main provision for the arrival and seizure of property.
The procedure is legally accompanied by two witnesses. These could be neighbors or relatives. A representative of the accused has the right to be present if he cannot be present at this action. Only an adult citizen can replace the main borrower. This may be a relative or representative of the housing authority.
To conduct an inventory, the state representative must present a document certifying the position and a resolution on enforcement proceedings.
Arrest is considered the final stage in such proceedings. It seizes all the property of the accused so that the latter cannot dispose of it, including donating and selling.
It is the inventory and subsequent arrest that causes the most controversy in the judiciary. Debtors often complain that bailiffs violate their rights. To clarify this, it is better to know the main nuances and legal norms.
Seizure is made at the end of the trial. Once it ends, the accused is notified. He has the right to pay the full amount of the debt within five days after receiving the document. Without prior notice, inventory and seizure of property is not possible.
If the debtor does not meet the payment deadline, then the state representative makes a decision on the sale of the property and its arrest. A copy of such a document is sent to the place of residence and registration of the accused. Only after all the above actions, the bailiff has the right to come to the place of registration and describe the property.
Who is required to make an inventory?
The debtor himself or a FSSP specialist will describe the property. For a defaulter who has already undergone FSSP proceedings, the inventory is compiled twice - first by bailiffs, and then as part of bankruptcy.
In bankruptcy
Bankruptcy proceedings are initiated at the request of the debtor or his creditors.
This affects the order in which the inventory is drawn up:
- if a citizen files for bankruptcy, he must immediately provide a list of all his assets and accounts;
- if bankruptcy is initiated by creditors, individuals. the person will describe his assets as required by the financial manager.
There is no need to describe the property if bankruptcy follows a simplified procedure through the MFC. In this case, physical the person submits to the center employee only a register of his obligations to creditors. The sale of assets in the MFC is not carried out.
For almost all documents filed during bankruptcy, there are special forms and requirements for completion. Violation of the rules for drawing up documents may be grounds for refusal to initiate a case. To eliminate such risks, it is better to draw up an inventory and other documents with the support of a lawyer.
In production FSSP
Bailiffs are engaged in the execution of judicial acts, including debt collection. To ensure collection, they can seize property assets and accounts of the debtor. Seizure is an interim measure to prevent the defaulter from selling the property, donating it or transferring it to other persons.
Basic rules for inventory and seizure of assets in FSSP proceedings:
- bailiffs can seize any property, even if it is not subject to sale;
- when filling out the act, the bailiff will immediately indicate the prohibitions and restrictions that the defaulter must comply with and clarify the procedure for use;
- Having described the assets, the FSSP specialist can leave them for safekeeping with the debtor or seize them.
Drawing up an inventory does not mean that the seized property will necessarily be sold at auction or through a specialized organization. If the citizen pays the entire debt to the collector, the arrest will be lifted. Also, Article 446 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation contains a list of assets that are not subject to sale. They can be listed in the inventory and seized, but such property will not go to auction.
Legal basis
This action is regulated by legal acts. All this must be within the framework of the rules of the federal service.
For this you need:
- Federal Law “229, Article 80. It stipulates the rules for seizure and the basic requirements for the property of the accused;
- Federal Law “118” stipulates the duties of government representatives and their work;
- Federal law with an additional agreement to allow government agencies to request and operate bank accounts.
The confiscation of the property of the accused is especially carefully prescribed in the legislative act on the seizure.
Do bailiffs describe the property of the house? Check the grounds!
Bailiffs can act on the basis of a writ of execution (writ of execution or court order).
Resolutions of state bodies of the Russian Federation have the status of a legal basis for starting collection procedures. For example, decisions of the Tax Inspectorate, the State Road Safety Inspectorate, and the Federal Social Insurance Service can be directly submitted to the enforcement authorities. The legislator allows situations when authorized bodies can independently issue documents, without going to court, which can serve as a basis for initiating enforcement proceedings. A good example is traffic police fines. In this case, traffic police officers themselves can make decisions to bring the guilty person to administrative responsibility. The resolution in the case of an administrative offense will be an executive document. By the way, I talked about how to cancel a writ of execution in this article.
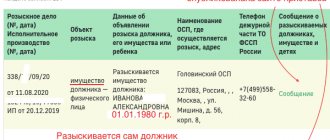
We will assume that the first condition is met. The claimant has a writ of execution. By law, the claimant must submit a writ of execution within 3 years. How does this happen in practice? The writ of execution is given to the department office along with the application. A seal stamp indicating acceptance of the documents is affixed to the copy of the claimant's application. At this stage, the enforcement proceedings number is formed. By the number of the enforcement proceedings, as well as by full name, you can check information about the existence of a debt.
The next stage is the decision by the official to start production. This stage is very important, since from the moment enforcement proceedings are initiated, the person officially becomes a debtor, risking being left without any hard-earned property.
Drawing up an inventory of the debtor's property by bailiffs
Drawing up an act is a labor-intensive and complex matter. So how does this procedure happen? What to do about this? And what can’t bailiffs describe?
When drawing up a property inventory document, the debtor has the right to stipulate what items he agrees to sell. This does not contradict current legislation. The bailiff is obliged to take this into account and satisfy the request. If the value of the goods presented does not satisfy the amount of the debt, then the inventory of the property continues until the debt is fully repaid.
A sample inventory act is established at the legislative level. The document details must include:
- place of compilation;
- time of compilation;
- Full name of witnesses;
- claimant and debtor under the writ of execution;
- citizen to whom property is transferred for protection;
- details of the writ of execution;
- a property name that is described with distinctive features;
- the weight of each item;
- quality and cost assessment;
- the period for the sale of this property.
In the legal document, notes are made about the responsibility of the person to whom these items are transferred for storage. His responsibilities are explained to him. The rights of debtors and other persons regarding the period for appealing the actions of bailiffs are also stipulated. The document specifies all appeal procedures and claims of persons for a given period of time.
In the event that, during the seizure of goods, other persons claim ownership of the property, it is entered into the documents, but the claim of a third party must be entered as a note. The act is signed by the bailiff, witnesses and the person who received such items under protection.
The document is drawn up in two copies. One remains for the debtor, one for the bailiff.
If enforcement proceedings involve a large debt, then the decision may affect real estate. Its implementation may take an indefinite period of time. Before the auction, the debtor himself becomes the guardian of the property.
This is formalized in accordance with the norms and procedures of the law. That is, a receipt must be signed for the transfer for safekeeping.
Often the storage of such real estate drags on for years, or even decades. Selling a product is not an easy task. And if it is not sold, then it is returned to the debtor.
An arrest is made only on legal grounds. This basis becomes the existence of enforcement proceedings. Applicable only to citizens who have not timely fulfilled their obligations to pay utility bills, loans or administrative fines.
The description applies:
- when the judicial authority orders the confiscation of the property of the accused for the sale of property in order to pay off debt obligations;
- when deciding to seize;
- while retaining the property for transfer to the applicant.
Seizure may be applied to any goods of valuable origin, such as:
- real estate;
- automobile;
- accounts opened with a bank;
- precious metals;
- household appliances and electronics.
All exceptions are stipulated in the Civil Procedure Code, or more precisely in Article 446.
Read the article on how to obtain debt collection in an arbitration court. On disciplinary action against military personnel. More details here.
Not subject to arrest:
- real estate objects that are the only home of the owner and his family;
- equipment necessary for a comfortable stay. These include a refrigerator and a stove;
- technique in singular;
- clothing excluding jewelry;
- goods for professional activities;
- animals;
- a car or other equipment of a disabled person;
- Food;
- badges, orders;
- mortgaged property.
Bailiffs do not have the right to search the apartment.
If this is a legal entity, then the seizure cannot be imposed on the property taking part in the proceedings. If no other goods are found, then any actions with this property are seized.
Responsibilities of bailiffs
According to the current bill, a state representative has the right to:
- seize property, guided by the laws and without violating the rights of the debtor;
- to forcibly collect the debt and initiate enforcement proceedings;
- look for the debtor and act ethically;
- resolve controversial and conflict situations.
How to make an inventory of property when drawing up a residential lease agreement?
From a legal point of view, an inventory of property when concluding an apartment lease agreement can be drawn up in two ways.
It can be included in the text of the residential rental agreement itself as a separate clause or drawn up in a separate document, in the form of an appendix to the main agreement. A sample inventory of property can be found on legal portals, where these documents are freely available.
When drawing up a rental agreement with an inventory of property, all property transferred by the lessor to the tenant along with the residential premises must be included in it.
When compiling an inventory, it is necessary to indicate detailed characteristics of things, namely:
- The exact name of the transferred items;
- Individual characteristics of the item (color, size, model features);
- Year of release (production);
- Other identification features that may be contained in property documents;
- Quantity.
When compiling an inventory, the tenant needs to be as careful as possible. If there is certain damage or inoperability of the property, this must be noted in the inventory. If there is no such mark, the property is considered to be transferred without damage and in working condition.
In addition to the list of items themselves, at the discretion of the parties, the inventory may also include such characteristics of things as:
- price;
- degree of wear.
This is necessary so that if possible conflicts arise, the parties can use this document to establish the degree of damage caused to the items and its monetary equivalent.
However, when assessing the cost and degree of wear and tear of items to be included in the inventory, you need to be quite careful. These characteristics of things are established by agreement of the parties. In reality, such an assessment may be far from reality and will be disputed in the future, which may lead to negative consequences for one of the counterparties.
Restriction of rights and complete arrest
When drawing up a document, all restrictions on the rights to use it are indicated. Violation of such a resolution is punishable in accordance with the law. The debtor faces criminal liability.
Seizure depends on certain actions, amounts and decisions of the executive body. In each case, this is your own decision. The moment is personal.
When making a decision, its assessment, purpose and type are taken into account.
The seizure cannot be directed to real estate if this is the only housing for the debtor and his family. To clarify this fact, the executive body sends a request to Rosreestr. If the debtor has additional real estate, then the property is subject to seizure. This type of notice is sent to the debtor.
From this moment on, he no longer has the right to dispose of it. Until its sale, it remains in the custody of the owner.
Where does the inventory take place?
Bailiffs come to the place of registration of the debtor or to the place of his temporary residence (including living in an apartment or renting a house where he has not yet registered). Bailiffs have the right to open (crack) doors to provide access to the premises and conduct a search there. But this can only be done if there are witnesses and a local police officer.
In practice, breaking the door is used only as a last resort if the debtor does not make contact at all and has repeatedly not allowed the bailiffs (investigator) into his premises.
Thus, the inventory can take place in any place where the debtor has property, be it his personal home, a rented apartment or a garage (storage), etc.
Property may be seized at the place of permanent or temporary residence