The term “maternity leave”, which does not exist in official legislation, usually refers to the period of absence from work associated with motherhood. Before and after the birth of offspring, a woman receives from the state the opportunity to temporarily not fulfill her professional duties, but to devote herself to her family, without losing either her work experience or losing financial assistance. It is useful for all working representatives of the fair sex to know how this type of leave is arranged, which most women have to encounter at least once in their lives, and often more than once. The nuances of such frequently arranged “rest” are also important for personnel service employees.
Maternity leave - comprehensive leave
The persistent jargon of “maternity leave” actually hides 2 different vacations, the only common feature of which is their connection with the birth of a child.
- Maternity leave
- Leave related to the need to care for a child up to 1.5 or three years of age.
Components of the maternity leave:
- have different bases;
- are issued separately and each in its own way;
- of various durations;
- payment differs between the employer and the state.
Rumor has united them into a common “maternity leave”, since in practice in most cases they go one after the other and have no breaks between them.
REFERENCE! Legislatively, the right to leave related to future motherhood is regulated by Art. 255-256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Special and work experience is not interrupted by a long maternity leave.
Payments
specified in the application are paid every month . Documents confirming the right to them are:
- birth certificate;
- birth certificates of older children, if the mother is still on leave to care for a previously born child at the time of writing the application, or if the benefit paid is the least possible;
- court decision on adoption;
- a certificate - presented by the part-time worker - stating that in another organization where he is employed, he is not accrued a similar benefit.
So, who pays for parental leave and how?
| Two types of payments: | |
| Compensation for parental leave | Child care allowance |
| The source of accrual is the employer’s salary fund. The accrual period is every month until the employee returns from vacation. The value is 50 rubles . If a person who has taken leave works part-time, he can demand compensation from all organizations where he works. But payments stop from the month following the one in which: • the person receiving it left work of his own free will; • or dismissed because the organization was liquidated and unemployment benefits are accrued to him; • or deprived of parental rights - with the transfer of the baby to full state support. | The source of accrual is the employer’s salary fund with subsequent compensation of this amount from the Social Insurance Fund (SIF) thanks to the mutual settlement of transfers. The accrual period is every month until the employee’s child turns 1.5 years old. The start of benefit accrual will be 10 calendar days from the date of receipt of the application, and the payment day will be the date on which salaries are paid to all other employees of the organization. The benefit amount is determined as follows: • average earnings for the previous 2 full calendar years are taken; • divided by the number of calendar days for the above-mentioned time (this does not include periods of release from work and temporary disability, parental leave and labor and employment); • multiplied by 30.4; • multiplied by 40%. Every woman needs to know how maternity leave is calculated in order to prevent fraud on the part of the employer. In terms of its value, average earnings cannot exceed the maximum and be below the minimum, which are established by the Social Insurance Fund . Their size changes every year. Currently these values are: • maximum: 23089.04 rub. – for those who retained their jobs and 12,262.74 rubles. – for those who lost it during the holidays; • minimum: 3065.69 rub. – for the first child and 6131.37 rubles. - for the next child. The amount of the benefit is directly proportional to the salary of its recipient . Moreover, it can be accrued even to an unemployed person. The source of its accrual is the federal budget. They go to the Population Protection Department (USPP) for it, and its value is minimal. If you have to give benefits to two or more children at once, they are summed up. However, the resulting total should not be higher than the full average monthly earnings paid over the past 2 years. |
In fact, mothers who have taken leave on labor and labor leave are in the most advantageous position - the benefit paid under it is equal to 100% of the average earnings for each day on maternity leave.
Here you can read in detail about the B&R benefit.
However, the State Duma is now considering Bill No. 22852-7 , proposing:
- extend the period of payment of child care benefits until the child reaches the age of 3 years;
- increase the smallest benefit for one child to the minimum wage - 7,500 rubles, and for two or more children - to two minimum wages - 15,000 rubles.
The accountant of the company where the woman is employed is responsible for calculating leave for accounting and accounting purposes. However, the expectant mother can calculate the approximate amount using one of the many calculators on the Internet.
Who is entitled to maternity leave?
The Labor Code enshrines the right of any working woman to go on maternity leave, namely:
- an employee who has signed an employment contract (work experience does not matter);
- registered with the Employment Service with the official status of unemployed;
- female students studying full-time;
- a woman in military service;
- the female part of the civilian personnel of military institutions.
NOTE! Some types of paid benefits during this leave are available to everyone, and some - only to officially employed expectant mothers.
Changing a diaper
Before changing a diaper, make sure that all supplies are within reach so that you do not have to leave your baby alone on the changing table.
To change a diaper you need:
- clean diaper;
- diaper ointment (or sterile vegetable oil);
- a soft diaper to dry the baby after washing.
- After each bowel movement, or if the diaper is wet, place the baby on his back and remove the dirty diaper.
- Wash your child with warm running tap water. It is important to hold girls correctly when washing: place the child's back on your left arm (if you are right-handed), and with your right hand, wash the perineum in the direction from the labia to the butt to avoid urinary tract infections. Boys can be washed by placing their tummy on their hand.
- If you are on the road or in another place where it is impossible to wash your baby, then clean your baby's skin using wipes. Gently wipe the baby's genitals. When changing a boy's diaper, do so with caution, as exposure to air can trigger urination.
- After cleaning the skin, dry the baby with a soft diaper using absorbent blotting movements. Do not rub your baby's skin under any circumstances!
- Lubricate the folds in the groin and buttocks with a special diaper cream or sterile vegetable oil.

Always wash your hands thoroughly before and after changing a diaper.
Most rashes occur because the skin is sensitive and irritated by a wet diaper. If you do not care for your baby correctly, a rash may occur in the diaper area. This is a fairly common problem. Typically, this rash is red and raised. When bathing in warm water or using diaper cream, it disappears.
To prevent your baby from developing a rash in the diaper area, you should:
- Change the diaper at least every 3 hours or after each bowel movement.
- Wash your baby with warm running water while changing a diaper (do not use wipes at home)
- After washing the baby, dry the skin and apply baby cream containing zinc.
- Leave the baby without a diaper for a while. Air baths are an excellent prevention of diaper dermatitis.
If the rash in the diaper area continues for more than 3 days or the skin condition worsens, consult a doctor. The rash may be caused by a fungal infection that requires medication.
Timing is an important issue in motherhood
When establishing the duration of maternity leave and the time of leaving for it, the legislation is guided not only by the natural rhythms of childbirth, but also by the conclusions of the doctor leading the pregnant woman, which is reflected in the relevant legal acts.
Each type of leave that constitutes maternity leave has its own specific timing.
Maternity leave (Maternity leave)
In the last months leading up to childbirth, it becomes difficult for a woman, and sometimes she cannot cope with her usual work duties, and often even the journey to her place of work. The state provides her with the opportunity to be considered temporarily disabled, that is, to issue a sick leave for the prenatal and postpartum periods. The duration of these periods varies:
- before the expected birth, a woman is allowed to rest for 70 days according to the calendar;
- after childbirth, sick leave will continue for another 70 days if the birth was normal, and for 86 days in case of complicated birth situations (in particular, a cesarean section);
- if not one baby is expected to be born, but several at once, the happy mother will be allowed to rest 2 weeks earlier - the prenatal period will be 84 days;
- the parent of twins and more children after childbirth is entitled to 110 days of paid sick leave;
- The countdown of these periods begins with the issuance of a sick leave certificate at the antenatal clinic, which occurs in a normal pregnancy at 30 weeks, and in a multiple pregnancy at 28 weeks.
ATTENTION! If unexpected inconsistencies arise in the estimated dates on which the leave is based (for example, a woman gave birth prematurely, postponed the pregnancy, or the gestational age was incorrectly calculated), the leave dates remain unchanged. To extend it, you need a new sick leave and, on its basis, additional leave.
When adopting a small child (up to 3 months), a woman is also entitled to leave similar to that provided under the BiR.
Instructions for expectant mothers: how to apply for leave under BiR
- At 30 weeks (or 28, if more than 1 baby is expected), the pregnant woman receives a certificate of incapacity for work from the antenatal clinic doctor and has it certified by her supervisor.
- A pregnant employee writes an application for maternity leave to her employer in her own hand. This document must indicate the reason for future absence from work (A&W) and the terms calculated from the sick leave. It’s worth immediately adding a clause about the request to accrue the corresponding benefits, otherwise they will have to be processed separately.
- The HR department, based on the application and sick leave, issues an order to provide this type of leave. The expectant mother is completely free from labor worries from the date specified in the order.
Additionally, you need to prepare the following documents:
- copy of ID;
- a certificate from the accounting department about income for the last 2 years;
- bank account number or plastic card (for transferring benefits);
- a certificate from the housing complex stating that the woman registered before the 12-week period (an additional payment is due for early registration).
Parental leave for up to 1.5 or 3 years
Issued after the birth of the child before the expiration of postpartum vacation days: the first vacation will smoothly transition into the second.
IMPORTANT! This type of leave, unlike the first, can be issued not only to the child’s mother, but also to any person who will care for him - father, relative, guardian, the choice is up to the child’s family: it is possible if the mother has resumed working activity after the birth of the baby.
Labor guarantees for those on this leave:
- maintaining the workplace at the “pre-maternity leave” workload;
- payment of monthly “employer” compensation;
- taking into account the first 1.5 years of child care in the pension period;
- impossibility of dismissal before going to work.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The difference between a 1.5-year and a 3-year vacation is only in the payment of monthly benefits from the employer and the pension period. These are not different types of leave, but one, issued once, which can be completed at any convenient time before the child turns 3 years old.
Documenting
- A mother or another officially employed loved one submits a written application to her employer (it also includes requirements for the calculation of 2 monthly payments - benefits and compensation).
- Providing a birth certificate for the baby.
- If it is not the mother who arranges the leave, a certificate is needed stating that she is not using her right to maternity leave.
- Registration of the order by the HR department (the applicant receives a copy).
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! Two maternity leaves cannot be taken out at the same time. If before the end of the maternity leave a woman is going on a second one, then the dates in the two orders should not overlap each other. In such a situation, it is financially more profitable for a woman to apply for B&R benefits than to continue to receive compensation from the employer. Thus, it is worth writing an application for going back to work, and then for a new leave for the second pregnancy and childbirth.
For adopted children, parental leave is issued in the same manner as for relatives.
Registration procedure
Employees often do not know how to properly arrange parental leave. First of all, the applicant supplies two documents:
- child's birth certificate;
- a certificate stating that the second parent (or one of the relatives, or the mother and father of the child, if another family member takes the leave) did not go on the same vacation - this certificate can be obtained from the organization where the child works.
He will submit them along with the application.

The algorithm for writing it is similar to the algorithm for writing all other statements addressed to the head of the organization. The difficulties here begin with the presentation of the essence of the issue:
- first, they ask for parental leave from a certain date
- then there is a request for a monthly child care allowance and a monthly compensation payment;
- and in the last paragraph - in the Applications section - submitted along with the applications are listed
The clause on benefits must be specified , since if it is absent, they simply will not be paid. So there will be a need to apply again.
Here it is important to know that the main document regulating the relationship between the applicant and the employer is the corresponding order, a copy of which the applicant receives.
An order for parental leave is issued by the personnel officer. For this purpose, a unified form T-6 , in which section B is filled out, where the name and duration of the vacation are indicated.
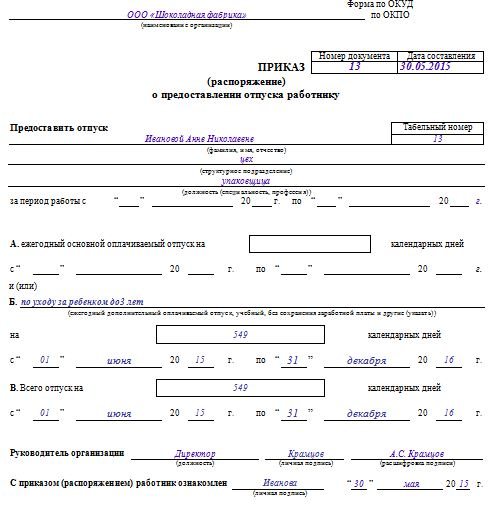
Click to enlarge
The vacation period itself is taken into account by the personnel officer in the timesheet . The form of this report card is also unified: it is T-12 or T-13. An appropriate note indicating that the applicant is on parental leave is placed on it every month - from the day the leave begins until it ends.
The symbol for coolant or digital code 15 serves as a mark.
If a person taking leave is officially employed in two jobs, that is, he is a part-time worker, he should submit the above application plus documents to each of the organizations. The problem here is only in the clause on benefits: to apply for their payment, he can choose only one place of work, usually with a higher salary.
Watch a video about the nuances of providing parental leave:











