A legal society guarantees that every person from birth has certain rights and freedoms. Moreover, regardless of age: even children have civil rights, which is guaranteed to them by the Constitution. As practice shows, today one can often encounter non-compliance with constitutional rights, including in relation to minor citizens. The reasons are different and one of them is ignorance of the rights of small citizens and the freedoms that they may have.
Children is our future.
Children's rights laws
The main guarantees of rights are the following documents: the Constitution of the country, the Family Code of the Russian Federation and the Convention on the Rights of Children . The last document was approved at one of the meetings of the UN Assembly. In addition, the protection of the rights of minor children is guaranteed by various federal laws, which stipulate the following points:
- Healthcare.
- Basic guarantees.
- Education.
- Guarantees of social support for children left without parental care.
- About equality.
- On social protection in the Russian Federation for disabled children, etc. (disabled people can also apply for a visa and travel).

Basic laws on children's rights in the Russian Federation.
Convention on the Rights of Children
The legal regulation of all emerging issues regarding the protection of the rights of the child is based on the Convention. This document is the fundamental one among all the listed laws. In other words, the Convention serves as a guarantee of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation. But that's not all: there are many other points that need to be mentioned.
The Declaration of the Rights of the Child contains many more points regarding the protection of children and their lives. It mentions the protection of orphanhood, the rights of disabled children, protection from sexual violence and cruel treatment. The Declaration of the Rights of the Child also contains the following guarantees:
- Protection of living space.
- The secrecy of telephone conversations and correspondence.
- Non-disclosure of personal information, in particular about adoption, personal life, etc.
- Opportunity to receive help in case of family deprivation. In such cases, the rights of minor children are protected by the state.
- Protection from being forced to work in hazardous work.

What does a child have the right to in Russia?
How does the state protect children?
Respect for the rights of every minor is the responsibility of government agencies. In particular, this is the task of institutions responsible for guardianship and trusteeship. If serious conflict situations arise, the prosecutor's office and the court may intervene.
To do this, the child himself (or his parents) can fill out a special application form and send it to the prosecutor's office. Next, the case will go to court, which will regulate the rights of the child.
Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 124-FZ
RUSSIAN FEDERATION
THE FEDERAL LAW
On the basic guarantees of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation
Adopted by the State Duma on July 3, 1998
Approved by the Federation Council on July 9, 1998
(As amended by federal laws dated July 20, 2000 No. 103-FZ, dated August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ, dated December 21, 2004 No. 170-FZ, dated June 26, 2007 No. 118-FZ, dated June 30, 2007 No. 120-FZ, dated July 23, 2008 No. 160-FZ, dated April 28, 2009 No. 71-FZ, dated June 3, 2009 No. 118-FZ, dated December 17, 2009 No. 326-FZ, dated July 21, 2011 No. 252-FZ, dated December 3, 2011 No. 377-FZ, dated December 3, 2011 No. 378-FZ, dated April 5, 2013 No. 58-FZ, dated June 29, 2013 No. 135-FZ, dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ, dated November 25, 2013 No. 317-FZ, dated 02.12.2013 No. 328-FZ, dated 29.06.2015 No. 179-FZ, dated 13.07.2015 No. 239-FZ, dated 28.11.2015 No. 358-FZ, dated 28.12.2016 No. 465-FZ, dated 18.04.2018 No. 85 -FZ, dated June 4, 2018 No. 136-FZ, dated December 27, 2018 No. 562-FZ, dated October 16, 2019 No. 336-FZ, dated December 27, 2019 No. 514-FZ, dated June 8, 2020 No. 178-FZ, dated July 31 .2020 No. 303-FZ, dated 04/05/2021 No. 77-FZ)
This Federal Law establishes the basic guarantees of the rights and legitimate interests of the child, provided for by the Constitution of the Russian Federation, in order to create legal, socio-economic conditions for the realization of the rights and legitimate interests of the child.
The state recognizes childhood as an important stage of a person’s life and proceeds from the principles of priority of preparing children for a full life in society, developing their socially significant and creative activity, and instilling in them high moral qualities, patriotism and citizenship.
CHAPTER I. GENERAL PROVISIONS
Article 1. Concepts used in this Federal Law
For the purposes of this Federal Law, the following concepts are used:
child - a person until he reaches the age of 18 years (the age of majority);
children in difficult life situations - orphans; children left without parental care; disabled children; children with disabilities, that is, having deficiencies in physical and (or) mental development; children are victims of armed and ethnic conflicts, environmental and man-made disasters, and natural disasters; children from families of refugees and internally displaced persons; children in extreme conditions; children are victims of violence; children serving sentences of imprisonment in educational colonies; children in educational institutions for students with deviant (socially dangerous) behavior who need special conditions of education, training and require a special pedagogical approach (special educational institutions of open and closed type); children living in low-income families; children with behavioral problems; children whose livelihoods are objectively disrupted as a result of current circumstances and who cannot overcome these circumstances on their own or with the help of their family; (As amended by federal laws dated June 30, 2007 No. 120-FZ, dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ, dated June 8, 2020 No. 178-FZ)
social adaptation of a child is the process of active adaptation of a child in a difficult life situation to the rules and norms of behavior accepted in society, as well as the process of overcoming the consequences of psychological or moral trauma;
social rehabilitation of a child - measures to restore the social connections and functions lost by the child, replenish the life support environment, and strengthen care for him;
social services for children - organizations, regardless of organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership, carrying out measures for social services for children (social support, provision of social, medical, psychological, pedagogical, legal services and material assistance, organization of recreation and health improvement, social rehabilitation of children in difficult life situations, ensuring employment of such children when they reach working age), as well as citizens carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity for social services of citizens, including children; (As amended by federal laws dated December 21, 2004 No. 170-FZ; dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ; dated November 28, 2015 No. 358-FZ)
social infrastructure for children is a system of objects (buildings, structures, structures) necessary for the life support of children, as well as organizations, regardless of organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership, that provide social services to citizens, including children, and whose activities are carried out for the purpose of ensuring a full life, health care, education, recreation and recovery, development of children, satisfaction of their social needs; (As amended by federal laws dated December 21, 2004 No. 170-FZ; dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ; dated November 28, 2015 No. 358-FZ)
children's recreation and their health improvement - a set of activities aimed at developing the creative potential of children, protecting and strengthening their health, preventing diseases in children, engaging them in physical education, sports and tourism, developing healthy lifestyle skills in children, and their adherence to diet and lifestyle in a favorable environment while fulfilling sanitary-hygienic and sanitary-epidemiological requirements and requirements for ensuring the safety of life and health of children; (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated December 21, 2004 No. 170-FZ; as amended by Federal Law dated December 2, 2013 No. 328-FZ)
organization of children's recreation and their health improvement - organizations (regardless of their organizational and legal forms) of seasonal or year-round operation, stationary and (or) non-stationary type, with round-the-clock or daytime stay, providing services for organizing recreation and health care for children (organizations of recreation for children and their seasonal or year-round health improvement camps, camps organized by educational organizations that organize recreation and health improvement for students during the holidays (with round-the-clock or daytime stay), children's work and recreation camps, tent-type children's camps, children's specialized (profile) camps, children's camps of various types thematic focus). For the purposes of this Federal Law, individual entrepreneurs providing services for the organization of recreation and recreation for children are equated to organizations for children's recreation and their health, if the requirements established by this Federal Law are met; (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated December 21, 2004 No. 170-FZ; as amended by Federal Law dated October 16, 2019 No. 336-FZ)
night time - time from 22:00 to 6:00 local time; (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated April 28, 2009 No. 71-FZ)
trafficking in children - purchase and sale of a minor, other transactions in relation to a minor, as well as recruitment, transportation, transfer, harboring or receipt committed for the purpose of his exploitation; (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated 04/05/2013 No. 58-FZ)
exploitation of children - the use of prostitution by minors and other forms of their sexual exploitation, slave labor (services) of minors, servitude of minors, illegal removal of organs and (or) tissues from minors, illegal adoption of a minor for mercenary reasons; (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated 04/05/2013 No. 58-FZ)
victim of child trafficking and (or) exploitation of children - a minor who has suffered from child trafficking and (or) exploitation of children, including those involved in child trafficking and (or) exploited, regardless of the presence or absence of his consent to carry out actions related to trafficking children and/or exploitation of children. (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated 04/05/2013 No. 58-FZ)
Article 2. Relations regulated by this Federal Law
This Federal Law regulates relations arising in connection with the implementation of the basic guarantees of the rights and legitimate interests of the child in the Russian Federation.
Article 3. Legislation of the Russian Federation on basic guarantees of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation
The legislation of the Russian Federation on the basic guarantees of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation is based on the Constitution of the Russian Federation and consists of this Federal Law, relevant federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, as well as laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in the field of protection of rights and legitimate interests of the child.
Article 4. Goals of state policy in the interests of children
1. The goals of state policy in the interests of children are:
implementation of children's rights provided for by the Constitution of the Russian Federation, non-discrimination against them, strengthening the basic guarantees of the rights and legitimate interests of children, as well as restoration of their rights in cases of violations;
formation of a legal basis for guaranteeing the rights of the child;
promoting the physical, intellectual, mental, spiritual and moral development of children, instilling patriotism and citizenship in them, as well as the realization of the child’s personality in the interests of society and in accordance with the traditions of the peoples of the Russian Federation and the achievements of Russian and world culture that do not contradict the Constitution of the Russian Federation and federal legislation ;
protecting children from factors that negatively affect their physical, intellectual, mental, spiritual and moral development. (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated April 28, 2009 No. 71-FZ)
2. State policy in the interests of children is a priority and is based on the following principles: (As amended by Federal Law No. 122-FZ of August 22, 2004)
legislative provision of children's rights;
family support in order to ensure the education, upbringing, recreation and health of children, protect their rights, prepare them for a full life in society; (As amended by federal laws dated August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ; dated December 21, 2004 No. 170-FZ; dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ)
(Paragraph no longer in force - Federal Law of August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ)
liability of legal entities, officials, citizens for violation of the rights and legitimate interests of a child, causing harm to him; (As amended by Federal Law dated April 5, 2013 No. 58-FZ)
support for public associations and other organizations engaged in activities to protect the rights and legitimate interests of the child. (As amended by Federal Law No. 122-FZ dated August 22, 2004)
Article 5. Powers of state authorities of the Russian Federation and state authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation to implement guarantees of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation
1. The powers of state authorities of the Russian Federation to implement guarantees of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation include:
establishing a federal policy framework for children;
choosing priority areas of activity to ensure the rights and legitimate interests of the child, protecting his health and morals;
(Paragraph no longer in force - Federal Law of August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ)
(Paragraph no longer in force - Federal Law of August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ)
the formation and implementation of federal target programs for the protection of children’s rights and childhood support and the identification of bodies, institutions and organizations responsible for the implementation of such programs;
(Paragraph no longer in force - Federal Law of August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ)
(Paragraph no longer in force - Federal Law of August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ)
establishing a procedure for judicial protection and judicial protection of the rights and legitimate interests of the child;
fulfillment of the international obligations of the Russian Federation and representation of the interests of the Russian Federation in international organizations on issues of protecting the rights of the child;
establishing the foundations of state regulation and state control of the organization of recreation and health improvement for children. (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated December 28, 2016 No. 465-FZ)
2. The powers of state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation to implement guarantees of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation include the implementation of state policy in the interests of children, resolving issues of social support and social services for orphans and children left without parental care (with the exception of children studying in federal state educational organizations), street children, disabled children, organization and provision of recreation and health improvement for children (except for the organization of recreation for children during the holidays), development and approval of a list of recommended tourist routes (other travel routes) for groups of tourists with the participation of children as part of the implementation of amateur tourism and for the passage of organized groups of children staying in organizations for children's recreation and their health, posting it on the official website of the executive body of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation on the Internet. (As amended by federal laws dated August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ; dated December 17, 2009 No. 326-FZ; dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ; dated April 18, 2018 No. 85-FZ)
CHAPTER II. MAIN DIRECTIONS OF ENSURING CHILD'S RIGHTS IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
Article 6. Legislative guarantees of the rights of the child in the Russian Federation
From birth, a child has and is guaranteed by the state the rights and freedoms of a person and a citizen in accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, generally recognized principles and norms of international law, international treaties of the Russian Federation, this Federal Law, the Family Code of the Russian Federation and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation.
Article 7. Assistance to the child in the implementation and protection of his rights and legitimate interests
1. State authorities of the Russian Federation, state authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, officials of these bodies, in accordance with their competence, assist the child in the implementation and protection of his rights and legitimate interests, taking into account the age of the child and within the scope of the child’s legal capacity established by the legislation of the Russian Federation through adoption of relevant regulatory legal acts, carrying out methodological, informational and other work with the child to explain his rights and obligations, the procedure for protecting the rights established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as by encouraging the child to fulfill his duties, supporting law enforcement practice in the field of protecting the rights and legitimate interests of the child . (As amended by Federal Law No. 122-FZ dated August 22, 2004)
2. The child’s parents (persons replacing them) assist him in carrying out independent actions aimed at realizing and protecting his rights and legitimate interests, taking into account the child’s age and within the scope of the child’s legal capacity established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
3. Pedagogical, medical, social workers, psychologists and other specialists who carry out the functions of upbringing, training, health protection, social support and social services for the child, promoting his social adaptation, social rehabilitation, may participate in events in accordance with the procedure established by the legislation of the Russian Federation to ensure the protection of the rights and legitimate interests of the child in state bodies and local governments. (As amended by Federal Law dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ)
4. Public associations (organizations) and other non-profit organizations may carry out activities to prepare a child to exercise his rights and fulfill his duties. (As amended by Federal Law No. 122-FZ dated August 22, 2004)
Article 8.
(Repealed - Federal Law of August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ)
Article 9. Measures to protect the rights of the child when carrying out activities in the field of his education
1. When carrying out activities in the field of education of a child in a family or in an organization carrying out educational activities, the rights of the child cannot be infringed.
2. The governing bodies of organizations carrying out educational activities do not have the right to interfere with the creation, at the initiative of students over the age of eight, of public associations of students, with the exception of children's public associations established or created by political parties, children's religious organizations.
3. Students of organizations engaged in educational activities, with the exception of students in educational programs of preschool and primary general education, have the right, independently or through their elected representatives, to apply to the commission for the settlement of disputes between participants in educational relations.
(Article as amended by Federal Law dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ)
Article 10. Ensuring children's rights to health care
In order to ensure children's rights to health care, in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, medical organizations of the state health care system and the municipal health care system take measures to provide children with free medical care, providing for the improvement of children's health, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases, including dispensary observation, medical rehabilitation of disabled children and children suffering from chronic diseases, and sanatorium-resort treatment of children. (As amended by federal laws dated August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ; dated November 25, 2013 No. 317-FZ)
Article 11. Protection of the rights and legitimate interests of children in the field of vocational guidance, vocational training and employment
(Name as amended by Federal Law dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ)
1. In accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation carry out measures to provide vocational guidance and vocational training for children who have reached the age of 14 years. (As amended by federal laws dated August 22, 2004 No. 122-FZ; dated July 2, 2013 No. 185-FZ)
2. If children over 15 years of age are hired, they are guaranteed remuneration for work, labor protection, reduced working hours, and vacation. Employees under 18 years of age are provided with benefits when combining work with training, conducting an annual compulsory medical examination, quotas for employment, termination of an employment agreement (contract) and other benefits established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Article 12. Ensuring children’s rights to rest and recovery
1. In order to improve the quality and safety of children’s recreation and health, federal executive authorities, executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local government authorities, within the limits of their powers, take measures:
on the adoption of normative legal acts regulating the activities of children's recreation organizations and their health;
to create safe conditions for children to stay in recreational organizations and their health;
to ensure maximum accessibility of services provided by children's recreation organizations and their health;
to monitor compliance with legal requirements in the field of organizing recreation and health improvement for children.
2. In order to improve the quality and safety of children’s recreation and health improvement, the organization of children’s recreation and their health improvement is obliged to:
create safe conditions for children to stay there, including disabled children and children with limited health capabilities (in the case of accepting these categories of children into the organization of children’s recreation and their health), supervision and care for children; provide their maintenance and food, organize the provision of first aid and medical care to children during their stay in the organization of children's recreation and their health in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation, including in the case of the following events in the natural environment with the participation of children: routes, other routes before
Until what age is a child considered such?
A child is considered a person who has not reached the age of majority (eighteen years of age). But there are also exceptions. The first case is if a 16-year-old teenager, with the consent of his parents (guardian, adoptive parent), gets a job, signs a contract or employment agreement, and engages in volunteering.
As an option, a 16-year-old teenager begins to engage in entrepreneurial activity, then he can already be declared legally competent. Another case is marriage before adulthood. In this case, the teenager is considered legally competent from the day the marriage was concluded.
For information about what emancipation of minors is, see the following video.
Minors and minors
By law, children were divided into two categories - minors and minors. Depending on the category of children in the Russian Federation, whether they are minors or minors, children and their parents are provided for by law with various rights and freedoms. A child is considered a minor from birth to the age of fourteen.
At the age of 14, a teenager becomes a minor. The rights and freedoms of each child depend on which category he belongs to. So, until he turns 14 years old, all issues are resolved by his parents (guardians, adoptive parents).
At the age of 14, a person already has the right to independently make decisions about small transactions, and upon reaching adulthood, he acquires the rights of an adult, becomes fully capable and has all the civil rights and responsibilities of other citizens of the state.

According to the law of the Russian Federation, 14 years is the period for obtaining a passport.
What rights does current legislation guarantee for a child?
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights issued by the UN regarding the rights of the child contained the following declaration: due to the fact that children are still physically and mentally immature, they must be guaranteed legal protection.
This will help ensure protection and care from the moment of conception until the age of 18. To ensure that children can live a happy life, several important principles have been established to ensure a happy childhood.
Principles of the Declaration
The most important of them states that every child has all fundamental rights that should be recognized by both other children and adults. Discrimination on grounds such as religion, language, gender, skin color, race, political or other opinions, national or social origin, property status or any other circumstances that affect both children and members of their family is prohibited.

Principles of the Declaration of the Rights of the Child.
Every citizen of the Russian Federation from birth has the right to receive a last name, first name and patronymic. They can be given by both parents and adoptive parents. If a father and mother have different surnames, which one their son or daughter will bear is decided by mutual agreement. If the parents could not agree, the child’s first and last name is given by the guardianship and trusteeship authority.
If parents do not like the name chosen by themselves or a government organization, they have the right to change the surname or first name, but until their child turns 10 years old. If the daughter or son is over 10 years of age, then, according to legal protection, it is possible to change the child’s last name or first name only if he agrees with this decision.
Social protection
Under the current law, a minor citizen is provided with social protection. He is also provided with favorable conditions so that he has the opportunity to develop spiritually, morally, mentally and physically, his freedom, dignity, social rights and interests are not oppressed by other people: the main goal of all legislative acts of the Russian Federation regarding children is to best ensure the interests of each child until 18 years.
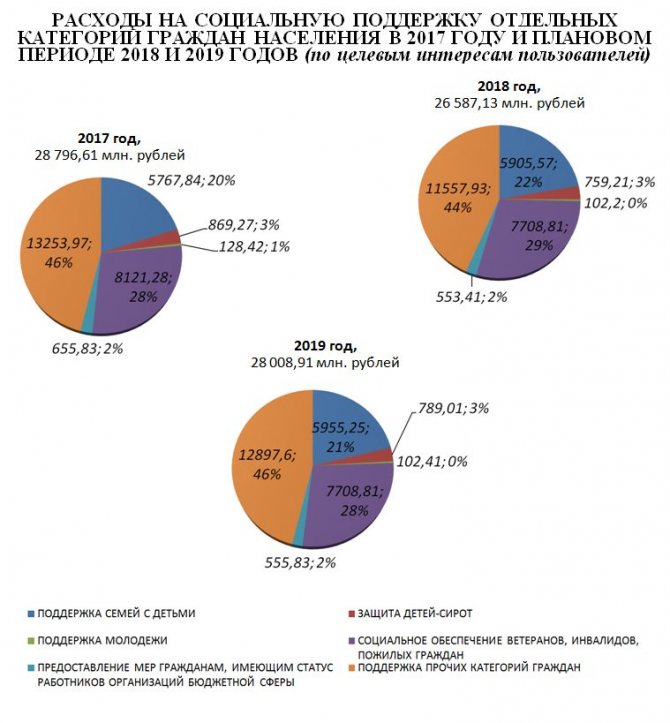
Expenditures on the social sphere of the Russian Federation.
Family law
Family law says: in order for a child to develop fully and harmoniously, he needs love and understanding, which only a family can give - natural or adoptive parents, guardians.
Material and moral security, an atmosphere of love in the family circle, parental responsibility - all this ensures a happy childhood for every child. The most important right of minor children is to always remain with their mother and only in exceptional cases is separation from her allowed. Society and public authorities are obliged to take care of the rights of orphans who have no family and no means of subsistence.
If a child lives in a large family, the ombudsman for children’s rights in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation must ensure that this family is provided with benefits from the state so that they can support the children.
Just about the main thing. Family law in the Russian Federation. We recommend watching it.
Why is it important?
The older generation in our country takes a very active part in the life and upbringing of children. Many minors often spend more time with their grandmother than with their parents. The same is true in some cases for siblings. However, this gives rise to some legal difficulties.
Finding a child with his closest people, but not his parents, can be interpreted as a lack of parental care. And this, in turn, may cause some “interest” among the guardianship and trusteeship authorities. This entails the strengthening of such a phenomenon as “juvenile justice,” which is unacceptable, deputies believe.
Education
Education is the most important condition on which not only the career, but also the well-being of every citizen depends. Therefore, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that every child can study at school for free. Moreover, the state legislatively regulates the education system so that it helps every student:
- develop culturally;
- develop personal judgment;
- foster moral responsibility.
All this will help everyone, over time, benefit the society that gave him all these opportunities.
Responsibility for the quality of education lies not only with educational institutions, but also with parents: the child must be provided with all the conditions for learning, as well as games, the purpose of which is to improve education.
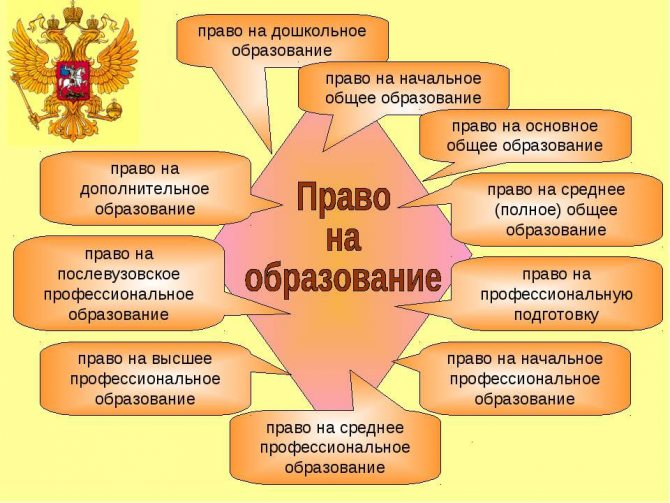
Realization of the child's right to education.
The state also defends the right of people with disabilities to education: for this purpose, various educational institutions of various types have been opened.
Child's rights to education
The types of rights associated with education are as follows. The child can:
- Take an accelerated course.
- Use information and library resources.
- Get additional education.
- Study in your native language or choose any other language of instruction provided by the educational system.
- Move to another educational institution if the educational institution ceases its activities. But at the same time, according to the rights of the child in the Russian Federation, he must agree on his decision with his parents.
- Defend and defend your decision to change professional training. If he does not like his future profession, it is unacceptable to violate the child’s personal rights in this matter.
- Realize your desire to obtain higher education.
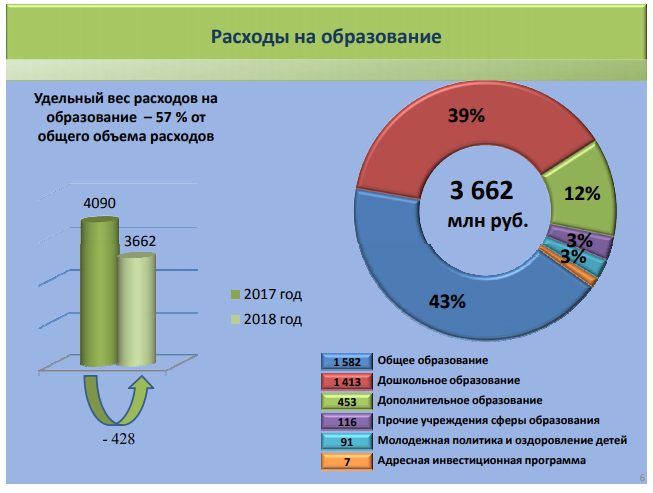
Expenses on education in the Russian Federation.
The essence of the problem
The family legislation of the Russian Federation defines quite a lot of different circumstances related to family life. However, most of these provisions relate to property in one way or another. But the articles of the RF IC concern the relationships between relatives. For example, issues of communication and other interaction between children and their families.
Deputies note that the rights associated with children more or less belong to their parents. As for grandparents, as well as brothers and sisters, the situation is different. In fact, these relatives only have the right to see minors. Otherwise, the rights of grandparents and brothers and sisters are severely limited.
Medical support
As for health protection, the rights of the child in the Constitution of the Russian Federation also contain clauses regarding health protection. They state that every minor has all rights and freedoms in the field of medical care. He can:
- Get treatment and observation at a dispensary.
- Take advantage of preferential conditions for food and medical care.
- Receive information about his/her health status in a form that, according to the protection of children's rights, is accessible to his/her age.
- Study and work in conditions that exclude the adverse effects of various factors on his health.
What is very important, the protection of children’s rights in the Russian Federation allows minors who have reached the age of 15 to voluntarily agree or refuse medical intervention in writing.
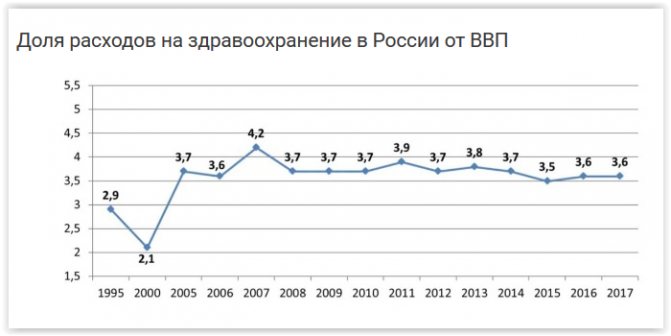
Healthcare costs in the Russian Federation.
Property rights of children
In the law on the fundamental rights of the child, one of the important points is the right of every minor to their own property. This applies to children’s housing rights and property purchased with personal funds, donated or inherited. According to the Civil Code, each child can dispose of his property at his own discretion.
Responsibilities of parents to support children
As for maintenance, the documents on children's rights say: parents must support their children until they receive an education. If the mother (father) receives child support, then, as indicated in the Federal Law, she (he) can spend the funds received on the maintenance of the child.
The amount of alimony is regulated by the court, but the amount cannot exceed 25% of the earnings of the party paying the elements. In addition, the party paying alimony may deposit the amount into a bank account opened in the name of the minor son or daughter. To see what types of alimony are provided for by law, see the following video. Upon reaching 18 years of age, according to the guarantee of children's rights in the Russian Federation, the owner can use the funds for education or for other purposes.
Rights of disabled children
What can the most vulnerable category of children count on? The Constitution of the Russian Federation guarantees equal rights to all citizens without exception.
Right to study
According to the Federal Law, children with disabilities have a number of advantages over their peers:
- Priority admission to kindergartens and free attendance;
- Education in specially created correctional classes, if the state of health does not allow being in general education classes, as well as at home;
- Free meals at school;
- Gentle mode of passing exams.

Features of inclusive education.
The right to treatment, rehabilitation and socialization
Every disabled child has the right to treatment, rehabilitation and social adaptation in society. So what exactly can families raising a child with disabilities expect?
- Treatment in medical institutions and rehabilitation;
- Everything you need for a comfortable life for a minor (wheelchairs, orthopedic shoes, literature for visually impaired children, etc.);
- A ticket to a sanatorium, and the state provides free round-trip travel for both the child and his accompanying person.
- Free travel on public transport.
- Monthly cash benefits in accordance with the disability group and region.

Children with disabilities need comprehensive care.
Basic principles for the development of a system for protecting children's rights
Every country in the world has its own adopted declaration on the rights of the child.
The recommendations to this document contain instructions on what you need to pay attention to and what problems should be solved first, as well as what methods and ways to solve them are available.
The main provisions of such a declaration in our country include:
- creating favorable living conditions for each child (nutrition, professional medical care, social services and much more);
- provision of quality education (school, university);
- providing young children and adolescents with the opportunity to actively participate in society.
One of the serious problems in this area is the problem of child abuse.
These are all forms of physical and mental violence, beatings and insults, poor treatment, child exploitation and sexual assault.
Nearly half of all child abuse cases occur in the home, with the remaining half occurring in schools and other child care settings.
Therefore, a special system that helps monitor such violations of the rights of the child is of great importance in this case.
The key problem in this area is the lack of preventive work.
Measures of influence are applied to violators of rights when it is no longer possible to correct the situation.
You will probably be interested in looking at the mental map, which explains in detail who can go to court with a claim for restriction of parental rights
Or HERE you will learn about assistance to large families
How to get an SSN for a child: