From this article you will learn:
- What procurement methods exist under 44-FZ: table
- Advantages and disadvantages of different procurement methods under 44-FZ
- How to choose the right procurement method under 44-FZ
There are different procurement methods under 44-FZ. At the legislative level, a more precise term is used - supplier selection. The determination of a particular tendering method is influenced by many factors: the subject of procurement, the contract price and other aspects.
It is important to be able to navigate these criteria in order not to fall under FAS sanctions when conducting procurement under 44-FZ, which may result in the results being canceled or fines.
What procurement methods exist under 44-FZ: table
The table below discusses in detail all procurement methods under 44-FZ:
| Way | In what cases is it used? | Peculiarities |
| Contest | Used if it is important to select a performer based on a number of criteria | It is considered the most suitable option for bidding. It takes place in an open and closed form, with limited access to participants, in two stages |
| Request for proposals | In accordance with Art. 83 44-FZ, used in the following cases:
| The winner is the participant whose final proposal most fully meets the customer’s wishes. |
| Request for quotation | Used to select a winner based only on the proposed price. The initial maximum price is within 500,000 rubles | The volume of purchases cannot exceed 10% of the total and exceed the amount of 100 million rubles |
| Auction | The contractor is selected based on the cost proposed by the participants. Auctions are a mandatory format for purchases included in the list of Order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated March 21, 2016 No. 471-r. During such bidding, the NMCC gradually decreases, participants communicate their intention to provide the service at a lower price | Takes place in closed and open form |
| Purchasing from a single supplier | Cases of using this procurement format are listed in Art. 93:
| With this procurement method under 44-FZ, two approaches are used when the customer:
|
Where can I find information about ongoing government procurement?
According to the requirements of Article 4 44-FZ, all public procurement must be placed in a unified information system (abbreviated as UIS).
The official website of the unified information system in the field of procurement is www.zakupki.gov.ru. All information contained in the UIS is publicly available and is provided free of charge.
Those. in order to find information about all ongoing government procurement, you just need to use the website zakupki.gov.ru.
Advantages and disadvantages of different procurement methods under 44-FZ
Most often in practice, the following procurement methods are used under 44-FZ:
- electronic auction;
- purchases from one seller;
- request for quotations;
- open competition.
The listed forms are recognized as competitive, transparent, and beneficial for customers. Closed procurement, such as a request for proposals, a competition with limited participation, a two-stage competition, can be selected by the organizers of the tender in cases established at the legislative level.
When choosing a bidding format, the customer is guided by the prevalence, accessibility, advantages of the method, personal preferences, as well as the restrictions and norms established in 44-FZ. The listed approaches are associated with a certain set of requirements for the buyer and the text of the contract, and therefore are used in situations established for them by law.
The choice of an unlawful procurement method entails holding the auction organizer accountable at the administrative level.
Let's look at each method of procurement under 44-FZ:
1. Purchasing from a single supplier

Customers choose this procurement format when the contract is concluded for a small amount. The law makes it possible to enter into a contract with a seller once for an amount of up to 100,000 rubles. But in paragraph 4 of part 1 of Art. 93 fixes several important conditions that should not be forgotten.
Key advantages of purchasing from a single contractor:
- the customer has the opportunity to work with an already familiar seller;
- there are no large expenses required for the procedure for signing an agreement;
- low risks of violations occurring during trading that are independent of the organizer, that is, failures in the operation of the ETP or other difficulties;
- simplicity, short terms of implementation of the procedure, when compared with other methods of procurement under 44-FZ.
But when choosing one organization as a supplier, you need to be prepared for the following difficulties:
- There is a high probability of claims from inspectors, because this procurement method provides great opportunities for spending budget money on purposes not originally intended. There is a possibility of collusion between the parties to the contract.
- Difficulties in reducing the price of the agreement and establishing optimal conditions to obtain the desired result, since there is no competition.
Procurement Fundamentals: Basic Concepts of the Contract System
This guide will help you understand what tenders are, what they are, how they differ, and how to participate as a supplier.
WHAT IS A TENDER
The word “tender” has already become firmly established in business usage, but is not used at all in Russian legislation, because it originally came from Western practice. Instead, 44-FZ operates with the concept of “purchase,” defining it as “actions aimed at meeting state or municipal needs.”
What then is a “tender”? The Cambridge Dictionary defines the term tender as follows: “an offer to supply goods/work at a pre-agreed price.” The modern economic dictionary describes a tender as a competitive form of placing an order. From this we can conclude that only those purchases that are carried out in the form of tenders - competitions and auctions - can be considered tenders. However, in a broad sense, the term is used for any form, including non-competitive.
Therefore, we will consider the concepts of “tender” and “purchase” as synonyms, denoting the method of selecting a supplier for a government order within the framework of a contract system. Now let's take a closer look at the forms of tenders.
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF PURCHASES
1. COMPETITIVE – there are many participants, they compete with each other for the right to sign a contract with the customer.
1.1. With bidding, participants can bargain: after studying the conditions offered by competitors, offer even more attractive ones.
1.1.1 Auction - is held when the customer knows exactly what product he needs, with what specific characteristics and in what time frame. He indicates them in the tender documentation, and the participants indicate the price for which they are willing to supply this product. The one who offered the lowest wins. If during the auction the price was reduced to zero (more precisely, less than 0.5% of the initial price), then an auction for an increase occurs next. That is, the contract will be signed with the one who offered the highest price, and this money will not be paid by the customer to the supplier, but by the supplier to the customer.
Note: your experience, technology or number of personnel does not matter for the auction - only the price offered matters. However, you should not succumb to the temptation of a beginner and strive to win at any cost. It is important to evaluate in advance the amount of payment that is economically justified for your company. It makes sense to participate in a promotion auction if you want to receive an image order for your portfolio or, for example, have a unique technology and are confident that if you win, the next tenders in the line will also go to you as the only supplier.
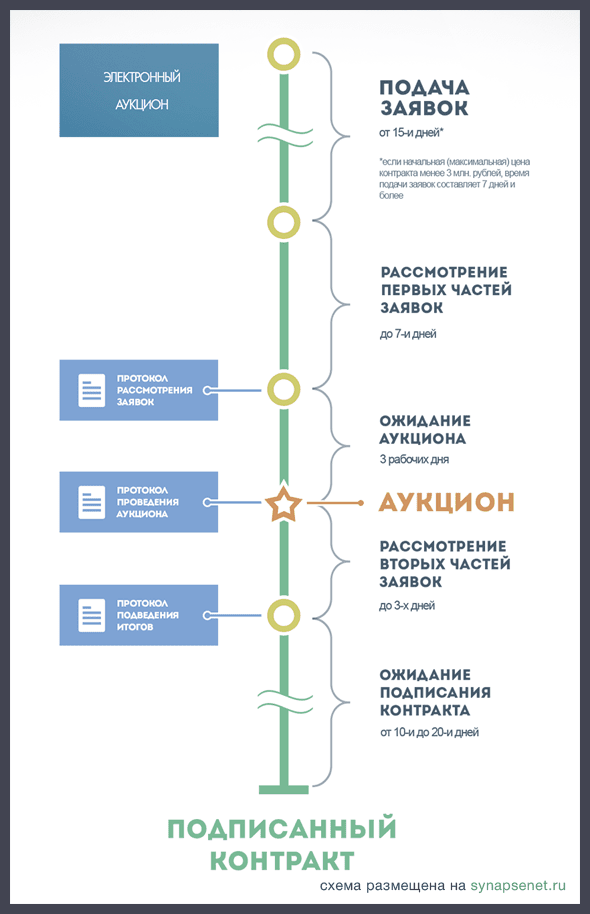
Fig. 1 Terms of electronic auction
1.1.2 Competition – held when the customer is interested not only in price, but also in a number of other parameters of the product (at least two). The customer sets criteria for evaluating these parameters, establishing the significance of each - the number of points that are assigned for it - and the algorithm for calculating them. The winner of the competition is the participant who offered the best terms for the execution of the contract: in terms of price, terms and specified parameters.
Note: in the competition, companies with more experience and better technical equipment have an advantage - points are also awarded for each similar parameter (price, personnel qualifications, etc.).
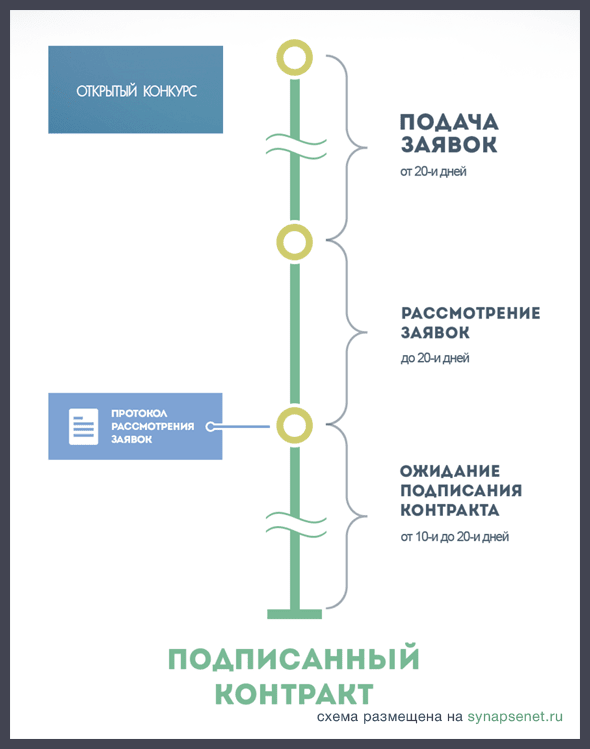
Fig. 2 Open competition deadlines
1.2. No bidding - in such procurements, participants offer their contract price only once. Bargaining - that is, changing it after familiarizing yourself with competitors' offers - is not allowed. For this reason, and also because there is less tender documentation, requests for quotations and proposals are carried out much faster than auctions and tenders. Customers give them preference if the purchase is standard and needs to be done quickly. Often such methods are chosen if the contract for an auction or competition has been terminated, and there is no time to repeat the bidding procedure.
1.2.1 Request for quotations. The word “quote” means “price”. This form of procurement is similar to an auction, but without bargaining. The customer describes in the notice exactly what product he wants to purchase and under what conditions, and asks the participants for the price for which they are willing to supply such a product. Participants can announce their quotation – price offer – only once. After this, the customer checks the applications for compliance with the law and the terms of the notice and selects the one in which the contract price is minimal. If there are several of them, then the participant who submitted the application earlier wins.
Note: requesting quotes is considered the fastest way to conduct procurement and one of the most popular among customers, since the procedure itself is shorter and there is no need to prescribe criteria for evaluating applications. Participating in it is also easier, since there is less documentation, which means there is less chance that the application will be rejected due to inconsistency.
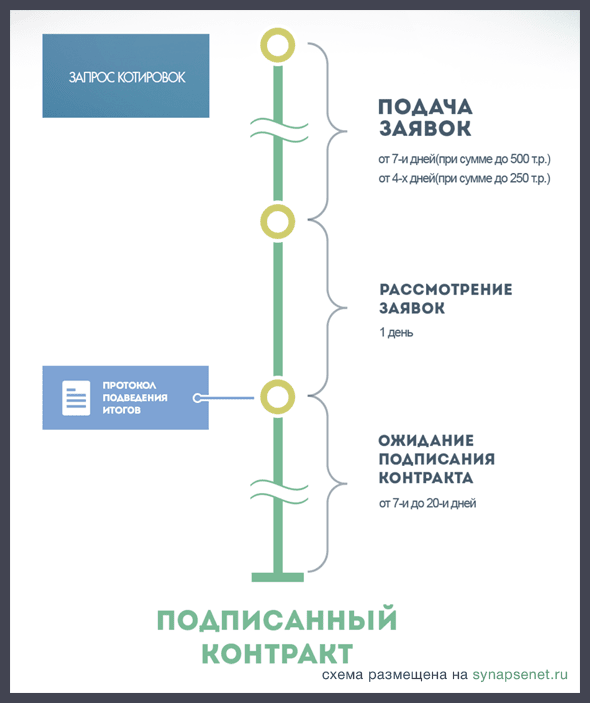
Fig. 3 Deadlines for requesting quotes
1.2.2 Request for proposals is an analogue of a competition held without bidding. The customer compares not only the price, as in the case of a request for quotation, but also other parameters specified by him in the notice (quality, terms, etc.) - that is, in general, the suppliers’ proposals. The application with the best conditions wins.
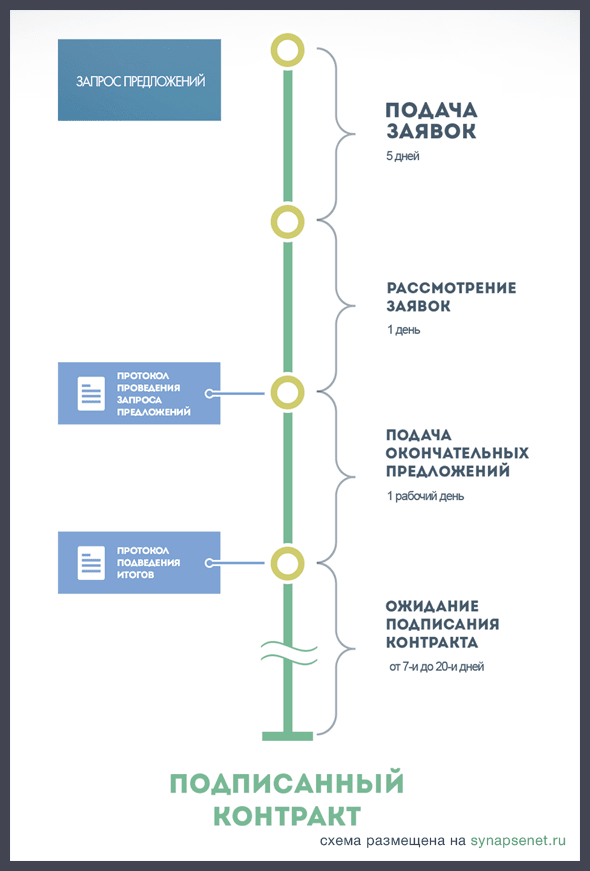
Fig. 3 Deadlines for request for proposals
2. NON-COMPETITION
Purchasing from a single supplier is the only non-competitive type of tender. The customer purchases goods from a specific seller - quickly and without the difficulties typical for public procurement. Article 93 of Federal Law 44-FZ contains more than forty grounds for purchasing from a single supplier. The most popular of them: concluding contracts with natural monopolies, small purchases (up to 100,000 rubles), as well as cases when a purchase carried out using a different method was declared unsuccessful (that is, all applications were rejected except one). If the choice of a single supplier is not so obvious, the customer needs to justify in detail why it is impossible or inappropriate to conduct a competitive tender.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE IN PROCUREMENTS UNDER 44-FZ AND 223-FZ?
Federal Law 44-FZ regulates procurement of state-owned enterprises, organizations and structures at the federal and municipal levels - all that operate at the expense of the budget. It describes in detail how various hospitals, schools, city and regional administrations should purchase goods, works and services. The law clearly defines the procedures, their deadlines, documents to be processed, and fines for violations. Tenders under 44-FZ can be found on six federal electronic platforms.
Federal Law 223-FZ controls purchases by state corporations, natural monopolies and other “special” customers. It outlines only the basic principles, leaving a significant degree of freedom. The details of the procedures are reflected not in the law, but in the Procurement Regulations, which all customers develop independently and approve again every year. It can be found in the EIS and on the organization’s website. The same procedure for different customers, and even for the same customer in different years, can differ significantly, so you have to carefully study the Regulations each time. Tenders under 223-FZ are sought on both federal and commercial trading platforms.
Read more about the differences between the two federal laws regulating public procurement in our article.
HOW TO PARTICIPATE IN TENDERS: ACTION PLAN FOR A NEWER
1. Registration of an electronic signature. It is required to enable you to enter into contracts electronically. Different ETPs and procurement forms require different types of digital signature: simple, enhanced (qualified and unqualified). What documents are needed to obtain an electronic signature, where and how to obtain it, read in our blog.
2. Accreditation on electronic platforms. On electronic trading platforms, you can register as on a regular website - fill out information about yourself, create a personal account. This is usually enough to be able to search and view tenders. However, to participate in them, you must go through the accreditation procedure - receive confirmation from the administration of the ETP. At federal sites this takes no more than 5 working days. Commercial terms vary.
Look in our blog for step-by-step instructions on accreditation for popular ETPs: RTS-tender, Russian Federation Order, PRO Tender and others.
3. Monitoring. To understand how often tenders are held in your industry, what is purchased, who wins and at what price, you need to conduct a little monitoring:
- Go to zakupki.gov.ru –> “Purchases” –> “All purchases”.
- Select your region.
- In the filters field, check the box at the “Purchase completed” stage.
- In the search bar, enter keywords for your industry, for example, “office supplies.”
The site will display all purchases that might be of interest to you. Since they are already completed, you can see the winners and the offered price. Such statistics will help you analyze and build your tender policy.
4. Planning. In order to know in advance when and in which auctions to participate, and which ones it is better to skip, it is worth making a rough schedule for yourself. To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with the two-year plan and annual procurement plan of the customers you are interested in, which they publish in the Unified Information System.
5. Search for procurement. Hundreds of tenders are posted on electronic platforms every day. You can search for them manually. For example, in this article we tell you how to search for purchases placed on the RTS-tender ETP.
You can use special aggregator services, for example, Synapse.Pro. They greatly facilitate and speed up the search for suitable purchases and offer convenient analytics.
In Synapse.Pro you can customize the search to suit your needs: by keywords, exception words, region, initial maximum price range, completion date, type of purchase. The system will review all posted tenders on all electronic platforms, filter by your parameters and provide a clear list, immediately with customer cards. Check out the additional features of Synapse.Pro and reach a new level of business with us!
Test yourself by answering the questions:
1. Tender is:
2. What happens when the initial maximum price during an auction drops to 0.5%?
3. Federal Laws 44-FZ and 223-FZ




