Non-residential real estate has become such a part of our lives that it is difficult to imagine any city in the country without it. And even in a small locality, you can easily find many types of non-residential real estate. When will you know what it might be like and where it might be.
After reading this article, you will understand what non-residential premises are like. And you will begin to distinguish them from each other. Familiarize yourself with the types of permitted uses of non-residential premises and their intended purpose. You will learn all the pros and cons of owning such real estate and other nuances.
Let's start our study of non-residential real estate with the most familiar apartments and so-called residential premises, or boathouses. Which each of us encounters when renting inexpensive housing on vacation by the sea.
Residential premises - what are they and how do they differ from apartments?
Apartments
Recently, a fashionable trend among developers.
The construction of residential apartments belonging to the non-residential real estate stock began. The first apartments appeared after one of the developers was refused by the state commission to put the house into operation and assign it the status of a residential apartment building.
But the enterprising developer did not despair about this, and since the new building was located in a prestigious area of the city. They decided to sell the apartments without the possibility of registration in them.
The apartments for sale had all the same functions as regular housing in a neighboring building.
The only difference is that utility bills for such a “pseudo” apartment had to be paid as for non-residential premises.
And the size of the communal apartment itself was slightly higher than in ordinary apartments, but this difference was not critical.
But the cost per square meter of such real estate was significantly lower than the cost per square meter in an ordinary apartment. For sale in the same area of the city.
Boathouses
In the southern regions of Russia and in the central areas of large cities, residential garages have become popular.
Related to non-residential property. People called them boathouses because of their original purpose. Such garages were first built on the coastline of reservoirs, rivers and lakes for the purpose of storing motorboats and small boats.
And the top floor of the boathouse was an insulated living space with the possibility of being used as a summer house near the water.
Living spaces
Over time, in the southern regions of Russia. Another type of non-residential premises was added to the boathouses.
They turned out the same way as the apartments due to the fact that the state commission did not accept the new building. Due to the impossibility of connecting the required communications to it or due to other violations.
Allowing the constructed building not to be recognized as a self-construction and to receive the status of an independent real estate object. But it was impossible to call this building a residential building with apartments.
Therefore, the property documents issued for such pseudo apartments are in the line, the real estate object. Contained the entry “residential premises”, not “apartment”
That is, registration in residential premises belonging to the non-residential real estate fund was also prohibited.
Enterprising citizens of the southern regions, at first, took advantage of the ignorance of citizens from other regions of the country. After all, people have never encountered the new term “living space.” And they thought they were buying an apartment.
The number of deceived citizens grew like a snowball until bloggers began to cover this problem. Which posted explanatory videos on YouTube video hosting. With signs of a living space and its differences from an ordinary apartment.
The reason why entrepreneurs managed to fool people for so long and sell non-residential real estate under the guise and at the cost of apartments.
It turned out that the building, which housed residential premises, was externally similar to an ordinary apartment building.
That is, looking at the boathouse, a person immediately sees a garage with an upper residential floor above it in the form of a superstructure.
And when inspecting a residential premises, the client is cunning realtors. It looks like an ordinary new building with ordinary apartments selling below market.
And the realtor’s promises that the price is lower, since there is no water in the house yet. But she's about to be connected.
But in fact, technically it is simply impossible to connect water to the house. And why do this when all the living spaces in the house are already sold out. Like hot cakes.
Now let's see if it's worth getting involved with the purchase of such non-residential real estate.
After all, boathouses, apartments and living quarters have both their advantages and disadvantages.
Residential and non-residential premises: signs

Let us immediately make a reservation that the law does not provide clear definitions of these concepts.
From established practice, it can be established that a building is a complex real estate property, or rather a complex of real estate, an architectural and construction facility that creates conditions for work, social and cultural services for the population, residence, storage of valuables and consists of walls, a roof, and foundation.
The components of a building are premises, which can be both residential and non-residential.
Thus, we conclude that a premises is a unit of a real estate complex, a part of a building that is intended for independent use for residential and other purposes, owned by individuals, legal entities, the state or its subjects.
Real estate and isolation of premises
Any premises, in the civil and housing law aspects, have two characteristics:
- any premises is real estate
- The rooms are distinguished by their isolation
Let's take a closer look at each of the signs.
First of all, both residential and non-residential premises must be real estate. This means that they must be firmly anchored to the ground and cannot be moved without significantly affecting their intended use.

That is why trailers, cabins, and various prefabricated houses are never recognized as residential premises. Non-residential premises should also be classified as real estate, since the rights to them are subject to state registration in accordance with the law.
The next sign is isolation. This sign means that both types of premises must be an isolated object, i.e. must be materially limited by walls, floors and ceilings.
Any room must also have an entrance.
Condition and characteristics of residential premises

The remaining signs of residential and non-residential premises indicate precisely the difference between them.
Thus, residential premises, in addition to the above features, are characterized by their suitability for permanent residence of citizens in it. In accordance with this criterion, the residential premises must be located in a residential area, it must be in good condition: all building structures must be operational, without any damage or destruction, so that their load-bearing capacity is not impaired.
The premises must be equipped in such a way that any possibility of injury to residents while staying inside and leading a normal lifestyle is eliminated.
In addition, the residential premises must be equipped with the necessary engineering systems, such as sewerage, electricity, gas, water supply, heating, etc.
Access to residential premises located above the 5th floor must be via an elevator. The premises must comply with noise insulation, lighting, air exchange and microclimate standards.
To be recognized as residential, the premises must meet all the requirements established by sanitary and epidemiological documentation. In addition, it must comply with technical and fire regulations and standards.
In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, residential premises are recognized as a residential building, or part of it, an apartment, or part of it, as well as a room.
Condition and characteristics of non-residential premises
Non-residential premises are characterized, first of all, by the fact that it must belong to the non-residential stock.
Moreover, such objects can be located in both residential and non-residential buildings.
By functional purpose, this can be: property that is not intended for permanent residence of individuals, as well as property intended for any production and public purposes.
As for residential buildings, non-residential premises in such objects are all isolated spaces that are not the home or common property of the owners.
Owners: difference in rights and responsibilities
Owners of residential and non-residential premises have similar legal obligations and rights, justified by legislative norms. For homeowners, these categories are most fully disclosed in Article 30 of Chapter 5 of the Housing Code (Housing Code) of Russia, which states:
- the exercise of the right of ownership, disposal and use of residential premises must be carried out in accordance with its purpose and limited to its limits;
- it is available to the owner of residential property to provide it for use to other persons on contractual rights of lease, lease, or transfer it for free use on the basis of the letter of the law;
- the owner’s responsibility is to maintain personal real estate and common property in the apartment building in accordance with the standards;
- the homeowner must respect the interests of his neighbors;
- It is the responsibility of the owner of residential property to properly manage MSW (municipal solid waste) in accordance with the requirements of housing legislation.
The burden of expenses for maintaining the local area and common property falls on all owners of premises, regardless of the category of ownership - residential or non-residential real estate.
The owner of the office, as a rule, does not use the garbage chute or elevator, but he is obliged to pay a monthly fee for its maintenance in accordance with the agreement concluded with the HOA. Not only obligations, but also rights apply to the owner of non-residential real estate. Thus, he can participate in general meetings, choose a management company, decide on repairs, etc.
Such an owner has the right to enter into an individual agreement with resource supply companies, but can receive water, gas, heating or electricity by agreement with the HOA.
The intended purpose of housing and non-residential parts of buildings is taken into account at the design stage in the design and estimate documentation. The project calculates and fixes the possibilities for implementing the functions of different types of premises.
Purpose of objects
The intended purpose of residential real estate is for citizens to live in them (Part 1). The use of such buildings for other purposes entails administrative liability. Private individuals can register an individual entrepreneur in their home and carry out certain types of professional activities that will not violate the interests of other citizens.
The concept of housing stock is introduced in. According to the law, it includes all residential premises recognized as suitable for habitation. Non-residential premises cannot be part of the housing stock.
The advantages of apartments, living quarters and boathouses include:
- Low rental cost from the owner;
- Quite a large area.
Since a boathouse usually consists of several floors and a basement;
- Low cost per square meter when purchasing a boathouse or residential premises and apartments.
Cost 1 m2 of non-residential real estate, with the possibility of living. It can be 20 - 50% lower than the cost of 1 m2 of apartment;
- No complaints from neighbors when running a rental business in non-residential premises;
- Relaxations in legalizing redevelopment in such premises.
Since this is already a non-residential premises, supervision is not carried out as closely as in apartments.
Non-residential premises in an apartment building - is this possible?
In addition to defining residential premises, it regulates the ways of its use. Such properties are intended for human habitation. They are not permitted to be converted for industrial production purposes.
Important. The laws of the Russian Federation contain a loophole that allows individual entrepreneurs to carry out professional activities in the premises of the housing stock that they own.
This becomes possible if a number of conditions can be met:
- the rights and interests of other people are fully respected;
- technical and sanitary requirements for residential premises are not violated.
Residential premises can be legally used as work offices, for example, by lawyers. This right gives them.
If an entrepreneur rents housing in which he intends to conduct professional activities, he must obtain permission from the owner of the premises, as well as from all members of his family who have reached the age of 18. Theoretically, such a room could be a separate private house. Thus, the residential building will be used for purposes for which non-residential premises are usually used .
The disadvantages of owning non-residential premises include:
- Low liquidity of such non-residential premises.
If you want to sell such real estate, you will either have to wait a very long time for your buyer (possibly 3-4 years). Or make a significant discount on this premises, sometimes reaching up to 30% of the cost at which the premises were originally purchased;
- The next disadvantage will be the high property tax rate.
The rate will be 1.3 - 2% of the cadastral value, instead of 0.15 - 0.3% as for ordinary apartments;
- And the most important disadvantage will be the lack of possibility of registration in such a premises. Even despite the possibility of living in it. And the external resemblance to an ordinary apartment.
Thus, apartments and boathouses are suitable only for those people. Who already have an apartment and registration. And such non-residential premises are purchased as a second home.
Otherwise, the owner and his family members will not have continuous Moscow registration.
You need to be registered in Moscow for 10 years to receive the Moscow supplement.
These are new rules. And compliance with them is necessary to receive monthly social benefits. Persons who have reached retirement age.
Attention!
Many people only learn this fact when they reach retirement age when they come to fill out documents for a pension payment. So prepare your straws in advance. And by the time you retire, you should already have a residence permit in Moscow of 10 years or more.
Since from 2021 the total amount of the Moscow pension has been adjusted to a minimum of 21,100 rubles. Pensions may be higher, but not lower. (This is provided that you were registered in Moscow for 10 years at the time of retirement).
That is, even if you didn’t have much work experience, and your pension is only 12,500 rubles.
Moscow pays up to 21,100 rubles as a social benefit to people registered for over 10 years.
- Also, in the absence of registration, the whole family will be forced to visit private clinics.
Since you won’t be given a medical policy without Moscow registration either.
After all, without being attached to a clinic at your place of residence under a health insurance policy. Any appointment, even in a city clinic. There will be a fee for all family members.
And this is by no means a cheap pleasure. Any consultation with a doctor will cost 1500 – 2500 rubles. And this is not to mention the cost of the treatment itself, which will also need to be paid out of pocket.
- Also, families with children will experience inconvenience if they need to place their child in a state kindergarten or school located at the child’s place of residence.
In some cases, of course, it will be possible to do this if you have a temporary registration coupon in hand at some address in Moscow. In the house next door.
But if such registration is not possible for the child and his parents, then he will have to attend a private kindergarten. Or hire a nanny for the child.
And this is not cheap in Moscow either. A kindergarten or private school will cost from 15,000 to 70,000 rubles per month.
And a nanny for a preschool child will ask for 50,000 rubles a month for her work.
You may also need to provide her with a room for personal residence in your apartment.
- The absence of permanent registration in your passport will prevent your family members from finding employment in any government organization.
And for any other good position in a company that offers a high salary.
They probably won’t take you without registration either.
After all, a person without a permanent place of residence does not inspire confidence in the head of the company.
And you don’t know what to expect from him. And most importantly, where to look for it later. In case something happens due to the fault of such an employee.
Is a garden house a residential or non-residential premises?
Based on the above, a garden house can be considered both a residential and non-residential building, it all depends on its condition, arrangement and many other factors. Until 2021, the concept of “garden plot” was divided into several others. It was allowed to build both residential and non-residential buildings. And if the building was at one time registered as residential, then after 2021 no amendments are required. The house will automatically receive residential status.
On the other hand, if the house is being built after 2021 or has not previously been registered as residential, it will first have to be given the status of a residential building. Otherwise, you will not be able to register in it.
What is the best way to register a country house?
If the country house is already registered as a residential building (until 2021) and the only problem is to give it an address (and get the opportunity to obtain permanent registration), then it is enough to contact the local administration and demand that a real address be assigned to this property. Usually this is done on demand.
If the house is not yet residential, you will have to first recognize it as such and only then require an address to be assigned.
Procedure
- Order a technical report. Since a commission is not appointed to inspect the house and the decision is made only on the basis of the documents provided by the applicant, such a conclusion from any qualified expert who has all the necessary licenses is mandatory. The conclusion indicates all the basic information with which the administration can decide whether to consider a given house residential or not.
- Prepare all documents (see sample list below).
- Submission of documents and applications to the MFC (My Documents) or local administration.
- Waiting and receiving a decision.
- Making changes to Rosreestr.
- Request to assign a house address.
Documentation
The main point in the procedure for recognizing a house as residential is contacting the administration or the MFC. To do this you need a certain list of documents:
- Expert opinion regarding the condition of the house.
- Application to the MFC or local administration (filled out on site).
- Passports of all property owners.
- Notarized consent of all property owners to change its status.
- Permission from the guardianship authorities if there are minors among the co-owners.
- Extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
- Technical passport and cadastral passport.
- Legal documents.
Expenses
Despite the fact that the procedure for transferring a garden house to residential status is formally free, in fact you will have to incur some costs associated with the preparation of documentation and subsequent registration of changes:
| Type of expenses | Approximate amount |
| Technical conclusion | From 15 thousand rubles |
| Notarial consent of owners | From 1 thousand rubles for each owner |
| Changes in Rosreestr | 2000 rubles |
| Extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate | 350 rubles |
| New technical passport | From 10 thousand rubles |
| Document recovery | From 5 thousand rubles |
Deadlines
The timing largely depends on the applicant himself, but there are some points he cannot control:
- Drawing up a technical report: up to 3 weeks (less often, more).
- Receiving a decision from the administration: up to 45 days from the date of submission of all papers.
- Registration of changes in the registry: up to 2 weeks.
FREE CONSULTATIONS are available for you! If you want to solve exactly your problem, then
:
- describe your situation to a lawyer in an online chat;
- write a question in the form below;
What is the difference between built-in and built-in and other types of premises?
According to the type of construction, all non-residential premises are divided into:
- Built-in;
- Built-in and attached;
- Attached;
- Detached buildings (abbreviated as OZ).
You can easily distinguish a built-in room from an attached one.
Based on the same principle as the difference between a balcony and a loggia in an apartment building.
If nothing protrudes on the façade of an apartment building and looks monolithic, as if it were a continuation of the wall, then it is a loggia.
And when it sticks out and sticks out a meter forward from the facade, it’s a balcony.
Therefore, the same principle differs between built-in and attached premises.
Built-in room
It is very easy to distinguish a fully built-in non-residential premises.
Such premises are located on the first floors of residential buildings or any other administrative buildings.
The glass showcases of the built-in premises seem to be a continuation of the monolithic walls of the house.
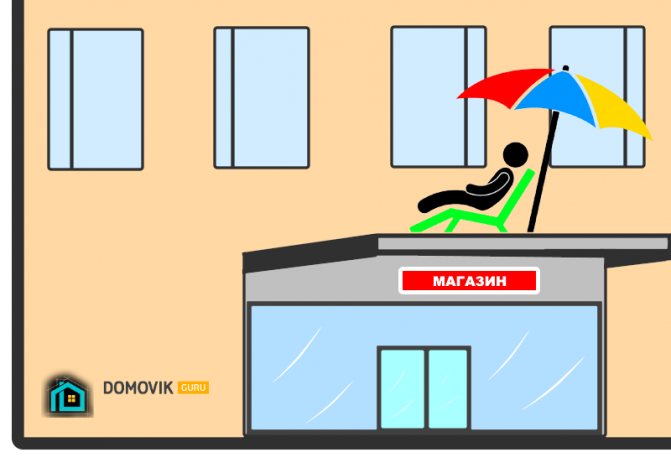
Built-in and attached premises
The built-in and attached room protrudes greatly beyond the boundaries of the building's façade.
Typically, such premises are seen by residents of the second floors under their windows.
When the canopy of the store forms a fairly large area under the windows.
Where can you even play football? Or go out in the summer, put up a sun lounger and sunbathe under the sun.
Attached room
The attached premises are generally connected to the apartment building only by a small part of the wall and general communications located in the basement.
The attached premises are somewhat similar in appearance to free-standing buildings.
It may seem that they are simply built next to an apartment building and are not connected with it in any way.
But if you take a closer look or walk around such an extension, it becomes clear.
That the attached premises are physically attached to the residential building and are one with it.
Detached building (abbreviated as OSZ).
The next type of non-residential real estate is a detached non-residential building.
Which, judging by its name, stands apart from other houses and buildings.
NEOs have a fairly wide range of applications. Therefore, it is worth understanding them in more detail.
The NEO is being built on an individual foundation. And it has its own communications and its own boiler room for heating in the winter.
NEOs can act as administrative buildings, housing on their premises plant administration buildings, railway stations and airports, sports complexes, auto centers, institutions, ministries and departments of the Government of the Russian Federation or other government agencies.
So have a commercial purpose. Acting as a single platform where a large number of different organizations are represented that rent individual offices.
Such clusters with numerous offices are called Business Centers.
When an NEO consists of shops and entertainment venues, it is called a Shopping Center (or shopping center for short)
A smaller shopping center with many stores of different types, but owned by one owner. They are also representative offices and branches of large enterprises in a particular region. It is called the Trading House (abbreviated as TD).
In the early 2000s, in large cities of Russia, a fight against illegal buildings and unauthorized trade was announced.
Therefore, numerous markets, stalls, bazaars and flea markets were rebuilt by their owners into NEOs. Received the name Trade Complex (abbreviated as TK). Where, in one territory, the client received a lot of different services. Starting from the opportunity to buy building materials, ending with hair cutting or solarium.
The fight against illegal garage cooperatives and parking lots was carried out using the same principle. In this regard, underground and above-ground comfortable parking lots have appeared. Consisting of several floors and having connected communications.

The indoor parking lot is also a public safety zone, and activities there are conducted according to the established principles of a garage cooperative. With the difference that its territory has become more and more cultivated. And there are a number of advantages compared to the poorly guarded old-style parking lots of the past.
As a non-residential real estate property, the NEO also has a number of advantages and disadvantages.
The advantages of NEOs include:
- Complete absence of neighbors.
Having such a building you will be your own master;
- Possibility to organize your own parking spaces on the territory adjacent to the OSZ for parking visitors’ vehicles.
Of course, if the free area of land for the NEO allows.
- A very important advantage of NEOs is the presence of their own communications.
Since in other types of buildings, communications are common throughout the building and are usually connected to other rooms.
This threatens that your utility bills will be inflated and you will not be able to do anything.
After all, all losses of water and electricity, even those that occurred through no fault of your own.
Will be extended to all owners of premises that have twin communications.
That is, the neighbors will have a leak, and all non-residential premises connected by communications will pay.
But the main advantage of the NEO is also its disadvantage.
Disadvantage of the non-residential real estate property NEO:
The absence of neighbors is good on the one hand, but expensive on the other.
For example, when a pipe breaks. All repairs will have to be done at your own expense.
Since communications are the property of the owner of the NEO.
Supplying gas or water nowadays is not a cheap pleasure.
For example, gasification of non-residential premises in the Moscow region.

With the supply of a gas pipe from the nearest gas distribution center to the OSZ (the length of the trench and the pipe itself was 500 linear meters). It cost the owner of the building 3.5 million rubles.
And this is far from the maximum price for gasification of non-residential premises within a populated area.
Since everyone around understands what benefits the owner will receive when renting out such a separate building.
Types of non-residential real estate
All non-residential real estate, for convenience, is divided into subtypes that have their own purpose.
The purpose of non-residential real estate is fixed in the property documents as a separate line.
This allows you to avoid confusion when conducting real estate transactions and charging tax on property ownership to owners by the state.
Below are the main ones. Which you encounter every day in your everyday life.
All non-residential real estate objects have their own classification according to their intended purpose and type of permitted use.
Industrial real estate:
These days, real estate is of this type.
It occurs in the form of large industrial complexes located on land plots with an area of 15 - 20 hectares. On the territory of which numerous enterprises are located.
And also in the form of production bases and buildings of restored old factories.
Factories with workshops on their territory. In which raw materials are processed or finished products are produced.
Strategic importance of industrial non-residential real estate
This type of non-residential real estate is rightfully placed first on our list.
After all, industrial real estate is the engine of progress of any state that can ensure its sovereignty and independence.
Thanks to the existing production facilities producing advanced types of weapons. Our country is now able to protect its borders and the peace of its citizens.
After all, many people don’t even understand why funding is still happening. Essentially an outdated and subsidized enterprise.
But this is vital for our country. After all, if our own cars are produced abroad. That is the country on whose territory the automobile plant will be located. In any difficult time for our country. It may simply break the contract and cut off the supply of (even bad and ugly) cars to Russian territory at the most inopportune moment.
All foreign factories producing foreign cars in our country. They can also curtail their activities at the moment and stop producing cars.
We can also be blocked from importing used foreign-made cars at any time.
Therefore, this is not just a domestic auto industry, but a strategically important production for our country.
So it may happen that only this plant will remain with us. And the good news is that “our cars” are still capable of driving.
Which means no matter what happens. Citizens of the country will not be left without cars.
Social and cultural real estate objects:
Real estate objects intended for cultural leisure by citizens. Recently, more and more attention has been paid in large cities of Russia. And budget funds are allocated annually for their construction.
Each district of the city has its own points of attraction consisting of cultural objects and cultural heritage, such as:
- Cinemas;
- Theaters;
- Museums;
- Art galleries;
- Art exhibitions.
Sports properties:
For the sports development of children and maintaining the shape of adult citizens, the following are being built:
- Swimming pools;
- Sports complexes that combine several real estate objects for sports on their territory;
- Stadiums;
- Racing tracks and karting tracks;
- Ski slopes;
- Shooting complexes for sport shooting from various types of weapons and shooting ranges for sport clay shooting.
Communal real estate properties:
This type of non-residential real estate houses employees and equipment that are responsible for landscaping and cleaning the territories of populated areas. And also to maintain a decent standard of living for citizens.
- Buildings housing many workshops for minor repairs and public service.
The so-called “Houses of Public Service”, “Household Services” or Centers of Consumer Services;
- Equipped beaches for swimming;
- Dormitories for visitors;
- Gas, heat and electricity supply facilities for the population;
- Motor transport enterprises;
- Harvesting equipment bases;
- Car service stations and other special premises intended for maintenance and repair of housing and communal services.
Educational non-residential real estate objects:
Non-residential real estate objects of this type accommodate the entire group of educational institutions. Which are engaged in training and advanced training of specialists.
Training of scientists and researchers with doctoral degrees. As well as educational and extracurricular activities.
Such non-residential real estate objects include:
- Buildings of kindergartens and preschool preparatory institutions;
- Schools, lyceums, colleges, gymnasiums or other educational institutions with different modes and forms of education;
- Technical schools, colleges and other vocational schools (vocational schools) that prepare highly specialized specialists;
- Universities, institutes and their branches.
Allowing you to obtain higher education and an academic degree, or defend a doctoral dissertation.
Real estate of this type can occupy huge areas.
On which an entire residential area could easily be located, consisting of several multi-storey buildings.
Which speaks to the importance given to this type of non-residential real estate in any state.
After all, the training of high-quality specialists directly affects the future development of all sectors of the country and the standard of living of society as a whole.
Non-residential real estate objects housing medical institutions:
Doctors working in medical institutions. Located in non-residential real estate objects of this type, they allow citizens to increase their life expectancy and maintain their health.
- Polyclinics and their district branches for the initial examination of citizens;
- Medical centers for the detection and prevention of diseases;
- Hospitals for operating and treating seriously ill patients;
- Oncology centers and dispensaries for the treatment of life-threatening diseases;
- Commercial medical clinics with general practitioners performing simple hardware examinations of patients or other procedures using licensed medical equipment.
They also include separate medical rooms where doctors conduct appointments. Those running a private practice who are engaged in... Mainly by consulting patients.
Attention!
Having trusted treatment in a commercial (private) clinic, people are often left without money and with the same set of diseases that they had before visiting it.
If possible, use public medical institutions or at least those with government participation.
Is it possible to change the purpose of the house?
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 671 and paragraph 3 of Art. 288 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, residential premises are intended only for the residence of citizens, and their use for other purposes (for example, as an office) is allowed only after the latter are transferred to the status of “non-residential” in compliance with a certain procedure. However, there are exceptions here.
It is worth saying that clause 2 of Art. 17 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation is still allowed to use residential premises in business activities, provided that this does not violate the rights of other residents and also meets all necessary requirements.
Thus, a lawyer, on the basis of clauses 6, 7, can use residential premises that are his property or the property of members of his family to provide his services.
However, this is an isolated case. Arbitration practice generally prohibits the use of residential premises for purposes other than their intended purpose. Thus, the law almost completely excludes cases when a residential building may have a non-residential purpose.
How to change the status of an area
Transferring an apartment to another fund and vice versa simply won’t work.
The Housing Code specifies a number of requirements, compliance with which is mandatory . If the listed conditions are not met, you can not count on changes in status.
In order for an apartment to become non-residential, you need to consider:
- If the area is more than 100 sq. meters, provide a second exit to the street;
- If the premises in which you plan to carry out your activities are located on the second floor or even higher, prepare for the fact that you will have to change the status of all the apartments that are located below. According to the rules, these square meters must also become non-residential;
- Provide all engineering communications;
- Check out of your home before starting the transfer procedure, because... no person can be registered in non-residential premises either on permanent or temporary terms;
- Legalize all redevelopments.
Remember that premises located in a building classified as a cultural heritage site cannot become non-residential.
In addition, only the owner has the right to change the status.
You cannot make non-residential the area where you live under the terms of a social tenancy agreement.
Not everything is so simple with the transfer to housing stock. It must also meet certain requirements:
- The building in which non-residential premises are located must have durable structures. It also should not be classified as an emergency fund or subject to reconstruction or demolition;
- The premises must be absolutely safe and equipped in such a way that future residents cannot be injured or injured. The same requirement applies to the adjacent territory;
- All utility networks must be in order and suitable for use. We are talking about heating networks, sewerage, water supply and electricity. Utilities located in the house must also meet safety requirements.
When converting to a living space, the owner will have to think about the height of the ceilings, the concentration of harmful substances in the air, the number of floors of the building, and sound insulation. All this must also comply with the standards that were determined by the Housing Code.
In addition, during the transfer, no matter to which fund, the property should not be encumbered with anything : debts, loans, etc.
Why translation is needed
Transferring your home from residential to non-residential and vice versa may become necessary for many reasons.
Most often, businessmen convert purchased apartments into shops, pharmacies, restaurants and cafes, and offices.
The status of residential premises is needed because only in it you can register and live too.
If you decide to convert your property to non-residential use, consider whether this process can be avoided.
According to the Housing Code, Article 17, it is possible to engage in commercial activities in a residential area in some cases, under which the following conditions are met:
- Your house and apartment neighbors will not suffer from your activities;
- The house in which your home is located does not belong to a dilapidated building;
- A potential entrepreneur is registered in the area where he plans to do business.
However, in most cases they still prefer to change the status of housing, and this has its advantages.
The main benefit of the owner who transfers his apartment to non-residential stock is that it becomes more expensive by about 20% when sold.
But here you may encounter another difficulty: will you be able to sell your non-residential property later? How interested will an entrepreneur be in this? So, before you run for profit, you need to calculate all the risks.
The downside for you here will be the wasted time on paperwork and searching for buyers.
While the property is idle waiting for a buyer, you will have to pay utility bills, which are approximately twice as high for non-residential premises . You will also have to pay property tax , namely 2.2% of the residual value of the premises every year.
That is why the translation is carried out by the entrepreneurs themselves who bought housing.
Where to go for translation
Today, the procedure for submitting documents in many regions has been simplified thanks to Multifunctional Centers that operate on a one-stop-shop principle. In one place you can submit all documents, in some cases, order certificates and receive the corresponding document after all procedures are completed.
- Application for transfer;
- Documents that confirm your right of ownership;
- Documents from the BTI: technical plan, technical passport, floor plan of the house;
- If, when changing the status, some kind of redevelopment is necessary, you are also required to provide a design for it.
You must find out whether you can transfer your premises to another fund or not within 45 days. This is how long it takes to review the application and check the documents provided.
Once the decision is made, the authorized bodies have three days to notify you of their consent or refusal. The relevant paper can be sent by mail or sent to the Multifunctional Center.
Remember the little things
Whatever plans you make to transfer your apartment, there are also some nuances that will not allow you to implement them:
First of all, remember that only the owner is responsible for the use of the space. That is, if you decide to rent out the area where a store later appeared, and at the same time did not make it non-residential, you will have to be solely responsible for this.
All orders from law enforcement agencies will be issued in the name of the owner;
You have the right to use your apartment not only as a home address, but also as a legal address.
In order to conduct business from home, it is not necessary to collect documents and transfer the premises to another fund. The main thing is to follow the rules mentioned above.
This has its advantages: you can work from your own apartment, and the law does not prohibit you from living there.
However, you will still have to change the housing status if you plan to receive mass visitors;
- Be prepared for utility prices to skyrocket as soon as you carry out the procedure for converting residential to non-residential. After all, tariffs for sewerage, water and electricity supply, heating for commercial premises are much higher.
All details about non-residential premises: definition, characteristics, differences from residential real estate, types and purposes of use
With the development of market relations, the concept of “non-residential premises” has become widely used in real estate transactions. However, in Russian legislation there is no clear definition of this concept. In this regard, citizens have many difficulties and questions.
This problem is especially of concern to merchants who want to convert residential real estate into non-residential real estate for business purposes . This question also often arises for residents of apartment buildings, who confuse common property with non-residential premises when calculating utility bills.
Unfortunately, confusion in the concepts of residential and non-residential premises often leads to illegal real estate transactions and legal disputes.