What does the Federal Law say about government positions?
The Russian Federation has approved a list of government positions. It includes:
- President of the Russian Federation;
- The Chairman of the Government and his deputies;
- Federal Minister;
- Supreme Court Judge;
- others.
The full list was approved in Decree of the President of the Russian Federation No. 32 dated January 11, 1995 (current edition dated May 15, 2018, relevant for 2021). Persons holding these positions are not classified as civil servants.
Article 14 of Federal Law No. 79 on civil service
A complete list of rights that a civil servant has. Among others are:
- the right to rest, which implies limiting the working day, establishing days off and vacation;
- the right to demand that the employer provide the logistics of the work;
- the right to access state secrets and government bodies, including municipal level departments;
- the right to protection of the life and health of the civil servant himself, his relatives and property by the state.
Article 15 Federal Law 79
The provisions of this section regulate the main duties of a civil servant. Among other things, an employee of government agencies must:
- comply with the requirements of regulatory acts of the Russian Federation;
- comply with official rules and job regulations;
- maintain a sufficient level of qualifications;
- protect state property (for example, turn off electrical appliances after finishing work);
- do not disclose state secrets.
A civil servant must not carry out an unlawful order from a manager.
Article 16 Federal Law 79
A citizen cannot be accepted into the civil service in the following cases:
- the citizen’s legal capacity is limited by a court decision;
- the presence of a court ban on holding certain positions;
- lack of Russian citizenship;
- refusal of access to state secrets;
- submission of false documents when applying for a job;
- the restrictions established by the legislation on corruption were not observed;
- the employee did not indicate information about his income or provided false information;
- the citizen did not indicate the Internet resources on which he published personal information about himself in the public domain, in accordance with Article 20.2 of Federal Law No. 79;
- in other cases.
Art. 17 Federal Law 79
There are certain prohibitions for current employees.
It is prohibited to fill a position if the person has:
- elected to a local government body;
- elected to the trade union;
- appointed or elected to public office.
A government agency employee may not:
- engage in commercial activities;
- open accounts in financial institutions established in another state, in a branch not on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- receive gifts from companies and citizens, the transfer of which is due to official position;
- use state property to satisfy personal needs;
- disclose proprietary information or use it outside the scope of official duties;
- represent the interests of third parties at the place of work;
- create political parties and public organizations at the place of work;
- perform other actions prohibited by this article.
Art. 18
The article approves a list of rules that a citizen must follow when performing his duties in the service:
- perform work at a high professional level;
- do not go beyond the competence of the department;
- understand that the basis of work is determined by respect for the rights and legitimate interests of citizens of the Russian Federation;
- exclude the influence of personal interests on decision-making;
- meet the moral and ethical requirements for civil servants.
- comply with other requirements specified in Article 18 of Federal Law-79.
The model code of ethics for employees of government agencies was approved by Order No. 79 of April 26, 2011 of the Judicial Department under the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. Based on this document, various departments are developing their own acts regulating the behavior of employees from an ethical point of view.
Art. 25
The article concerns the period for concluding a contract with a citizen entering the civil service.
The employer and employee have the right to set the contract period from 1 to 5 years. The law defines a list of cases when an agreement is concluded for a limited period.
Art. 31
The article regulates cases when a position is reduced or an agency is liquidated. The employee must be notified of the upcoming changes and offered to take another position in accordance with his professional level.
Art. 33
The content of the article concerns cases of contract termination. The following reasons are given:
- expiration of the contract period;
- agreement of the parties;
- a citizen’s refusal to be transferred to another locality if a government body moves there;
- obtaining citizenship of another country;
- others.
Article 37
Here are the reasons when employees quit at the initiative of the employer. The reasons may be:
- non-compliance with certain requirements imposed on civil servants in accordance with the law;
- unsatisfactory passing of tests to determine the level of qualifications;
- showing up at work while intoxicated;
- gross violation of official duties.
Article 46
In this part, the law regulates the procedure for calculating and granting leave to civil servants.
Art. 50
The provisions of the article regulate the remuneration of employees. The monetary allowance consists of several parts:
- salary according to position;
- payments for class rank;
- bonuses for length of service;
- allowances for work under special conditions;
- awards.
Art. 57 Federal Law 79 on the state civil service
The article approves a list of penalties for disciplinary offenses. An employee may be subject to:
- dismissal;
- reprimand;
- remark;
- warned about incomplete suitability for the position held.
Art. 59
The article regulates the verification of the employee’s performance of his duties. The event is initiated by a representative of the department on his own initiative or after receiving a written request from the state. employee.
Management must establish the presence or absence of a disciplinary violation. The maximum verification period is 1 month.
During the inspection, a civil servant has the right:
- give comments, submit applications;
- complain about the actions of inspectors;
- review the final conclusion and other inspection materials after its completion.
General characteristics of the law
The main regulatory act that regulates the activities of civil servants in the Russian Federation is Federal Law No. This act contains all the basic tenets of the country's civil service.
The main purpose of this normative act is to legislatively regulate the activities of state civil servants. In general, this document can be compared with the Labor Code, since it reflects all the nuances of labor relations with civil servants.
Civil service structure
To start working in a government agency, a person must meet several requirements:
- At the time of employment, the candidate must be 18 years old.
- He must speak Russian well.
- The candidate must have skills that demonstrate that he has a sufficient qualification level.
All of the above requirements are stipulated in this federal law.
From Federal Law No. you can glean the following information:
- The procedure for employment in a government agency.
- Dismissal from service.
- Civil servant status.
Attention! The provisions of this regulatory act do not contradict the norms of labor legislation. They partially duplicate the norms of the Labor Code, but do not contradict them.
The draft law began back in 2003. The finished normative act was adopted only on July 7, 2004, but it came into force only six months after its first publication.
Federal Law of July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ “On the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation”
Content
Key points that relate to the implementation of the state civil service are stipulated in 17 separate chapters of Federal Law No.
Each chapter has its own title. The first part of the law is a description of the main points of the service. Here is a brief information about existing positions and a list of responsibilities. Separate explanations are given on the activities of civil servants:
- Conditions under which citizens are hired.
- The employee’s location at work, his work and rest schedule.
- Carrying out certifications.
- List of provided guarantees.
- Maximum age for an employee.
- Features of legal relations between employees.
- Formation of personnel.
Important! The normative act stipulates a ban on employees engaging in entrepreneurial activities.
Regulations on the civil service
The general provisions of the state civil service are contained in 7 articles of the federal law.
It is these articles that are considered to be the main act, since they contain all the main essence, giving an understanding of the document and its features. These articles contain the following information:
- Basic terminology.
- Areas of legal relations that are subject to regulation by law.
- The concept of civil service.
- The principles by which the activities of civil servants are carried out.
- List of regulations on which relations in the civil service are based.
- Interrelation of public services.
- List of relationship aspects.
It is these seven articles that contain the fundamental basis on which the entire regulatory document is built. Thanks to the presence of such an introduction, a person understands the act and the features on which it is applied in the legislative system.
Legal status of the employee
The third chapter of the normative act contains basic information about regulating the status of an employee. It is in this part of the document that the aspects of the activity are fully disclosed:
- The concept of a state civil servant.
- The full range of responsibilities assigned to a person and the rights given to him.
- Existing restrictions.
- Existing prohibitions.
- Permissible limits of behavior.
- Features of conflict resolution.
- Transfer of information about the income received by a civil servant and the property he has.

Benefits and prohibitions for officials
Law prohibiting certain categories of persons from opening and having accounts
The ban was introduced by Law No. 79-FZ of 05/07/2013. Persons holding positions in government bodies at the federal and local levels were deprived of the right to have deposits and accounts in financial companies established in other states, in branches outside the Russian Federation. Also, spouses of government employees and their minor children cannot have these assets.
This issue is also regulated by the provisions of Article 7.1 of Federal Law No. 273 “On Combating Corruption” and Article 17 of Federal Law No. 79.
Changes in the law
Let's take a closer look.
Read also: Right to privacy
Latest edition of the Federal Law
In 2021, the law on civil servants has undergone significant changes. From this moment on, higher requirements are placed on candidates for entry into the service.
Citizens who apply for a high position must have a complete higher education (bachelor's degrees are not taken into account). The new changes do not apply to those persons who entered service before they entered into force. The requirements do not apply to citizens who graduated from a higher educational institution before August 1996.
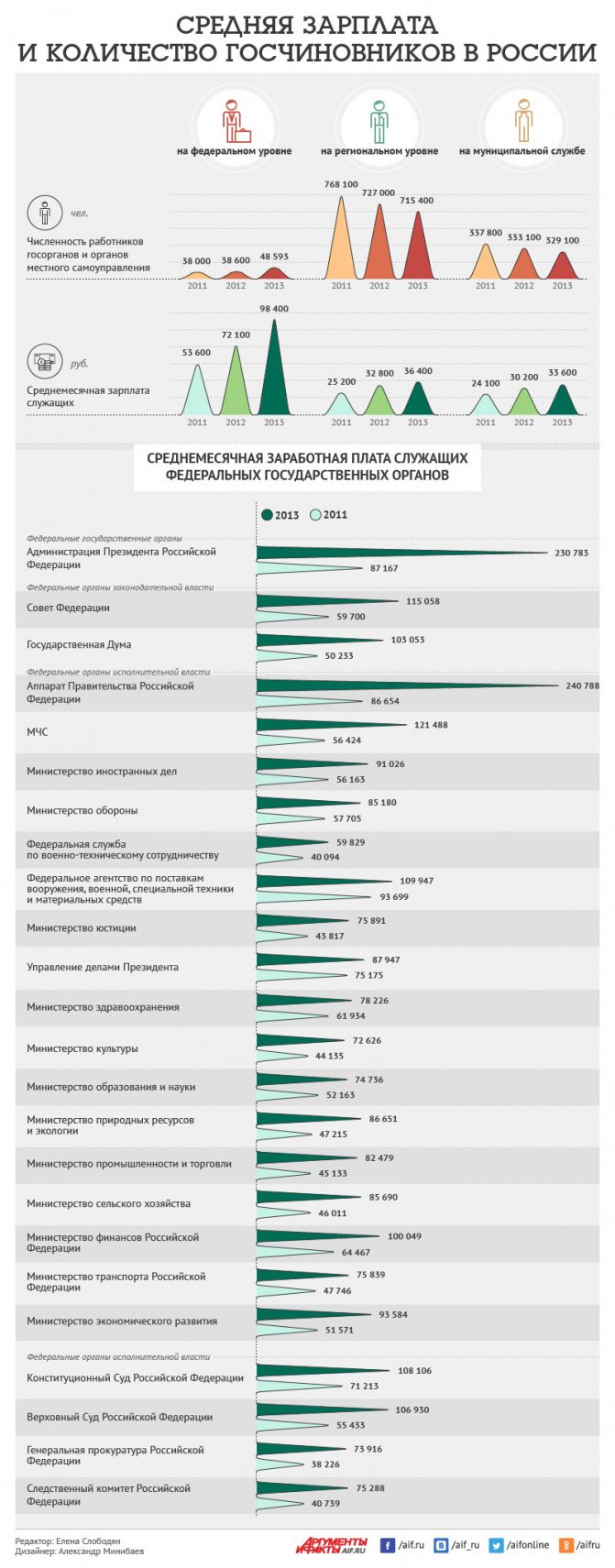
Average salary and number of officials in Russia
All requirements for the employee’s qualifications must correspond to his position. All employees must meet the following requirements:
- Availability of professional training.
- The presence of knowledge that allows him to efficiently perform all professional duties assigned to him.
Certain citizens are given preference due to the availability of special training - such persons undergo special training for service in a certain government agency.
In general, the following changes were made to the new edition of the regulatory act:
- Correcting Article 7 consists of changing the sound of the first paragraph without changing the meaning of what is written.
- Article 12 has been amended, and now it states that in order to enter a certain position, a person must have the appropriate education, level of training and sufficient work experience. Specific conditions directly depend on the position held.
- A new clause has appeared in Article 16, according to which a number of mandatory information specified in Article 20.2 of this normative act may not be indicated.
- An adjustment was made to Article 17, according to which a civil servant, his spouse and minor children should not have a bank account outside the Russian Federation.
- According to Article 20 of the act, every employee has the right to use the Internet for the purpose of transmitting personal data, if this is necessary for the subsequent identification procedure. Persons who represent the interests of the employer have the right to process the information received if it was exchanged by the applicant for the position. Employees have the right to check how completely a person has provided information about himself.
- Article 22 of the act also underwent changes in sound, but this did not affect the semantic load of the norm.
Changes in the law
In December 2021, some changes were made to the federal law.
They mainly concerned the procedure for calculating length of service in the civil service and the abolition of such a thing as law enforcement service. Length of service is the total length of periods during which a person performed public service or other activities that are taken into account when determining the right to receive a civil servant's pension and the amount of such provision.
The length of service includes the following time periods:
- Periods of work as an employee in government agencies.
- Periods of work as federal civil servants and in other positions.
To receive a supplement to the insurance pension, a person must accumulate sufficient work experience in an elective position:
- With five years of work experience, the increase will be 55% of the official salary.
- If the work experience is ten years, the increase will increase to 75%.
Employee certification
Part 3 of Art. 31 of Law No. 79-FZ establishes that within two months of warning, a government agency may conduct an extraordinary certification of civil servants.
Based on its results, employees who have a preferential right to fill a civil service position may be given other civil service positions to fill, including in another government body. The next certification of a civil servant is carried out once every three years.
Certification is carried out in accordance with Art. 48 of Law No. 79-FZ. Certification of a civil servant is carried out in order to determine his suitability for the position being filled.
According to Part 5 of Art. 48 of Law No. 79-FZ, an extraordinary certification of a civil servant may be carried out earlier than the specified period after a decision is made in the prescribed manner:
– on the reduction of civil service positions in a government agency;
– on changing the conditions of payment for civil servants.
We emphasize that the employer is not obliged to conduct an extraordinary certification, but has the right.
Based on the results of certification of a civil servant, the certification commission makes one of the following decisions:
– the employee corresponds to the position being filled in the civil service;
– corresponds to the position being filled in the civil service and is recommended for inclusion in the personnel reserve for filling a vacant position in the civil service in the order of job growth;
– corresponds to the position being filled in the civil service, subject to successful completion of additional professional education;
– does not correspond to the position being filled in the civil service.
Within a month after the certification, based on its results, a legal act of the state body is issued stating that the civil servant:
– is subject to inclusion in the personnel reserve to fill a vacant position in the civil service in the order of job growth;
– sent to receive additional professional education;
– is demoted in the civil service position and is subject to exclusion from the personnel reserve if he is in it.
If an employee refuses to fill a lower position or to undergo professional retraining or advanced training, the service contract with him may be terminated. In this case, the basis will not be paragraphs. “b” clause 1 part 1 art. 37 of Law No. 79-FZ (due to insufficient qualifications confirmed by certification results), and clause 8.2 part 1 art. 37 of Law No. 79-FZ (in connection with the reduction of civil service positions in a government agency) or clause 8.3 of Part 1 of Art. 37 (abolition of a state body).
Preferential right to fill a vacant position
In accordance with Part 4 of Art. 31 of Law No. 79-FZ, a priority right to fill a civil service position is granted to a civil servant who has higher:
– qualifications;
– level of professional education;
– results of professional performance, –
and with a longer duration of experience in the civil service or work (service) in the specialty or area of training.
Please note that civil servants are not covered by Art. 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , according to which the priority right to remain at work in the event of a reduction in the number or staff of workers with equal labor productivity and qualifications is given to: family - in the presence of two or more dependents (disabled family members who are fully supported by the employee or receive assistance from him, which is their constant and main source of livelihood); persons in whose family there are no other independent workers; employees who received a work injury or occupational disease while working for this employer; disabled people of the Great Patriotic War and disabled people fighting in defense of the Fatherland; employees who improve their qualifications in the direction of the employer without interruption from work.
Yes, indeed, based on Art. 73 of Law No. 79-FZ The Labor Code can be applied to relations related to the civil service only to the extent not regulated by Law No. 79-FZ . However, by virtue of clause 30 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2 “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation,” when considering cases of reinstatement of civil servants dismissed due to the reduction of civil service positions, one should be guided by the provisions of Art . 31 , 33 and 38 of Law No. 79-FZ .
Therefore, we can conclude that only the criteria for preferential right to fill a vacant position established by Part 4 of Art. 31 of Law No. 79-FZ . This is also confirmed by judicial practice (see, for example, the Appeal ruling of the Novgorod Regional Court dated November 7, 2012 in case No. 2-3240-33-1819 ).
Abstract from Federal Law-79 and Federal Law-58
Civil service system
Public service is the professional service activity of citizens of the Russian Federation to ensure the execution of the powers of government agencies.
The civil service is divided into civil service (federal and constituent entities of the Russian Federation), military and law enforcement.
A civil servant is a citizen who carries out activities in a civil service position and receives remuneration for this from the relevant budget (federal or subject of the Russian Federation).
State positions are positions established for the direct execution of the powers of government agencies.
- Priority of rights and freedoms;
- Unity of the legal and organizational foundations of the federal civil service and the civil service of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
- Equal access for citizens of the Russian Federation who own state. in the language of the Russian Federation, to the Civil Code, regardless of any circumstances not related to their professional and business qualities.
- Professionalism and competence
- Stability
- Availability of information
- Interaction with public associations and citizens
- Protection from interference in professional and official activities
Classification of state civil service positions
They are divided into categories and groups.
- Managers and their deputies. Replaced for a specified period or without limiting the term of office.
- Assistants (advisers). Established to assist managers. The term of authority is limited (as long as the authority of the manager to whom they assist is valid).
- Specialists. Established to professionally ensure that government agencies perform their tasks and functions. No term limit.
- Supporting specialists. Positions are established for organizational, informational, documentation, financial, economic, and economic support for the activities of government agencies.
Managers, assistants, advisers - senior, main, leading groups of positions
Specialists – Higher, main, leading senior groups of positions
Supporting specialists – senior, main, leading, senior, junior groups of positions.
Qualification requirements: higher education (mandatory for employees of the highest, main, leading, senior groups of positions or for managers, advisers, specialists and supporting specialists of the main and leading groups of positions).
Full qualification requirements are specified in the job regulations.
Restrictions and prohibitions related to the state civil service
- Incapacity or limited legal capacity (by court decision!)
- Criminal record. Conviction by court verdict
- Refusal of the procedure for obtaining access to information constituting state secrets (if his position requires this)
- Presence of diseases that prevent entry or completion of service (see List)
- Close relationship with civil servants, if the activity is related to subordination or control of one another (close relatives are considered to be spouses, parents, children, siblings, as well as similar relatives of spouses)
- Renunciation of Russian citizenship or acquisition of citizenship of another state
- Providing false documents (including upon admission), false information (including about income, property)
- Non-compliance with the Anti-Corruption Law
Block "Commercial activities". Prohibited:
1. participate on a paid basis in the management of a commercial organization;
2. conduct business activities;
3. purchase securities from which income can be received. And if a civil servant already has securities, shares in the authorized capital of other organizations, and their ownership may lead to a conflict of interest, then he is obliged to transfer them to trust management.
Block “Gifts-rewards”. Prohibited:
4. accept remuneration from individuals or legal entities (gifts, money, loans, services, entertainment, recreation, payment of travel expenses). Gifts are considered the property of the government agency in which the citizen serves. Transferred by deed. If you want to get them for personal use, you need to buy them.
5. travel outside the Russian Federation in connection with the performance of official duties at the expense of legal entities and individuals, except for cases provided for by special international treaties.
Block "Publicity". Prohibited:
6. disclose confidential information, official information not for purposes related to the public service;
7. allow public statements and assessments, including in the media, regarding government agencies and their leaders, if this is not part of the job duties.
Block “Relations with public organizations”. Prohibited:
8.accept, without the permission of the employer’s representative, awards, special titles (except for scientific ones) from other states, international organizations, parties, religious and public associations, if job responsibilities include interaction with them.
- use official powers in the interests of parties, religious and public associations. Publicly express your attitude towards them if this is not part of your job duties.
- create political parties, public associations (with the exception of public amateur activities), religious associations in government agencies or contribute to their creation.
Block “Relations with international organizations”. The following is prohibited:
- participate in the management of foreign non-profit organizations or their divisions in the Russian Federation (except for special cases provided for by international treaties);
- engage in paid activities at the expense of foreign states, international organizations, foreign citizens and stateless persons.
Block related to Elections. Prohibited:
- use the advantages of official position for election campaigning;
- fill a civil service position in the event of election or appointment to a position in local government bodies, a trade union, in the event of election to a public office)
Block “What is not included in the rest.” Prohibited:
- use state property, material and technical support for purposes other than those related to the performance of official duties, as well as transfer property to third parties
- represent the interests of third parties in the government agency where the citizen holds a position
- stop performing official duties in order to resolve an official dispute.
Entry into the state civil service. Registration of admission
Citizens of the Russian Federation who speak the state language of the Russian Federation have the right to enter the civil service. Ages 18-65. Meeting qualification requirements. Admission is based on the results of the competition. The competition is held to assess the professional level and compliance with the qualification requirements for the position.
The competition is not held:
- Managers and assistants for a certain period of time.
- Or appointed by the President or the Government
- Fixed-term contract
- From the personnel reserve
- Junior positions
A fixed-term contract (one year - 5 years) is concluded:
- Managers, assistants
- Temporary duties
- Study at a university (with the obligation to pass the GS)
- Dip. representative offices, consulates.
- In a body created for a specific period
- After 60 years.
Conflict of interest - when the personal interest of a civil servant affects the performance of his official duties or a contradiction may arise between the personal interest of a citizen and the interests of a subject of the Russian Federation, citizens, etc.
Service contract: an agreement between a representative of the employer and a citizen entering the civil service. Or GS about passing the GS and filling the GS position.
Start date of duties
Rights and responsibilities of the GS, job regulations
Types of medical and social insurance
Rights and obligations of the employer's representative
Working time and rest schedule
Terms of payment
- Trial
- Non-disclosure of information
- After studying – SG duty for a certain period of time
- Performance - payment
A probationary period (3 months - a year) is not established for:
- Pregnant women
- After university – obligation to pass the GS
- Managers, advisors for a certain period of time.









