Author of the article: Lina Smirnova Last modified: January 2021 14774
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains grounds on which an employer can terminate an employment relationship with an employee. The list of such reasons is defined in Article 81 of the Labor Code. However, for some violations, the employer has the right to dismiss the employee only by court decision, since they require criminal punishment. In this article, we will look at what violations are eligible for dismissal by court decision, what are the features of such dismissal, and what is the procedure itself.
Why is an application to court necessary?
Those who nevertheless decide to assert their rights usually start by contacting the labor inspectorate, and this is the right decision.
But it is effective only when it is quite obvious that the dismissal was not legal. If this is not so, the result is unpredictable. In this case, you can go to court only within a month from the date of receipt of the work book or order (Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). After this, the court can accept the claim only if the reason for the delay was valid. But contacting the state inspectorate is not included in the list of valid reasons. So the best solution would be to contact both authorities at the same time.
“Clean” work record
It is likely that the employee does not want to present the new employer with a work book with a record discrediting him, even if it is declared invalid. In this case, he has the right to demand the production of a duplicate in which the invalid entry will be absent. It is with this book that he will get a new job. In this case, the first copy remains “as a keepsake” for the employee.
The costs of making a duplicate are borne by the employer who fired the employee on illegal grounds.
Dismissal by court decision: date of dismissal
Clause 6 of Part 1 of Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates the possibility of terminating an employment contract if an employee dies. Alas, people die not only from old age.
Death can also overtake the young - illnesses, accidents, disasters, military operations, natural disasters, etc. lie in wait for a person. And often the victims are people of working age.
Of course, when formalizing the termination of an employment contract due to the death of an employee, the company’s management must take into account a number of nuances that distinguish this case from a regular dismissal. For example, as a general rule, when dismissing an employee, he must familiarize himself with the dismissal order against signature (Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
According to current legislation, anyone suspected of committing a crime is considered innocent until his guilt is proven and the court pronounces an appropriate sentence. It is for this reason that it is impossible to dismiss an employee against whom criminal or administrative proceedings are still ongoing until the end of the legal proceedings, i.e.
- Art. 46 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation: fine.
- Art. 49 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation: compulsory work, because they are performed in free time from the main activity.
- Art. 48 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation: deprivation of class rank, special title or awards.
Since April 15, employee of Vygoda LLC Ivanova T.I. stopped showing up at work, but the employer simply put “N” (no-show) on the report card, because there was no explanation from her. A month later, he learned that criminal proceedings were underway against her. The verdict was pronounced on September 20, but the leader learned about it only on October 10.
Thus, the dates of actual dismissal and issuance of the order may be different, because in this case, the employer does not have the right to issue this document until the verdict enters into legal force. The fact is that within 10 days after the court pronounces it, the lawyer of the convicted person can appeal it in an appeal or cassation procedure and there is a possibility that the petition will be granted and his client will be found innocent.
The dates of the order and filling out the work book may coincide if the manager learned about the entry into force of the court verdict on the same day.
What happens after a court decision on a claim?
The judicial method of protecting rights in case of illegal dismissal has many advantages:
- Efficiency. During the process, you will be able to provide evidence that the law was violated. The court is obliged to understand all the nuances of the relationship between you and the employer, but the labor inspectorate is not.
- Price. The plaintiff does not pay the state duty and does not pay other costs (Article 393 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Possibility to demand compensation for moral damage. Only the court has such powers.
But, of course, there is a minus - the timing. According to the law, cases of illegal dismissal must be considered within 1 month (Article 154 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), but this rule is rarely observed.
So, you filed a claim for restoration, it was granted. What's next?
According to the law, a court decision is executed the next day after its announcement (Article 396 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). And even if the employer decides to appeal, he is still obliged to reinstate you.
If he was not present at the hearing, the fact that the claim was satisfied can be confirmed by providing a writ of execution or an extract from the court decision.
Once a claim has been granted, the employer must do three things:
- Issue an order to cancel the dismissal or reinstatement at work - and give them to the employee for signature. He has the right to refuse to sign, in which case he will need to draw up an act. If he does not show up for work the next day, he can be fired legally.
- Confirm in the work book that the dismissal was illegal. Issue a duplicate in which the dismissal record is not entered. The latter is at the request of the employee.
- Provide the employee with the opportunity to return to his duties.
Changes are also made to the work shift sheet. Days of forced absence are marked with codes PV or 22.
It happens that organizations evade execution of a court decision. Then contacting the bailiffs will help. Enforcement proceedings will be initiated against the legal entity. If he fails to comply with the requirements of the bailiffs, he will also be held accountable. And for the entire time the proceedings are ongoing, you can receive compensation for your average salary.
If you are faced with a violation of the law and your rights, you should not pretend that this is in the order of things. The more precedents there are when employees were able to regain their previous positions, the less employers will violate the law.
If you are an employer, your former employee filed a claim in court, and this claim was satisfied, do not under any circumstances deny reinstatement to the employee. Failure to comply with a court decision is illegal; it will entail very serious problems that can lead to irreversible consequences.

Labor legislation regulates not only the grounds for dismissal, but also the procedure for terminating an employment contract with an employee. The rules established by Art. 84.
1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation must be fully observed, because the absence of at least one document or signature entails the recognition of the dismissal as invalid, which will negatively affect, first of all, the head of the organization.
Important! Registration of termination of an employment contract is a procedure established by Art. 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and represents the commission of legally significant actions leading to the termination of the employment relationship between the employee and the employer.
The general procedure for registering the termination (termination) of an employment contract is as follows: it begins with the issuance of a special Order by the head of the enterprise, which indicates the date of dismissal of the employee and the grounds established by law, and ends with the entry into the employee’s work book of the corresponding entry and the organization of accounting for the final settlement with fired.
The registration procedure is the same, regardless of the grounds for termination of the employment contract.
Differences will be indicated:
- in the name of the reason for dismissal in the Order, work book and personal card;
- in the types of payments in accordance with the grounds for dismissal and their reflection in the accounting documentation of the organization.
Before formalizing the termination of an employment contract with an employee, the following factor must arise:
- the employee’s desire to resign of his own free will (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) - a written statement from the employee with a date and signature;
- mutual decision of the parties (Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) - a written agreement with the signatures of the employee and the head of the organization and the date of dismissal;
- employer's decision (Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) - a written notice issued to the person being dismissed under his signature (dismissal is also allowed orally, in the presence of witnesses);
- liquidation of an organization (clause 1, part 1, article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) - an order for liquidation and written notification of each employee under their signature (an open-ended contract and a fixed-term employment contract for more than 2 months - notice of at least 2 months, fixed-term employment contract for a shorter period - 3 days before liquidation);
- reduction of staff or position (clause 2, part 1, article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) - an order for reduction and written notification of employees who were laid off (the terms are similar to the previous basis);
- termination of a fixed-term contract due to the expiration of the term (Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) - written notification to the employee 3 days before the specified period;
- dismissal of a part-time worker in connection with the hiring of a main employee (Article 288 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) - written notice signed by the part-time worker 2 weeks before dismissal.
We invite you to read: Goodbye to work: dismissal after maternity leave at will.
If the decision of the head of an organization to dismiss was made in connection with the guilty actions of an employee, the basis will also be written evidence of the actions (for example, a final verdict in a criminal case for theft of the organization’s property or other employees), explanations of the dismissed person, etc.
Dismissal may also be made for other reasons. For example, due to health conditions that do not allow the employee to continue his activities. Accordingly, the medical opinion will become the basis, which will also be reflected in the Order.
Further, the termination of the employment relationship (dismissal) is formalized in the manner established by Art. 84.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The order is issued by the HR department and signed by the head of the organization. This act is necessary not only for dismissal, but also for accounting for employees with whom the employment contract was terminated.
The order contains the following information:
- date and place of drawing up the order;
- information about the dismissed employee (full name, position);
- grounds for termination of labor relations (wording and reference to the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- link to a document - the basis for dismissal (employee statement, agreement, doctor’s opinion, etc.);
- date of termination of the employment contract;
- absence/presence of material claims against the dismissed person (if his position involves responsibility for the organization’s property, etc.).
The order is signed by the head of the organization. A copy of it is sent to the dismissed employee (or the original document is reviewed if the employee continues to work until the date of termination of the contract). After familiarization, the latter puts his signature.
The day of dismissal is actually considered the employee's last working day, but there are exceptions. If the employee:
- wrote an application for leave with subsequent termination of the employment contract;
- was on sick leave;
- or the date fell on a weekend or non-working holiday,
then the date of termination is considered to be the day specified in the application or other document that is the basis for dismissal.
Important! Separately, there is the issue of familiarizing yourself with the Order of the remote worker. In accordance with Art. 312.1, he must receive the act in electronic form, certify it with an electronic digital signature and send it back to the employer.
If a copy of the Order cannot be given to the employee, or he himself refuses to familiarize himself with the original document, the corresponding mark is placed on the act (Part 2 of Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
On the last working day, the management of the organization:
- fills out the personal card (personal file) of the dismissed person;
- issues a work book to the employee;
- makes a full settlement with him.
Like the Order form, a personal card can be established by the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation (Form T-2), or it can be developed by the organization independently. An entry about the termination of the employment contract is entered into it (in form T-2 this is item 11):
- grounds for dismissal;
- date of termination of the contract;
- number and date of the Order;
- employee signature;
- signature of the head of the personnel department.
The registration of the work book is established by Government Decree No. 225. It is filled out as follows:
- first column – record number;
- second column – date;
- the third column is the reason for termination of the employment relationship and a reference to the norm of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- fourth column – link to the document – grounds for dismissal.
Payments to the dismissed person are also made using an individual form or form T-61.
The calculation note indicates:
- information about the employee (full name, position);
- date and reason for termination of the employment contract;
- reference to the Order of dismissal;
- whether the vacation was used in advance or the employee has unused vacation days;
- calculation of vacation pay;
- calculation of payments (salaries, benefits, bonuses, etc.);
- total amount;
- accountant's signature with transcript.
It is important to note that the employee is given only the amount with which he agrees. If he does not agree, for example, with the amount for unused vacation, the accounting department must recalculate based on his application.
If the employee was able to prove in court the illegality of his dismissal, then the employer is obliged to reinstate him in his previous place after receiving a court decision. It is on the basis of this document that he issues an order for employment, after which he makes entries in the work book and the employee begins to perform his duties. You don’t have to wait for a decision, but enter into a settlement agreement with your subordinate, however, it must also be approved by a court ruling.
Termination of a fixed-term contract

A notice of termination of an employment contract is sent by mail to an employee of the enterprise if the contract concluded with him expires in at least three days. There are other methods used by companies, depending on the situation, to terminate a fixed-term employment contract.
Such an agreement is concluded when it is necessary to perform a certain amount of work and upon completion of the work the contract is terminated. The same applies to cases when a person is hired instead of another employee, for example, while on vacation, on sick leave, on maternity leave or absent for other reasons. When the previous employee returns to the place, the contract also ceases to be valid. The most common option is seasonal work, after which the fixed-term employment contract is terminated.
Nuances here arise due to certain categories of workers, which include pregnant women. Until she goes on maternity leave, no one has the right to terminate the contract.
The employee himself may express a desire to end the relationship before the end of the term. To do this, the three-day deadline for submitting a statement of intent must also be met.
Is it possible to be reinstated at work after dismissal by a court decision?
- If an employee considers his dismissal illegal, he has the right to go to court within one month after receiving a copy of the order (Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- After a court decision on reinstatement is made, the employer is obliged to immediately execute it (before it enters into legal force). If there is a delay in execution, the employee can go to court, which, in turn, will issue a ruling on the payment of average earnings for the period of delay (Article 396 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The court decision is the basis only when issuing an order for reinstatement at work. When filling out a work book, you need to indicate not a court document, but an act issued by the employer.
- If another person has already been hired to replace the reinstated employee, the director has the right to dismiss him due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties (Clause 2, Part 1, Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition to the court, an illegally dismissed employee can also seek reinstatement through the labor inspectorate, although it is more effective to go to court to resolve labor disputes. To act through the inspection, you must write an application and submit it by email or in person to the inspector.

After receiving the complaint, employees begin to study all the nuances and check the organization, based on the results of which they make their decision, and upon completion, they inform the applicant about the results of their investigation and send an order for reinstatement to the employer. If he does not fulfill it, then you can achieve justice through the court by following these steps:
- Write a statement of claim and bring it to court, keeping the second copy with you.
- Wait for the decision to set a court date. It also stipulates the list of documents that will need to be provided.
Most often, it is possible to be reinstated at work through the courts, and illegally dismissed employees should remember that they can not only regain their previous position, but also receive compensation from the employer for moral damage caused by his unlawful actions (Article 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) .
In addition, the obligation to pay legal costs rests entirely with the defendant organization on the basis of Art. 393 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, therefore, all that is required of an employee for restoration is to timely file a claim, attend court hearings and go to work the next day after the court decision.
Legal aspects of dismissal by court decision
As mentioned earlier, in order to terminate the employment relationship, the employer must wait until the court verdict enters into legal force. It often happens that an employee commits an offense at work and the manager prefers not to contact the police or conduct an internal investigation, but forces his subordinate to resign of his own free will or for other reasons.
To avoid this, employers need to be guided by the legal aspects when dismissing and follow the procedure:
- If theft, embezzlement or other offense falling under the scope of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation is detected, the manager must call police officers who will inspect the scene of the incident, interview witnesses and prepare relevant documents for legal proceedings.
- Within 10 days after the verdict is passed, the employee cannot be fired, because this period is given for appeal, and if the convicted person is found innocent, he will have to be reinstated at work.
Separately, it is worth considering the case of violation of labor protection requirements, which is also grounds for dismissal if serious consequences were discovered as a result. In such a situation, not only a report is required from the employee who identified this act, but also the conclusion of the labor protection commission, which will establish the guilt of a particular employee and that as a result of his actions, damage was caused to the organization or the health of other employees. Without such a conclusion, dismissal will be considered unlawful.
The procedure for dismissal by a court verdict that has entered into legal force is not much different from the usual termination of employment, with the exception of some points:
- It is necessary to take into account the time limits for appealing the verdict.
- An employer can issue an order of dismissal only after receiving a copy of the sentence passed against the employee.
- If the offense was committed on the territory of the organization, it is necessary to conduct an internal investigation by the commission or contact law enforcement agencies.
Nuances of termination
Regarding pregnant women, it is worth paying attention to other categories of workers with whom there are nuances of terminating an employment contract. There is a state commission on juvenile affairs. If the employer wishes to dismiss such a person, then the decision must be agreed upon with government officials.
When an agreement with persons who are members of the trade union at an enterprise is terminated, then everything must be coordinated with this structure and nothing else. Here, all cases are regulated by labor legislation, namely Article 373 of the code.
Separately, it is worth paying attention to foreign citizens if they are hired. After the expiration of the contract, within three days the employer is obliged to notify the migration service authorities at the location of the enterprise about his actions. A notification is also sent to the employment center, as well as the tax inspectorate. Their dismissal may occur upon the expiration of the documents allowing them to remain in the country legally. This is a residence permit, a corresponding permit, and a concluded insurance contract. Free legal advice over the phone will resolve any of your controversial issues.
Save
Dismissal of a convicted employee - termination of an employment contract
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains a complete list of grounds for dismissal of employees. Thus, Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of termination of labor relations due to circumstances beyond the control of either party. These include the conviction of an employee (clause 4). However, it is applicable only if two conditions are met:
- The court verdict on the basis of which the employee was convicted entered into legal force. Any decision can be appealed to a higher authority. The time for filing an appeal is determined by Art. 390 Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation. Moreover, when filing a complaint, the entry into force may be delayed until the verdict is recognized as legal.
- The sentence imposed prevents the convict from further work. This does not necessarily have to be imprisonment for any period of time. A person may be prohibited from conducting a certain type of activity (for example, economic or related to material values).
There are known situations where a sentence against an employee was overturned. If the employer has already fired him and hired another person in his place, then according to the law the manager must:
- reinstate the former employee in his position, since there are no longer grounds for terminating the employment contract;
- dismiss the person hired, referring to clause 2, part 1, art. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for personnel changes in this case is initiated by a former employee. He informs about the cancellation of the sentence, and then the employer acts.
- the arrest of an employee implies his isolation from the outside world, in which case the fixed-term employment contract is terminated if its duration does not exceed the period of arrest;
- imprisonment (and the term is not important - the fact itself is already grounds for dismissal);
- life sentence;
- punishment in the form of a ban on holding a certain position (usually the civil service or managerial positions in self-government bodies) or engaging in any activity.
In the latter case, the dismissal of an employee is not an option, but an obligation of the employer. The manager, having received a sentence, must act in the following order:
- within a maximum of 3 days after receiving a copy of the verdict, terminate the employment contract with the convicted person or impose a ban on conducting any specific activities in relation to him and transfer information about the fulfillment of obligations to a higher authority;
- in case of receiving requests from the inspection, provide supporting evidence demonstrating timely compliance with the requirements;
- if amendments and changes are made to the contract or the employment relationship is terminated in principle, this must also be reported to the inspectorate;
- make entries in the work book (it is necessary to indicate not only the basis and reference to a specific article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but also the circumstances of the criminal case - how long he was sentenced to, what position he should not hold) - this is necessary so that the next employer is aware of what activities and until what period the position applicant has no right to engage in activities according to the law.
We suggest you read: What to do if bailiffs have seized a credit account
Other types of punishment do not lead to the dismissal of an employee. Of course, receiving information about a lawsuit against an employee may change the employer's opinion about him. However, he will not be able to use the punishment itself as an argument - he will have to be fired for other reasons.
Often employers are faced with a situation where their employees are sentenced to correctional labor on the basis of Art. 50 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. This format of punishment involves carrying it out at the employee’s place of work.
However, in this case, the employer has another obligation - to withhold income in percentage terms for the benefit of the state budget.
Its final size is determined individually; the court verdict specifies the percentage of earnings (5 – 20%).
Issuance of an order
The dismissal order is drawn up exclusively after receiving a court verdict. No special form of document is required - standard T-8 is used. The main difficulty for the employer is determining the last working day.
Here you need to start not from the moment of absence from work and not from the date of the verdict. Dismissal occurs only after it enters into legal force. That is, if a sentence was passed on September 10, it will come into force 10 days later - on September 20.
This day will be considered the day of dismissal of the employee.
If the employee was in custody at the time of sentencing, then the 10-day count begins not from the moment the sentence was passed, but from the date when the convicted person received a copy of the court decision.
The effective date (and, accordingly, the day of dismissal) may be postponed if a party files an appeal. Then the dismissal process may be delayed. We will have to wait for confirmation of the verdict.
Familiarizing the employee with the order is one of the important steps. However, when the employee is in prison, this is not possible. In this case, the order must include a note indicating the impossibility of familiarization. When drawing up the order, a calculation note is also drawn up in form T-61. The corresponding entries are made in the personal T-2 card.

The work book is a strict reporting form. The employer is responsible for the correctness of the information entered into it. Therefore, recording a dismissal due to an employee’s imprisonment is important in accordance with the law. The work book must reflect:
- on what basis is the employment contract terminated (reference to the court verdict and a specific article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- date of entry and dismissal;
- link to the title document (date and number).
The manager must sign the entry and put a stamp, if available (for legal entities, it is required).
In this case, it is impossible to hand over a work book. Therefore, the procedure begins with sending a written notification by mail of the need to pick up documents.
It is usually sent to your home address. If the letter remains unanswered, then the labor force remains to wait for its owner.
If the former employee asked to send the book by mail, then the employer sends it at his own expense.
Carrying out calculations
The dismissal procedure itself is not particularly complicated. The main thing is to correctly determine the date of dismissal.
A situation may arise at an enterprise when an employee will not be able to return to work due to his stay in prison.
Registration of termination of the contract must occur in a certain order, taking into account all the nuances.
According to the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, a criminal record is considered to be penalties (temporary or lifelong) provided for a person who has committed a crime and changing his status.
Such people have their rights limited, and a permanent ban on a certain type of activity is possible. All conditions for serving a sentence are regulated by the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
The dismissal of a convicted employee is carried out regardless of the opinions of the parties - this is what Labor Law says.
Termination of the contract is carried out under Article 83 (clause 4, part 1), but for this the following conditions must be met:
- official entry into force of the court decision;
- placing an employee in custody for a certain period of time;
- deprivation of the right to hold a specific position.
The moment the court verdict comes into force is the employee’s last working day, which occurs when:
- the 12-day period for appealing the verdict has expired;
- the parties did not take measures aimed at mitigating the punishment.
A convicted person is suspended from certain activities not only as punishment for an offense committed.
The second reason is the high probability of committing a similar crime in the future. Therefore, all requirements of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation must be observed unconditionally.
As soon as the enterprise has received notice from the criminal enforcement authorities about the court decision, it must take the following actions:
- Immediately formalize the termination of the employment contract. The law provides a period of 3 days for completing formalities.
- Prepare documentary evidence of fulfillment of obligations.
- Send a notification to the penal authority regarding compliance with the requirements of the court sentence. If necessary, provide a copy of the dismissal order, an entry in your personal file and other supporting documentation.
- At the request of a person who has served his sentence or a released person, the enterprise provides a duplicate of the work book without recording the reason for termination of the contract.
Attention! Two points need to be taken into account:
- If a court decision is not made, the manager cannot consider the option of terminating the employment contract due to a disciplinary violation. Such an action is considered illegal, since the employee’s detention is a valid reason for absence from work.
- If an employee is sentenced to correctional labor, dismissal while serving the sentence is a violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. You can terminate the employment relationship either by agreement of the parties or at your own request only with written permission from the criminal-executive inspection.
When the company has received a copy of the court verdict, it is necessary to perform the following actions:
- For this, the established T-8 template is used.
- Form of dismissal order (form T-8)
- Usually an employee does not have the opportunity to familiarize himself with it due to his stay in prison, so it is advisable to make an appropriate entry in the document.
- A sample order is presented below:
An example of filling out form T-8 when dismissing a convicted employee
Entries are made in the work book and the employee’s personal card.

Example of filling out a work book
Example of an entry in a personal card
These documents must also contain a note stating that the employee does not have the opportunity to familiarize himself with the order.
There may be uncertainty with the return of the Labor Code, since it is transferred on the day of dismissal.
If the last working day does not coincide with the moment of termination of the contract, the employer is not responsible for the delay in the document. He is obliged to send a notice to the home address of the convicted employee with a request to pick up the book.
Employee initiative
A company employee may express his desire to terminate all relations with the employer on his own initiative. In order for the employment contract to be terminated at the employee’s initiative, it will be sufficient to contact the manager with a written application at least two weeks before the date on which there is a desire to terminate all relations. There should be no explanation or indication of reasons. Here the will of the employee comes first.
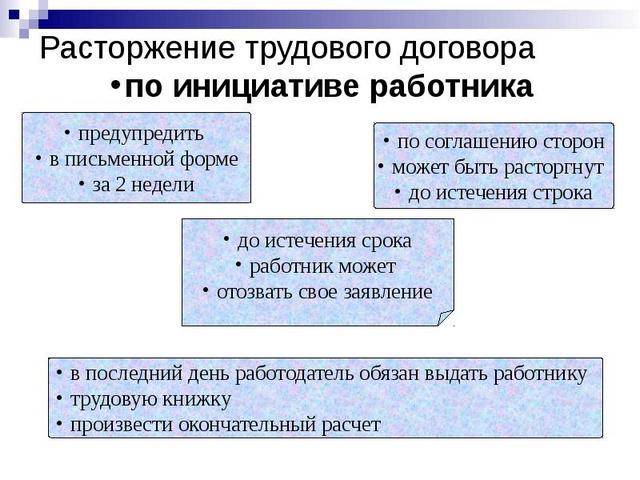
There may also be some medical indications. That is, the employee develops some diseases, contraindications for working in these conditions, and other issues. After submitting the documentation to the manager, he may be offered possible vacancies where he can be transferred. But a person does not always agree to this, since in most cases conditions deteriorate sharply, wages become lower and other restrictions occur. But even in such a situation, it is better to stay in the position that is offered, because not every employer will be able to take such an employee to their team. Otherwise, the date and time of dismissal is agreed upon, and an order is issued to terminate the employment contract by the employee. The form of this type of document is provided for by legislative acts.
Compensation for illegal dismissal
If you were deprived of your job illegally, a court decision will award compensation for reinstatement to work by the court:
- Compensation for the average salary for the entire period when the employee was not at work (Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), that is, from the date of dismissal to the date of reinstatement.
- Compensation for moral damages for illegal dismissal, which can be assessed by a psychologist. At the hearing, a specialist’s opinion, medical record and other similar documents have weight.
- Compensation for legal costs. Since the plaintiff does not pay a fee, he only spends money on legal services. If the decision is in favor of the employee, all legal services are paid by the employer.
Overall, if done correctly, you will gain more than you lose from a wrongful termination.
When the position is already filled
Sometimes it happens that a new employee is immediately hired to replace a recently fired employee. But if the court decides to reinstate the employee in his position, the one who currently occupies it will have to be fired. The procedure must comply with clause 2, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
But there is one caveat. The currently working employee must be offered other vacancies in writing, if the organization has them. And he can be fired only when these vacancies do not exist, or the employee does not agree to them - otherwise it is illegal.







