How to properly file a complaint to Roskomnadzor about the use of personal data
complaints to Roskomnadzor about the use of personal data free in word format
If a citizen notices personal data (full name, address, telephone number or even passport data) on a third-party resource, you should immediately contact Roskomnadzor with a corresponding complaint, because the distribution of personal information without the owner’s permission is prohibited by federal law.
If all conditions are met, Roskomnadzor will draw up a protocol on an administrative violation by the resource. A complaint can be made using a free form.
To register, a citizen will need:
- Full name, place of registration and telephone number,
- name of the organization, link to the official website.
In your complaint, describe all violations noticed by the resource. Links to laws that support the victim's case are welcome. A common mistake is expressing your emotional state in a document, as well as using unnecessary language.
Note! A mandatory point is the measure of responsibility that a violator of the administrative code of the Russian Federation must bear. You should also exclude grammatical errors and obscene language; all these factors will only distract from the essence, and this will not lead to anything good.
The following should be used as evidence:
- recording a telephone conversation,
- video materials,
- information published in newspapers,
- photographic materials confirming the fact of violation of laws,
- website screenshots,
- copies of receipts for payment of services, checks.
ATTENTION! View the completed sample complaint to Roskomnadzor regarding the use of personal data:
Attention! Our qualified lawyers will assist you free of charge and around the clock on any issues. Find out more here.
Roskomnadzor answers to questions about personal data
Author: Anatoly Antonov, July 22, 2021 at 19:46 Good afternoon!





9) on the average number of employees of the organization for the calendar year preceding the year of posting the specified information on the Internet information and telecommunications network in accordance with paragraph 1.1 of this article; 10) on the amounts of taxes and fees paid by the organization in the calendar year preceding the year of posting the specified information on the information and telecommunications network “Internet” in accordance with paragraph 1.1 of this article (for each tax and fee) without taking into account the amounts of taxes (fees) paid in connection with the import of goods into the customs territory of the Eurasian Economic Union, the amount of taxes paid by the tax agent, the amount of insurance premiums; 11) on the amounts of income and expenses according to the accounting (financial) statements of the organization for the year preceding the year in which the specified information was posted on the Internet information and telecommunications network in accordance with paragraph 1.1 of this article; 12) on registration with the tax authorities of foreign organizations in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code. 13) on registration with the tax authorities of individuals in accordance with paragraph 7.3 of Article 83 of this Code. Information about the organization specified in subparagraph 3 (in terms of information on the amounts of arrears and debts for penalties and fines (for each tax and fee, insurance premium), tax offenses and penalties for their commission) and in subparagraphs 7, 9 - 11 of paragraph 1 of this article are posted in the form of open data on the official website of the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees, on the Internet information and telecommunications network, with the exception of information about the organization that constitutes a state secret. Information to be posted is not provided upon request, except in cases provided for by federal laws. The terms and period for posting the information specified in paragraph one of this paragraph, the procedure for their formation and placement are approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees. Tax secrets are not subject to disclosure by tax authorities, internal affairs bodies, investigative bodies, bodies of state extra-budgetary funds and customs bodies, their officials and attracted specialists and experts, except for cases provided for by federal law. Disclosure of tax secrets includes, in particular, the use or transfer to another person of information that constitutes a trade secret (trade secret) of a taxpayer, payer of insurance premiums and which has become known to an official of the tax authority, internal affairs body, investigative body, body of a state extra-budgetary fund or customs body , to an engaged specialist or expert in the performance of their duties. It is not a disclosure of tax secrets if a tax authority provides information to the responsible participant in a consolidated group of taxpayers about the members of this group constituting a tax secret, as well as submitting information about projected income tax revenues to the financial authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in whose territories the participants of the consolidated group of taxpayers operate. organizations to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation from a consolidated group of taxpayers in the current financial year, for the next financial year and planning period and on factors influencing the planned revenues of corporate income tax received in accordance with subparagraph 9 of paragraph 3 of Article 25.5 of this Code. The internal affairs bodies, investigative bodies, state extra -budgetary funds or customs authorities received by tax secrets have received a special storage and access regime received. Access to information constituting a tax secret has officials determined by the federal executive body, authorized to control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees, the federal executive body authorized in the field of internal affairs, the federal state body exercising the powers in the field of criminal legal proceedings, the federal executive body authorized in the field of customs. The loss of documents containing tax secrets, or the disclosure of such information entails liability provided for by federal laws. The provisions of this article in terms of determining the composition of information about taxpayers (payers of insurance premiums) that make up the tax secret, prohibition on the disclosure of these information, requirements for a special storage and access to these information, as well as responsibility for the loss of documents containing the indicated information, or disclosure Such information extends to information about taxpayers (payers of insurance premiums) received by organizations subordinate to the federal executive body authorized to control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees that enter and process data on taxpayers (payers of insurance premiums), as well as for employees) these organizations. The provisions of this article regarding the prohibition on the disclosure of information constituting tax secrets, requirements for a special storage regime for these information and access to them, responsibility for the loss of documents containing these information, or for the disclosure of such information applies to information on taxpayers (payers of insurance premiums) , received by state bodies, local governments or organizations in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on counteracting corruption. Access to information constituting tax secrets in state bodies, local authorities or organizations that such information was received in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on combating corruption, are officials determined by the heads of these state bodies, local authorities or organizations. The provisions of this article regarding the prohibition on the disclosure of information constituting a tax secret, requirements for a special storage regime for these information and access to them, responsibility for the loss of documents containing the indicated information, or for the disclosure of such information apply to information about the amount of employees' income sources (their spouses and minor children) organizations with state participation received by state bodies in accordance with regulatory legal acts of the President of the Russian Federation, the Government of the Russian Federation. Access to the tax secrets indicated in this paragraph in state bodies in which such information was received in accordance with the regulatory legal acts of the President of the Russian Federation, the Government of the Russian Federation, have officials determined by the heads of these state bodies. The information contained in a special declaration submitted in accordance with the Federal Law “On voluntary declaration by individuals of assets and accounts (deposits) in banks and on amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation”, and (or) the documents attached to it and (or ) information, recognized as a tax secret taking into account the following features: 1) such information is recognized as a tax secret without exceptions established by subparagraphs 1 - 3 and 5 - 8 of paragraph 1 of this article; 2) the disclosure of such information and the loss of the submitted special declarations and (or) the documents attached to them and (or) information are the basis for bringing to criminal liability for illegal disclosure of information constituting a tax secret, in accordance with the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation; 3) the official of the tax authority, to whom such information has become known, cannot be held accountable for refusing to testify due to circumstances that he became known from the information indicated in the first paragraph of this paragraph; 4) such information can be claimed by the tax authority only at the request of the declarant itself, recognized by such in accordance with the first paragraph of this paragraph by federal law; 5) if it is necessary to confirm the fact of the submission to the tax authority of a special declaration and (or) information attached to the declaration, and the reliability of the information contained in them, the official of the state authority or bank, which as the basis for the provision of guarantees stipulated by indicated The first paragraph of this paragraph by the Federal Law, a copy of a special declaration was presented with a note of the tax authority on its adoption, has the right to send it to the federal executive body, authorized to control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees, for reconciliation with the original of a special declaration located in a centralized storage. The federal executive body authorized to control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees, within a five -day period after receiving such a copy of the special declaration, sends a return notification about whether the received copy of the special declaration of the original corresponds or does not correspond to. The provisions of this article regarding the ban on the disclosure of information constituting a tax secret, requirements for a special storage regime for these information and access to them, responsibility for the loss of documents containing these information, or for the disclosure of these information apply to information received by the financial bodies of the subjects of the Russian The Federation, in the territories of which participants in the consolidated group of taxpayers carry out activities, as part of the information on the predicted income tax income income to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation from participants in the consolidated group of taxpayers in the current financial year, on the next financial year and planning period and on factors that affect for the planned income tax income tax. Access to the tax secrets indicated in this paragraph, in the financial authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, have officials determined by the heads of these financial bodies. Thus, any person can collect and process perosnal data, but your consent to the processing of personal data, with the exception of cases provided for by law, is necessary. Answer
Is it possible to apply anonymously?
Unfortunately, Roskomnadzor does not accept complaints without information about the person filing. If the application does not contain the required information (more details below), the citizen will receive a refusal to consider the complaint.
How to write a complaint to the Prosecutor's Office (sample)?
Required items:
- When submitting, please indicate the address to which the verification results will be sent and the identity of the sender. There must also be a signature. Without this, the complaint will not even be considered,
- If a citizen decides to file a complaint electronically, he will be forced to undergo verification in order to identify his identity.
Watch the video. Why do we need a law on personal data?
Personal data of company representatives in the contract
Typical situation: two legal entities have entered into an agreement with each other. On the one hand, the agreement was signed by a representative by proxy.
An organization that has issued a power of attorney to its employee is obliged to obtain consent from him to transfer personal data to the counterparty under the contract.
For the counterparty who has received the power of attorney from this employee, it is not necessary to obtain separate consent for processing, because processing of the authorized person's PD is carried out within the framework of the agreement.
Procedure for filing a claim
Please note that the procedure is free, no government fees. you will not have to pay duties. From the above, we can conclude that you can file a complaint in 3 ways, namely in person, by sending an application by mail, or through the official website.
When submitting via the Internet, you should carefully fill out all forms in order to avoid mistakes and not be rejected because of such a trifle.
There is a special section on the official website of Roskomnadzor that will require the applicant to fill out a form with personal data. Submitting an application through State Services is also encouraged.

What to do if debt collectors call you at work?
How to write an application to the Prosecutor's Office for an inspection, read here.
What is the statute of limitations for credit debt, read the link: https://novocom.org/banki-i-kredity-2/srok-iskovoj-davnosti-po-kreditnoj-zadolzhennosti.html
Important! When filling out an application or filing a complaint electronically, pay attention to the website’s email address. Today there are many clones that make an identical design to the original.
The purpose of these clones is simply to obtain data and use it for their own purposes. Also, when logging in to such a clone, attackers will receive the password for the real site, and the site will give you an error asking you to wait a little.
To avoid falling for phishing, you should carefully check the link; on phishing sites it differs from the original one, sometimes greatly, sometimes almost imperceptibly. Be carefull!
How to file a complaint to Roskomnadzor against debt collectors?
Procedure for destruction of personal data

The procedure for destroying personal data of employees and other persons must be fixed in the local acts of the operator. All interested parties must be familiar with the acts.
The operator must provide unrestricted access to these documents, and if personal data is collected using the website, Roskomnadzor recommends placing links to the personal data processing policy directly next to the web forms.
Reasons for appeal

Why should you contact Roskomnadzor? It is this organization that controls the security of personal data and punishes in case of its illegal distribution.
The complaint will not be accepted if the submitter himself has given permission for his personal information to be publicly displayed (provided that the information is used for its intended purpose, in accordance with the permission of the data owner).
I would also like to pay attention to what data is personal and fits the criteria:
- FULL NAME,
- Date and place of birth,
- current marital status,
- place of work, information about income,
- telephone number, address, children's information, etc.
Such information is personal and cannot be disseminated just like that, so if confidentiality is violated, you should immediately contact Roskomnadzor, and the problem will soon be corrected.
An exception is that the citizen himself has given the go-ahead for the dissemination of his personal information, unless the terms of the permit have been violated.
Contacting Department "K"
This unit of the Ministry of Internal Affairs deals directly with crimes in the field of information technology (not to be confused with the Department of Information Technology of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, you can send an appeal to Department “K” if we are talking about the protection of personal data on websites, online portals, etc.
To submit information:
- Go to the Ministry of Internal Affairs appeals page.
- In the list of departments, select Management “K”.
- Read the information that opens and make sure once again that your case corresponds to this particular unit.
- Click the "Continue" button below.
- Read the information on the page that opens, check the box below to confirm that you have read it, and click the “Submit Appeal” button.
- Fill out the fields of the request, understanding that the “*” symbol indicates mandatory information. Enter the message text.
- Click the "Submit" button.
The appeal must be registered within 3 days. If Department “K” considers that the application was sent to the wrong address or sees other reasons not to respond to the information, information about this should be sent to the applicant within 7 days. If the application is accepted for consideration, a response will be received within a month.
Result of the complaint consideration
If the test result is positive, the problem will be immediately corrected and the data will be erased from public view. Also, the company’s website may be blocked due to violation of the laws of the Russian Federation.
Complaints are usually accepted without problems, the main thing is to fill out the form correctly, provide reliable data (so that there are no problems with personal identification), and write the application correctly.
Remember! It is necessary to exclude any abuse towards the offender, emotional coloring, or grammatical errors. It is these factors that negatively affect consideration and ultimately cause refusal.
If the complaint was rejected, the citizen receives a refusal with an explanation of the reasons.
Where should I go for personal data protection?
Federal Law (N 152-FZ “On Personal Data”) established a special Authorized Body for the protection of subjects of rights related specifically to personal data. Roskomnadzor is assigned to perform the functions of this body .
Thus, it is Roskomnadzor today that is the main institution where you need to file a complaint about violation of legislation in the field of personal data. We will consider the request to this body in detail further, however, there are other services (departments) to which you can report a violation:
- Prosecutor's Office of the Russian Federation.
- Directorate "K" of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation.
Let's consider the possibilities of contacting these organizations. At the same time, we will focus on online submission of applications.
Responsible person
Will the operator be held liable if he has not appointed a person responsible for the processing of personal data?
RKN will not be held administratively liable. But if such a fact is revealed during the inspection, the inspector will issue an order indicating the deadline for its execution. And if the operator does not eliminate the violation within this period, he will be brought to administrative liability under Art. 19.5 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Is it possible to appoint several persons responsible for processing personal data?
The notice of intention to process personal data must indicate only one individual responsible for the processing of personal data. Of course, the person in charge can delegate part of his functionality, but this needs to be indicated only in the operator’s local acts.
Is it possible to indicate in the notification the legal entity responsible for processing personal data?
Yes, if a legal entity is involved in the processing, it may be indicated in the notice of intention to process personal data in addition to the information provided for in Art. 22 of Law No. 152-FZ.
Where to send claims?
Any citizen of Russia has the right to send a complaint to the site to Roskomnadzor, send a document by fax, or make a call. What phone number can I call and send a fax? 8 (495) 987-68-00.
It is possible to send a complaint to a particular malicious site using other resources, for example by creating a direct appeal. One of such institutions that receives complaints is the Center for Safe Internet in the Russian Federation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
A complaint can be submitted in the following ways:
- Through the reception desk of Roskomnadzor. In this case, the complaint must be submitted in two copies, one of which must be marked as received.
- Via Russian Post by registered mail. In this case, the citizen will have the opportunity to track the location of sent correspondence.
We suggest you read: Low voltage in the network - what to do and where to complain
Then, when the complaint is “global” and, in the opinion of the sender, should be delivered to specialists as quickly as possible, it is recommended to contact the FSB.
Each search engine has special pages that give any user the right to file a complaint against the site. However, care must be taken to ensure that the complaints made are substantiated and provable.
Page for submitting a complaint to Google
Google's Webmaster Tools provide the ability to report web spam, copyright infringement, and many other legal violations. To select the appropriate form for filling out a complaint, you first need to correctly assess the situation and make an accurate decision that this complaint falls into this category. Next, use intuitive tips.
Having received your complaint, the search engine, if it is justified, forwards it to the offending site with a requirement to take measures to eliminate illegal materials. It must be said that Google reacts to justified complaints quite quickly and harshly - because of one “wrong” page, the entire site of the offender can suffer.
To file a complaint about a site with Yandex, you also need to fill out special forms. Here you can complain about viruses or spam, or problematic content. For other questions, you can write to technical support or send a complaint by fax to 7 495 739-70-70.
Page for sending a complaint to Yandex
Personal reception
Citizens' appeal through a personal meeting with the general director of the institution requires a pre-registered appointment for the meeting. To do this, you need to go to the page of the official website of Roskomnadzor “Pre-registration for an appointment” and fill out the form provided.
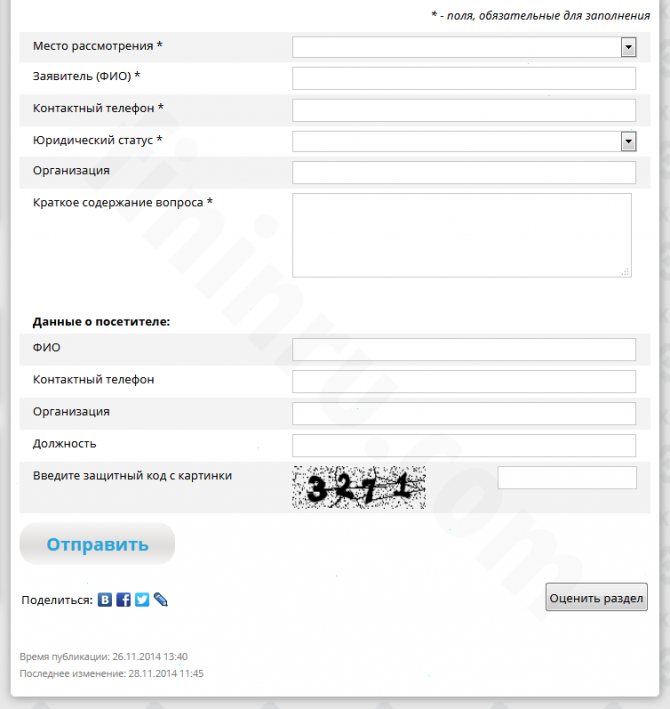
Pre-registration form for an appointment on the RKN website
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyright
Applications will be ignored if they contain false names, contain insults, or contain Latin or unreadable characters.
How to properly file a complaint against a malicious site?
How to complain about a particular resource? It is recommended to send the paper by registered mail. Thanks to this, the sender will receive a corresponding message about the delivery of the application to the desired addressee. More details below.
Information in the letter
How to write and submit an application? A complaint about a malicious resource can be made in any form for the user. However, it should reflect the following information:
- name of the institution that is the recipient of the letter;
- Full name of the applicant, his contacts;
- the actual text of the complaint, written in a publicly accessible style;
- references to laws that the website violates;
- the sender's suggestions for solving this problem;
- attachments (copies of the sender’s passport, etc.);
- signature with transcript and date of sending the complaint.
Roskomnadzor processes specific violations of laws specified in this legislation of the Russian Federation.
General terms
When preparing a document with Roskomnadzor, the compiler needs to focus on business style:
- avoid obscene expressions, as well as emotional and evaluative statements;
- the problem is presented in fact, i.e. no deviations from the topic - just the essence;
- there is no need for employees of a government agency to put pressure on feelings, as this may aggravate the situation;
- express your thoughts adequately, maintain human dignity.
It is strictly forbidden to make any mistakes in the submitted paper. The citizen works with legal documentation, which will later become an official document. Data about the citizen must be complete. This will allow Roskomnadzor operators to contact the sender.
In what cases is it not necessary to obtain consent to distribute personal data?
There are relaxations for the media: it is not considered a violation of the law on personal data when journalists and media editors disseminate some information in the performance of their direct duties.
If interviews are often published on your website, you should think about registering the media. This will make it possible to avoid obtaining consent to distribute personal data.
Another case when consent is not required is if the public is interested in the information made public. It is important here not to confuse curiosity, for example, about the lives of famous people, with public interest ─ when information directly affects the life, health, and well-being of citizens. An example is the dissemination of information about criminals who are wanted.
Complaint against debt collectors
A citizen has the right to complain about employees of collection agencies if they provide his relatives, acquaintances, friends and other people with information:
- about the presence of debt to a credit institution;
- amount of debt;
- passport details;
- phone number.
To file a complaint against debt collectors, it is wise to provide some evidence in favor of the complainant.
A complaint against debt collectors is made in any form. The following information is indicated on the paper:
- Full name, place of residence, telephone number of the sender;
- name and address of the company violating the current legislation of Russia.