What does reprimand mean?
A reprimand is one of the forms of disciplinary action provided for by the Labor Code. The following types of violations are grounds:
- disciplines;
- labor protection requirements;
- failure to comply with job descriptions, which led to an error in work.
The list of offenses for which penalties are imposed is not indicated in the code. This is decided within the company.
IMPORTANT! Penalties are imposed on employees for violations, regardless of their social security.
The punishment period lasts for a year, the employee is deprived of the opportunity to receive bonuses and incentive payments. Early removal of a penalty occurs at the request of the manager.
How to reprimand an employee
Chapter 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the rules for applying disciplinary sanctions. Violation of the law by an employer leads to sanctions: from cancellation of penalties to fines from supervisory authorities.
The reprimand is issued in the following order:
- The fact of misconduct is revealed (the statute of limitations is no later than one month).
- The employee writes a written explanation within two days. This time does not include the period of legal absence of a person (vacation, sick leave, time off).
- An order to impose a reprimand is issued, which the offender reads and signs.
IMPORTANT! If there is no explanatory note, this does not affect the application of the penalty. The punishment depends on the severity of the consequences of the offense and the circumstances under which the offense was committed.
If an employee refuses to give an explanation or sign an order, acts of refusal are drawn up. According to the law, it is not required to make an entry about the imposition of a disciplinary sanction in the work book or personal file (Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An employee may receive repeated disciplinary punishments, which do not affect dismissal.
The concept of disciplinary action in the context of labor relations
Disciplinary sanctions are a special type of punishment that is used mainly in the field of labor relations for the commission of one or another type of misconduct by an employee. The use of disciplinary sanctions is carried out without the involvement of government enforcement authorities (for example, without issuing a corresponding court verdict or other type of decisions).
In the field of labor relations, such types of penalties are most often used that can effectively influence the behavior of a particular employee. Moreover, when imposing this type of punishment, the employer is obliged to take into account a number of factors, which include:
- the severity of the violation that was committed by the employee;
- information about the circumstances of the violation>;
- the imposition of a particular disciplinary sanction will also be influenced by information about the previous work of the employee subject to sanction;
- how the employee relates to the existing labor discipline>;
- general employee character traits.
Only on the basis of the addition of these factors can one or another type of disciplinary action be used.
Reasons for disciplinary action
The latest version of the domestic Labor Code clearly states the available disciplinary sanctions:
- making a comment}
- reprimand}
- dismissal.
The employer takes into account:
- gravity of the violation committed}
- circumstances of the incident}
- information about the employee's previous work}
- attitude of the offender to production discipline}
- human character traits.
Formalities related to the issuance of disciplinary sanctions
If a disciplinary violation is detected, the employer must take a detailed explanatory note from the employee outlining his version of what happened. If the employee refuses to write an explanation, the administration writes a report. It must be taken into account that an employee’s refusal to explain his violations in writing is not an obstacle to disciplinary action.
The employer must familiarize the employee with the collection order against signature and no later than three days from the date of issue of the document.
In the absence of these actions by the employer, the violator of discipline can challenge the punishment of the boss. You have three months for this. The employee can appeal to the court or labor protection authorities.
How to reprimand an employee
Chapter 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the rules for applying disciplinary sanctions. Violation of the law by an employer leads to sanctions: from cancellation of penalties to fines from supervisory authorities.
The reprimand is issued in the following order:
- The fact of misconduct is revealed (the statute of limitations is no later than one month).
- The employee writes a written explanation within two days. This time does not include the period of legal absence of a person (vacation, sick leave, time off).
- An order to impose a reprimand is issued, which the offender reads and signs.
IMPORTANT! If there is no explanatory note, this does not affect the application of the penalty. The punishment depends on the severity of the consequences of the offense and the circumstances under which the offense was committed.
If an employee refuses to give an explanation or sign an order, acts of refusal are drawn up. According to the law, it is not required to make an entry about the imposition of a disciplinary sanction in the work book or personal file (Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An employee may receive repeated disciplinary punishments, which do not affect dismissal.
Is a disciplinary sanction recorded in the work record book?
The procedure for bringing employees to disciplinary liability is strictly regulated by the Labor Code. In particular, here is an algorithm for imposing and documenting penalties.
When an employee is employed for the first time, he must be familiarized with the labor regulations in force at the enterprise. If an employee partially violates them or fails to comply completely, the employer may bring him to disciplinary liability.
Disciplinary action may result from:
- Absence from work.
- Being drunk at work.
- Refusal of medical examination.
- Failure to comply with safety regulations.
When issuing a penalty, the employer should take into account the severity of the offense committed, the circumstances of the incident, information about previous work, the employee’s attitude towards work and his character traits.
Violation of the procedure for bringing to recovery threatens the employer with liability under the norms of the Code of Administrative Offenses. The employer may be subject to administrative punishment under Art. 5.27 of the Administrative Code, which threatens him with a large fine. For officials and individual entrepreneurs, fines amount to 1000-5000 rubles, for legal entities - 30000-50000 rubles. Officials may also face disqualification, and the employer may face suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
The rules regarding what information should be included in the work book are contained in Art. 66 Labor Code. According to Part 4 of Art. 66 of the Labor Code, the following information must be entered into the work book:
- About the employee himself.
- About the work they perform and about transfers to other work.
- On termination of employment contracts with employees and the grounds for their termination.
- About rewards for an employee for his work successes.
This legal norm contains a direct ban on entering information about disciplinary sanctions into the work book.
It is important to understand that, according to Art. 192 of the Labor Code, forms of punishment for committing disciplinary offenses include: reprimand, reprimand and dismissal. If the most severe penalty in the form of dismissal is applied to an employee, then such a note with reference to the grounds for dismissal must be written in the work book.
If the employer decides to dismiss an employee for gross or repeated violation of labor discipline, he must make a note in the work book in the “Work Information” section within a week. Such a notice of dismissal must be certified by the signature of the employer and the seal of the personnel officer.
The work book does not indicate that the employment contract was terminated due to the imposition of a disciplinary sanction . Here is a link to a specific article of the Labor Code, which became the basis for termination of the employment contract. For example, at st. 81 Labor Code, 336 or 348. Such grounds may be immoral behavior, absenteeism, being intoxicated at work, failure to prevent a conflict of interest, etc.
If the employer nevertheless entered information about the disciplinary sanction into the work book, then he will have to issue a duplicate of it or make changes accordingly.
The procedure for adjusting the work book is contained in clause 27 of Rules No. 225, approved by Government Decree No. 225. But if information about dismissal as part of a disciplinary sanction was entered into the work book, which was later declared illegal, then the employee has the right to issue a duplicate work book without this entry.
The concept of disciplinary action in the context of labor relations
Disciplinary sanctions are a special type of punishment that is used mainly in the field of labor relations for the commission of one or another type of misconduct by an employee. The use of disciplinary sanctions is carried out without the involvement of government enforcement authorities (for example, without issuing a corresponding court verdict or other type of decisions).
In the field of labor relations, such types of penalties are most often used that can effectively influence the behavior of a particular employee. Moreover, when imposing this type of punishment, the employer is obliged to take into account a number of factors, which include:
- the severity of the violation that was committed by the employee;
- information about the circumstances of the violation;
- the imposition of a particular disciplinary sanction will also be influenced by information about the previous work of the employee subject to sanction;
- how the employee relates to the existing labor discipline;
- general employee character traits.
Only on the basis of the addition of these factors can one or another type of disciplinary action be used.
What is meant by collection in the context of labor relations?
The term “collection” in the Labor Code is considered in the context of:
1. Material penalties from the employee:
- due to damage caused to the employer;
- withheld by the employer on the basis of enforcement documents (for example, when paying alimony);
- withheld by the employer in cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (for example, when overpaying vacation pay in the manner prescribed).
2. Disciplinary sanctions applied to the employee, which may be presented:
- remark;
- reprimand;
- termination of the employment contract on the grounds provided by law.
But is the disciplinary sanction recorded in the work record book?

Types of such penalties
In accordance with Labor legislation, an employer can currently use in relation to an employee:
- making an official comment;
- reprimand or severe reprimand;
- dismissal or termination of an employment contract.
Can also be used:
- warning the employee about his inadequacy for the position held;
- dismissal from a position.
Is information about a reprimand included in the work book?
Such information has the right to be entered into the work book only after compliance with certain mandatory actions.
The first step of the employer is to notify the employee in writing of the violation, on the basis of which the employee prepares a written explanation. The second step is to issue a disciplinary order, which is presented to the employee.
Within three days the latter must sign it. If this is not possible, a special report is drawn up on the identified violation and a reprimand issued as a result.
At the same time, a reprimand cannot be entered into the work book on the basis of current labor legislation. Such data is entered only in cases where the punishment for a violation of labor discipline is dismissal.
Deadlines
The timing of the imposition of penalties is regulated by Art. 193 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. A reprimand may be issued within 30 days from the moment the offense was discovered. However, illness or vacation cannot be taken into account in this period.
Based on the results of inspections, a reprimand cannot be imposed within a period exceeding six months from the date of discovery of the offense.
If the question concerns an administrative and economic inspection, then the statute of limitations is no more than 2 years.
A severe reprimand entered into the work book must be recorded in an order, which the employee must read within three days and sign. If there is no signature, you need to draw up a corresponding act.
The maximum validity of a reprimand is one year. In this case, the employer can mitigate the punishment and remove the reprimand. If punished again, the employee may be fired.
What is meant by the concept of “disciplinary action”?
This measure is taken against an employee who has violated labor discipline. This means improper performance or failure to fulfill labor duties. Disciplinary liability implies the adoption of measures provided for by the provisions of labor law. And such responsibility refers to the types of legal responsibility.
Types of such penalties
In accordance with Labor legislation, an employer can currently use in relation to an employee:
- making an official comment;
- reprimand or severe reprimand;
- dismissal or termination of an employment contract.
Can also be used:
- warning the employee about his inadequacy for the position held;
- dismissal from a position.
Carrying out the procedure
Documented, the foreclosure process itself consists of several stages:
- Establishing a misdemeanor.
- Requesting an explanation from an employee.
- Providing an explanatory note by the employee.
- Imposition of penalty.
If an employee refuses to provide the employer with an explanation for his action, this does not mean that he will not be reprimanded and entered into the work record book. The reasons for this do not disappear, but are only aggravated by the employee’s reluctance to prove his innocence.

The hardest and most important thing is to record the employee’s misconduct. To do this, the employer must prove:
- An employee’s abstinence from certain actions was his job responsibility.
- Job duties are performed improperly.
- The employee's behavior is illegal.
- The illegality of behavior must be related specifically to work activity.
- The employee's actions must be intentional or careless.
At the same time, punishment cannot be applied if:
- the employer does not have the necessary conditions for work;
- the employee is disabled;
- natural disasters occurred that prevented the employee from going to work;
- the employee performed other assignments of the employer and the simultaneous performance of several duties is impossible.

If one of the above facts is proven, the next step is for the employer to request an explanation from the employee. The explanatory note must indicate:
- reasons for committing the offense;
- whether the employee considers himself guilty;
- in the absence of guilt, the employee must indicate the guilty person.
If the employee refuses to provide an explanation, the employer must draw up a corresponding report.

The penalty imposed must satisfy the following conditions:
- The severity of the offense was taken into account.
- The conditions under which the offense was committed were taken into account.
- The previous behavior of the citizen is taken into account.
- The employee's attitude towards work in general is taken into account.
If the employer bypassed at least one of the points, the employee has the right to appeal the reprimand and enter it into the work book. Which, in turn, will lead to the obligation to reinstate the employee in the workplace with payment of compensation.
Can a disciplinary sanction or reprimand be withdrawn?
Article 194 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicates the possibility of removing disciplinary punishment from an employee. Including in the event of a reprimand. In accordance with this article, if there are no new disciplinary sanctions within a year after they are issued, they are automatically canceled.
In the case where the employer intends to lift a disciplinary sanction, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide special recommendations for meeting the deadlines for early removal. There are several options for withdrawal:
- issuance of a special order on removal at the initiative of the employer;
- at the initiative of the employee upon his personal written application addressed to the employer;
- on the initiative of the direct head of the structural unit in which the offender works;
- at the request of the representative body of employees, including such a decision may be made at a general meeting of employees.
Is information about collection entered into the work book?
Information about the imposition of a disciplinary sanction is entered into the work book only in a situation where the dismissal of an employee is recognized as a measure of punishment.
Is information about a reprimand included in the work book?
Such information has the right to be entered into the work book only after compliance with certain mandatory actions.
The first step of the employer is to notify the employee in writing of the violation, on the basis of which the employee prepares a written explanation.

The second step is the issuance of a disciplinary order, which is presented to the employee.
Within three days the latter must sign it. If this is not possible, a special report is drawn up on the identified violation and a reprimand issued as a result.
At the same time, a reprimand cannot be entered into the work book on the basis of current labor legislation. Such data is entered only in cases where the punishment for a violation of labor discipline is dismissal.
Can a disciplinary sanction or reprimand be withdrawn?
Article 194 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicates the possibility of removing disciplinary punishment from an employee. Including in the event of a reprimand. In accordance with this article, if there are no new disciplinary sanctions within a year after they are issued, they are automatically canceled.
In the case where the employer intends to lift a disciplinary sanction, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide special recommendations for meeting the deadlines for early removal. There are several options for withdrawal:
- issuance of a special order on removal at the initiative of the employer;
- at the initiative of the employee upon his personal written application addressed to the employer;
- on the initiative of the direct head of the structural unit in which the offender works;
- at the request of the representative body of employees, including such a decision may be made at a general meeting of employees.
How is a reprimand given to an employee?
An alternative option for imposing punishment is to reprimand the employee.
It is also submitted in writing and presented to the employee against signature. To impose such a punishment you will need:
- prepare a memorandum on making a comment;
- require the violator to provide explanations in writing;
- issue an order imposing such punishment;
- present the order to the employee against signature.
A reprimand is considered a more loyal punishment option than a reprimand. Like a reprimand, in the absence of repeated violations, it is automatically canceled one year after issuance.
It, like a reprimand, can be lifted early at the initiative of the employee, employer, immediate supervisor of the punished person or the work collective.
In what cases is information about punishment entered into the work book?
Data on punishment can be entered into the work book in accordance with the requirements of current legislation only if it is the basis for the dismissal of an employee.
Moreover, information about such a punishment is always communicated to the employee in writing in advance and must be accompanied by a separately issued order in which the imposition of such a disciplinary measure is clearly motivated.
A sample of entering a disciplinary sanction into the work book with the subsequent dismissal of the employee.
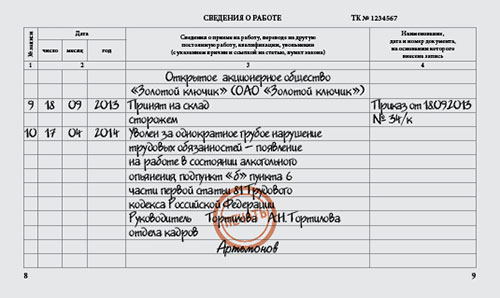
Entry into the work book
Based on the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as a normative act that regulates issues related, including the imposition of disciplinary sanctions, the employer is prohibited from entering into the work book any penalties other than dismissal.
At the same time, when making a record of dismissal due to a disciplinary sanction, it is necessary to indicate the reason for such a sanction (for example, showing up at the workplace while intoxicated).
In addition, you will need to indicate the paragraph of the article of the Labor Code, which is the basis for such dismissal.
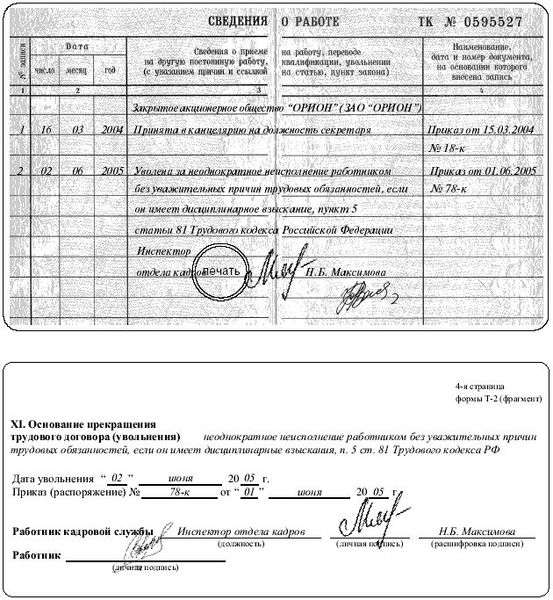
Sample entry in the work book about the dismissal of an employee
Other types of penalties are entered only into the employee’s personal file, which is kept by the employer in his archive. At the same time, recording in a personal file is possible only after the employee himself has been familiarized with the order to impose a disciplinary sanction of one kind or another. Otherwise, such an employer’s decision may be challenged, including in court.
Dismissal
You can't just fire an employee. The grounds for termination of an employment contract at the request of the employer are clearly listed in Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- the employee has not passed the certification;
- absenteeism (absent from work for more than 4 hours in a row);
- came drunk, under the influence of drugs or other illegal drugs;
- grossly violated official duties;
- received disciplinary punishment and still did not do the work;
- disclosed commercial (state, official) secrets;
- stole and damaged the property of the organization or colleagues and was sentenced by the court to liability;
- violated labor protection and caused an accident or knowingly created such a threat;
- committed guilty actions related to material values and lost trust;
- did not submit a certificate of income or provided false information (for civil servants under the Law of July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ “On the State Civil Service...”);
- committed an immoral act (for educational workers);
- made an unreasonable decision that led to damage to the organization’s property (for directors, deputies and chief accountants);
- When applying for a job, he brought false documents.
In addition, when the owner changes, the new owner can appoint his own director, deputy and chief accountant. And when an enterprise is liquidated or its workforce is reduced, the employees are first offered another job. And, if they refused in writing, you can fire them under Art. 74 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It is impossible to dismiss an employee on sick leave or on vacation, except in cases of liquidation of the enterprise or termination of activities by an individual entrepreneur.
Punishing an employee: step-by-step instructions
The procedure for applying disciplinary sanctions is set out in Art. 193 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Let's look at the procedure using a specific example.
Example 2
Lyudmila, a cloakroom attendant at a medical center, left her workplace without warning. As a result, patients were unable to return clothing and were late for appointments. The misconduct was discovered by a senior nurse who received a complaint from citizens. She wrote a report, and now we have to issue a disciplinary punishment.
We draw up an act
The time of the woman’s absence can be confirmed by security guards at the exit of the building, video recording from a surveillance camera, testimony of witnesses, etc.
Having made sure that the cloakroom attendant is not present, the head of the department (the immediate superior of the violator) will draw up an act of misconduct indicating the place, time and circumstances of the employee’s absence. He will sign it himself and ask for the signatures of witnesses confirming the contents of the document.
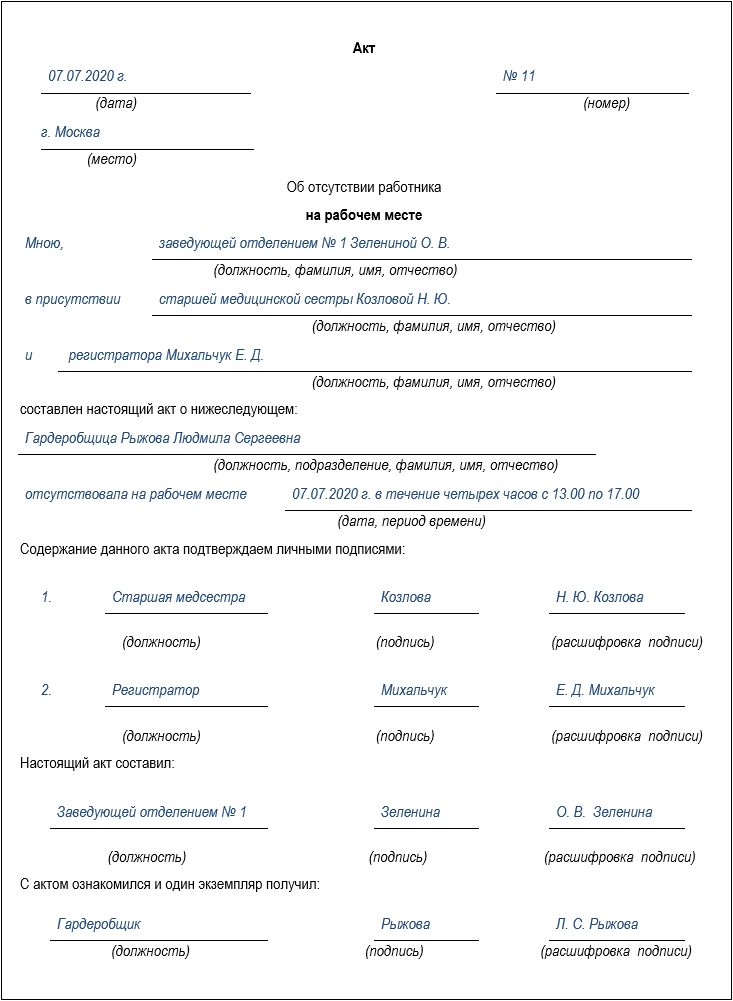
We ask for an explanation from the employee
Before punishing, you need to find out the reasons for what happened. Perhaps the person has serious circumstances. For example, it became bad and he ran out into the street and fainted. The arguments of the culprit are very important; based on them, the type of punishment will be determined.
When Lyudmila appears, she will be given an act (for signature) and asked to give the reasons for her actions on paper in any form within 2 days. If she does not bring an explanation on time, it is possible to punish her without it. But you will have to draw up another act in the presence of at least two witnesses.

We issue an order to impose a disciplinary sanction
In our case, the employee left the place for 4 hours - this is absenteeism. He refused to give an explanation and did not give any valid reasons. You can fire Lyudmila - Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows. But the chief doctor took pity on her and reprimanded her.
It is impossible to delay with the order; disciplinary action is applied no later than a month from the date of discovery of the offense, and not its commission. But in our case, absenteeism was discovered on the same day (July 7), which means that the employee must be punished before August 7. In a month it will be too late, because Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation clearly limits the time.

The violator must be familiarized with the order within 3 working days from the date of issue, not counting the time of absence (illness, business trip, shift change, vacation, etc.). If the culprit refuses to sign the order, then it is necessary to draw up a report about this.

You can also remove a reprimand or reprimand early. Both the employee himself and his immediate superior or trade union have the right to appeal disciplinary liability. A statement or memo is drawn up, and if the employer agrees to cancel the order, then a corresponding order is issued.
Upon dismissal, an order is drawn up and an entry is made in the work book. Earned money is paid on the day from which the employee is dismissed. You cannot deprive your salary or part of it. An exception may be cases when a financially responsible person has appropriated or damaged the company’s assets.
What to do if the entry is not made
What to do if the required entry was not registered in a timely manner? We need to bring it in. To do this, simply fill in the missing entry. It is entered after the last entries, if any. This information is indicated:
- Serial number.
- Date of.
- Basic information.
- Order number and date of issue.
The record contains current information about hiring and dismissal. What to do if a missing entry is discovered after the employee has started a new job? You must contact the HR department of the employer who did not enter the information. If the previous employer went into liquidation, the missing entry can be made in the personnel department of the new employer.
The procedure for action in case of errors is specified in section 3 of Rules No. 225. However, these are general recommendations. The procedure for working in the absence of a record is not established by the Rules. Therefore, in this case, you should be guided by the standard procedure for correcting errors.
Paragraph 27 of Rule No. 225 states that errors in the book must be corrected by the former employer. But sometimes this is not possible. In this case, the corrected entry can be made by the new employer. But this is done on the basis of documents from the previous place of work.
Paragraph 29 of Rules No. 225 states that entries in the book are made on the basis of documents such as an employment contract, an order from the manager on hiring/dismissal. The entries in the work book and the data in the papers must correspond to each other.
Video
Formalities related to issuing a reprimand
If a disciplinary violation is detected, the employer must take a detailed explanatory note from the employee outlining his version of what happened. If the employee refuses to write an explanation, the administration writes a report. An employee’s refusal to explain his violations in writing is not an obstacle to disciplinary action.
The employer must familiarize the employee with the order (instruction or resolution) on disciplinary punishment against signature and no later than three days from the date of issue of the document.
In the absence of these actions by the employer, the violator of discipline can challenge the punishment within three months. The employee can appeal to the court or labor protection authorities.
Issuing an order
After all the necessary materials have been collected, the manager is obliged to study them in detail and make a decision. To do this, you need to draw up and approve an order with the appropriate content. It is such a document that will be the basis for issuing a reprimand.
The order is drawn up using ordinary office paper or a printed form.
The text must reflect:
- Full company name.
- Date and registration number of the document.
- Information about the offender.
- The circumstances of the offense.
- The measure of influence that will be applied to the employee. In this case it is a reprimand.
- Manager's signature.
The worker must be familiarized with the order within three working days from the date of its approval. Refusal to familiarize yourself with the document is documented.
Formalities related to the issuance of disciplinary sanctions
If a disciplinary violation is detected, the employer must take a detailed explanatory note from the employee outlining his version of what happened. If the employee refuses to write an explanation, the administration writes a report. It must be taken into account that an employee’s refusal to explain his violations in writing is not an obstacle to disciplinary action.
The employer must familiarize the employee with the collection order against signature and no later than three days from the date of issue of the document.
In the absence of these actions by the employer, the violator of discipline can challenge the punishment of the boss. You have three months for this. The employee can appeal to the court or labor protection authorities.
Is a reprimand included in the work book?
Information about the reprimand is not entered into the work book. If reprimanded again within a year, dismissal is possible. However, this happens extremely rarely.
If an employer dismisses an employee as a violator of discipline, the personnel officer makes an entry in the “Work Information” within a week. Only the record of dismissal is certified by the signature of the employer or personnel officer and a seal. It is very important that the legal basis for the dismissal of an employee fully complies with the clause and article of the modern Russian Labor Code.
Is it possible to challenge a reprimand?
Any employee, if he disagrees with the manager’s decision, can appeal the latter’s actions. To cancel an approved order, the interested person must contact the authorized official bodies.
It would be correct to first send the application to the labor dispute commission. CTS is created in almost every enterprise. Its competence includes, among other things, resolving issues of this nature. If this does not give the desired result, then you can send a complaint to the labor inspectorate.
In turn, going to court is a last resort, but can give more guarantees to a person in a positive solution to his problem.
The period for contacting these organizations is three months from the moment the employee became aware or could have learned of a violation of his rights. This period can be restored if time is missed for valid reasons.
Are there time limits for disciplinary action?
The fact of such collection is regulated by Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It indicates the possibility of applying such a measure no later than within a month from the date of the violation.
The duration of an employee's illness or vacation is not taken into account in this calculation. Adopted based on the results of inspections, such a measure cannot be imposed within a period of more than 6 months from the date of commission.
Separately, the imposition of a penalty based on the results of an administrative and economic audit is taken into account. In such a situation, the period is extended to 2 years.
Upon detection, a collection order is issued, which must be personally endorsed by the employee within 3 days after signing.
Results
Question: “Are penalties included in work books?” - regulated by Art. 66 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It says that only penalties associated with dismissal due to a disciplinary offense can be reflected in the work book. If information about disciplinary dismissal, which is recognized as illegal, is included in the labor report, then instead the employer draws up a duplicate, where such information is not indicated.
Sources
- https://o-kadrah.ru/otvetstvennost/vygovor-v-trudovoy-knizhke
- https://pravo.team/trudovoe/trudovaya-knizhka/disciplinarnye-vzyskania.html
- https://hr-portal.ru/article/vnosyatsya-li-svedeniya-o-disciplinarnyh-vzyskaniyah-rabotniku-v-trudovuyu-knizhku
- https://pravo.team/trudovoe/otvetstvennost/trudovay-knizka-vzyskania.html
- https://pred-pravo.ru/vnosyatsya-li-svedeniya-o-disciplinarnyh-vzyskaniyah-v-trudovuyu-knizhku/
- https://BusinessMan.ru/vyigovor-s-zaneseniem-v-trudovuyu-knijku-osnovaniya.html
- https://naim.guru/trudovaya-knijka/zapolnenie/distsiplinarnoe-vzyskanie.html
- https://www.klerk.ru/buh/articles/503588/
- https://hr-portal.ru/article/chto-nuzhno-znat-kadroviku-o-vygovore-s-zaneseniem-v-trudovuyu-knizhku
- https://pravograjdan.ru/prava-trudjashhihsja/vygovor-v-trudovoj/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/trudovye_knizhki/vnosyatsya_li_v_trudovuyu_knizhku_zapisi_o_vzyskaniyah/






