Home / Labor Law / Personnel Management / Personnel Records
Back
Published: 08/07/2016
Reading time: 9 min
0
7504
Labor legislation provides for several modes (schedules) of working time distribution. Each employer is obliged to develop and establish a work schedule that does not contradict the legislative norms reflected in the Labor Code and local documents, and also satisfies the production or commercial needs of a given legal entity.
The working hours can be established by local documents, for example, a collective agreement or special rules recorded in writing. Typically, these documents are agreed upon with trade union bodies in order to avoid unnecessary disputes with the work team .
Such a schedule is individual for each individual enterprise, organization or company, as it reflects the characteristic features of the activities of a legal entity. However, there are general scheduling rules that employers need to consider.
- Legislation
- Main types and their features Single-shift schedule
- Irregular schedule
- Flexible work schedule
- Shift schedule Shift schedule
When are schedules drawn up?
If an organization has adopted a single working time schedule for all employees (a 40-hour work week (five days) with two general days off), such a document does not need to be drawn up. The following are situations when it is necessary to enter a work schedule and record of hours worked:
- irregular working hours (Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- work in flexible working hours (Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- shift work mode (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- summarized recording of working time (Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- division of the working day into parts (Article 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In these cases, a monthly work schedule in the form of a table with the days of the week in Excel or another convenient program is drawn up in order to monitor compliance with the normal working hours for the accounting period (month, quarter and others, but not more than one year). Based on the data for each employee for a certain accounting period, wages are calculated, including taking into account the hours of overtime or underwork.
IMPORTANT!
The duration of the accounting period is set by each organization independently. It should be taken into account that it is advisable to set a month as an accounting period if the employee works a monthly number of hours corresponding to the normal working hours, or more hours than provided for by the norm (i.e. overtime hours are initially included). This will allow you to determine the number of overtime hours each month and make appropriate additional payments.
If the employee’s schedule shows that in some months he works more hours, and in others less than the norm, it is fair that overtime in one month is compensated by underwork in another. In this case, it is advisable to set the duration of the accounting period to more than one month. The number of months in the accounting period should be set so that the sum of working hours according to the accounting document coincides with the standard working hours. The number of overtime hours is determined not monthly, but once for the entire accounting period.
Characteristics
An enterprise can establish one of the following types of work schedules according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- Daily 5-day work with 2 days off.
- Daily six-day work with 1 day off.
- Working week with days off on a rotating schedule.
These regimes are provided for in Article 100 of the Labor Code. In Art. 104 of the Code provides for the possibility of applying summarized time tracking at an enterprise.
Daily types of work schedules are in practice called single-shift.
Types of work schedules
Let's take a closer look at what work schedules there are, the differences between a flexible work schedule, irregular working hours, shift work, summarized recording of working hours and a fragmented working day.
Flexible
A flexible working mode requires employees to independently regulate the start and end of their shift. It is important to work a specific number of hours set for a specific accounting period.
Irregular working hours provide for periodic involvement in labor duties outside the standard working day. The list of positions with such working hours is fixed by a collective agreement or internal rules of the organization.
Removable
Shift work involves working in two, three or four shifts during the day. This mode is needed when the duration of the working cycle exceeds the norm for one person. In this case, employees replace each other.
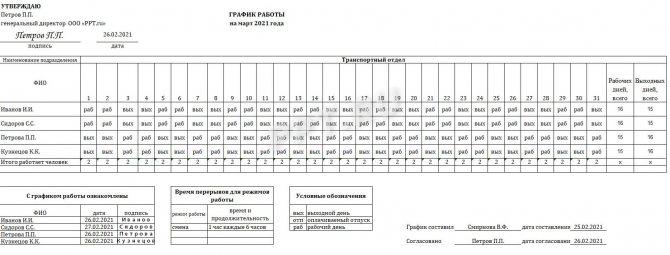
Companies draw up monthly work schedules using the template presented below.
The local act is approved by the head of the enterprise. Employees must confirm that they have familiarized themselves with and agree to work according to the approved schedule by signing.
Summarized accounting
Cumulative recording of working hours allows you to count longer periods of work. The bottom line is that the average duration of work during the day should be equal to the norm for a specific period - week, month, quarter, year.
Let’s say you need to work 40 hours a week, but you can set the shift to 12 hours or 24 hours. This is how salespeople in convenience stores, watchmen, and cleaners often work. Now the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not regulate the duration of the break between two 12-hour shifts, but previously, when distributing the load, they took into account the recommendations of the resolution of the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR dated September 24, 1929, which prescribed that a break between 12-hour shifts be set at least twice the duration of working hours the day before, that is at least 24 hours. Now this resolution has lost force, but some departmental regulations contain similar conditions. For example, the order of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation No. 541 dated December 30, 2001 “On departmental security of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation” says:

We will show with a specific example how to create a monthly work schedule in Excel for 4 people, 12 hours each. The sample uses the following conventions:
- U - work from 07:00 to 19:00;
- B - evening shift from 19:00 to 07:00;
- * - day off.

The proposed example is universal; such ready-made tables for filling out work schedules are used in stores, warehouses, transport companies, and security agencies.
Another sample for cases when work is carried out according to schedule 2 in 2 days:
Dividing the day into parts
Dividing the work day into parts is allowed in accordance with the regulatory local act of the organization and taking into account the opinion of the trade union. The day is divided into parts by a break, which is not paid. This procedure is used in trade, in transport companies, and in government agencies.
ConsultantPlus experts discussed how to make corrections to a timesheet. Use these instructions for free.
Important point
It is necessary to take into account that with an irregular schedule, employees can only be involved in the performance of those duties that are specified in the employment contract. This means that the employer cannot oblige the employee to perform other work, including outside the normal working hours.
Article 60 of the Labor Code expressly prohibits requiring an employee to perform duties that are not specified in the contract.

Timesheet for 2021 (timesheet): how to fill out
There are two unified forms: T-12 and T-13. The difference between them is that the T-12 form is filled out only manually or in a text editor; it has a special section for calculating wages. Time sheet T-13 can be filled out using specialized computer programs and access control systems, which are used to record the presence of employees at workplaces. This duty schedule template for further accounting does not contain a block for calculating wages; it must be calculated in other documents.
The working time sheet is the primary document on the basis of which wages, payments from them and additional payments accepted in the organization are calculated. Since the listed payments reduce corporate income tax or taxable income under the simplified tax system, the document should be fixed as a primary document in the organization’s accounting policy. It is not necessary to use the unified form from 01/01/2013. It is important to consolidate your own version of the form in the accounting policy and ensure that it contains all the necessary details, the mandatory presence of which in primary documents is established by law 402-FZ.
The time sheet is drawn up in one copy by a person authorized to monitor the control of working hours throughout the organization or in a separate structural unit. The list of persons signing it is established by the internal administrative act of the organization. At the end of each month, the completed timesheet is transferred to the accounting department.
Let's look at the procedure for filling out the timesheet using the T-13 form as an example.
Duties of the parties
It must be said that when applying the provisions of Article 101 of the Labor Code, the employer does not have to obtain consent from either the employee or the trade union to engage in work beyond the standard duration. This right is initially stipulated in the employment contract.
The employee, in turn, cannot refuse to perform his duties on an irregular schedule. Otherwise, his actions will be regarded as a gross disciplinary offense.
The establishment of an irregular regime, however, does not mean that employees will not be subject to the provisions of the Labor Code on norms of rest and work time. In this regard, their involvement in work activities beyond the shift duration determined for them can only be carried out sporadically.

Step-by-step instructions for registration
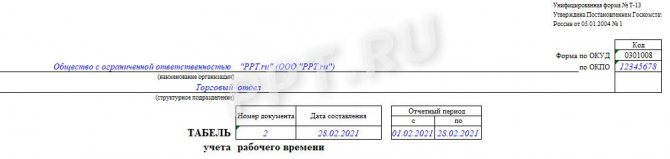
Step 1. Design the header
The name of the organization and structural unit must be indicated in the header (when monitoring working hours in structural units). The serial number is assigned in accordance with the numbering accepted in the organization. The date of compilation and the reporting period must be indicated as details of the primary document.
Step 2. Fill in columns 1–3
Column 1, containing the serial number, is filled in according to the number of employees in the time sheet. Columns 2–3 contain identification information about each employee: full name, position and personnel number.

Step 3. Fill in columns 4–6
Column 4 contains notes on attendance and absence from work for each date in the corresponding month. In the example of a timesheet for February 2021, there are 28 days, so there are 28 cells to fill out the data. For this information, the table has four rows (two for each half of the month).
In the top line of each half of the month, letter designations of the reasons for appearances and absences are placed (the letter correspondence of the reasons is presented on the title page of the T-12 form) - these are codes for appearances and absences for the working time schedule. The decoding of the codes is given in the file at the end of the article.
Notes explaining the reasons for absence from work, notes about working part-time or outside normal working hours, and others are made on the basis of documents: certificate of incapacity for work, certificate of fulfillment of state or public duties, written warning of downtime, written consent of the employee to work overtime in cases established by law, etc.
Under the letter designation there is a numerical indicator equal to the number of hours and minutes actually worked by each employee.
Columns 5 and 6 contain the total indicator of time worked by each employee for each half of the month in hours, minutes and days (column 5) and for the entire month (column 6) in hours, minutes and days.
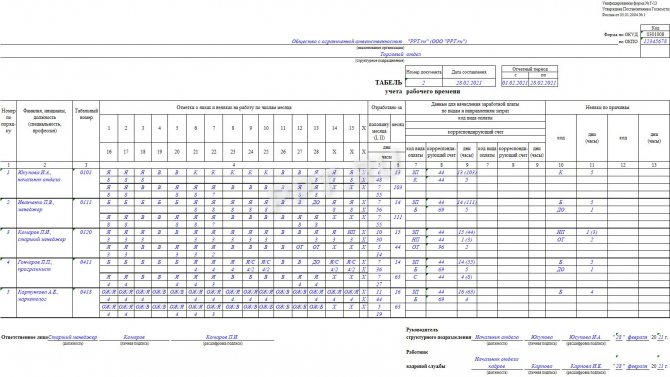
Step 4. Fill in columns 7–9
Columns 7–9 in form T-13 are filled out when using an automated accounting system. The following features must be taken into account:
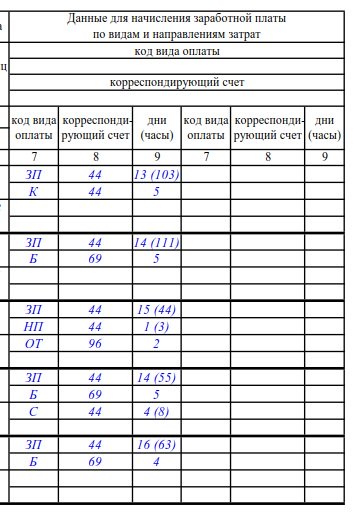
- if all employees of the organization are paid wages only according to one type of remuneration and using one corresponding account, then the indicators “Wage type code” and “Corresponding account” can be placed above columns 7, 8 and only column 9 can be filled out - for the total indicator of days worked and hours (in brackets) for each employee;
- if accruals are made for several types of payment (2 or more) and using several accounting accounts, then columns 7 and 8 are filled in with the relevant data, and column 9 reflects the total number of days and hours worked (in parentheses) for each employee;
- an additional block with similar columns is provided in case the number of types of remuneration exceeds 4.
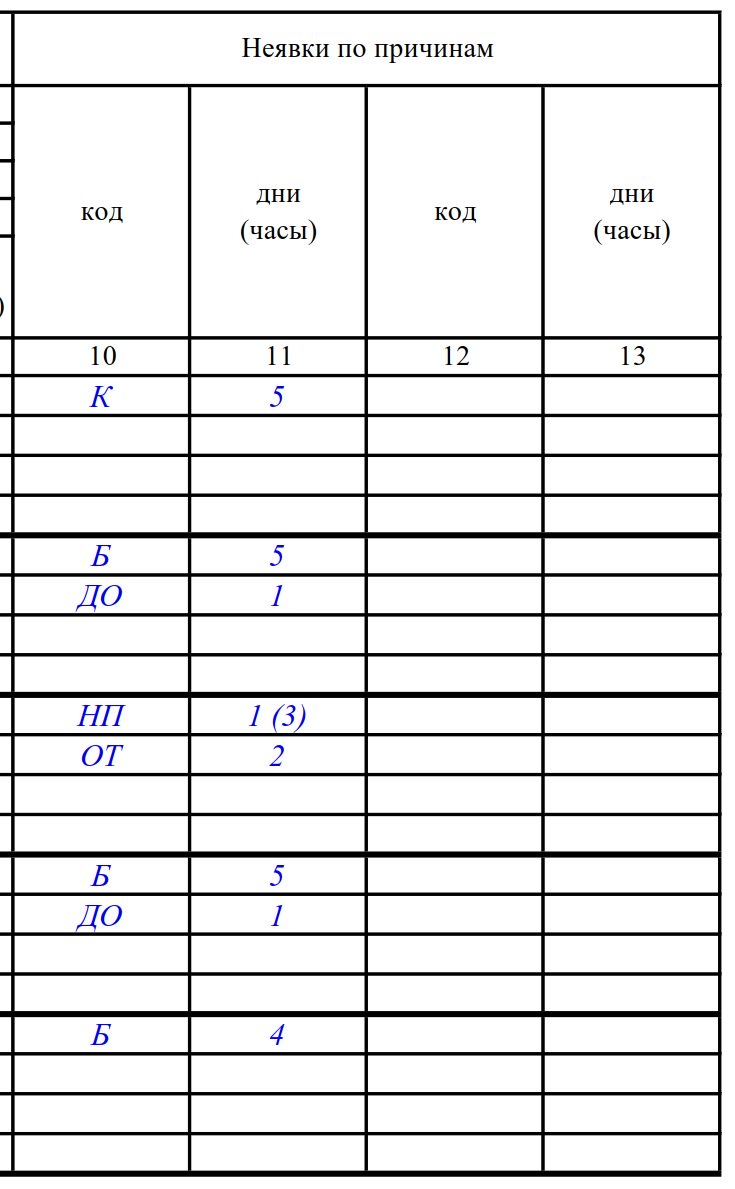
Step 5. Fill in columns 10–13
Information is provided on absences for the accounting period according to the corresponding codes in days and hours (indicated in parentheses). Two blocks are provided in case the number of reasons for absence exceeds 4.
It should be remembered that the timesheet does not include persons working under civil contracts. The timesheet can be maintained in one of two ways, which the organization records in its accounting policies:
- in a continuous way, that is, to register all attendances and absences from work;
- a method of recording deviations, that is, registering only deviations (absenteeism, being late, overtime, etc.).
At the end of the month, the timesheet is signed by responsible persons, the list of whom is established in the regulatory act of the organization, and transferred to the accounting department for calculating wages and other payments.
If in an organization the salary for the first half of the month (advance) is calculated for the time actually worked, the time sheet is allowed to be drawn up separately for the first and second half of the month.
Job categories
As mentioned above, not all employees can be subject to an irregular work schedule. Types of positions may be provided not only in a collective agreement or work rules, but also in industry, regional and other regulatory documents.
An irregular schedule may apply to persons:
- Technical, administrative, economic, management personnel.
- The labor activity of which cannot be taken into account in time.
- Distributing their working time at their own discretion.
- The schedule of which is divided into parts of indefinite duration.
Prerequisites
To apply a flexible mode, the enterprise must have a clear system for recording the time worked by employees and their completion of production tasks. In addition, control over the most complete and rational use of time by each employee in both fixed and flexible periods must be ensured.
It should be noted that the use of this regime is regulated by several regulations. For example, the Order of the Ministry of Communications approved a list of employees for whom a flexible schedule may be provided.
Features of application
Flexible mode is used when other types of work schedules are inappropriate or ineffective due to various reasons (domestic, social, etc.). Often it allows for more coordinated team activities.
At the same time, the use of a flexible mode is impractical in continuous production and shift work schedules (their types can be installed in both discontinuous and continuous production) if there are no free places at the shift junctions.
The flexible mode can be used for both a five- and six-day week, as well as for other modes. At the same time, the conditions for rationing and payment of wages do not change. The conditions for providing benefits, accrual of length of service, and other rights are also preserved. It must be said that the registration of work books is carried out without mentioning the mode of labor activity.
Working hours
The types of sliding work schedules vary depending on the established accounting period in the organization, the time characteristics of the elements of the regime, and the conditions of their use in a particular department.
The maximum permissible length of the day (with a 40-hour week) does not exceed 10 hours. In some cases it can be within 12 hours.

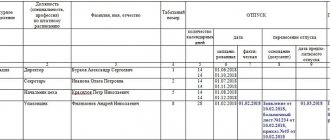
Additional leave
Due to the fact that with an irregular schedule, certain overtime occurs in excess of the standard length of the day, the Labor Code, as some compensation, establishes the possibility of employees receiving additional leave. Its duration is determined in the collective agreement or rules of procedure. Leave is paid and provided annually.
If such a vacation period was not provided, with the written consent of the employee, overtime is counted as overtime.
The conditions and rules for providing paid additional leave for employees of organizations financed by federal, regional, and local budgets are established by the Government, authorities of constituent entities or territorial self-government, respectively.